Content
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms of gallstone disease
- Variety
- What is the danger of the disease, complications
- Diagnostics
- Drug treatment
- Colic (pain syndrome) treatment
- Removal of formations
- Dissolving stones
- Diet
- When is surgery for gallstones needed?
- Surgery
- Video about ZhKB
GSD (symptoms and treatment depend on the type and stage of pathology) is a disease accompanied by the appearance calculi in the gallbladder, ducts. In older adults, the risk of stone formation increases significantly. Treatment of gallstones is mainly medication, but in some cases - only with the help of surgical intervention.
Causes of the disease
CLD (symptoms and treatment of the disease are discussed below in the article) often occurs due to improper diet. In adults, additional risk factors for the development of the disease appear. Spicy, fatty foods, certain foods, drinks (for example, eggs, pastries, cream and alcohol) provoke the attacks of pain. Sometimes the cause is stress, long-term work at an angle.
Stagnation of bile is of a different nature.
Mechanical cause:
- scarring;
- tumors;
- kinks of the ducts;
- an increase in lymph nodes located nearby;
- adhesions;
- strictures;
- inflammation of the bladder, accompanied by edema of the walls.
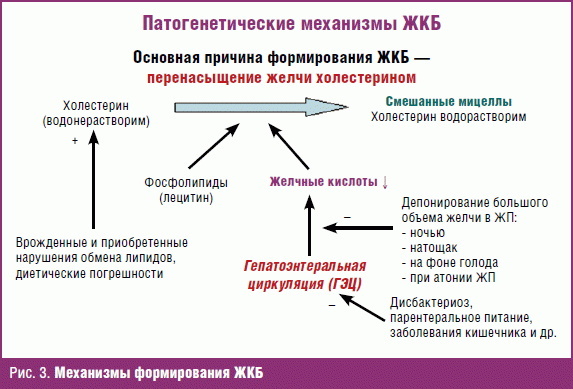
Functional disorders occur due to impaired motility of the organ and bile ducts. Gallstones can be caused by infections, allergic reactions, inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
The risk group includes the elderly, taking certain medications that disrupt the concentration of bilirubin and cholesterol, and genetic factors. LCB can cause obesity, starvation, rapid weight loss, and junk food. The likelihood of the appearance of calculi increases with diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, gastrointestinal diseases.
Symptoms of gallstone disease
Symptoms begin in the third stage of the disease. Manifestations depend on the size and location of calculi, the severity of the inflammatory process and functional disorders.
The first signs of gallstone disease:
- Heaviness in the abdomen. It appears in the epigastrium or under the right ribs. Often occurs suddenly, due to intense physical exertion. This sensation indicates stagnation of bile, and the bladder increases in size.
- Nausea, belching, heartburn, sometimes accompanied by vomiting. If there are already calculi, little bile is secreted. This is not enough for the processing of fats and enzymes. As a result, nausea appears, and the return of bile and food into the stomach causes heartburn, belching, flatulence and vomiting. Most often this happens after eating.
- Pain after eating. Localization - in the right hypochondrium, less often in the form of biliary colic. The first attacks are of low intensity, but it gets worse over time. The pain becomes bursting. Attacks occur 1-1.5 hours after eating. For example, after consuming fatty foods or alcoholic beverages.
- Jaundice. The color of the sclera and skin changes. But this symptom often appears after pain, disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract. Bilirubin begins to accumulate in the liver (normally it comes out with bile), then enters the skin, and its excess gives a yellow tint.
-
Stool change. Diarrhea, constipation causes uncontrolled secretion of bile. This is often the second symptom from the initial ones. In the later stages of the disease, the stool becomes colorless, indicating a blockage in the ducts.

The main symptom of gallstone disease is pain. It occurs due to muscle spasms or when stones move. The pain is severe, acute, paroxysmal. Occurs in the right hypochondrium. Then it spreads along the same half of the body, but the limbs are usually not affected. Each attack lasts from 2 to 6-7 hours. Gradually, the pain concentrates in the gallbladder region.
During an attack, strong sweating begins, the temperature rises to 38 degrees and above, chills. Nausea may appear. It is often accompanied by vomiting, in which bile is present. Moreover, after emptying the stomach, relief does not come. Sometimes the pain radiates to the region of the heart, provoking the appearance of angina pectoris.
Chronic asymptomatic cholecystitis can proceed for a long time without negative signs. From the moment stones are found in the gallbladder to the onset of symptoms, it often takes 5-6 years. But complaints appear only in 10-20 percent of patients.
Variety
CLD (symptoms and treatment in adults often require closer attention) develops gradually. The formation of calculi occurs in two stages. First, the balance of phospholipids, acids, and then cholesterol is disturbed due to a decrease in the activity of certain enzymes. The concentration of cholesterol rises. Then bile stagnation begins, crystals form first, then stones. Their sizes can reach up to 5 cm.
There are several stages of ZhKB:
- Initial. At this time, there are no symptoms. The diagnosis is made only after examining the bile masses. Small crystals are found in it.
- Latent. Symptoms are absent, but stones are already found in the organ. The diagnosis is made after transcribing an ultrasound scan.
-
The appearance of signs. The patient begins to have biliary colic. These are bouts of acute pain lasting 2 to 6 hours. Most often they appear in the evenings or at night. The pain occurs first under the right ribs, then spreads along the same side - under the scapula, cervical spine. More often, physical activity, abundant or fatty foods become the cause of attacks.
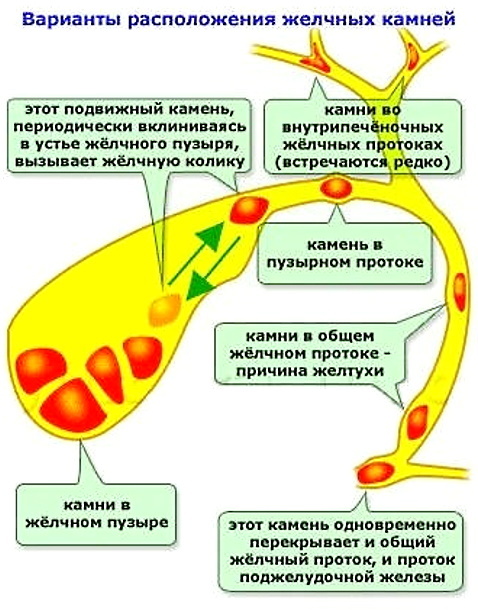
At the last, fourth stage, various complications arise (for example, acute cholecystitis, bladder perforation, dropsy, hepatic abscess).
What is the danger of the disease, complications
Concrements often form gradually over the years. In this case, the pathological process is asymptomatic, and the stones are discovered by chance during an ultrasound scan. It happens that drug therapy already becomes impossible and the only way out is to remove the bladder completely.
The easiest complications of gallstone disease include indigestion. If the disease is still at an initial stage, then stones can be removed from the bladder and the work of the gastrointestinal tract can be restored.
In other cases, gallstone disease is fraught with serious and life-threatening complications:
- Reactive hepatitis. This is when the inflammation of the bladder is transferred to the liver. As a result, her blood supply deteriorates. But as soon as the source of inflammation (it is the gallbladder) is removed, then the liver is restored.
- Empyema of the bladder. This is a collection of pus directly in the bladder. When a stone gets stuck in the excretory canal, stagnation of bile begins. This leads first to dropsy, when mucus accumulates, then pressure increases in the organ, as a result of which its walls stretch, periodically contract. This is accompanied by severe pain. If an infection additionally gets, then the mucus is transformed into pus, empyema appears. Pathogenic microorganisms can become causative agents. They enter the bladder from the intestines or together with the blood. The more pus accumulates, the worse the patient feels. The pain intensifies, the temperature rises greatly. An urgent operation is required, otherwise, if the bladder ruptures, its contents will enter the peritoneum and cause peritonitis, which is usually fatal.
- Paravesical abscess. In this case, pus accumulates near the bladder. The abscess is separated from the peritoneum by adhesions, and is covered from above by the edge of the liver. The danger of this complication is the rapid spread of infection, followed by peritonitis. The liver is impaired, and it can be fatal.
-
Acute cholangitis. In this case, inflammation occurs, blockage of the excretory ducts. The outflow of bile is stopped due to a stone stopped in the passage. But since the ducts of the bladder are connected with the channels of the pancreas, pancreatitis often occurs in parallel. This is accompanied by chills, severe pain in the hypochondrium, fever and jaundice.
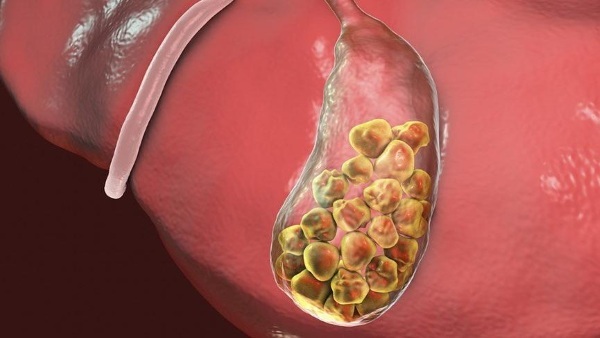
- Bubble perforation. This is an organ rupture caused by severe spasms or the movement of stones. As a result, the contents of the bladder are in the abdominal cavity. Even without the presence of pus, bile causes severe inflammation, irritation of unprotected tissues. The process quickly covers all internal organs. There are conditionally pathogenic microorganisms in the gallbladder; when they enter the peritoneum, they are activated. They begin to multiply rapidly, leading to peritonitis.
- Biliary fistulas. Even if the presence of stones is not accompanied by pain, the inflammatory process still develops around the calculus. Gradually, the organ wall collapses in this place and connects with neighboring structures. Then a fistula is formed. More often it appears when the walls of the bladder merge with the stomach, intestines. Even if calculi do not cause discomfort and pain, air accumulates in the bladder and the flow of bile is disrupted, which provokes additional symptoms and complications.
- Acute pancreatitis. Most often, it appears due to the absence of bile when the bladder or common duct is blocked. As a result, stagnation of pancreatic enzymes occurs, which provokes its necrosis (death). This can provoke the death of the patient.
- Cicatricial strictures. This is a narrowing of the duct. A complication occurs against the background of inflammation or after the removal of calculi. Strictures often persist even after complete recovery, interfering with the normal assimilation and digestion of fatty foods. With this complication, patients often have relapses.
- Biliary cirrhosis. It occurs due to prolonged stagnation of bile in the organ. Its overflow also provokes a dysfunction of the liver. This leads to the destruction of her cells. They are replaced by fibrous tissue. Consequence - blood clotting is disrupted, severe poisoning of the body occurs, fluid accumulates in the peritoneum.
Any of the above complications can be fatal. The likelihood of their appearance is much less with early treatment, in extreme cases - removal of the organ.
Diagnostics
JCB (symptoms and treatment in adults largely depend on the size and type of stones) requires mandatory diagnosis before therapy. This is necessary in order to assess which drugs should be prescribed, whether there are indications for surgical intervention. When anxiety symptoms appear or as a preventive examination, they turn to a therapist.
First, he listens to the patient's complaints, conducts a general examination. Then he finds out the details of nutrition when the deterioration sets in. If the patient feels pain, then he is asked to lie on his right side and pull the bent legs to the stomach. With ZhKB, the sensations will intensify when you turn over to the other side.
On palpation, abdominal hardness, tense muscles, high sensitivity in the area on the right under the ribs are felt. When pressing deeper, an increase in the bladder is felt (normally it cannot be felt). Deep probing can determine Murphy's symptom (the occurrence of pain when pressing under the right ribs) or Ortner (the same sensations appear when tapping the ribs).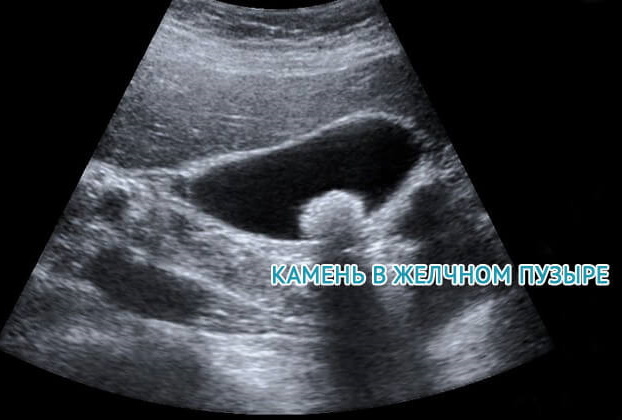
The therapist then directs the patient for an ultrasound scan. The presence of calculi in the gallbladder is indicated by solid inclusions, their movement, a hypoechoic trace, which appears in the image as a white smear under the stone. The walls of the bladder are thickened - more than 4 mm. Calcium salt calculi are clearly visible.
Holicystography with contrast is performed (to get a clearer picture of the bladder), CT. To determine the localization of the stone in the duct, endoscopic cholangiopancreatography is performed.
Drug treatment
Gallstones (symptoms and treatment in adults depend on the stage of the disease, size, location and type of calculi) is treated in several stages. They prevent the movement of calculi, the development of complications, crush stones, restore metabolic processes.
Treatment usually begins with a reduction in spasms. Prescribe Atropine, Platifilin - 1 ml intramuscularly. If they turned out to be ineffective, then they are changed to antispasmodics. For example, No-Shpu, Drotaverin or Papaverine - 2 ml intramuscularly.

Odeston is usually prescribed. It acts pointwise, in several directions at once, suitable for most pathologies of the biliary system. The drug increases the secretion of bile, prevents contraction of the bladder and is safe even in the presence of calculi. At the same time it acts as an antispasmodic - only on the muscles of the bile ducts. The drug reduces stagnation of bile, prevents the formation of crystals and stones, and improves digestion.
Colic (pain syndrome) treatment
Antispasmodics somewhat reduce pain. But with intensive pain relievers are prescribed. Most often Baralgin or Pentalgin - 5 ml intramuscularly. If the pain is very severe, then 1 ml of Promedol is injected.
Removal of formations
The calculi are crushed by shock waves that generate outside the human body. This hardware method of treatment is called lithotripsy. The devices are available in several versions. Some waves are created using a laser, others are generated by ultrasound or an electromagnetic device.
The apparatus is attached in the area of the bladder. Then the device is turned on and the waves begin to crush the stones into small crystals. After that, they will freely leave through the bile duct. But lithotripsy can be used only in the presence of calculi up to 1 cm and with the condition of normal functioning of the organ.
Dissolving stones
Many calculi can be dissolved. But for this they should be no more than 5 mm, by age - up to three years. Cholesterol stones dissolve well. Therapy will be more effective if the patient is not obese. Preparations for dissolving calculi are selected depending on the structure of the stones. Usually, Ursosan or Ursofalk is prescribed at the rate of 8-13 mg / kg. Course therapy - from six months to two years. Another method is the introduction of drugs into the bladder that quickly destroy stones.
Diet
In case of gallstone disease, it is imperative to follow a diet. Especially in the asymptomatic period, in order to prevent the development of pathology and complications. Meals - fractional, 5-6 times / day, in small portions. Food temperature - not lower than 15 ° С and not higher than 62 ° С.

| Products | |
| Forbidden | Allowed |
|
|
Cooking food in only one of three ways - bake, stew, boil. The meat is recommended to be cut into small pieces or rolled through a meat grinder. Non-acidic juices, compotes, mousses are allowed from drinks. Tea is possible, but not strong.
When is surgery for gallstones needed?
Surgical operation for gallstones is performed when there is a high risk of complications or there is a threat to the patient's life:
- A large accumulation of stones. Cholecystectomy is required if calculi occupy more than 30 percent of the organ's volume. It becomes impossible to dissolve or crush the stones, and the bubble does not work at full strength, which creates additional problems and risks.
- Stones in the ducts. This provokes a blockage of the biliary tract. The secretion of bile stops, the soreness increases, obstructive jaundice appears.
- Frequent colic. They are very intense and are relieved by antispasmodics. But if attacks are frequent during treatment, it means that drug therapy was not effective. Then the optimal solution is to remove the bubble.
- Biliary pancreatitis. This is an inflammation of the pancreas, which has one excretory stream with the gallbladder. In this case, the outflow of bile is disrupted, and tissue destruction can result in the death of the patient.
- Some complications are peritonitis, canal strictures, biliary fistulas, and accumulation of pus.
- When medication fails.
Relative indications for surgery - this means there are also other methods of treatment. In a chronic disease, there are no negative symptoms, colic rarely occurs, and there is no inflammatory process. The patient is offered elective surgery.
Surgery
Gallstones (symptoms and treatment in adults are usually sufficient medication) sometimes requires surgery. This is indicated for an acute attack, the presence of large stones (over 3 cm) and complications. Surgical treatment involves removing the gallbladder. This is done in one of two ways.
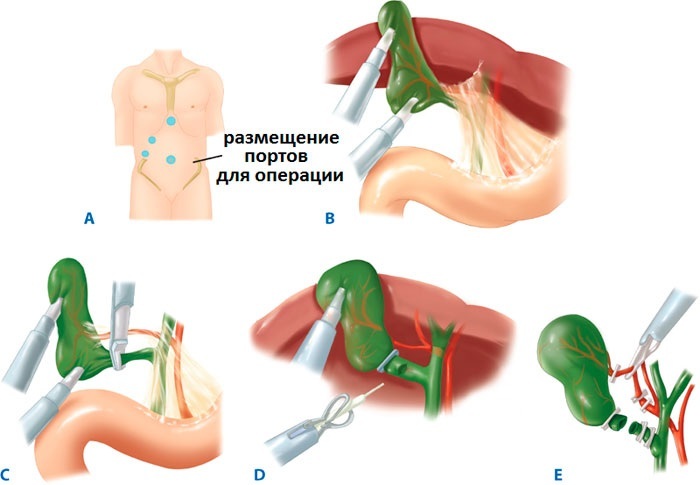
Standard cholecystectomy has been used for a long time. This is a lane operation, when an incision is made in the abdominal cavity and the gallbladder is cut through it. But more often they use a more modern method - laparoscopic. It is less invasive, there are no scars on the body, and recovery is faster. The operation is performed using a laparoscope, at the end of which there is a built-in mini-video camera.
First, several punctures are made in the abdominal wall. Surgical instruments are then inserted into them. With the help of a laparoscope with a camera, the doctor sees what he is doing. The gallbladder is carefully excised, immediately stopping bleeding from damaged tissues. The instruments are then removed and cosmetic stitches are applied to the holes. After healing, they are almost invisible.
Both operations require immersion of the patient in medication sleep (anesthesia). But with a cavity, the risk of complications, bleeding is higher, the tissues heal for a long time. All this is practically excluded during laparoscopy. Recovery is three times faster.
Gallstones (symptoms and treatment largely depend on the size and type of stones) occurs more often in adults than in children. But you cannot self-medicate. If the medicines are chosen incorrectly, then this can provoke a deterioration in the condition or lead to serious complications. Therefore, if alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Video about ZhKB
Symptoms and treatment of gallstone disease: