Content
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Training
- Procedure step by step
- Subclavian access
- Puncture of tissues of the operating field
- Receiving a reverse blood flow
- Explorer introduction
- Installation of a catheter with an infusion system
- Care procedures after
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Subclavian catheter video
Catheter care, installed in the subclavian vein, provides for strict adherence to sanitary and hygienic rules, the implementation of sterility standards during infusion therapy of a patient with drugs.
Catheterization of this part of the human circulatory system is a surgical operation that has medical indications and a number of contraindications for its use. Violation of the protocol for installing a subclavian catheter is fraught with the development of severe complications that disrupt the work of the heart, arterial and venous vessels of the patient.
Indications
The care of the intravenous subclavian catheter begins immediately after the completion of the final stage of its introduction into the cavity of the venous vessel.
This type of catheterization is indicated for use in the following cases:
- after a preliminary examination of the patient, it was found that his peripheral vessels on the upper and lower extremities are inaccessible for intravenous administration drugs (for example, if the patient has chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, is an injection addict with a long experience dependencies);
- long-term surgical intervention on internal organs is performed, which involves the loss of a large amount of blood;
- rehabilitation of a patient or his complex treatment using several groups of drugs, the introduction of which occurs with the use of multi-day infusion therapy;
- an urgent need to perform parenteral nutrition for a severe patient who needs a transfusion of high-concentration hypertonic solutions;
- the need for control studies and diagnostic measures aimed at fixing the central pressure inside the heart, venous vessels;
- examination of the patient with X-ray contrast examination;
- multiple sampling of venous blood for its biochemical or clinical analysis.

Subclavian vein catheterization is performed in patients who have undergone major surgical operations in the form of elective or traumatic amputation of the extremities. Through the installed catheter, anesthetic, anti-inflammatory, nutritional and antibacterial drugs in the form of injectable solutions are continuously supplied.
Contraindications
Subclavian catheter care is performed by qualified medical personnel of the highest category.
Carrying out a surgical operation for catheterization of the main vessel below the location of the clavicle has the following contraindications:
- the patient has concomitant diseases of the blood and hematopoietic system associated with the manifestation of hypocoagulation;
- congenital or acquired pulmonary emphysema, regardless of the nature of its occurrence;
- superior vena cava syndrome;
- traumatic or surgical damage to the clavicle, below which the installation of the catheter should be carried out;
- pneumothorax of bronchopulmonary tissue of bilateral type;
- acute respiratory failure;
- Paget-Schroeder syndrome;
- local inflammatory process in soft tissues, which are subject to puncture for the installation of an intravenous catheter.
Before deciding to install a subclavian catheter, the attending physician conducts a comprehensive examination patient in order to detect other pathologies that may be a contraindication to venous catheterization vessels.
Possible complications
The care of the subclavian catheter is carried out by the responsible employees of the inpatient department of the hospital in compliance with all rules of sterility. Incorrect positioning of the infusion therapy guidewire, too long exposure of the device inside the blood vessel, or a violation sanitary and hygienic standards leads to the development of the following complications:
- perforation of a venous vessel with a puncture needle;

- violation of the rhythmic work of the heart muscle;
- infusion of an injection solution into the fiber structure;
- migration of component parts of the catheter through the venous circulation system with the risk of blockage;
- hydrothorax;
- twisting of the catheter system with the formation of nodes on it, disrupting the permeability of infusion solutions inside the main vessel;
- air embolism of the cardiovascular system;
- thrombosis of the subclavian vein (dangerous by the development of local inflammation, separation of a blood clot and the onset of death);
- suppuration of body tissues damaged as a result of puncture to insert a catheter into a blood vessel;
- infectious blood poisoning by especially dangerous pathogenic microorganisms that can cause acute sepsis (the frequency of diagnosing this complication of catheterization of the subclavian vein ranges from 5 to 40% of all cases);
- thrombosis of the catheter system.
Complications caused by improper placement of the catheter inside the vein require its correction. In case of further deterioration of the patient's well-being, the installed system is completely removed. To prevent air embolism, care must be taken to maintain the tightness of the catheter tubes.
To eliminate the risk of developing pneumothorax of the lung tissue, the patient is prescribed a chest x-ray. This diagnostic procedure is performed immediately after the completion of the catheterization. Complications caused by tissue puncture during catheter installation are prevented by meeting the established standards of sterility.
Training
Subclavian catheter care is performed by nurses in the inpatient department of surgery, cardiology or general medicine.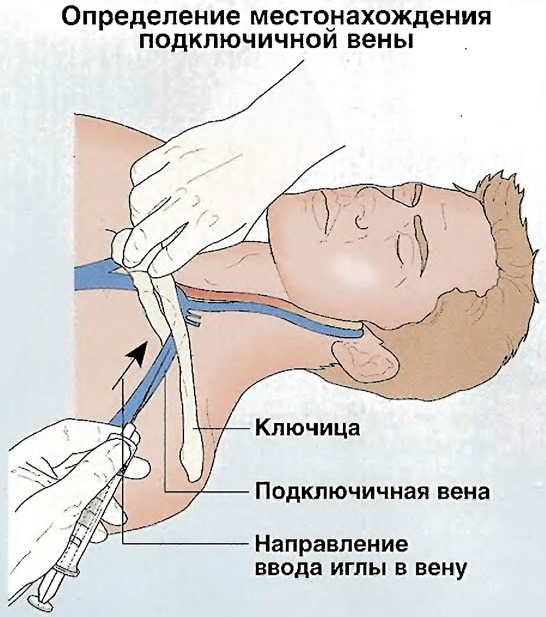
Preparing the patient for the passage of the venous vessel includes performing following rules instructions:
- The patient is placed on the surface of a surgical table, the head edge of which is lowered by 15 degrees. This norm is mandatory to comply with to minimize the risk of air embolism.
- The patient's head is turned to the side that is opposite to the punctured part of the chest.
- The patient's arms are pulled along his torso at the sides.
- The medical staff, observing the rules of sterility, puts surgical instruments on the operating table for installing a subclavian catheter.
- The surgeon washes his hands thoroughly, as before performing a planned operation, and then puts on disposable sterile gloves. The unpacking of this consumable is carried out immediately before the start of the surgery.
- A double treatment of the surface of the operating field is carried out using an antiseptic agent in the form of a solution of 25 iodine concentration.
- The skin surface to be punctured is covered with a sterile film, and then re-treated with ethyl alcohol at a concentration of 70%.
Catheterization of the subclavian vein begins immediately after the high-quality performance of the above steps to prepare the operating field. These manipulations are carried out by only one surgeon or a group of doctors at once.
Procedure step by step
Installation of a catheter into the subclavian vein cavity is performed in several stages. The process of catheterization of the main vessel begins with the opening of a surgical access to the general blood flow of the patient.
Subclavian access
The opening of the subclavian access begins with the fact that the surgeon, using a syringe with a very thin needle, intradermally injects a solution of Procaine with a concentration of 0.5% into the site of a potential puncture. These manipulations are carried out to create the "lemon peel" effect of epithelial tissues. An intradermal injection of anesthetic is injected 10 mm below the clavicle bone at the level of the line that separates the inner and middle third of the clavicle.
The syringe needle is advanced medially towards the upper edge of the articulation of the chest and clavicle, evenly distributing the Procaine solution over the soft tissues of the operated area. The final stage of opening access to the venous vessel is the introduction of a needle under the collarbone, where the rest of the Procaine solution is injected. After that, the syringe is removed from the patient's body.
Puncture of tissues of the operating field
The next step in the installation of a subclavian catheter is to perform a puncture of the soft tissues of the upper chest. Using a thick and sharp needle, limiting the depth of its advance with the index finger of the hand, pierce the skin in the area of the "lemon peel" to a depth of 1 to 1.5 cm. After that, the needle is removed from the patient's body.
Receiving a reverse blood flow
A sodium chloride solution of 0.9% concentration is taken into a 20 ml syringe. Then a not very sharp needle with a length of 7 to 10 cm is put on it, which has a bluntly beveled end. Using consumables with a sharper edge may result in perforation of the subclavian artery, which could result in severe bleeding.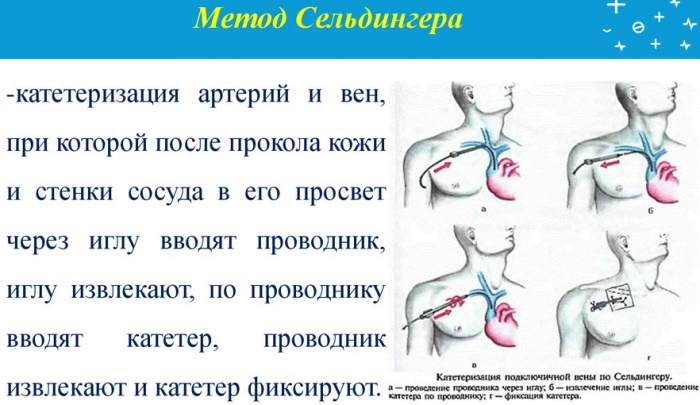
A 20 ml syringe with a sharp needle is inserted medially into the hole previously made with a thick needle. During the movement of the syringe towards the upper part of the articulation of the chest and clavicle, its piston is periodically pulled back. With the help of these actions, the fact of opening access to the venous blood flow is checked.
In the absence of venous blood flow into the cavity of the syringe with a saline solution, the needle is pulled back 0.5 mm or 1 cm, but not completely removed from the patient's body. After that, the degree of inclination of the needle changes with its re-introduction towards the location of the subclavian vein. Immediately, as soon as blood appears in the cavity of the syringe, it is injected back into the systemic circulation, and then re-aspirated by pulling the plunger back.
Carrying out these manipulations is necessary in order to obtain a reliable flow of venous blood, and also minimize the risk of postoperative complications due to incorrectly installed catheter. After establishing a stable flow of venous blood, the patient is asked to hold his breath. Then the doctor removes the syringe from the needle, closing the hole with his finger.
Explorer introduction
The process of introducing the conductor of the subclavian catheter into the cavity of the venous vessel is as follows:
- The surgeon, using screwing movements, inserts the guidewire into the needle, advancing it to half, since its length is 2.5 times greater than the parameters of the catheter.
- The patient is again asked to hold his breath.
- The opening of the catheter is blocked with your thumb, and then a rubber-based plug is put on it.
- The patient is allowed to breathe again.
In relation to patients who are on the operating table in an unconscious state, a special technique is used to introduce a catheter guide. All of the above manipulations associated with the process of depressurization and blocking of the lumen of the needle, as well as the catheter, are performed at the moment when the patient exhales.
Installation of a catheter with an infusion system
The sterile IV infusion catheter is secured using a single stitch silk suture. A sterile aseptic bandage is applied on top of the operated subclavian part of the body. 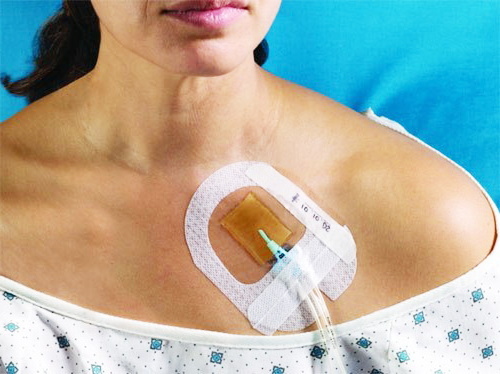 If the surgical operation took place without complications, the patient is in a clear consciousness, the stable work of his internal organs and life support systems, then he is transferred to the general therapy ward for further treatment with infusion solutions.
If the surgical operation took place without complications, the patient is in a clear consciousness, the stable work of his internal organs and life support systems, then he is transferred to the general therapy ward for further treatment with infusion solutions.
Care procedures after
The subclavian catheter is cared for daily, and any complications associated with its insertion are displayed in the shift transfer log by the medical staff. Elimination of the negative consequences of catheterization of the subclavian vein occurs with the direct participation of the doctors who performed the introduction of the infusion system.
Installation of a subclavian catheter is a complex vascular operation. After successful surgical manipulations, it is necessary to follow the rules of caring for the operated area of the patient's body, which are described in detail in the table below.
| Rules for the care of the subclavian catheter | Description of actions of medical personnel |
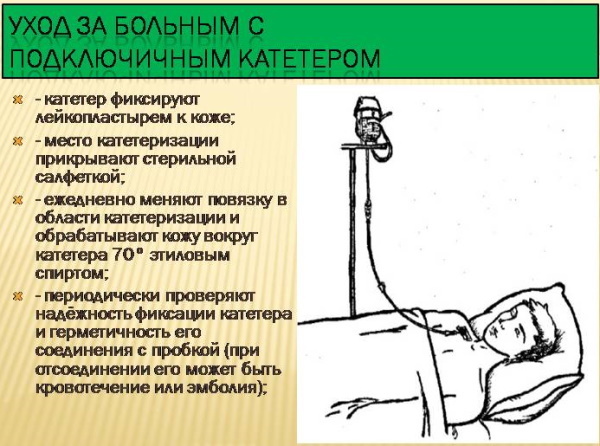
| 1. Compliance with standards of sterility. | Before carrying out planned and emergency manipulations to correct the position of the catheter or clean it from drug residues, it is necessary to always wash your hands thoroughly with soap, dry them with an electric dryer, and then treat the skin with a solution of ethyl alcohol 70% concentration. |
| 2. Prevention of infection with infectious diseases. | To prevent infection of the patient and medical personnel with the AIDS virus, hepatitis serum type and other pathogenic microorganisms must be worn sterile disposable gloves. Consumables in this category are used during the examination of the subclavian catheter. |
| 3. Replacing the sticker. | The aseptic sticker that is applied over the catheter must be replaced daily. On the surface of this dressing, there is a gradual accumulation of infectious microflora, which can cause suppuration of the wound surface with further spread of the inflammatory process to the circulatory system sick. The aseptic sticker must be replaced at the same time of day. |
| 4. Antiseptic treatment of the operated area of the body. | For the prevention of an infectious and inflammatory process, antiseptic treatment of epithelial tissues located within a radius of 8 cm from the site of installation of the subclavian catheter is carried out. Apply a solution of iodine 2% concentration, brilliant greens 1%, or methylene blue. To apply these drugs, sterile cotton swabs are used. |
| 5. Replacing the infusion system. | Upon completion of the planned administration of a complex of drugs that were prescribed to the patient by the attending physician, a new infusion system is installed. All consumables for intravenous drug delivery must be sterile, and their removal from individual packaging is carried out directly at the moment of connection with the subclavian catheter. The replacement of the infusion set must take place at the same time of day. |
| 6. Flushing the catheter. | After each use, the subclavian catheter should be flushed with heparin solution. At this stage of caring for the operated area of the body, it is necessary to ensure that venous blood does not accumulate inside the catheter. Otherwise, the risk of developing an infectious and inflammatory process increases. |
| 7. Replacing the catheter. | The planned change of the subclavian catheter is carried out every 5-10 days along the guidewire. Timely replacement of the intravenous infusion device allows prevention of complications, and also preserves the patient's vascular system from infection with pathogenic microorganisms. |
The attending physician conducts a daily examination of the condition of the patient's subclavian catheter. If the first signs of complications are detected, this device is immediately removed for intravenous administration of medicinal solutions.
Advantages and disadvantages
Subclavian vein catheterization is a surgical operation that has its own advantages and obvious disadvantages.
There are the following advantages of using an intravenous catheter with its installation in this area of the circulatory system:
- medical personnel carrying out complex therapy of the patient receives constant and fastest access to the patient's circulatory system;
- drugs injected through a subclavian catheter begin to realize their pharmacological properties within 20-60 seconds after the drug enters the general bloodstream;
- provides nutritional support for the body of critically ill patients who are in an unconscious or vegetative state without the physiological ability to eat independently;
- round-the-clock monitoring of the patient's venous pressure is performed;
- the planned blood sampling of the patient for its laboratory examination is carried out directly from the catheter without further damage to the venous vessel;
- with the help of catheterization, it is possible to carry out complex therapy for critically ill patients who need simultaneous receipt of a large number of drugs produced in the form of infusion solutions.
Placement of a subclavian catheter is performed using a local anesthetic. Therefore, this procedure is absolutely painless. At the stage of catheterization, the patient feels only short-term discomfort at the moment of puncturing the soft tissues with a syringe needle, inside which there is an anesthetic.
The disadvantages of a surgical operation for the installation of a subclavian catheter include the following negative aspects and risks:
- catheterization can only be performed by a qualified surgeon with sufficient experience in installing this type of infusion device;
- mechanical perforation of a venous vessel with a syringe needle occurs in 19% of all complications;
- the formation of thrombosis occurs in 26% of patients faced with the negative consequences of subclavian catheterization;
- catheter care can only be carried out by specially trained medical personnel (otherwise there is a high probability of postoperative complications);
- infectious contamination of blood and tissues in the area of catheterization is not excluded.
Studying the disadvantages of catheterization of the subclavian vessel, we can come to the conclusion that all the negative aspects of this procedure are associated with a greater risk of severe complications. Especially if there was a medical error at the stage of catheter installation.
Care of the catheter inserted into the subclavian vein begins from the first day of its connection to the infusion system for the delivery of medicinal solutions. The introduction of this device into the main vessel is carried out under sterile conditions in the operating room. Puncture of the subclavian vein is performed by a surgeon using local anesthesia.
All manipulations are carried out in strict compliance with sterility standards. Installation of a subclavian catheter is indicated for critically ill patients who need to receive round-the-clock infusion therapy with a large amount of medicinal solutions.
Subclavian catheter video
Subclavian vein catheterization technique: