Content
- Types of coordination disorders and manifestations
- Causes of poor coordination and dizziness
- Physiological causes
- Pathological causes
- Who to contact
- Video about the causes of dizziness
Ataxia is manifested by inconsistency of motor function. The state is lack of coordination, dizziness, which can be caused by physiological processes and various pathologies. About 20-30% of the world's adult population complains about the condition. Experts have noticed that symptoms are much more common in women and the elderly.
Types of coordination disorders and manifestations
A person prone to ataxia is characterized by clumsiness in movement, loss of coordination and imbalance. The central nervous system is responsible for the coordination of the motor skills of the upper and lower extremities and other parts of the body. In case of malfunctions in its functioning, disorders in the musculoskeletal system are observed. The condition refers to the symptoms of various processes, both physiological and pathological.
Signs of the disease are the following conditions:
- Change in gait. It may become wider or the hips may sway from side to side.
- Falls are observed when walking.
- The instability of the gait becomes permanent.
- Making precise movements is difficult.
- There are cases when it is difficult for a patient to bring a spoon or a mug to his mouth without spilling its contents.
- Speech abnormalities.
- Loss of breathing rhythm.
- Systematic dizziness.
- Sometimes there is vomiting, nausea, headaches.
In each individual case, the symptoms are varied, they depend on the form of the disorder.

Physiologically, the symptoms are explained by lesions of the central nervous system, namely the cerebellum - its area that regulates the coordination and sequence of actions, as well as maintaining balance body. With damage to this area, there is a loss of coherence in the work of different muscles and joints. A person ceases to control his posture, his gait becomes unsteady, the width of his step increases, and his hands can make zigzag waves.
Also, other conditions can be observed as concomitant phenomena:
- Dysmetry. The patient does not regulate the amplitude of his movements. For example, he is not able to take an object lying on the table: the hand reaches further or closer.
- Dysarthria or speech impairment. As a result of the loss of coordination, the muscles synthesizing speech become more solid, because of this, the language loses its agility, and the speech itself is clear and loud. In this case, the movements of the muscles near the mouth are more pronounced.
- The chanted speech is manifested by monotony, stuttering at the beginning of words or syllables.
- Nystagmus is the inability to concentrate and keep the gaze on the object of interest, that is, the eyeballs are in constant motion. They turn and walk from one side to the other, then return to their original position.
- Tremor (tremor) appears when trying to make targeted movements. This can happen at the moment when a person is drawn to some object (intentional) or trying to stay in one position.
Interactive tremor differs from other types in the inability to carry out purposeful movements. Symptoms are similar to Parkinson's disease, which is manifested by tremors and muscle stiffness. In addition, coordination and control over the muscles of the face, tongue, arms and legs is lost. Painful and involuntary muscle contractions (dystonia) appear.
Loss of coordination and dizziness, which can be determined by the Romberg test, can lead to falls. In more pronounced severe forms of pathology, a person loses the ability to walk, pick up objects, and eat independently. In milder forms, there is a loss of coordination between the upper and lower extremities, which manifests itself in the inability to perform precise movements.
Systemic physiological causes can be far-fetched. For example, it might be an illusion of rotation or swinging for no external reason. True vertigo is called systemic. They appear suddenly, often accompanied by nausea, sometimes vomiting, and a shaky gait. In such cases, the sick person can accurately describe the symptoms they are complaining about.
Non-systemic dizziness has the appearance of an illusion, which is manifested by unsteady walking, a feeling of imbalance and fear of falling. In such cases, the patient cannot accurately describe his symptoms or identify complaints.
Ataxia is a loss of coordination, the acquisition of an unstable gait. In this case, it becomes necessary to hold onto pieces of furniture, walls or other support when walking. When diagnosing a condition, muscle tone may be reduced.
The most severe forms of the disease are those that are caused by hereditary factors.
Among them, the following diseases can be distinguished:
-
Friedreich's ataxia is a hereditary pathology. Scientists have identified a recessive gene (the disease manifests itself when the patient inherits 2 copies of it from each parent), which is responsible for the deviation. Pathology is a progressive disease that manifests itself between the ages of 5 and 15 years.
 It is accompanied by symptoms:
It is accompanied by symptoms:
- gait loses stability;
- movements of the upper and lower extremities become uncontrollable, uncoordinated;
- speech becomes indistinct and difficult to understand.
A large proportion of children who suffer from the disease are born with the inherent clubfoot, curvature of the spine (scoliosis). Such people are unable to feel vibration. They have no idea about the position of their arms, legs and body in space.
Their reflexes disappear. Mental abnormalities are sometimes observed. Concomitant heart disease often develops and progresses over time. Usually, by the age of 20, patients are confined to a wheelchair. They live no more than 50 years and die of heart failure or arrhythmias.
- Spinocerebellar ataxia tIt is also inherited, but unlike the previous species, the mutated gene is dominant, that is, during transmission, it is enough to get one copy from one parent. Pathology has many varieties. The most common form is Machado Joseph disease. The pathology progresses rapidly and is fatal. There is no cure for her. Symptoms are manifested by the following symptoms:
- loss of sensitivity;
- muscle weakness;
- restless legs syndrome;
- loss of coordination and balance;
- problems with speech and involuntary eye movements.
Causes of poor coordination and dizziness
Impaired coordination and dizziness, the causes of which can be of different nature, have been studied for a long time.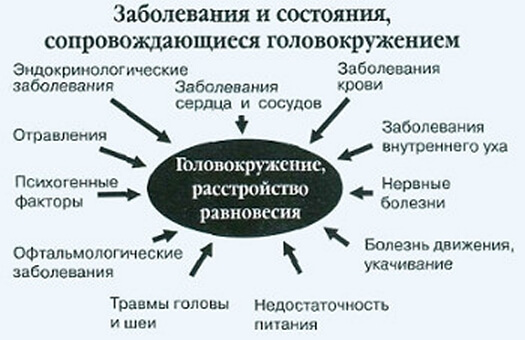
Scientists managed to derive the following frequency statistics detection of pathologies:
- 50% are defects in the inner ear;
- 5% - neurological pathologies;
- 5% - high blood pressure and side effects from the drugs used;
- 15% - mental disorders;
- in 25% of patients, an unknown cause remains.
Among all the factors of the appearance of balance disorders, dizziness, there are only 2-3%, which belong to diseases that pose a threat to human health and life.
The coordination of movements and the function of balance depend on the coordinated work of various structures of the nervous system, and namely the cerebellum, pathways, vestibular apparatus, cerebral cortex and receptors (proprioception).
Pathways that implement the contact of the cerebellum with the rest of the central nervous systems, as well as with muscle fibers, in case of injury, they can contribute to impaired coordination movements.
The vestibular apparatus is an analyzer responsible for balance and preservation of body position, orientation in space, and it also controls muscle tone. Its receptors are located in the inner ear (labyrinth). From there, impulses go to the central nervous system and to the visual analyzers.
Proprioception is a loss of self-awareness, disorientation in the placement of one's body in relation to space. The musculoskeletal sense works at the expense of receptors that are located in the corresponding parts of the musculoskeletal system. From them, the impulse enters the central nervous system.
There are many reasons for the development of ataxia, which include the following disadvantages:
- congenital deformity of the brain;
- infringement of arterial vessels in the central nervous system;
- neoplasms;
- decreased thyroid function;
- deviations in hormonal balance;
- hereditary pathologies;
- overdose of certain medications (anticonvulsants, sleeping pills) or toxic substances;
- lack of cyanocobalamin (B12).
Physiological causes
Impaired coordination and dizziness (the causes of the conditions are often physiological) should not always be a cause for concern. They are explained by the occurrence of sensations under the influence of movements, which appear during motor manipulations or after their termination. An example of the appearance of such feelings is the fear of heights.
The list of physiological causes includes the following processes:
- menopause;
- deterioration of the body over time;
- decrease in blood sugar;
- seasickness;
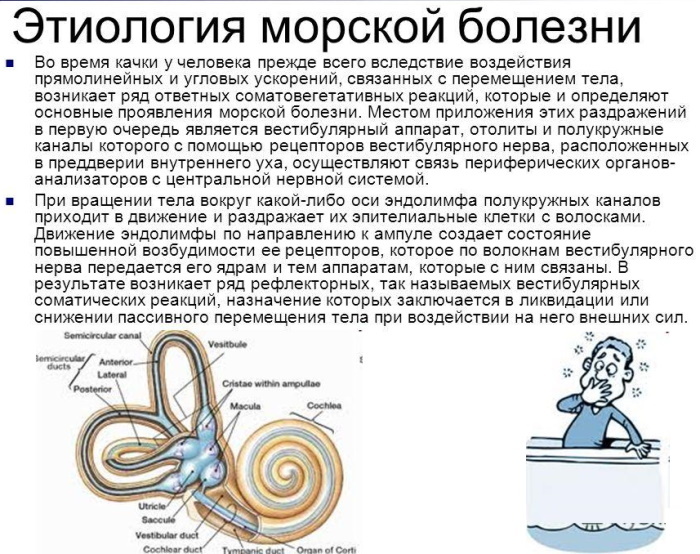
- increased noise level;
- getting into the ear of a foreign object;
- clogging of the ear canal with a secretion of the sebaceous glands (sulfur).
Natural causes of ataxia should not be alarming. You need to pay special attention to the symptoms that are diagnosed for the first time in life, and they cannot be correlated with physiological natural processes. An urgent need to respond to conditions when other accompanying symptoms appear. This is especially a sharp headache, loss of sensation in the limbs, paralysis of a part of the body.
Pathological causes
The list of pathological causes includes conditions:
- inflammation of the outer, middle or inner part of the ear canal;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- disorders in cerebral vessels with a deficiency of cerebral circulation;
- tumors of the nerve responsible for the transmission of impulses;
- multiple sclerosis;
- epilepsy;
- attacks of severe headache;
- brain damage;
- depressive mood, panic attacks;
- autoimmune diseases;
- drops in blood pressure.
Impaired coordination and dizziness (sometimes pathological causes) can be classified according to the nature of the disease. The types with the reasons and description of the state are summarized in the table.

| View | Cause | Description |
| Sensitive | Polyneuropathy, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord tumors, lack of vitamin B12. | The condition is characterized by the fact that a person moves, raising his legs high, and when you lower them, then with great force it seems to stamp each step. Loss of balance is observed when closing the eyes, there is also a deficit in sensitivity. Such patients walk with caution, as if controlling every movement. |
| Vestibular | Disorders in the department responsible for maintaining balance. | Dizziness, nausea and vomiting are possible signs of the disease. With changes in position and tilt of the head or body, the symptoms increase. |
| Cerebellar | Stroke, traumatic brain injury, tumors, multiple sclerosis, body intoxication. | The condition is characterized by a lack of coordination in movements with closed eyes and in dark rooms. However, motor skills are not affected when the eyes are open. There is a possibility of falls. The spoken center is upset: slurred slow speech may appear. There is a deterioration in reaction and handwriting. |
| Cork | Disorders of the function of the cortex in the front of the brain. | Symptoms of the disease are instability when walking during turns, at the start. The syndrome of "tangled legs" is manifested, deviations in the "standing" position are also possible. Patients often have mental disorders in the form of auditory hallucinations. There is a loss of the grasping reflex, the impossibility of adopting a "sitting" position. |
| Psychogenic (hysterical) | Mental disorders. | The condition is characterized by the loss of the ability to walk in a straight line. It manifests itself in the "gait of a skater", "weaving braids" or in gait like "on stilts". The distinctive properties of the type of ataxia are the absence of organic pathologies in the central nervous system. |
Who to contact
Neurologists or neuropathologists are involved in the treatment of pathology.
Diagnostics consists in performing the following steps:
- Consultation with a specialist.
- Hardware research.
- Genetic analysis of movement coordination disorders.
At the consultation, the neurologist first of all collects a family history, that is, conducts a survey the state of health of the next of kin, asks the patient whether there are similar symptoms. Based on the results of the conversation, the doctor can draw preliminary conclusions about the reasons that cause the condition. In the event that relatives with similar disorders are identified, then the patient is assigned a genetic analysis.
Next, the doctor performs neurological tests and functional tests. The set of exercises may include the Romberg test, synchronized walking. Thanks to the results of tests and samples, the specialist gets a more detailed picture of the symptoms.
Dizziness and lack of coordination are caused by different reasons, therefore, the diagnosis is not carried out without hardware diagnostics, which may include:
- CT scan;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- electroencephalography (EEG);
- duplex scanning of cerebral vessels.
If there is a suspicion of neurological causes of pathology, appropriate examinations are carried out, which help to establish the existence of objective symptoms indicating damage to the central nervous systems. If such signs of damage are found, then the patient is referred for brain imaging, that is, for CT or MRI. Such studies are capable of detecting vascular pathologies, multiple sclerosis, the consequences of trauma, and neoplasms of nerves. If there is suspicion of ataxia, which is often the only sign of dizziness, then an electroencephalographic study is performed.
Clinical trials may include a complete blood count, biochemistry, and a test for genetic abnormalities.
Based on the research results, the neuropathologist can issue a referral to the patient for consultation with an otolaryngologist or neurosurgeon (if there is such a need). So, when vestibular pathologies are detected, an examination by an ENT is necessary, which will show possible changes in the outer, inner or middle ear.
If there is an opportunity to remove the cause of the condition, then experts prescribe the appropriate therapy. In some cases, motor coordination is lost with excessive drinking or high doses of medication. The problem is solved by removing the intoxication of the body. Brain tumors are treated with surgery. Hypothyroidism is controlled by correcting the functioning of the thyroid gland. Vitamin B12 deficiency is also treatable. Genetic inherited disorders cannot be cured. Here, doctors prescribe only symptomatic therapy.
In all cases and for any reason for the condition, patients undergo physical therapy and occupational therapy. Physiotherapy exercises can improve balance, posture and coordination of movements through exercise. In occupational therapy, specialists refer to devices that can assist with walking, eating, and self-care. To correct speech disorders, speech therapists come to the rescue.
When coordination disorders and dizziness appear, it is necessary to find out the cause of the conditions. In most cases, it refers to natural physiological processes. And only in a small number of people, the cause is pathological in nature, requiring treatment.
Video about the causes of dizziness
How to determine the cause of dizziness:



