Content
- Characteristic
- Signs
- Schroeder
- Alfelda
- Dovzhenko
- Klein
- Kustner-Chukalova
- Mikulich-Radetsky
- Strassmann
- Hohenbichler
- The ways
- According to Schultz
- Po Duncan
- Methods for forced discharge of a separated placenta
- Abuladze method
- Genter's way
- The Crede-Lazarevich method
- Placenta separation video
Branch placenta after childbirth Is a natural process aimed at cleansing the uterine cavity from the remnants of biological tissues that provided stable nutrition for the developing fetus. There are classification signs of the allocation of the placenta according to different authors of scientific literature in the field of gynecology.
Characteristic
The separation of the placenta is the final stage of labor. Isolation of the placenta occurs within 5-60 minutes. after the birth of the child. The rate of exit of the placenta from the uterine cavity depends on the tactics of childbirth, which were used in a particular clinical case.
Schroeder, Alfeld, Strassman, Dovzhenko are well-known gynecologists, authors of scientific publications that describe the basic signs of the afterbirth department. Placenta formation occurs from the embryonic membranes of the embryo (chorionic villous tissue) and allantois (urinary sac).
The temporary organ of the woman's reproductive system is in close contact with the wall of the uterus, forming multiple villi. The placenta establishes a close connection between the mother's body and the developing fetus.
Through the tissues of this organ, useful substances are exchanged, the child receives oxygen and emits carbon dioxide. After the natural birth of the baby, the need for further preservation of the placenta is lost. Within 1 hour, the woman's body rejects the intermediate tissue that feeds the child. Removal of the placenta occurs through the birth canal.
Signs
The separation of the placenta (signs according to the authors of scientific works in the field of gynecology differ, but not significantly) is an important stage in the completion of labor. The afterbirth left inside the uterus becomes the cause of an infectious and inflammatory process, which is a threat to a woman's health.
Schroeder
Isolation of the placenta based on Schroeder is characterized by the following clinical manifestations:
- the mother's uterus becomes flatter;
- there are signs of increased muscle tone;
- the bottom of the genital organ rises slightly above the navel, but slight deviations to the right side are allowed.

Separation of the placenta. Attributes by authors
A distinctive feature of the physiological process of separation of the placenta according to Schroeder is that just before the birth of the placenta, the uterus becomes narrower, its walls contract. In conditions of hypertonicity and spasm of the genital organ, the exfoliated tissues of the endothelium and amniotic membranes are released.
Alfelda
The separation of the placenta on the basis of Alfeld occurs as follows:
- The postpartum placenta, rejected by the woman's reproductive system, descends into the lower part of the uterus.
- Further movement of the placenta into the vaginal cavity is observed.
- The Kocher clamp, which is applied to the umbilical cord at the time of its bandaging, moves 8-10 cm down.
Diagnosing signs of postpartum placental exit according to Alfeld allows the obstetrician to adjust his actions related to the ligation of the umbilical cord. After the descent of the placenta into the vaginal cavity, there is a further release of the rejected tissues in a natural way.
Dovzhenko
The separation of the placenta (signs according to the authors of the scientific literature in the field of gynecology and obstetrics, describe the physiological process of the release of the birth placenta) is a painless process.
According to the sign of Dovzhenko, the isolation of amniotic tissues is as follows:
- The obstetrician delivering childbirth asks the woman in labor to take measured, but deep breaths and unhurried exhalations.
- The process of umbilical cord contraction is monitored. If at the time of lifting the chest on inspiration, the umbilical cord is not drawn into the vaginal cavity, then this is a clear sign of the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall.
- The presence of the effect of retraction of the umbilical cord into the birth canal after a deep inhalation indicates that the postpartum placenta has not separated from the surface of the genital organ.
Based on the above signs, the doctor decides on the tactics of further actions aimed at completion of the patient's labor activity with complete cleansing of her reproductive system from the remnants of the amniotic fluid fabrics.
Klein
The separation of the placenta according to Klein's signs is determined by the doctor after performing the following actions:
- The doctor asks the woman in labor to push.
- A visual observation of the condition of the umbilical cord is carried out.
- The lack of mobility of the tissues of the umbilical cord after the cessation of attempts indicates the complete separation of the placenta from the wall of the uterus.
- Pulling the umbilical cord into the vagina immediately after the woman stops pushing indicates the preservation of the biological connection of the placenta with the genital organ.
By the nature of determining the rate of release of the placenta, the Klein sign resembles the Dovzhenko method. The differences between these diagnostic methods are in the activation of different muscle groups that affect the contractile function of the uterus.
Kustner-Chukalova
To determine the sign of placental separation according to Küstner-Chukalov, the obstetrician will need to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- Take a position on the side of the left side of the woman in labor.
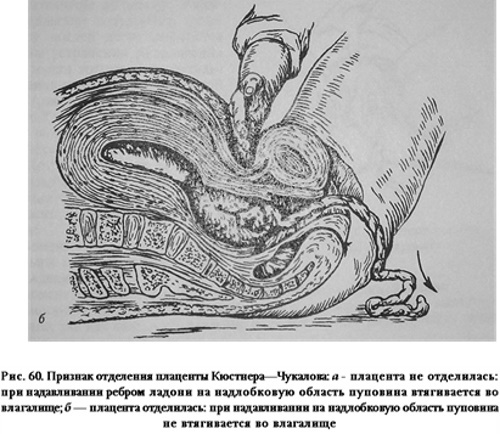
- Place the palm of the right hand on the surface of the anterior abdominal wall in the area of the pubic joint, where the uterus is located.
- Press with the right hand on the tissue of the genital organ.
- Monitor the mobility of the umbilical cord.
If there is a detachment of the placenta, then at the moment of sharp hand pressure on the surface of the abdomen, the umbilical cord is not pulled into the birth canal. The presence of signs of active tightening of the umbilical cord in the vagina indicates the preservation of the placenta on the wall of the uterus.
Mikulich-Radetsky
Determination of signs of placental abruption according to Mikulich-Radetsky is as follows:
- The doctor visually monitors the state of the woman's reproductive system.
- The doctor asks the woman in labor to perform the attempts as during the birth of the child.
- When the placenta is removed, its tissues must descend into the birth canal.
- As the next attempts are made, the placenta moves inside the vagina with its further removal outside the female body.
A distinctive feature of the sign of placental detachment according to Mikulich-Radetzky is that the doctor does not carry out any actions that involve squeezing the anterior wall of the uterus. The woman performs the activation of the muscles of the genital organ independently with the help of attempts.
Strassmann
Diagnosis of signs of placental separation according to Strassmann can be attributed to one of the most difficult ways to determine the release of the placenta. The doctor who delivered the baby will lightly tap the bottom of the uterus with his fingers. If at the moment the placenta is still not separated, then the vibrations from the genital organ pass through the umbilical vein, which is filled with blood.
This wave vibration is felt by the fingers of the hand located on the surface of the umbilical cord, higher from the place of its fixation with the clamp. In the event that at the time of tapping the fundus of the uterus, the placenta has already been separated, then there should be no vibration in the umbilical vein. To obtain more reliable data on the state of a woman's genital organ, it is recommended to use additional methods for diagnosing signs of placental abruption.
Hohenbichler
Hohenbichler's sign is determined by examining the umbilical cord of a woman in labor. In the absence of a physiological process of separation of the placenta from the uterine wall, rotation of the umbilical cord protruding from the genital slit around its axis is observed. This symptom occurs as a result of contraction of the muscles of the genital organ with simultaneous squeezing of the umbilical vein overflowing with blood.
The ways
The separation of the placenta (the signs according to the authors are based on the contractile function of the uterus and the mobility of the umbilical cord) occurs during the first 20-30 minutes. in primiparous girls. In women who have already given birth to the 2nd or 3rd child, the afterbirth leaves on average within 10 minutes.
The maximum duration of placenta separation is 1 hour. The absence of the process of birth of the placenta for a longer period of time requires doctor's intervention in order to carry out measures for the forced separation of the placenta from the wall uterus.
After the birth of the baby, the muscles of the uterus contract, the genital organ acquires a more rounded shape, its lower part is located in the navel. After a few minutes, postpartum contractions begin. With the next contraction of the muscle tissue of the uterus, a gradual displacement of the placenta occurs. In this regard, there are 2 main methods of natural exfoliation of the placenta with its further removal outside the female body.
According to Schultz
The method of postpartum detachment of the placenta according to Schultz is characterized by the separation of the central part of the placenta. A retroplacental hematoma is formed between the separated segments of the placenta and the wall of the uterus. The presence of this bruise contributes to further detachment of the placental tissue. According to Schultz, the natural birth of the placenta occurs in such a way that the tissues that provided the baby's nutrition are turned outward.
Further isolation of the retroplacental hematoma occurs simultaneously with the exit of the placenta. The main advantage of this method of birth of the placenta is minimal damage to blood vessels and much less blood loss. Separation of the placenta according to Schultz is considered a moderately painful process.
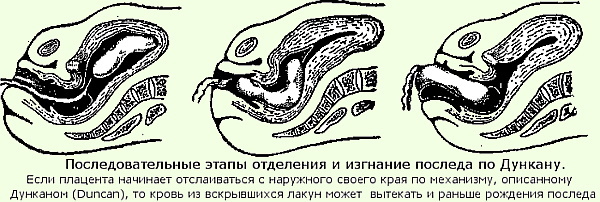
Po Duncan
The birth of the placenta according to Duncan differs in that the detachment of the placenta begins from its peripheral areas. The central part of the tissue remains firmly attached to the surface of the uterine wall. With each contraction, the placenta is displaced from the edge to the middle. After 2-3 attempts, the placenta is born with the preservation of the integrity of its membranes.
The shape, structure and size of the placenta remain exactly the same as they were at the time of attachment to the uterus. A significant disadvantage of the birth of the placenta according to Duncan is greater vascular damage and profuse blood loss. The absence of a retroplacental hematoma in the central part of the uterus leads to the fact that the process of separation of the placenta becomes longer and more painful.
The table below shows the main rates of blood loss at the time of detachment of the placenta according to Duncan and Schultz.
| Type of blood loss | Average norms and characteristics of the state of the woman in labor |
| Physiological | Physiological blood loss at the time of placenta separation is 250 ml. This is the result of natural damage to the blood vessels in the uterus. The woman's condition remains stable and satisfactory. |
| Border | In this case, the woman in labor loses from 300 to 400 ml of blood during the entire process of birth of the placenta. There may be signs of deterioration in general health, increased heart rate, lower blood pressure. A woman with symptoms of pathological blood loss needs qualified medical care to stabilize the vital functions of the body. |
| Pathological | The most severe consequences of placental separation occur if, during this process, the woman in labor has lost more than 400 ml of blood. There is a real threat to life. |
Permissible blood loss during placenta separation according to Schultz and Duncan is 0.5% of the total weight of the woman in labor.
The following factors contribute to the detachment of the placenta:
- the attempts of a woman in the postpartum period;
- the presence of a retroplacental hematoma;
- own weight of tissues that provided nutrition for the child;
- reflex contraction of the muscles of the uterus during labor.
After separation of the placenta, a spasm of the muscle tissue of the uterus occurs naturally. The blood vessels of the genital organ are compressed, which ensures a rapid stop of uterine bleeding. In gynecological practice, the most common method of separation of the placenta according to Schultz.
Methods for forced discharge of a separated placenta
The separation of the placenta (signs according to the authors are set out in medical publications devoted to gynecology and obstetrics) should occur independently without the intervention of a doctor. In the absence of positive dynamics to the exit of the placenta, the doctor applies one or several alternately at once several methods to stimulate the process of placental exfoliation.
Abuladze method
Stimulating the function of the uterus to separate the placenta using the Abuladze method provides for the following algorithm of actions:
- The doctor receives permission from the woman in labor to forcefully remove the placenta.
- The doctor explains to the woman the procedure that he will perform to cleanse her genital organ from the remnants of the placenta.
- The woman in labor empties the bladder. This happens naturally or through a catheter.
- The obstetrician performs a gentle massage of the uterine tissue by acting on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
- With massage movements, the doctor brings the uterus to the middle position.
- The doctor stands to the side on the right side of the woman in labor.
- With both hands, the doctor grabs the musculature of the anterior wall of the peritoneum with its direction to the area of the longitudinal fold, while lifting the muscle tissues.
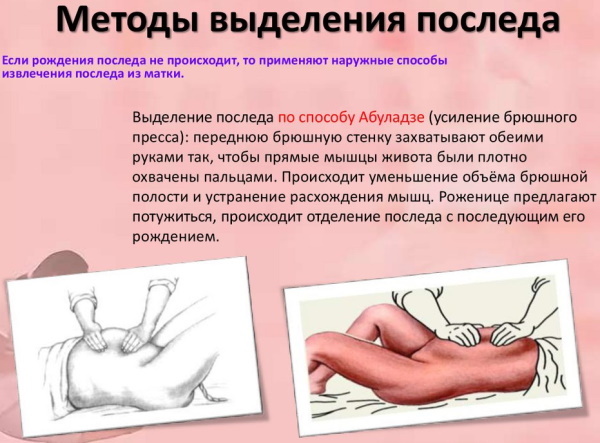
Immediately after the obstetrician has performed the above manipulations, the woman should begin to push. If the doctor did everything correctly, then the process of displacement of the placenta into the lower part of the uterus should begin with a gradual exit into the lumen of the vagina.
Genter's way
In order to stimulate postpartum placental abruption according to the Genter method, the following manipulations are performed:
- The doctor obtains permission from the woman in labor to perform actions for the forced separation of the placenta.
- The woman empties the bladder.
- The doctor performs a leisurely massage of the anterior wall of the uterus through the tissues of the abdominal cavity. The flow of additional blood volume to the organs of the reproductive system is ensured.
- With the help of massage movements of the obstetrician, the uterus of the woman in labor is brought to the middle position.
- The doctor stands on the side so that the woman's legs are in front of his face.
- The doctor clenches the hands of the upper extremities into fists.
- The outer side of the phalanges of the fingers is fixed in the area of the fundus of the uterus from the side of the tubal corners.
- The obstetrician asks the woman in labor to temporarily stop pushing.
- The doctor squeezes the uterus towards the sacrum.
Depending on the situation and signs of the appearance of the placenta in the vaginal cavity, the doctor may ask the woman to perform several attempts to completely release the placental tissues from the genital organ. Failure to comply with the above rules during the application of Genter's method is fraught with spasm of the pharynx of the uterus with subsequent infringement of the placenta.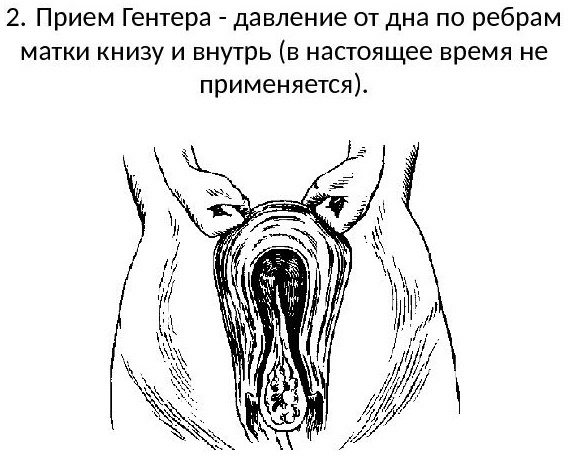
To eliminate the spastic effect, an antispasmodic drug in the form of 2 ml of a 2% solution of No-shpa and Papaverine hydrochloride is immediately administered to the woman in labor. It may be necessary to use 1 ml of an injection solution of Atropine sulfate 0.1% concentration and a similar amount of Platyphyllin with a mass fraction of the active substance of 0.1%. Immediately after the removal of the spasm of the pharynx of the uterus, the obstetrician continues to remove the exfoliated placenta from the woman's body.
The Crede-Lazarevich method
Forced detachment of the placenta according to the Krede-Lazarevich method is carried out in compliance with the following algorithm of actions:
- Obtain consent from the woman for this procedure.
- Inform the woman in labor about the nature of the actions that will be performed after 1-2 minutes. for faster and more complete cleansing of the uterus from the placenta.
- Ensure that the mother's bladder is emptied.
- Massage the tissues of the uterus by palpating the anterior abdominal wall.
- Bring the woman's reproductive organ to the middle position.
- Take a position to the left of the woman in labor.
- With the help of your right hand, grasp the bottom of the uterus so that the phalanx of the thumb is located on the front wall of the genital organ, the entire palm area is at the bottom, and the remaining 4 fingers are on the back wall of the uterus.
- Ask the woman in labor to relax.
- Press on the muscles of the uterus at the same time with all fingers, but in two intersecting directions, so that uniform physical pressure is exerted on all tissues of the genital organ.
- Squeezing with the fingers of the right hand is carried out in the direction from the anterior to the posterior wall of the uterus, and palm pressure is applied from top to bottom towards the lumbosacral spine.
After the cessation of pressure on the muscles of the uterus, it is necessary to visually monitor the appearance of the placenta inside the vagina with its further exit outside the woman's reproductive system.
In especially difficult cases, when, despite the performed manipulations for the forced detachment of the placenta, it is removed, the woman in labor is required to lean on the feet while lifting the pelvis up. Under their own weight, the tissues of the postpartum placenta hang down, and are separated much faster from the anterior wall of the uterus.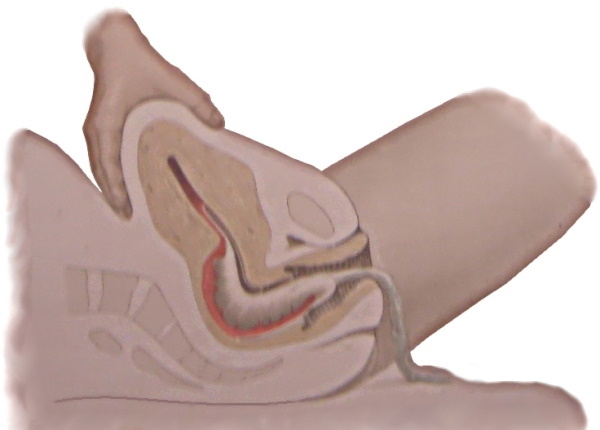
The separation of the placenta is a natural process of cleansing the uterus from temporary tissues that have formed in its cavity to provide the baby with nutrients, as well as to carry out gas exchange. Signs of the exit of the placenta are determined during a visual examination of the woman's vagina. The symptoms of placental abruption are described by several authors at once, who are specialists in the field of gynecology and obstetrics.
The imminent exit of the placenta from the reproductive system of a woman is indicated by the simultaneous combination of several signs at once. Diagnostic methods according to Alfeld, Schroeder, and Küstner-Chukalov are considered the most informative methods for establishing the separation of the placenta. The afterbirth leaves on its own after the birth of the child, or the doctor takes measures to remove it using a special gynecological procedure.
Placenta separation video
Manual removal of the placenta: