Content
- Differential diagnosis for numbness of the limbs, the appearance of a feeling of goose bumps on the skin
- Blood analysis
- Neurological examination
- Causes of numbness, creeping sensations, accompanying symptoms and treatments
- Numbness
- Feeling goosebumps
- Diabetes
- Tunnel neuropathy
- Spine diseases: osteochondrosis, herniated disc
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Sciatica
- Infectious diseases
- Vascular disorders
- Lack of vitamin B1 and B12
- Numbness Videos
Every person knows the feeling when arms and legs are numb, goosebumps run through the body. In healthy people, this more often occurs when exposed to cold or after being in an uncomfortable position for a long time, which interferes with the normal blood flow in the limb. In this case, the condition goes away on its own and rather quickly, provided that the cause of its occurrence has been eliminated.
Differential diagnosis for numbness of the limbs, the appearance of a feeling of goose bumps on the skin
Hands and feet go numb and goosebumps run for no apparent reason, often or lasting more than half an hour only in those who suffer from certain types of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. If you find suspicious symptoms, you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible.
The therapist can handle the initial diagnosis. After a thorough questioning and examination, he will assess the severity of the patient's condition, decide how urgent it should be consultation with a neurologist, will send you to the laboratory for a blood test, recommend magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Blood analysis
For a more complete differential diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a study of venous blood:
- UAC;
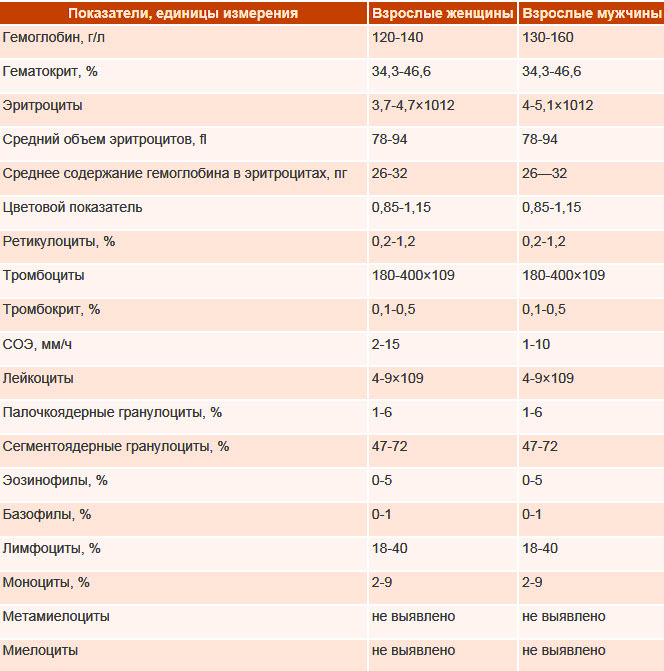
- biochemical indicators:
- acute phase reactions;
- kidney function;
- ionogram;
- enzymes;
- lipid profile;
- diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: glucose, glucose tolerance test;
- diagnostics of thyroid diseases;
- vitamins;
- tests for infections: syphilis (Wasserman reaction, RW), HIV, Lyme disease, tuberculosis, herpes.
Neurological examination
Numbness of the limbs and the associated feeling of crawling through the body is dealt with by a neurologist. First, he asks several specific questions that clarify the signs of diseases, then examines and examines the patient, conducts neurological tests for using a neurological hammer with a special needle to determine sensitivity and some other instruments available to him at the time consultations.
After reviewing the available results of blood tests, determining the type and level of lesions of the nervous system, the doctor will need auxiliary studies to substantiate the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Additional methods can be:
- neurophysiological:
- electroencephalography (EEG);
- electroneurography (ENG);
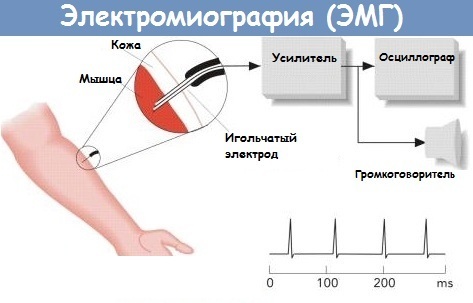
- functional MRI (fMRI);
- positron emission computed tomography (PET-CT);
- echoencephalography (EchoEG);
- MRI of a specific part of the nervous system (brain or part of it, a segment of the spinal cord or a specific peripheral nerve);
- computed tomography (CT) is not the method of choice, except in emergency cases when there is no time to perform an MRI (for example, if a stroke is suspected);
- spinal puncture and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid;
- immunoelectrophoresis of plasma and electrophoresis of blood plasma proteins (with suspicion of multiple myeloma or multiple sclerosis).
Causes of numbness, creeping sensations, accompanying symptoms and treatments
Hands and feet go numb and goosebumps for various reasons. To establish their source, the doctor will need to clarify additional symptoms.
He analyzes the criteria:
- a decrease or total loss of the ability of a skin area to perceive external stimuli;
- muscle weakness or inability to move at all;
- the emergence of all sorts of unusual sensations in the body.
In the understanding of a specialist, such a problem is more multifaceted and needs to be concretized.
Numbness
In medical science, numbness is a partial (hypesthesia) or complete (anesthesia) loss of sensitivity, which is divided into:
- superficial, responsible for sensations of touch, temperature and pain;
- deep, which includes the perception of vibration and the position of a part of the body in space.
 This division depends on the level of damage to nerve structures and, depending on this, the patient may have many different complaints, up to a violation of gait, difficulty in driving and an increased risk of injury from falling.
This division depends on the level of damage to nerve structures and, depending on this, the patient may have many different complaints, up to a violation of gait, difficulty in driving and an increased risk of injury from falling.
Feeling goosebumps
Creeping crawl refers to a type of paresthesias (sudden inappropriate sensations that have no real stimulus) and is often combined with pain and other symptoms described earlier.
Diabetes
Numb limbs and a creepy feeling in them are usually complained of by elderly patients at an appointment with a therapist or endocrinologist. The largest group suffering from sensitivity disorders are patients with diabetes mellitus, therefore the diagnostic search must begin with the determination of the blood glucose level, especially if this is an older person age group.
At the same time, the sensations are characteristic: more often bilateral and symmetrical in the type of gloves and socks, but other localizations are also possible (for example, on the back), usually monotonous, independent of external factors, developing and increasing slowly, gradually.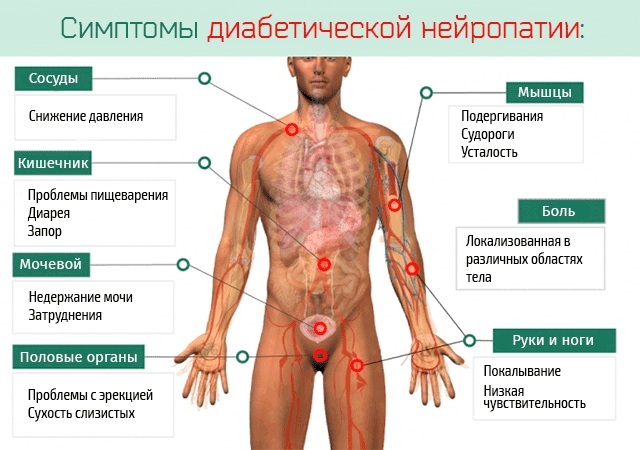
Drug therapy for diabetic polyneuropathy includes drugs:
| Active substance | Tradename | Dosage regimen |
| Vitamins B1, B6, B12 | Combilipen (contains lidocaine) | Intramuscularly deeply, 2 ml every day for 5-10 days, then the next 2-3 weeks, 2-3 injections per week. |
| Alpha Lipoic (Thioctic) Acid | Neurolipon | First, slowly intravenously, 600 mg once a day for 2-4 weeks, then 1 tablet (600-1800 mg) once a day for 1-3 months. |
| Pregabalin | Lyrics | Inside, outside the meal, starting with a dose of 150 mg per day, breaking into 2-3 doses, then with good tolerance, a gradual increase in the dose to a maximum daily dose of 600 mg is possible. Long-term use. |
| Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline | Inside, 25-50 mg at night, then a gradual increase in the dose to the recommended daily dose of 50-100 mg, from 3 months. |
| Ibuprofen | Nurofen | Inside, 200-400 mg, re-use is possible after 4-6 hours, but not more than 1200 mg per day. The course of admission is up to 10 days, then in agreement with the attending physician. |
| Versatis (plaster) | Stick the plaster on the painful surface of the skin for up to 12 hours. Reapplication is possible after 12 hours. | |
| Tramadol + Paracetamol | Zaldiar, Ramlepsa, Rutram | Inside, 1-2 tablets (37.5 mg of paracetamol + 325 mg of tramadol), the next dose is not earlier than 6 hours later. The dose, if necessary, can be increased to a maximum daily dose of 8 tablets. The course of treatment is determined individually. |
Tunnel neuropathy
Compression syndromes, including tunnel neuropathies, widespread among the young population, mainly male floor. The nature of the lesion in pathology is often one-sided. Pathology develops due to the clamping of the nerve between the bone and soft tissues (muscles, tendons) due to edema.
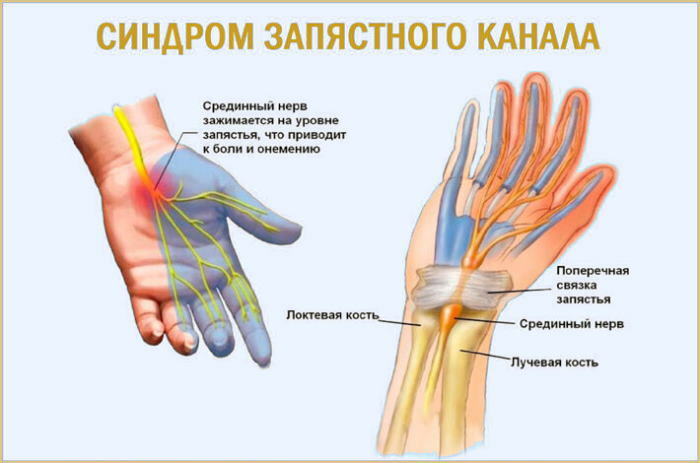
The reasons may be:
- trauma;
- prolonged stay in an unnatural static position (not uncommon for people who have fallen asleep on a hard surface after falling intoxicated);
- some cases of the "wedding night" syndrome (drooping of the forearm and hand like a whip due to prolonged pressure on the vessels and nerves of the shoulder);
- syndrome of "French tulip bulbs diggers" (changes at the level of the lower leg and foot, after a long stay in the poses of the legs to the feet or squatting).
In the treatment, the same drugs are used as in diabetic polyneuropathy (Ibuprofen, Tramadol, Paracetamol, Amitriptyline, Pregabalin, lidocaine patches) in equivalent doses.
Additionally apply:
- temporary immobilization according to the principles of splinting with the use of orthoses, bandages or splints;
- cold compresses;
- injections of meloxicam and hydrocortisone into the area of the tunnel.
To relieve puffiness and reduce pain, physiotherapeutic methods are shown:
- electrophoresis of novocaine or other anesthetic;
- phonophoresis of Dimexide.
In the future, when acute manifestations subside, exercise therapy will be useful. It can also be justified to take B vitamins, muscle relaxants (mydocalm, 50-150 mg once a day for 5-7 days) and drugs that improve blood supply and functioning of the nerve (ipidacrine 10-20 mg 1-3 times a day for 1-2 months), the use of ointments with an anesthetic substance (for example, with diclofenac).
Surgical correction is resorted to only in an emergency or after all possible non-invasive techniques have been tried. However, there are studies proving the absence of a significant difference in the results, one year after the start of therapy and the operation.
Exercise therapy for rehabilitation after tunnel syndromes of the upper limb:
- clench each fist with effort and then fully open the hand, 5 times;
- rotate with brushes clockwise and counterclockwise, 5 times in both directions;
- rotate each finger in turn for a few seconds;
- clench your fists several times and relax, shake your hands;
- press your palms together, pull your fingers back as much as possible, linger, then squeeze into the lock for a few seconds, repeat 5 times;
- connect your fingers into the lock and strain, raise your wrists up, and bend your fingers down, then repeat 5 times;
- press the brushes tightly to each other and alternately remove the fingers of the same name, 3 times for each pair;
- put your palms together, press the fingertips of one hand on the fingers of the other hand with effort, alternate 10 times in each direction;
- join palms near the chest, slowly lower to the navel, linger and raise again to the starting position, 5 times;
- on each hand, in turn, connect the thumb pad with all the others in a different order, for 30 seconds.
Spine diseases: osteochondrosis, herniated disc
Hands and feet go numb and goosebumps with one of the most common diseases of the spine. Due to a predominantly sedentary lifestyle, osteochondrosis of the spine is common even among young people.
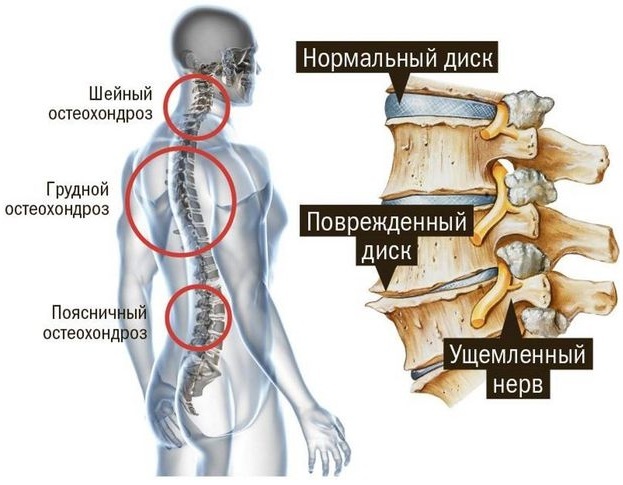
By itself, it does not significantly reduce the quality of human life, but in the later stages, rather serious complications arise, such as deformities of the vertebrae, herniated intervertebral discs, which often lead to radiculopathy (compression of the spinal roots nerves).
With such a pinching, burning pain and symmetrical numbness in various parts of the body and stiffness of movements from intensification soreness, which increases significantly in the upright position of the body, from which the patient's general well-being is visible worsens.
In therapy, the main emphasis is on pain relief and, as soon as possible, elimination of the cause of the compression. Otherwise, drug treatment repeats the therapy regimen for tunnel syndrome.
Stroke
The main percentage of stroke cases is due to brain lesions, and its spinal forms are less common. Clinical manifestations depend not only on where the stroke occurred, but also on its type (hemorrhagic or ischemic), the volume, the involved significant nerve structures, the timeliness and completeness of the help. There are usually many complaints in patients who have undergone this condition, but the leading ones are disturbances in the sensitivity of the skin of varying degrees and localization.
After timely provision of specialized care (thrombolysis in ischemic stroke and neurosurgical intervention in hemorrhagic), the main role in rehabilitation is played by:
- classes with a speech therapist;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy methods (massage and manual therapy, mud, paraffin and ozokerite applications, laser therapy, acupuncture, electromyostimulation (amplipulse therapy (SMT)), electrophoresis of drugs, magnetotherapy and many others according to indications).
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a poorly understood condition and therefore it is quite severe downstream and difficult in terms of medical impact on the disease. Symptoms of its "scattered", varied, but still there are some characteristic features (undulating current, average the age of patients is from 20 to 60 years old, rapid disability, sudden onset, starting precisely with the disorder sensitivity).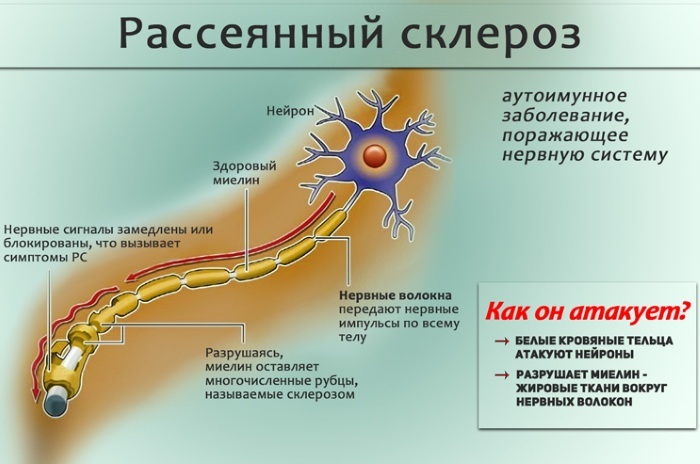
It is assumed that latent viral infection (herpes, including a virus Epstein-Barr), which in turn disrupts the functioning of the human immune system and leads to an "attack" by the body of its own nervous fibers.
There are many multiple sclerosis centers around the world to study and combat.
For diagnostics are used:
- neurological examination;
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord;
- examination of cerebrospinal fluid.
The course of the disease is unpredictable, therefore, it is impermissible to linger at the examination stage, you should rather start treatment for stopping the rapid development of disabling manifestations, reducing the frequency and severity of exacerbations and improving the overall quality of life the patient.
A large number of drugs are used in the treatment:
- corticosteroids - intravenous methylprednisolone 500-1000 mg once a day, in a short course of 3-5 days;
- immunomodulators (injectable and oral forms, long-term use):
- Interferon beta-1b subcutaneously at 8 million IU every other day;
- Interferon beta-1a intramuscularly at 6 million IU (30 μg) once a week;
- Interferon beta-1a subcutaneously 44 mcg 3 times a week;
- Fingolimod 0.5 mg orally once a day;
- Teriflunomide orally 14 mg once a day;
- Dimethyl fumarate inside 240 mg divided into 2 doses per day.
- Muscle relaxants - baclofen (orally with meals, 5 mg 3 times a day with a gradual increase to 30-75 mg per day, but not more than 100 mg) or tizanidine (by mouth 2-4 mg 3 times a day with a possible increase in the daily dose to 36 mg);
- Gabapentin (orally during a meal on the first day 300 mg 1 time, on the second day 300 mg 2 times a day, from the third days, 300 mg 3 times a day with a gradual increase in the dose until a therapeutic effect is achieved, but not more than 3600 mg per day);
- Pregabalin (by mouth outside meals, starting with a dose of 150 mg per day, breaking into 2-3 doses, then with good tolerance, a gradual increase in the dose to a maximum daily dose of 600 mg is possible, long);
- Amitriptyline (by mouth 25-50 mg at night, then increasing the dose to the recommended daily dose of 50-100 mg, from 3 months);
- Amantadine (100 mg orally 3 times a day until fatigue decreases);
- vitamin D (inside 800-1000 IU per day in the morning after meals).
Additionally, depending on the prevailing symptoms, physiotherapeutic effects, physiotherapy exercises, occupational therapy with a positive effect are used.
Sciatica
Sciatica is usually called a disease that is characterized by severe one-sided burning pain along the sciatic nerve (from the affected half of the lower back and "shooting" along the entire length legs), arising from the infringement of the roots of the spinal nerves of the lumbosacral region of the herniated disc, bone formations of the vertebrae or a tumor, an abscess of the spinal brain.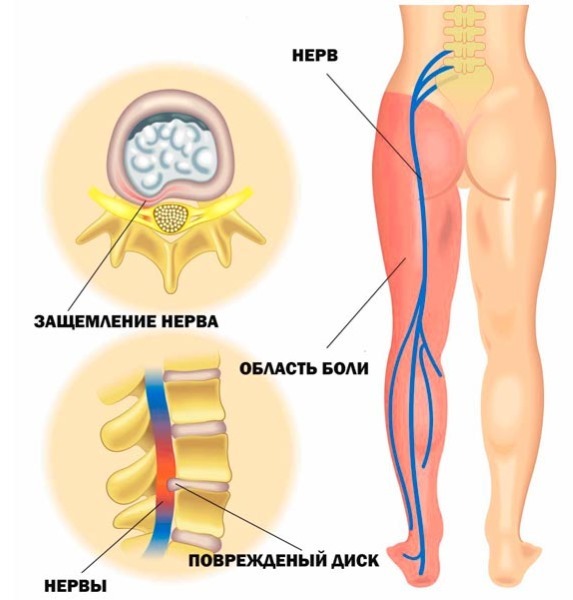
Recently, experts are moving away from this term, replacing it with sciatica, although it is still preserved in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10).
Due to the intensity of the pain syndrome, patients rarely experience sensitivity disorders.
Treatment is symptomatic and repeats the algorithms used for tunnel syndrome and polyneuropathy.
In severe cases, the possibility of injecting hormones into the epidural space of the spinal cord to reduce swelling and pressure on the nerves is being considered.
Surgical intervention is used as a last resort.
Infectious diseases
Some infectious agents can affect the nerve tissue and lead to numbness in various parts of the body.
- With herpes zoster (caused by the herpes virus), a painful, itchy rash appears, mainly along the intercostal nerves, after subsiding which the skin at the site of the lesion has a reduced sensitivity, which patients describe as touching through the layer cotton wool.
- With HIV, tuberculosis, Lyme disease and syphilis, nerve fibers also suffer, which can be accompanied by pain, muscle weakness, crawling creeps, disorder of perception of touch, temperature, pain stimuli and position in space.
- The most severe lesions of the peripheral nervous system occur with leprosy (leprosy), characterized by complete loss of sensitivity in places controlled by the affected nerves.
In addition to influencing the underlying infectious disease, standard symptomatic therapy is carried out, as described in the article earlier.
Vascular disorders
A vivid example of transient numbness associated with vascular pathologies is a hypertensive crisis. At the same time, it is not so important to what numbers the blood pressure has risen, the main factor is the rate of development of an attack, the presence of concomitant diseases (coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis) and the difference in values between systolic and diastolic pressure.
Patients note:
- a sharp headache;
- weakness;
- sweating;
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- visual impairment;
- paleness and numbness of the limbs (especially the hands and feet).
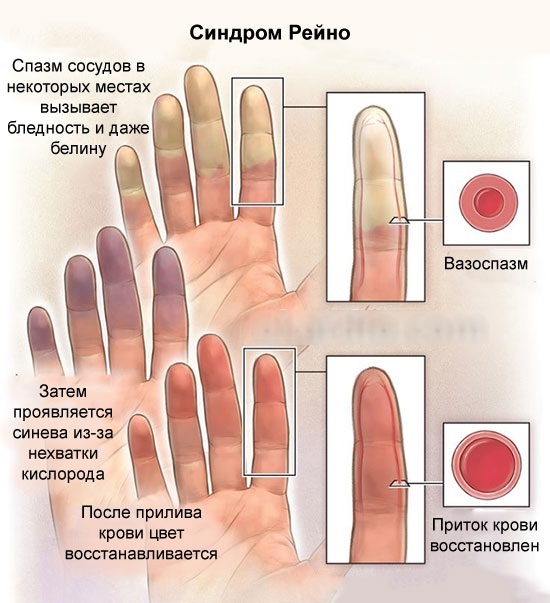
Raynaud's syndrome also belongs to vascular diseases, but it is usually one of the symptoms of other serious diseases (endocrine disorders, rheumatism or psychopathy). Its clinical picture is revealed after exposure to cold or stress: small vessels sharply narrow, which leads to a pronounced pallor of the terminal phalanges of the hands (less often feet) and their loss sensitivity. After the end of the action of the provoking factor, the state returns to its original state within several tens of minutes.
Lack of vitamin B1 and B12
With a deficiency of B vitamins, the restoration of the myelin sheath of the nerves is slowed down, which makes it difficult to transmit impulse along them and develop bilateral symmetric changes. Most often this is associated with damage to the spinal cord (then a violation of deep sensitivity (vibration and spatial)), but isolated damage to peripheral nerves is also possible (in this case, the perception of touch, pain and temperature).
The human body is very complex and there are countless examples of diseases that can cause numbness of the arms and legs, the feeling of running goosebumps, the article lists only the most common ones. Despite the similarities in treatment, sensitivity disorders are only a symptom, and only a doctor should be involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease.
Numbness Videos
Why arms and legs go numb:
