Content
- Dangers of hepatitis A, the pros and cons of vaccination
- Indications and contraindications for vaccination
- The expediency of the procedure for children
- Varieties of vaccine preparations for hepatitis A, names and characteristics
- Immunization scheme
- For children
- For adults
- Instruction for vaccination against hepatitis A
- How does the vaccine work?
- Possible side reactions and complications
- The cost of drugs
- Hepatitis A vaccine video
Common liver diseases include hepatitis A (Botkin's disease), which occurs as a result of the ingestion of a virus of the hepatovirus genus of the picornavirus family. This infection is dangerous: for a long time there may be no clinical and laboratory signs of the development of pathology. The incubation period for hepatitis A lasts from 7 to 50 days. The disease is accompanied by general malaise, rapid weight loss, increased fatigue, vomiting and nausea.
Botkin's disease is also characterized by discoloration of feces, yellowing of the sclera and skin. In a laboratory study of the patient's blood, an increased level of transaminase is recorded. You can become infected with hepatitis A through the fecal-oral, food and contact-household routes.
Modern medicine allows not only to cure this infectious disease, but also to help the body to form immunity to Botkin's disease even before infection. It is the vaccine that is the most effective means of protection against hepatitis A.
Dangers of hepatitis A, the pros and cons of vaccination
Botkin's disease is the least dangerous type of hepatitis, as in more than 93% of cases, complete recovery occurs. At the same time, the risk of complications remains at a minimum level. Hepatitis A is dangerous because of the high rate at which the virus spreads.
With an asymptomatic course of the disease, the patient does not have characteristic signs of the development of pathology, but he is a carrier of an RNA-containing virus from the Picornaviridae group, which is why the surrounding people are at risk of infection people. The first symptoms of Botkin's disease can appear only 14 days after infection.
The hepatitis A virus is transmitted from sick people to healthy people in the following ways:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene standards (dirty hands).
- Eating dirty food that is not fresh.
- Use with an infected person of general hygiene products, dishes.
- Drinking raw water.
In most cases, the causative agent of Botkin's disease is excreted along with the feces and enters the body through the mouth, which is why this method of infection is called "fecal-oral".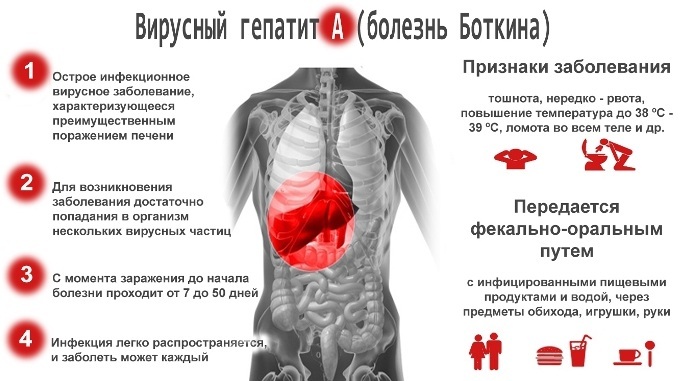
Seasonality is inherent in hepatitis A, as outbreaks of this disease occur mainly in the fall. Poor-quality water plays an important role in the spread of Botkin's disease. This is especially true for those settlements in which there are difficulties with cleaning and supplying centralized water supply using special stations.
The hepatitis A vaccine helps the body develop immunity to prevent the development of an infectious disease, which in 90% of cases is mild, but the liver is exposed to increased load. This affects the work of other organs, which is why complications may develop.
The danger of hepatitis A is due to the low sensitivity of the virus to adverse external factors. At normal temperatures, the infection can survive for up to 4 years. An RNA virus from the Picornaviridae group is resistant to disinfectants, formalin and ultraviolet light.
Thanks to the rapid development of science and traditional medicine, there are now many effective vaccines against hepatitis A. The World Health Organization is a proponent of global vaccination to avoid new outbreaks of infection.
For example, in Shanghai in 1988, in a short period of time, Botkin's disease was diagnosed in more than 300,000 people, 15% of whom required urgent hospitalization. In 95% of cases, the age of the patients ranged from 20 to 40 years. And in Argentina and Brazil, hepatitis A has become the main cause of the development of transient liver failure in the population.
Among the negative characteristics of vaccination, it is possible to single out only the fact that, in isolated cases, patients experience adverse reactions and complications. More often, short-term redness and coarsening of the skin is observed at the injection site. The formation of a small nodule under the skin is not excluded.
Hepatitis A vaccine has an 18% chance of causing nausea, diarrhea, and insomnia. Within a few days, these symptoms go away on their own, so that symptomatic treatment is not required.
The effectiveness of vaccination depends on the rules of storage of the drug and compliance with the norms of its transportation. Viral hepatitis can be quite difficult, causing destructive changes in the liver. For this reason, qualified infectious disease specialists recommend timely vaccination, which reliably protects the body of adults and children from pathogenic viruses.
Indications and contraindications for vaccination
Each person is shown the introduction of the vaccine against hepatitis A, but in traditional medicine there is a certain category of people who must be vaccinated without fail.
For example:
- Kindergarten and school workers.
- Children living in cities with an increased incidence of disease. If an epidemic of hepatitis A is recorded in the city, then it is necessary to contact the pediatrician as soon as possible so that the child is vaccinated.
- People in contact with someone who has been diagnosed with hepatitis A.
- Patients with chronic liver and blood diseases.
- People planning to visit a country with an epidemic of Botkin's disease.
- Employees of wastewater treatment plants and technical sewage services.
- People living in epidemically unfavorable areas.
- People working in the service sector, health care.
Inanimate, live and synthesized vaccines belong to the category of relatively safe drugs. For this reason, the occurrence of adverse reactions after the administration of the vaccine is not excluded.
Infectious disease specialists do not vaccinate against hepatitis A in the following cases:
- The presence of malignant oncological neoplasms in the patient's body.
- The period of bearing a child.
- Increased propensity of the body to develop an allergic reaction.
- The period of breastfeeding of the child.
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
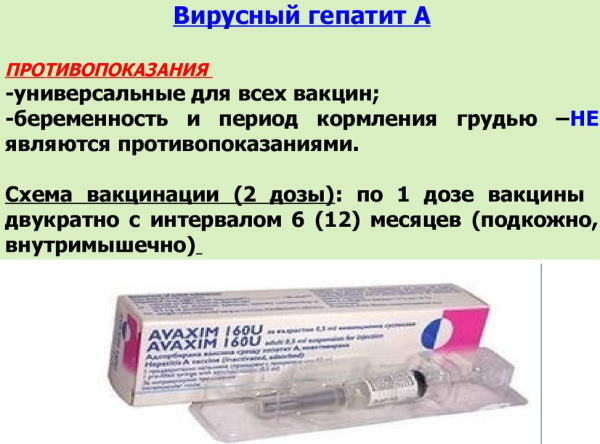

Only a healthy person can be vaccinated against Botkin's disease. If a person has no contraindications, and he is normally physically developed, then the likelihood of adverse reactions is only 1%.
The expediency of the procedure for children
The vaccine against hepatitis A is intended for the formation of a stable immunity in a child. The drug is recommended to be administered to children at the age of 1.5-2 years. The vaccine for Botkin's disease contains HAV (hepatitis A virus), which is reproduced in fibroblast cells, after which it is inactivated with formaldehyde.
Additionally, the drug may contain the following additional components:
- Neomycin.
- Aluminum hydroxide.
- Polyoxidonium.
In pediatrics, the drug for hepatitis A can be administered together with vaccines that are included in the mandatory vaccination calendar, but this is only if separate syringes are used. It is necessary to inject in different parts of the body.
The combination vaccine contains 2 pathogens at once, so that combined immunization can be carried out. The drug can simultaneously include hepatitis A and B viruses. It is permissible to use the vaccine against Botkin's disease simultaneously with other vaccines, but the child must first undergo a comprehensive examination of the body.
Varieties of vaccine preparations for hepatitis A, names and characteristics
The vaccine against Botkin's disease, provided that the patient has no contraindications, has a minimal risk of complications. This is due to the fact that only modern purified drugs are used in medicine, which undergo numerous tests. To date, 4 types of vaccines are used in Russia for immunization against hepatitis A.

| Vaccine name | Description |
| Avaxim | This vaccine is manufactured in France and is used in pediatrics to vaccinate children over 1 year old. 14 days after administration of the drug, 98.3% of patients develop antibodies, after 1 month - in 99.9%. |
| Hawrix | It is a highly sought after vaccine from the UK. The drug is safe for adults and children over 1 year of age. Two weeks after vaccination, antibodies are produced in 88% of patients, after 30 days - in 99%. The drug is effective in focal outbreaks of Botkin's disease. The product is available in vials and disposable syringes. |
| Wakta | American-made vaccine that is safe for adults and children over 3 years of age. The drug is highly effective, since according to medical statistics only 1 person out of 1,000,000 vaccinated can get sick. |
| GEP-A-in-VAK | An effective, safe vaccine made in Russia. The drug can be administered to adults and children over 3 years of age. The product is available in ampoules. The vaccine allows for the formation of stable immunity from hepatitis A for 20 years in 96% of adults and 90% of children. |
All described vaccines contain inactivated viral particles that cannot cause infection with Botkin's disease.
Immunization scheme
For the formation of stable immunity in adults and children, it is necessary to do 2 vaccinations. The break between them should last 4-18 months. Re-vaccination is carried out in cases where no allergic reaction occurs after the first injection. A safe immunization regimen can only be drawn up by the attending physician, taking into account the patient's age, general health and the presence (absence) of concomitant diseases.
For children
It is recommended to use 0.5 ml of the preparation for the vaccination of a child whose age ranges from 1 to 18 years. It is necessary to inoculate intramuscularly in the front of the thigh. For children from 3 years old, the drug is injected into the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. If the child has a history of blood diseases, the vaccine is administered subcutaneously. Pediatricians claim that 1 dose of the vaccine against Botkin's disease allows you to develop immunity in 7-14 days. The vaccination is valid for 18 months.
The imported hepatitis A vaccine must be administered 2 times with the obligatory observance of the interval between injections (from 4 to 18 months). Formed immunity will last for a maximum of 20 years.
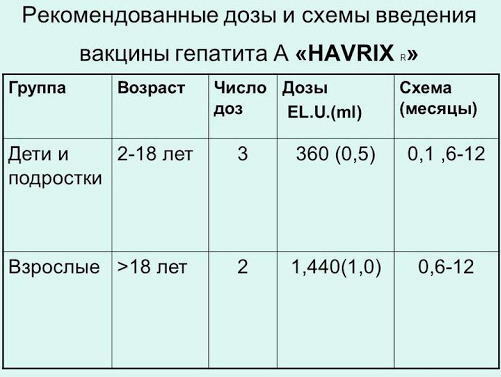
The Russian vaccine GEP-A-in-VAK should be administered to a child according to the following scheme:
- At 3 years old - 1 dose of the drug.
- After 30 days - 2 doses of the vaccine.
- After 18 months - 3 doses.
The vaccine can be given to a child on the same day as other vaccinations, but with the exception of BCG. Otherwise, there is a high risk of complications. In immunocompromised patients, after 3 injections, the level of antibodies produced may be insufficient, which is why the doctor may prescribe an additional vaccination.
For adults
Before vaccination, the patient must necessarily consult with a physician. The doctor measures body temperature and blood pressure. In the absence of contraindications, the patient gets access to vaccination. On the outpatient card, the nurse must indicate the name of the drug, the batch number and the dose to be administered.
An adult patient is vaccinated against hepatitis A in the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. Revaccination is carried out after 6-12 months. To obtain stable immunity, 2 injections of 1 ml are enough. If the patient is on hemodialysis, then the second dose of the drug is recommended to be administered 30 days after the first vaccination. A similar immunization scheme applies to people with impaired health.
Instruction for vaccination against hepatitis A
For children from 1 to 18 years old, a single dose of the vaccine against Botkin's disease should not exceed 0.5 ml. For patients aged 18 years and older, the dosage of the drug should be increased to 1 ml. The opening of the ampoules and the vaccination procedure should be carried out by a medical worker in compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. Before putting the drug into the syringe, the ampoule must be shaken well. The vaccine from the opened ampoule must be used within 30 minutes.
4 days before vaccination, it is necessary to exclude allergens from the diet: tomatoes, citrus fruits, chocolate, grapes and seafood. Overeating is not recommended in order to reduce the burden on the digestive organs and facilitate the post-vaccination period. For 3 days after the introduction of the vaccine, it is necessary to avoid places where a large number of people gather in order to reduce the risk of developing SARS.
In order to reduce the likelihood of negative local reactions, the vaccine should be given intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle. When injecting the drug, make sure that the needle does not enter a blood vessel.
It is not recommended to inject the vaccine into the gluteus muscle, as there is a risk of inducing an immune response of a reduced intensity. Only if the patient has a history of thrombocytopenia or an increased tendency to bleeding can the drug be administered subcutaneously.
How does the vaccine work?
The hepatitis A vaccine helps the body develop antibodies to reduce the likelihood of contracting Botkin's disease by 99.9%. severe cases can provoke the occurrence of pathologies of the biliary tract, inflammation of the myocardium and a violation of the quantitative composition blood.
After the introduction of the drug, various immune processes occur in the body, as a result of which protection against the infectious process develops. The vaccine lasts for 6-20 years. Permanent immunity is formed only in those patients who have had Botkin's disease.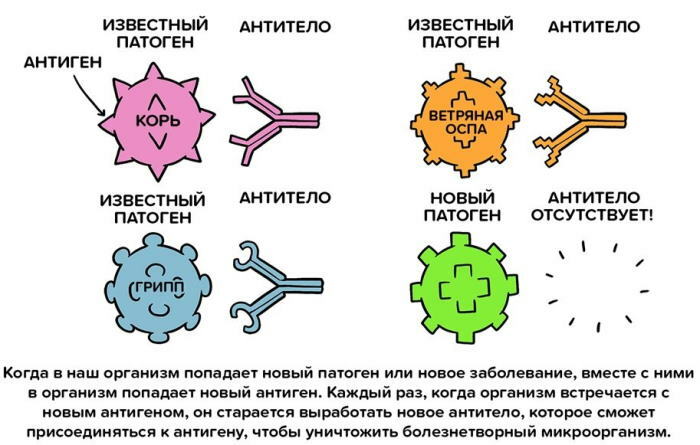
From a medical point of view, protection against disease-causing agents is a collection of antibodies that are produced by the immune system under the influence of a vaccine. In case of penetration of viral material into the body, immune complexes quickly destroy it. Antibodies circulate in the blood for decades until they encounter pathogens and eliminate them.
Possible side reactions and complications
Vaccination, as well as taking medications, can cause the development of side effects. The occurrence of an allergic reaction is possible. But compared to other vaccines, the hepatitis A vaccine is tolerated quite easily by people of all ages. In medical practice, isolated cases of death of patients after vaccination have been recorded. Infectionists claim that it is much easier for a person to undergo immunization than to get hepatitis A.
After administration of the drug, an increase in temperature is possible. Only when the + 38.5 C mark is exceeded, it is recommended to take an antipyretic agent. If the patient is prone to developing allergies, then an antihistamine should be used before vaccination. To eliminate itching and burning at the injection site, you need to treat the problem area with baby cream or Hydrocortisone ointment.
Among the most common adverse reactions to hepatitis A vaccination are:
- Headache attacks.
- General malaise.
- Swelling of soft tissues at the injection site.
- Breathing disorder.
- Bronchospasm.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- The development of vasculitis.
- Hives.
- Chills.
Most often, adverse reactions occur as a result of the patient's consumption of alcoholic beverages. Alcohol interferes with the production of specific antibodies to the HAV virus.
Only in 2% of cases after vaccination, patients experience the following complications:
- Meningitis. Inflammation of the lining of the brain, which is fatal in 10% of cases.
- Quincke's edema. In isolated cases, angioedema can lead to the death of a patient if medical assistance was not provided in a timely manner.
- Erythema. This is an atypical redness of the skin, which occurs when the capillary vessels of the skin overflow with blood.
- Neuritis. This is an inflammation of the peripheral nerves, which is accompanied by pain and decreased sensitivity (paralysis and paresis are possible).
- Multiple sclerosis. It is a progressive disease characterized by a malfunction of the central nervous system.
- Encephalitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the brain, which is characterized by damage to the nervous system.
- Decrease in blood pressure indicators to critical levels.
- Vasculitis (a common name for a group of diseases characterized by inflammation and destruction of the walls of blood vessels).
- Progression of previously diagnosed chronic diseases.
- Lymphadenopathy. This is a condition characterized by an increase in the size of peripheral lymph nodes, a change in their consistency and mobility.
- Coma. This is a life-threatening state of impaired consciousness, caused by damage to special structures of the brain and characterized by a complete absence of patient contact with the outside world.
Hepatitis A vaccines have a minimal risk of complications. This is due to the fact that in traditional medicine, only high-quality drugs that have passed a multi-level test are used. If at least 1 of the listed symptoms occurs, it is recommended to immediately call an ambulance, as self-medication can be life-threatening.
The cost of drugs
The final price of the vaccine against Botkin's disease directly depends on the manufacturer and the final sales margin. Russian and imported drugs do not differ significantly in their cost.
| Vaccine name | Average price in Russia (rub.) |
| GEP-A-in-VAK (Russia) | 4350 |
| Avaxim (France) | 2682 |
| Hawrix (UK) | 2651 |
| Wakta (USA) | 4790 |
| Twinrix (Belgium) | 3200 |
It is recommended to store vaccines against hepatitis A in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2 to +8 C. It is forbidden to freeze the preparations, otherwise they will lose their properties. The Havrix-720 vaccine has been developed for children and adolescents, and it is recommended for adults to administer Havrix-1440. The GEP-A-in-VAK means belongs to the category of interactive vaccinations.
Twinrix is a combination drug, as it helps to develop immunity against hepatitis A and B. Before vaccination, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination to make sure that there are no contraindications that can provoke the development of complications. Only qualified healthcare professionals can administer immunizations.
Hepatitis A vaccine video
Hepatitis A vaccine:



