Content
- Definition
- Ancient Egypt
- Ancient Greece
- Russia
- Works by Charcot and Freud
- Modern definition
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Drug treatment
- Folk methods
- Psychologist consultation
- Video about hysteria in psychology
Hysteria is a condition, in which patients have many symptoms from the nervous system, which worsen the general condition of the patient. In psychology, the concept of a disease appeared quite a long time ago, but today this condition is being studied in different countries by scientists to obtain details and develop treatment methods. Doctors identify several types of pathological conditions, as well as different methods of therapy, but in each case they may be different.
Definition
Hysteria is a pathological condition, the development of which occurs as a result of disruption of the work of certain centers in the brain. The disorder is accompanied by various emotional and mental disorders that worsen the general condition of patients and reduce the quality of life. Hysteria is translated from Greek as "womb".
For many centuries, doctors have studied the condition, its course and features. The nuances of the studies were recorded, they were different at the time of different doctors and researchers.
Ancient Egypt
The first description of the state occurs in 1950 BC. NS. The peculiarities of the course of hysteria are indicated in the Kakhunsky medical papyrus. The term is not yet used by specialists, but a theory has been put forward that disorders arise against the background of pathologies of the pelvic organs, namely the uterus.
The papyrus describes cases of such diseases, but doctors do not establish a diagnosis. Symptoms in different patients differ, as well as the degree of their severity, the duration of the course of the condition.
Ancient Greece
Hysteria in psychology is a condition that includes many different symptoms from the central nervous system. The ancient Greek healer and philosopher Hippocrates, who is considered the "father of medicine", described the condition in some detail. It was he who first introduced the term hysteria into medicine. In his numerous works, Hippocrates describes the state of women and the peculiarities of its course. At the same time, at the time of the description, there is no evidence that the disease can occur in men.
Plato, a contemporary of Hippocrates, called hysteria a kind of rabies that develops in women due to the inability to reproduce offspring. He, like Hippocrates, described the course of the violation. During the life of these specialists, mankind lacked basic knowledge about human anatomy and physiology.
That is why pathology has been attributed only to women for many centuries. It was believed that the uterus wanders through the body when the process of conception, natural for it, does not occur. During this "wandering" there is an approach to different internal organs, which leads to the appearance of certain symptoms.
Russia
For several centuries, namely the 17th-19th centuries, the diagnosis "hysteria" was quite popular. It was at this time that "male hysteria", which was also called "hysteria", was first described in the works of specialists.
Despite the fact that the description of the condition in men can be found in the works of other specialists much earlier, it was in the 17th century that doctors from various fields of medicine began to actively study the disorder. The peculiarities of the course of the condition gave people a reason to consider the sick as sorcerers, which is associated with inappropriate behavior and various disorders of the internal organs.
Works by Charcot and Freud
Hysteria has long been considered an understudied condition. In psychology, it appeared only in the 19th and 20th centuries. Specialists J. M. Charcot and Z. Freud studied mental disorders for many years and put forward the theory that it the disorder can develop in patients of different ages and sex, regardless of the state of reproductive systems.
Experts clarified that the disorder can occur against the background of dissatisfaction of any desires, but this does not have to be the desire for sexual intercourse and conception. The works of scientists included studies that provided grounds for the assumption that the disorder occurs in patients with a predisposition to it.
For example, childhood traumas, features of upbringing, any emotional upheaval can affect the formation of the human psyche, which in the future provokes the development of mental disorders. Based on their research, specialists were able to determine not only the alleged causes and predisposing factors, but also the characteristics of the course in different patients. The works of Charcot and Freud became the basis for further research.
Modern definition
Today, experts do not diagnose hysteria in patients; it is not in the international classification of diseases. Despite this, there are many other conditions that can be diagnosed in patients, and their course resembles hysteria.
Modern psychiatry today studies the condition, its features and possible complications. Doctors determine the principles of therapy for the disorder, identify new causes that were previously unknown.
Classification
A simple classification divides the condition into acute and chronic. In the first case, the symptoms appear suddenly, manifested by various disorders of the nervous system and internal organs. The general condition is usually worsened, concomitant disorders appear.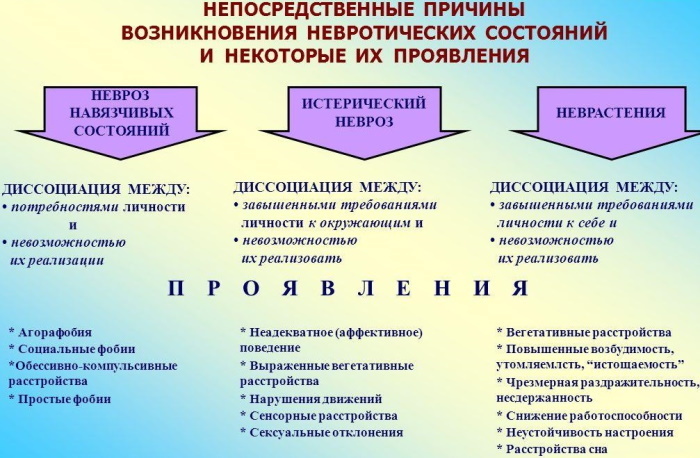
In the chronic course of the violation, the symptoms are aggravated at regular intervals, but the course is mild, complications may be absent or manifest in a mild form. Treatment for this course of the disease is complex and lengthy, despite the absence of acute manifestations.
There is no single classification of the condition, which is due to the absence of such a diagnosis in the international classification of diseases. But experts today distinguish several types depending on the age and gender of the patient.
| Variety | Peculiarities |
| Womens | This condition usually develops in women of reproductive age. At the same time, the likelihood of the appearance of symptoms in patients after the onset of menopause cannot be ruled out. The clinical picture of pathology differs in different patients, which is explained by the presence of certain concomitant deviations |
| Mens | In men, the condition develops somewhat less frequently. Usually, the pathology is diagnosed in middle-aged patients, accompanied by various emotional disorders. In most cases, the condition does not provoke complications, but requires special treatment to prevent them. |
| Children | In children, the disease manifests itself in preschool and early school age, but in most cases, the first symptoms appear in patients over 4 years of age. The clinical picture in children differs from the symptoms observed in adults. Often, frustration occurs against a background of emotional stress and difficulties in relationships with loved ones |
Experts note that the course of the pathological condition in patients of different sex and age is different, even in the absence of complications from the internal organs.
Depending on the nuances of the course of the disease, as well as the severity of symptoms, several disorders can be distinguished:
- Conversion hysteria is not identified by specialists as a separate diagnosis. The condition is a combination of many manifestations from the nervous system, accompanied by signs of hysteria. At the same time, many manifestations are characteristic of mental disorders, but upon examination, the patient has no other symptoms.
- Mass hysteria does not belong to psychology, but is considered quite common. It assumes the emergence of emotional and mental disorders in a large number of people at once under the influence of certain external factors. Symptoms are often similar, but their features differ from patient to patient.
- Fear hysteria was highlighted by Freud in the study of patient behavior. It is also not an independent diagnosis, most often associated with the presence of various phobias in the patient.
Doctors draw the attention of patients to the fact that there is no classification that would be developed by specialists in the study of hysteria. This is due to the absence of such a violation in the international list of pathologies. All varieties are conditionally identified by specialists, based on the nuances of the course of the condition in different patients.
Symptoms and Signs
Hysteria in psychology is a condition that has not been sufficiently studied to date. The symptomatology and the degree of its severity differ in different patients. Outwardly, the violation can manifest itself as poor skin, dark circles under the eyes and disorientation in space. But outward signs may be absent.

The most common manifestations of the violation:
- Sleep disturbance accompanied by anxiety and restlessness.
- Unreasonable and sudden change in mood. Symptoms usually manifest in the presence of other people. Alone, manifestations rarely occur.
- Temporary loss of basic skills. Experts note that during an exacerbation of symptoms, conditioned reflexes may disappear in a patient. At the same time, unconditioned reflexes are preserved.
- Increased excitability, which is accompanied by emotional outbursts, anxiety, motor activity.
- Hearing, vision and taste impairments are not observed with a mild course of the pathological condition. But in the acute stage, such symptoms may appear. Patients report a deterioration in the quality of vision, as well as a violation of taste. When eating food, the patient cannot name its taste. Usually at this stage, the patient refuses food, which provokes other disorders.
- Decreased mental performance. In the acute and subacute period, the patient is unable to concentrate on performing any action, which leads to a significant decrease in productivity. Rest does not help to normalize the condition.
- Deterioration in concentration, impaired coordination of movements.
- A taste in the mouth that occurs in patients during an exacerbation, when a person does not eat.
- Hallucinations can also occur in the acute stage, they include gustatory and auditory types of symptoms. Usually, such signs appear in patients who additionally suffer from mental disorders in a chronic form.
- Attacks of aggression, during which the patient can harm himself and those around him.
In women, the symptoms of the nervous system are manifested in an acute form, men are more likely to suffer from a mild form of hysteria. In children, the clinical picture is different. Usually the symptomatology manifests itself in the form of sudden hysterical attacks, tearfulness. The child refuses to perform any action, even a slight change in the situation can provoke a new attack.
Usually, the child's manifestations disappear quickly. Adults often require treatment to normalize the condition. Among the atypical symptoms are nausea and bouts of vomiting, upset stools. Patients often talk about severe headaches, dizziness, pain in joints, muscles. Sometimes in the acute stage, an increase in body temperature is observed, which only worsens the general condition.
The clinical picture differs from patient to patient. All patients may not have the same symptoms. Almost always, several signs predominate, the rest are less pronounced or completely absent.
Causes
Hysteria in psychology is a condition that is caused by a complex of different reasons. In children, emotional upheavals, a tense atmosphere in the house, and frequent quarrels, which the child witnesses, are considered a predisposing factor. Other factors rarely provoke the development of hysteria. Only sometimes the child has a history of mental disorder.
The main reasons for the development of the disease in adults:
- Frequent stressful conditions or constant stress as a result of exposure to negative external factors.
- Chronic somatic disorders.
- Pathology of the nervous system in the patient's anamnesis. Against the background of a disturbance in the functioning of the brain, hysterical seizures may occur.
- Cerebral circulation disorder. Patients with such disorders may experience complications in the form of hysteria.
- Constant negative loads on the nervous system, which provoke impaired brain activity.
- Traumatic brain injury. Symptoms do not appear during the recovery period, but if patients have a history of such injuries, the likelihood of developing hysteria increases.
- Congenital abnormalities in the development of the central nervous system.
- Chronic mental disorders. If the patient has previously suffered from acute disorders, the risk of developing hysteria increases.
- Vascular pathology of the brain.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, as well as the use of drugs that affect the functioning of the brain. Drug addiction is also thought to be a predisposing factor for the development of hysteria.
- Severe hormonal disorders. Usually this reason is more common in women.

These and some other reasons can provoke hysteria. Often, a deviation occurs against the background of several factors.
Treatment methods
Today there is no definite and universal therapy regimen that would suit all patients. In children, the condition rarely requires complex treatment; in most cases, behavior can be corrected with the help of a visit to a psychologist.
But in adults, mental disorders are often accompanied by somatic disorders, so special treatment is necessary. The patient is examined by a doctor beforehand. Standard methods are not suitable for diagnosing the condition.
Usually one of the psychological tests is used to assess the patient's condition, to determine his personality type. The Minnesota Multidimensional Personality Questionnaire is often used. It is within the framework of this questionnaire that there is a special scale for determining whether a patient has one or another form of hysteria.
After receiving the results of the survey, the patient is monitored by a psychiatrist. Long-term observation is often required. Only on the basis of a psychiatrist's conclusion can an accurate diagnosis be established.
Drug treatment
Hysteria in psychology is a condition that is successfully treated with the help of various medications, but only in the absence of severe complications and identifying the degree of neglect of the disorder. Patients cannot take medications on their own, as there are no universal remedies for everyone.
Depending on the symptoms and the presence of complications in the patient, herbal remedies, tranquilizers, hypnotics and sedatives, antidepressants from different groups can be used.
The most effective medicines:
- Persen contains herbal ingredients that have a mild sedative and hypnotic effect, eliminate signs of hysteria in a mild form, help prevent the appearance of complications against the background of progression disease. The tablets are taken in courses of 2-3 weeks, the daily rate is 2 tablets. The tool is considered effective as a stand-alone method or as an adjunctive therapy.
- Afobazol is a sedative, helps to improve the patient's sleep and reduces the risk of symptoms of a hysterical attack. Take tablets before bedtime, 1-2 pieces or throughout the day, 1 tablet 3 times a day with approximately equal time intervals. Treatment lasts from 10 to 20 days, depending on the severity of the manifestations. In combination with other drugs, the drug improves the patient's condition.
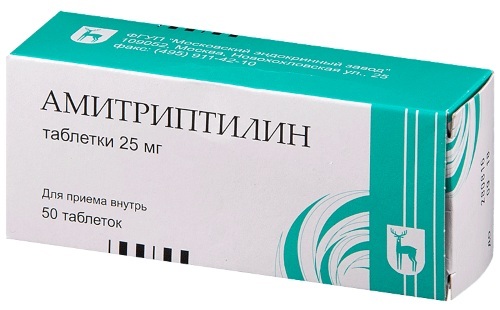
-
Amitriptyline belongs to the group of tricyclic antidepressants, therefore it has pronounced properties. The drug not only eliminates anxiety, symptoms of hysteria, but also normalizes sleep. Long-term administration of the medication is not recommended, usually 10 days are enough to obtain a therapeutic result. The daily rate is 1-2 tablets. It is recommended to take the product at bedtime to avoid sleepiness during the day.
- Motherwort from Evalar often used for hysteria, as it is highly effective. The drug contains motherwort extract, helps to eliminate anxiety, anxiety, and reduces the likelihood of disease progression and frequent recurrence of attacks. Tablets are taken 1 piece 2 times a day, and the treatment lasts 2-4 weeks.
- Donormil helps to normalize sleep, as emotional disorders often provoke insomnia. Take 1 tablet at bedtime, the duration of the therapeutic course is 10-20 days.
The dosage of drugs and the duration of their use may differ for each patient.
Folk methods
Alternative medicine prescriptions can also be used as part of a comprehensive treatment for hysteria. Usually they are used for mild pathology and the absence of complications. The most popular home remedy is herbal infusion or decoction.
An infusion based on mint and lemon balm has sedative and mild hypnotic properties. It is allowed to use it for 2-4 weeks, take 1 glass before bedtime. For 300 ml of boiling water, you need to take 3 g of each ingredient in dried form, leave for 30 minutes. It is better to prepare the product immediately before use.
Alcohol tincture based on valerian root is often used as part of the complex treatment of the disease. For 100 ml of alcohol, you need to take 20 g of crushed root, leave in a dark place to infuse for 14 days. The filtered infusion is taken 2 times a day, 35 drops. The duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
Any method is allowed to be used only after visiting a doctor. Folk remedies can provoke complications and have contraindications.
Psychologist consultation
A prerequisite for therapy is a visit to a psychologist. If the patient has a history of mental disorders, consultations of a psychiatrist are shown, who is observed not only for the course of hysteria, but also for the development of a concomitant disease.
During consultations, the specialist identifies the patient's personality traits, the alleged causes of the disorder, as well as ways to eliminate the disorder. The patient visits the doctor 2-3 times a week, and the number of sessions is determined individually. At the same time, the specialist is based on the course of the deviation and the patient's response to drug therapy.
Hysteria is considered a fairly common abnormality, which in psychology is not classified as a separate disorder. This condition can develop in children and adults and requires the consultation of a psychologist or psychiatrist. Sometimes drug treatment is required, which is determined individually for each patient.
Video about hysteria in psychology
Hysterical Personality Disorder:
