Content
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
- Classification and stages of development
- Complications of acute cholecystitis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of the acute form
- How to relieve an attack
- Diet for cholecystitis
- Tubage
- Surgery
- Forecast
- Video about cholecystitis
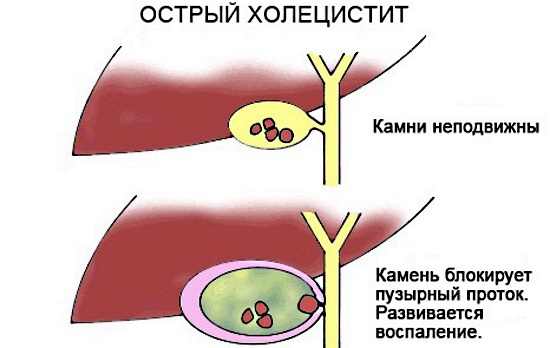
Acute cholecystitis is characterized by severe symptoms, and treatment in adults should be started immediately. This is a disease in which the outflow of bile is disturbed, and the ducts of the bladder are blocked.
Causes of the disease
The causes of the disease can be many; in the elderly, acute cholecystitis is more severe, the gangrenous form is more common. In the initial stages, pathology is treated with medication, more often only surgery helps.
Acute cholecystitis (symptoms and treatment in adults depend on the stage of the disease) often develops due to the appearance of calculi in the gallbladder. Even without blockage of the ducts, they deform the walls of the organ, causing inflammation.
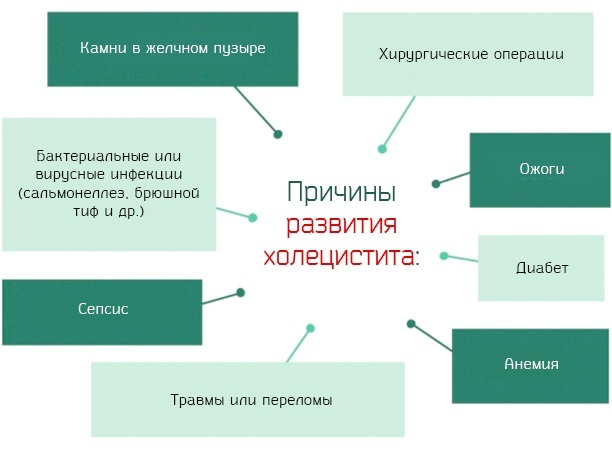
Other reasons:
- Improper nutrition, when a person eats a lot of spicy, fried and fatty foods. It provokes an intense secretion of bile, spasms of the sphincters (valves). As a result, pancreatic enzymes are thrown into the bladder, which causes inflammation.
- Gastrointestinal diseases, especially gastritis with low pH, become provoking factors. They weaken the body's defenses, which contributes to the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the bile ducts.
- Cholecystitis without stones is rarely diagnosed. It occurs against the background of infectious, vascular diseases, sepsis.
- Cystic artery thrombosis, which occurs due to atherosclerosis or bleeding disorders. In this case, a gangrenous form develops.
- Injuries, riding on bumps, when the body "shakes", intense physical activity - all this can provoke the displacement of the stone. As a result, the calculus enters the organ duct and disrupts the outflow of bile. Additionally, pathogenic microflora is activated in the bladder. This only makes the inflammation worse.
In older people, acute cholecystitis is diagnosed more often, since the existing diseases additionally affect the development of pathology. But gallstone disease is not always accompanied by the development of acute cholecystitis. Sometimes calculi do not interfere, do not manifest themselves. But there is a high risk of sudden development of serious complications.
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis
The onset of the disease is almost always accompanied by hepatic colic. These are severe pains under the right hypochondrium. Often they radiate to the epigastrium, lower back, the area above the collarbone, and can acquire a shingles in nature. But the epicenter of pain is more often concentrated at the Kera point (the intersection of the edge of the ribs and the rectus abdominis muscle), where it comes into contact with the abdominal wall.
Symptoms are due to severe biliary hypertension. It appears after a spasm of the biliary tract valves. Botkin's cholecystocardial syndrome, ischemia may develop. Then the pain is felt in the region of the heart. This makes it difficult to identify acute cholecystitis. Therefore, differential diagnosis is necessary.
You can only reduce the intensity of pain, but often it is not possible to stop it completely. It becomes dull, becomes bursting, localized in the area of the bladder. With complicated cholecystitis, pain spreads through the abdominal cavity. This indicates the development of peritonitis. Fatty foods can provoke biliary colic. After it, symptoms appear after 2 hours. It can be paroxysmal or continuous.
Intoxication of the body is additionally accompanied by:
- tachycardia;
- excessive sweating or dry skin;
- general weakness;
- an increase in temperature;
- lack or decrease in appetite;
- headaches;
- muscle pain.
The degree of temperature rise (indicated in degrees) depends on the intensity of the inflammation:
- catarrhal form - 37-38;
- destructive - more than 38;
- with empyema or perivesical abscess, sharp temperature fluctuations are observed (in addition, excessive sweating occurs).
Also, acute cholecystitis is accompanied by nausea, vomiting (it can be single or in the form of frequent attacks), after which there is no relief. An increase in pressure in the organ provokes the development of pancreatitis, cholangitis.
Classification and stages of development
Acute cholecystitis (symptoms and treatment in adults vary depending on the cause, stage of inflammation) is divided into 2 categories - uncomplicated and complicated.
The first includes:
- Catarrhal. The inflammation affects only the mucous and submucous membranes. This is accompanied by nausea, moderate pain. In acute inflammation, "dropsy of the gallbladder" may occur.
-
Destructive. This is a purulent form of cholecystitis. Symptoms depend on the type of disease.
Destructive is divided into subspecies:
- Phlegmonous. Inflammation covers all layers of the bladder membrane. Severe pain, flatulence, vomiting and fever appear. Palpation is painful, it is felt that the bladder is enlarged. Examination reveals three syndromes. Murphy, when palpation is observed interruption of inspiration, Ortner - when tapping on the ribs, soreness appears. Syndrome Mussi-Georgievsky (otherwise - the phrenicus symptom) is characterized by more intense pain on palpation.
- Phlegmonous and ulcerative. A variant when ulcers appear additionally in the organ.
- Gangrenous. With this form, tachycardia, dehydration, high temperature appear. There is irritation in the abdomen.
- Emphysematous. At the same time, gases accumulate in the gallbladder due to the active reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
- Gangrenous and perforated. There is a rupture of the gallbladder, severe peritonitis. The abdominal muscles are tense (Mendel, Razdolsky, Voskresensky or Shchetkin-Blumberg syndromes). Bloating, severe intoxication syndrome is observed.
According to another classification, acute cholecystitis is:
- Occlusal.
- Perforated with peritonitis (diffuse or local).
- With damage to the bile ducts. In this case, cholangitis, choledocholithiasis, stenosis of the duodenal nipple, and stricture of the common bile duct develop.
- With bilious peritonitis.
Also, acute cholecystitis is calculous, which is accompanied by the formation of stones. Without calculi, it is called non-calculus.
There are several stages of acute cholecystitis, smoothly passing from one to another. If calculi are the cause, then they touch the bladder membrane, causing irritation, inflammation. Then there is a blockage of the ducts. This triggers other pathological processes.
The most common cause of blockage in the ducts is calculus. Then reflex spasms begin in the bladder, bile ducts. The tissues gradually swell. Further, in the closed gallbladder, pathogenic microorganisms are activated or enter the organ with blood, through tissues. As a result, inflammation begins to progress, and the intensity of biliary hypertension largely depends on the degree of changes in the organ and its ducts.
Their blockage causes an increase in the normal pressure in the organ. This provokes the development of pancreatitis, cholangitis. The swelling of tissues gradually increases, microcirculation of blood is disrupted. All this leads to irreversible changes in the organ and life-threatening consequences.
Complications of acute cholecystitis
Complications arise after a long course of destructive types of the disease. If there is a delineation of inflammation, then a perivesical infiltrate is diagnosed. In the center is the gallbladder. Pathology occurs 3-4 days after the onset of the disease.
If the correct treatment is prescribed, then the infiltrate resolves in 3-6 months. When therapy has not yielded results, an abscess develops additionally. In this case, the symptoms of intoxication and pain intensify. Confirm the complication with ultrasound.
One of the most dangerous complications is peritonitis. This is a breakthrough of the bladder, after which bile spills over the abdominal cavity and severe inflammation and intoxication begins. As a result, the pain becomes unbearable, it is felt throughout the abdomen. The symptoms of intoxication are aggravated, intestinal paresis, flatulence and disturbance of peristalsis appear. The abdomen is tense, the ultrasound shows the accumulation of fluid. Emergency surgery is required.
An equally serious complication is cholangitis, when inflammation affects the biliary tree, abdominal sepsis appears. The patient is in serious condition, symptoms of intoxication are pronounced. There is a strong fever, in which the temperature fluctuates sharply, there is chills, excessive sweating.
The liver is enlarged, there is yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, cytolytic syndrome. Ultrasound shows the expansion of the ducts of the organ. Without treatment, liver failure occurs and the patient dies.
When the bladder membrane is perforated, areas of necrosis (dying tissue) are formed. More often this happens when there are calculi in the organ. Other complications are pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), empyema (accumulation of pus in the gallbladder), obstructive jaundice, which is caused by blockage of the ducts. And when they are damaged, the inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics begins with an external examination of the patient. First, the doctor collects anamnesis, listens to the patient's complaints. Finds out if the patient is following a diet. The stage is preliminarily determined by symptomatology. Then a general blood test is done, the concentration of leukocytes, ESR, bilirubin is assessed. These changes indicate the extent of the inflammatory process.
Instrumental research methods follow:
-
Ultrasound. This is a non-invasive and most informative diagnostic method. Evaluate the size and shape of the bubble. Check the contents of the organ, the condition of the membrane, tissues, ducts, whether there is an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. In acute cholecystitis, the bladder is enlarged. Its shell becomes layered. In the presence of calculi, their size, localization and number are assessed. Vesicles, dilatation of ducts, fluid in the abdomen are visible.
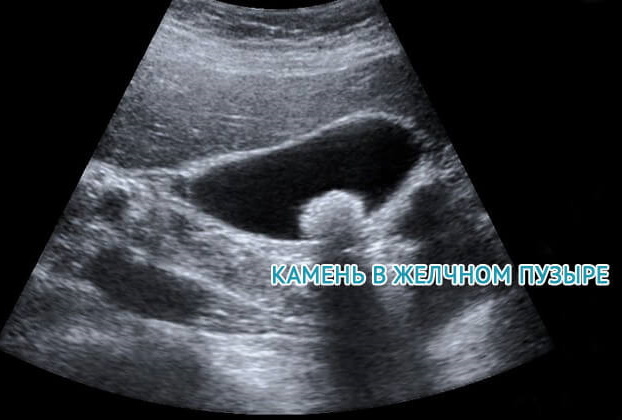
- Hepatobiliary scintigraphy. This is a method for assessing the secretion of bile, its excretion. Simultaneously check the patency of the ducts. Lateral projection images are important if you suspect that the gallbladder is filling incorrectly or with its abnormal development, localization. The accumulation of a radioisotope near the organ is observed with gangrene, extravasation indicates perforation of the walls. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy is the most accurate method in diagnosing calculous cholecystitis, obstruction of the cystic duct.
- X-ray. It is prescribed for suspected biliary obstruction. But stones are difficult to detect with the help of X-rays, since there is little calcium in the stones. But with peritonitis, signs of gastrointestinal paresis are revealed. To clarify the cause of canal blockage, endoscopic cholangiopancreatography and percutaneous transhepatic cholecystocholangiography are prescribed.
- CT scan (computed tomography) of the abdominal cavity. It is performed if it is difficult to make a diagnosis, and differential diagnosis is necessary. This helps to carefully assess changes in the bladder, its excretory canals, and surrounding tissues.
If there is a need for differential diagnosis, then laparoscopy is performed. It is done under anesthesia or local anesthesia. If surgical treatment is required, this is resolved immediately, while the patient is still on the operating table.
Treatment of the acute form
Acute cholecystitis has characteristic symptoms, and treatment in adults depends on the stage of the disease, inflammation, and the presence and type of calculi. In all cases, antibiotics are prescribed. They are selected depending on the pathogen (this is found out after examining bile). The course of treatment is 5-7 days.
With a mild severity of the disease with the need for immediate surgery, antibiotics are given within two days after cholecystectomy. A longer course is prescribed if the patient is in serious condition, and laboratory tests are not changing for the better. If the operation is postponed, then antibiotic therapy is carried out as soon as the patient is admitted to the hospital and before surgery (this can be up to 72 hours).
Treatment regimens depending on the severity of the disease:
| Severity | Treatment regimen |
| Mild to moderate, which developed outside the hospital |
|
| Severe or for the elderly, immunocompromised |
|
| Any severity (acute cholecystitis that develops in the hospital) | Similar 8 schemes, as in the case of severe disease, but each time Vancomycin is added at 15-20 mg / kg after 12 hours. |
Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs are included in the treatment regimen. For example, Diclofenac (75 mg), which prevents the progression of colic. If necessary, narcotic pain relievers are prescribed. For example, Meperidine (50-100 mg) by injection, with an interval of 3-4 hours.
Morphine is not used for treatment, as it intensifies spasms, and anticholinergics and antispasmodics are prescribed to eliminate them. Blockade of the round hepatic ligament with novocaine is effective. It can be performed blindly or by laparoscopy, under ultrasound guidance.
How to relieve an attack
In case of acute cholecystitis, you must immediately call an ambulance. Before she arrives, the patient must be put on the bed, ensuring complete rest and giving painkillers. For example, Tempalgin (analgesic) or Spazmalgon, which simultaneously eliminates spasms. Put ice wrapped in cloth on the gallbladder area. In case of severe vomiting, give a glass of still mineral water to drink.
It is forbidden to apply a heating pad, warming compresses, or an enema on the sore spot. Even painkillers are given only in case of a severe attack, but it is better to wait for the arrival of doctors. You can not take laxatives, wash the stomach.
Diet for cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis (symptoms and treatment in adults is already a reason to change the diet) is always accompanied by a diet. First, the patient is transferred to hunger (for 1-2 days), when you can only drink water and sweet tea. Then the patient goes to diet number 5. Spicy, fatty, frying and smoked foods are excluded from the diet. The use of muffins, hot spices, pickles and marinades is reduced to a minimum. Carbonated and alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited.
You need to eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions. Allowed cooking methods are boiling, baking or stewing. Dishes are eaten warm, but not hot. With constipation, you need to give up fiber-enriched foods (fresh fruits and vegetables), nuts.
Tubage
Tubage (blind probing) of the gallbladder is a common method for eliminating congestion in the organ and its ducts. This procedure can also be carried out at home, but only after consulting a doctor. The essence of the method is the intake of choleretic agents and the simultaneous warming of the area of the right hypochondrium. But the tyubage is performed in the absence of calculi in the bladder, otherwise it can provoke the advancement of calculi.
For the procedure, they take heated mineral water, with the addition of sorbitol, choleretic herbs, magnesia. Slowly drink 200-250 ml of liquid. Then the patient lies on his right side, placing a warm heating pad, covers himself with a blanket. Then he drinks another 250 ml of liquid. The total duration of the tubage is 1-2 hours. But in case of acute cholecystitis, the procedure may be contraindicated.
Surgery
Acute cholecystitis (symptoms and treatment in adults often indicate the need for surgery) can be resolved with surgery. If it is not performed on an emergency basis, then a little preparation is carried out. They restore blood microcirculation, do rinsing with crystalloid solutions, correct respiratory and heart failure.
If conservative treatment turned out to be ineffective, then the timing of the cholecystectomy is determined within a day. However, it is feasible when only 5 days have passed from the onset of the disease to the date of the surgical intervention. If it takes longer, more often they stop at conservative treatment.
The surgeon can choose one of three types of surgical intervention:
-
Cholecystostomy. This is an operation during which a fistula is artificially created between the cavity of the gallbladder and the external environment. Then a catheter is inserted into the organ, through which the accumulated infected bile is removed. This gradually reduces the severity of inflammation, restores normal pressure in the bladder, and eliminates congestion.
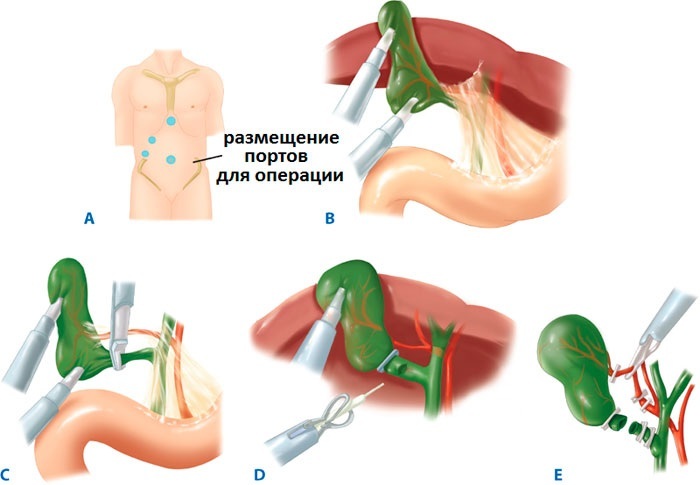
Laparoscopy of the gallbladder - Cholecystectomy. During the operation, the gallbladder is completely removed. This method remains one of the mainstay for surgical treatment. Cholecystectomy can be performed in two ways - from the bottom or from the neck of the bladder.
For debilitated and elderly patients, percutaneous cholecystostomy is recommended. Also, the operation can be abdominal, when the abdominal cavity is cut with a scalpel to perform manipulations. Or the laparoscopic method. In this case, several punctures are made, into which surgical instruments are inserted and the necessary manipulations are carried out. Laparoscopy is a less invasive and safer method of surgery.
Forecast
Acute cholecystitis in mild form usually ends with complete recovery without consequences. If the therapeutic regimen was not chosen correctly, the disease becomes chronic. When complications appear, the risk of death increases (in almost 50 cases). This most often occurs with empyema, perforation of the gallbladder, and the development of gangrene. Removal of an organ is not accompanied by a severe deterioration in the quality of life.
The liver will also produce bile, which will flow directly into the duodenum. But after surgery, postcholecystectomy syndrome often develops. Its manifestations are violation of the stool, frequent bowel movements, but this passes quickly. Persistent diarrhea is extremely rare. But to maintain the quality of life after removing the gallbladder, you must follow a diet. Exclude fried, fatty, spicy and dairy products. You should also give up alcohol.
Acute cholecystitis (its symptoms and treatment regimen in adults depend on the form and stage of the disease, the type of calculi) progresses rapidly and requires immediate therapy. Sometimes the only option is to remove the gallbladder. But this can be prevented by timely drug treatment, diet, disease prevention.
Video about cholecystitis
Types, signs and methods of treatment of cholecystitis: