Content
- What is Helicobacter Pylori, what does the bacterium eat
- How the bacterium is transmitted
- Causes of the appearance in the stomach
- Infection symptoms
- The danger of infection, what diseases develop against the background of infection
- Gastritis
- Peptic ulcer
- Stomach cancer
- How to detect Helicobacter pylori in the stomach, diagnostic methods
- Histological method
- Non-invasive and minimally invasive diagnostic methods
- Methods and treatment regimens
- Antibiotics
- Preparations of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate
- Proton pump blockers
- Nutrition, diet features, an approximate menu for 3 days
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Drug therapy regimens for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori
- First line eradication drugs
- Second-line eradication drugs
- Third-line eradication drugs
- Possible complications if untreated
- Video about Helicobacter Pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterial microorganism, which parasitizes on the walls of the human stomach, and is also able to penetrate into the duodenal cavity. The main danger of this pathogenic infection is that it can cause acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Recent scientific studies support the fact that Helicobacter pylori is the cause of recurrent ulcers gastrointestinal tract, the treatment of which is complicated by the high resistance of this microorganism to drugs antibacterial therapy.
What is Helicobacter Pylori, what does the bacterium eat
Helicobacter pylori is a pathogenic gram-negative bacterium that can infect any area stomach of a person, affects the duodenum, provoking inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the spread of ulcerative formations.
Under the microscope lens, this infection looks like a spiral organism with many small flagella that facilitate its introduction into the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases provoked by Helicobacter pylori infection includes complex antibiotic therapy, consisting of 3-5 drugs. The selection of medicines is carried out by a gastroenterologist on the basis of a laboratory study of the contents of the patient's stomach.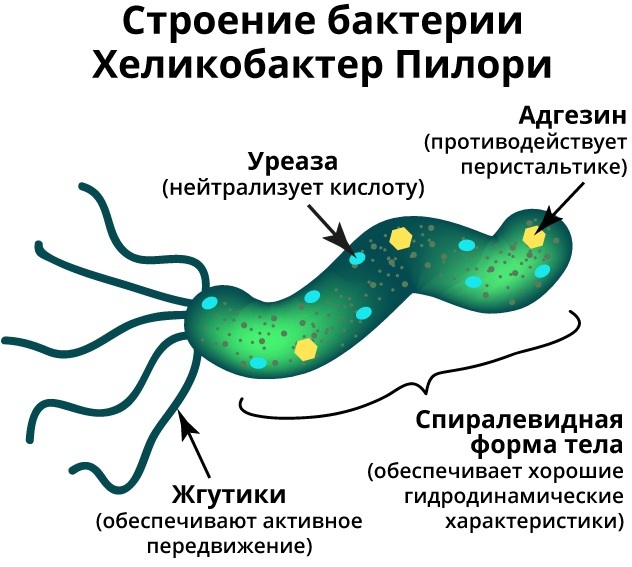
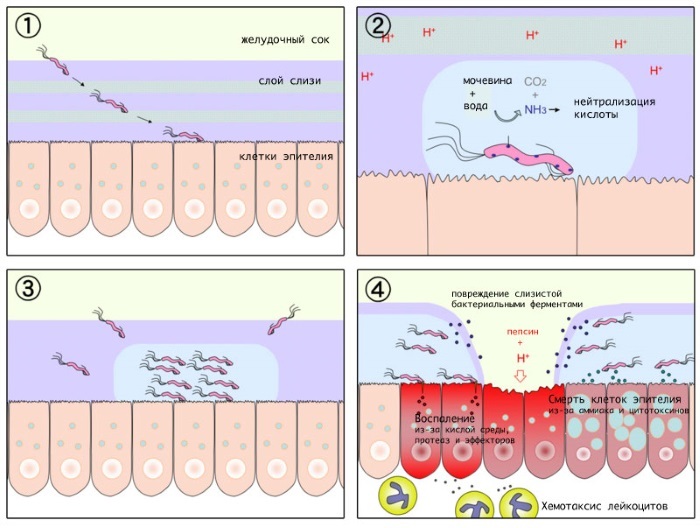
Individual preparation of a treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection is necessary in order to use antibiotics that are effective against a specific strain of the microorganism. This microbe is highly resistant to antibacterial drugs of various groups. Helicobacter pylori quickly adapts to the active substances of medicines, which further complicates the process of its destruction even with the help of potent antibiotics.
This microorganism feeds on the protective mucous layer of the stomach, and also damages the cells of its walls. Doctors-gastroenterologists classify Helicobacter pylori as a type 1 carcinogen, since this the infection can cause not only inflammatory processes and ulcers, but also the formation of malignant tumors.
How the bacterium is transmitted
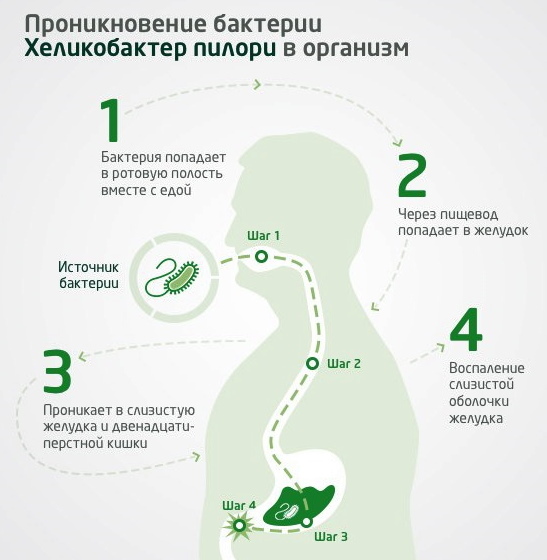
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the stomach (it is necessary to treat diseases caused by this infection in a complex manner) in 80% of the adult population of the Russian Federation. These are the results of scientific research in the field of gastroenterology regarding the prevalence of this microorganism.
In most cases, this infection enters the human gastrointestinal tract as early as childhood. The cells of the immune system are not able to independently get rid of this microorganism, which over time leads to pathological changes in the structure of the gastrointestinal tract tissues.
The table below describes the main routes of transmission of Helicobacter pylori infection, as well as a brief description of the process of infection with this microorganism.
| Modes of transmission | Description of the infection process |
| From sick person to healthy person | In this case, the spread of Helicobacter pylori occurs at the time of direct contact of the carrier of the infection with a healthy person. The transmission of a microorganism is possible during a kiss, eating food from the same dish or using a common cup, flask for water. |
| Together with water | Helicobacter pylori infection occurs through water, which contains this bacterium. People who drink raw tap water are at increased risk. |
| Through food | Helicobacter pylori can be found on the surface of fresh vegetables, fruits, and other foods. Eating contaminated food leads to infection of the digestive tract with the further development of the inflammatory process. |
| Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules | Lack of a good habit of washing your hands before eating can lead to infection with Helicobacter pylori. For example, if a person worked in the land, on a personal plot, visited public places, and then ignored the basic rules of hygiene. Regular hand washing minimizes the risk of infection with H. pylori. |
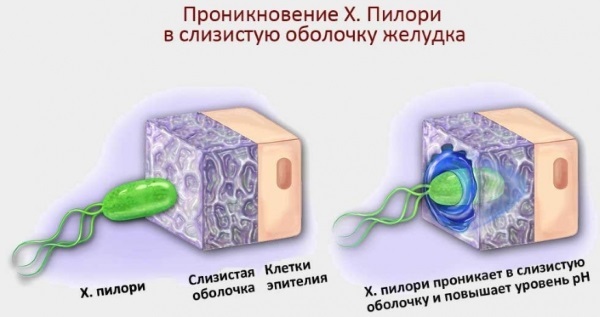
In most cases, gastroenterologists cannot find the source of the spread of the infection, since Helicobacter pylori is able to parasitize in the human gastrointestinal tract for a long period, without showing its presence.
Causes of the appearance in the stomach
The main reasons for the appearance of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach cavity is the infection of the human body with this bacterium through its pathways, which are described in the table above.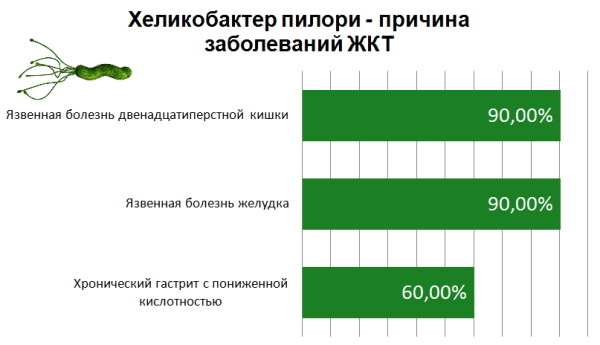
The pathogenic activity of this microbe in the gastrointestinal tract of an infected person can be triggered by the influence of the following factors:
- decreased immunity;
- constant stress and psycho-emotional overstrain;
- alcohol abuse;
- tobacco smoking;
- hereditary predisposition to inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- eating a lot of spicy, too acidic, protein foods.
In the process of examining a patient with signs of gastrointestinal diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori, a gastroenterologist is always interested in the patient's lifestyle, his diet, schedule eating.
Infection symptoms
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the stomach (it is necessary to treat the inflammatory process in the early stages of its development) is detected by microbiological examination of its mucous contents.
The presence of this infection is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a feeling of spasmodic pain or a feeling of pronounced discomfort in the area of the stomach;
- nausea;
- discharge of vomit;
- complete absence or loss of appetite;
- heaviness in the digestive tract, which appears immediately after eating;
- heartburn, provoked by an increase in the level of acidity of gastric juice;
- darkening of feces, which occurs due to the occurrence of ulcerative bleeding.
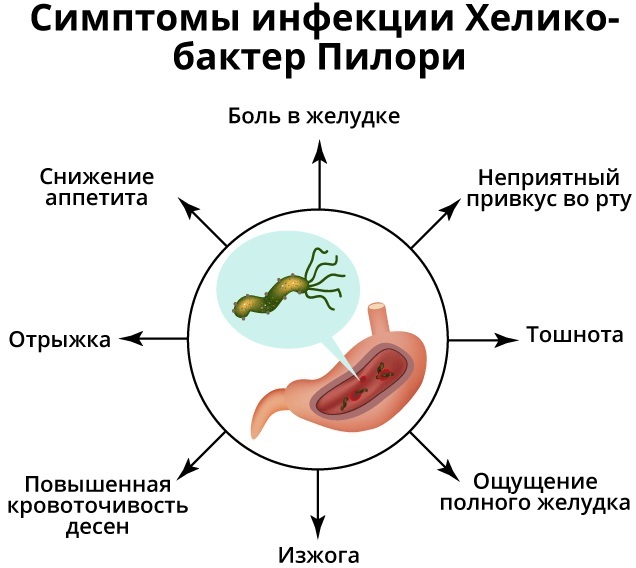
The difficulty in diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection is that the symptoms of its parasitic activity are typical for most gastrointestinal diseases. Only a timely laboratory study of the biological fluids of the stomach gives an unambiguous answer about the presence or absence of this pathogen in the organs of the digestive system.
The danger of infection, what diseases develop against the background of infection
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the stomach (the damaged walls of the gastrointestinal tract should be treated in the inpatient department of gastroenterology) exhibits pathogenic activity as its population increases. Against the background of invasion by this microorganism, it is possible to develop severe diseases of the stomach and duodenum, which can lead to death.
Gastritis
This disease is characterized by acute or chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Gastritis is accompanied by attacks of spasmodic pain in the upper abdominal cavity, lack of appetite, general physical weakness and malaise. The danger of this disease is that in the absence of treatment, chronic inflammation of the walls of the stomach passes into the stage of erosion, and ends with an ulcer.
Peptic ulcer
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the stomach (it must be treated immediately after detection) is an infectious a microorganism that can cause ulcerative lesions of the stomach, as well as the walls of the duodenum intestines.
The scale of the spread of the pathological process depends on the numerical population of pathogenic bacteria, the state of the immune system of the infected person. The danger of peptic ulcer disease lies in the periodic opening of internal bleeding, which can lead to anemia and death.
Stomach cancer
Oncology of the stomach is one of the most dangerous and severe complications caused by chronic H. pylori infection. The formation of a malignant tumor occurs against the background of an inflammatory process, which over time causes degenerative changes in the structure of the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract. Stomach cancer is difficult to treat with medication and surgery, and is also characterized by a high mortality rate.
How to detect Helicobacter pylori in the stomach, diagnostic methods
Helicobacter pylori bacterium in the stomach (it is necessary to treat infectious invasion under control gastroenterologist) can be detected by histological analysis, as well as by using laboratory testing.
Histological method
The histological method for detecting Helicobacter pylori in the digestive tract is considered one of the most informative. The principle of its implementation is that the patient undergoes the procedure of fibrogastroduodenoscopy.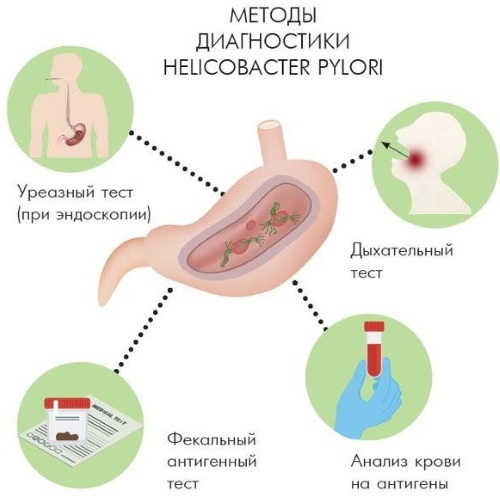
A probe is inserted into the patient's stomach, equipped with special equipment, which takes samples of the mucous contents and tissues of the stomach. The biological material is transferred to the laboratory, where it is examined for infection with Helicobacter pylori, the presence or absence of an inflammatory process. At the same time, an assessment of the risk of developing gastritis, ulcers and oncology is performed.
According to the results of histological diagnostics, the following degrees of infection of the patient's stomach with this microorganism can be detected:
- weak;
- moderate (the likelihood of complications is low);
- pronounced;
- extensive insemination.
An infectious disease doctor or gastroenterologist is responsible for decoding the histological examination. The selection of tactics and scheme of the therapeutic process depends on the information that will be indicated in the laboratory report.
Non-invasive and minimally invasive diagnostic methods
To detect Helicobacter pylori infection in the human gastrointestinal tract, the following non-invasive and minimally invasive diagnostic methods can be used:
- analysis of venous blood for antibodies to this microorganism;
- PCR study of feces;
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- urease breath test.
Depending on the complexity of the clinical case, the attending gastroenterologist may decide on using several methods at once for detecting Helicobacter pylori in the gastrointestinal tract the patient.
Methods and treatment regimens
The treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori infectious invasion is selected individually according to the results of the patient's examination.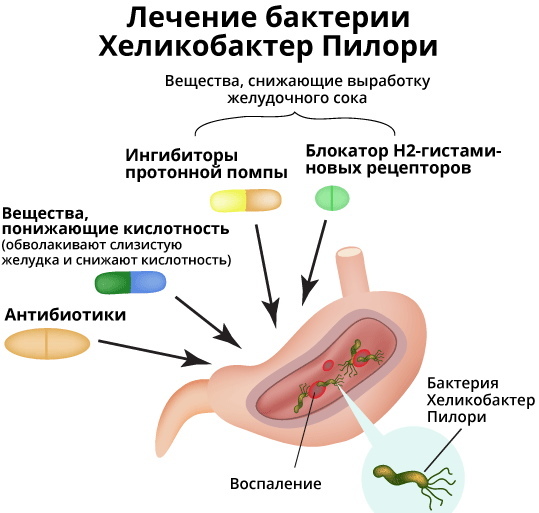 The degree of insemination of the stomach walls, the severity of the inflammatory process, the resistance of the detected bacterial strain to certain types of antibacterial agents are taken into account.
The degree of insemination of the stomach walls, the severity of the inflammatory process, the resistance of the detected bacterial strain to certain types of antibacterial agents are taken into account.
Antibiotics
Depending on the level of resistance of the diagnosed infection, Helicobacter pylori, a gastroenterologist, treating the patient, prescribes the following antibacterial drugs:
- Clarithromycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Levofloxacin;
- Tetracycline;
- Pilobact;
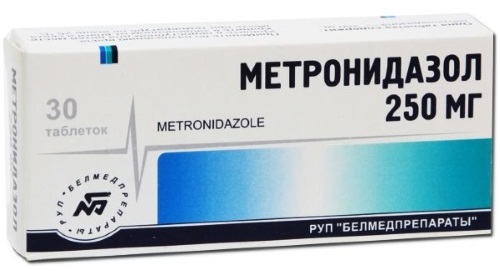
- Metronidazole;
- Klacid.
The dosage regimen and the duration of the therapy are also established by the doctor. Throughout the course of treatment, the dosage of antibacterial agents may vary depending on the dynamics of the patient's recovery.
Preparations of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate
Medicines based on bismuth tripotassium dicitrate protect the inflamed walls of the gastrointestinal tract from the aggressive environment of gastric juice, help relieve the inflammatory process. Healing ulcerative formations, and also suppress the pathogenic activity of Helicobacter pylori.
In this case, the following types of medicines are used:
- De-Nol;

De-Nol is a complete analogue of Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate - Vikalin;
- Bismofalk;
- Vikair.
The dosage of the above drugs depends on the condition of the patient's stomach walls. In most cases, bismuth preparations are combined with the simultaneous administration of antibiotic therapy.
Proton pump blockers
The general course of therapy includes the following drugs, which belong to the pharmacological group of proton pump blockers:
- Omeprazole;
- Ultop;

Nolpaza - Lansoprazole;
- Pantoprazole;
- Gastrozole;
- Ortanol;
- Nolpaza;
- Lancid;
- Helikol;
- Rabeprazole;
- Zulbex;
- Esomeprazole.
Treatment with the above drugs can be carried out in combination with the use of antibiotic therapy. The selection of the optimal dosage with these medicines is carried out by an infectious disease specialist or a gastroenterologist.
Nutrition, diet features, an approximate menu for 3 days
Diet food with Helicobacter pylori provides for a complete rejection of foods that irritate the gastric mucosa. Fried, salty, sour, pickled food is strictly prohibited. The table below shows an approximate menu for 3 days for a person in whose stomach Helicobacter pylori was found.
| Days | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Day 1 | Thick oatmeal cooked in milk. Chamomile tea. | Low-fat yogurt with cookies, banana. | Steamed chicken cutlet. Cauliflower cream soup. Boiled carrot salad. Berry jelly. | Natural fermented baked milk with croutons. | Hake baked in the oven. Beetroot salad with a small amount of vegetable oil. |
| Day 2 | Semolina pudding with jam. Not strong green tea. | Oven baked pumpkin and apples. | Soup-puree of carrots, pumpkin pulp and wheat croutons. Oven baked cod. Dried fruits compote. | Cottage cheese with slices of banana. | Boiled chicken breasts with potato salad. |
| Day 3 | Omelet with natural milk. Rosehip decoction. | Rice Pudding with Fruit Gravy | Potato soup. Steamed calf schnitzel. Vegetable salad and juice. | A glass of kefir with biscuit without adding cream. | Fish soufflé. Beetroot vinaigrette. |
Diet food for Helicobacter pylori includes fractional meals in small portions. To maintain the stable functioning of the digestive tract, it is recommended to observe the daily regimen, taking food at the same time of day.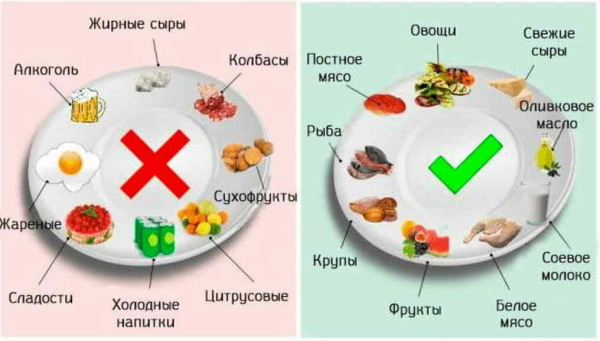
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the following drinks and food products should not be present in the patient's menu:
- mushrooms;
- fatty meats and fish;
- fast food;
- chips;
- canned fish and meat;
- sour berries, fruits, vegetables;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- smoked meat and fish.
A person in whose body an infection of Helicobacter pylori is found should remember that the above food products reduce the local immunity of the gastrointestinal tract, provoke a more acute development of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, and also contribute to an increase in the numerical population of this bacteria.
Treatment with folk remedies
Certain strains of Helicobacter pylori infection are resistant to the constituent components of potent antibiotics.
In this case, the use of traditional medicine will not bring a positive effect, but will only allow to temporarily reduce the severity of the inflammatory process.
Helicobacter pylori cannot be eliminated with cabbage leaves, cranberry juice, honey, or aloe pulp. The painful condition of the stomach, provoked by this infection, is treated only with the help of correctly selected antibiotics.
Drug therapy regimens for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori
The main scheme of drug therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori includes the use of 3 lines of treatment, which are based on the use of drugs.
First line eradication drugs
The first line of therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori is considered universal, since it is prescribed to most patients infected with these microorganisms.
In this case, the following drugs are used:
- Metronidazole;
- Clarithromycin;
- Amoxicillin.
The standard treatment duration is 7 to 14 days. Upon completion of the first line of eradication, the patient proceeds to the next stage of the therapeutic course.
Second-line eradication drugs
Eradication of the second line of therapy includes taking the following drugs with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties:
- Omeprazole;
- Tetracycline;
- Metronidazole;
- De-Nol or another bismuth-based drug prescribed by your doctor.
This quadruple therapy regimen is applied over the next 10 days. Depending on the level of resistance of the detected microorganism to antibiotics, the attending physician may use other types of medicines with antibacterial properties.
Third-line eradication drugs
The third line of eradication of the infectious invasion of Helicobacter pylori is carried out only if there is no therapeutic effect after treatment with 1st and 2nd line medications. At this stage, the patient undergoes an additional and more thorough examination for the resistance of the microorganism found in him to the above antibiotics.
Possible complications if untreated
The lack of timely treatment of the invasion by the microorganism Helicobacter pylori will lead to the fact that this infection will remain in the stomach cavity, and will also continue to destroy its internal shell.
In this case, the following complications may develop:
- an increase in the level of acidity of gastric juice;
- chronic or acute inflammation of the walls of the stomach, duodenum;
- poor digestibility of food;
- sharp or aching pains in the upper stomach that will bother a person regularly;
- the formation of a malignant tumor;
- weight loss;
- the need for constant adherence to dietary norms;
- the appearance of ulcerative formations of various sizes and depths of penetration into the walls of the stomach;
- internal bleeding, which is manifested by darkening of feces, as well as an admixture of ichor in vomit.
Complications provoked by a chronic infection of the gastrointestinal tract, Helicobacter pylori, can cause the patient's death.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative microorganism that parasitizes in the perverse section stomach of a person, penetrates into the duodenal cavity, where it also manifests its pathogenic activity. This infection of the gastrointestinal tract differs in that it is able to withstand the aggressive environment of gastric juice, penetrate into the cellular structure of the walls of the digestive system, causing their acute or chronic inflammation.
It has been scientifically proven that Helicobacter pylori is the cause of gastritis, peptic ulcer, and malignant tumors of the stomach. Treatment of this infectious invasion includes complex therapy with antibacterial drugs, adherence to a strict diet, and taking medications based on bismuth.
Video about Helicobacter Pylori
What is it and how to treat Helicobacter pylori:



