Content
- Anatomical features and localization of the gallbladder in humans
- Functions
- Histological structure
- How does the gallbladder work and what is it responsible for?
- Causes of pain in the gallbladder
- Pregnancy
- Biliary dyskinesia
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Acute purulent cholecystitis
- Cholangitis
- Cholelithiasis
- Parasitic invasions
- Postcholecystectomy syndrome
- Tumors of the gallbladder
- Diagnosis of pathologies of the gallbladder
- Methods used for treatment
- First aid for acute pain
- Conservative therapy
- Lithotripsy
- Surgery
- Treatment methods for specific pathologies
- Cholelithiasis
- Cholecystitis
- Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
- Gallbladder polyps
- Gallbladder cancer
- Nutrition with a diseased gallbladder
- Video about the gallbladder
A person has a gallbladder serves as a natural reservoir for the accumulation of bile. This organ is located in the area of the right hypochondrium next to the liver tissue. The gallbladder plays an important role in the digestive function of breaking down animal and vegetable fats.
Anatomical features and localization of the gallbladder in humans
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped sac with a musculocutaneous tissue structure located in the cavity of the lower segment of the liver. In humans, this organ is more elongated with wide and narrow edges. At the same time, there is a physiological regularity that the inner lumen of the gallbladder from its bottom towards the neck gradually narrows.
The neck of this organ smoothly passes into the cystic canal, which has a common connection with a single hepatic duct. The bottom of the gallbladder touches the surface of the parietal peritoneum, and its body is in contact with the lower stomach, transverse colon and duodenum.
The average length of the gallbladder in a healthy person is from 8 to 10 cm, and the width is in the range of 3-5 cm. The volume of this organ is 50-60 cm. cub.
The gallbladder has the following anatomical features:
- medium-sized neck;
- rich dark green color;
- very thin walls;
- sphincter of Lutkens, which is localized in the area of transition of the cervix to the bile duct;
- rounded bottom;
- a narrow section that is peripheral;
- wide distal area.
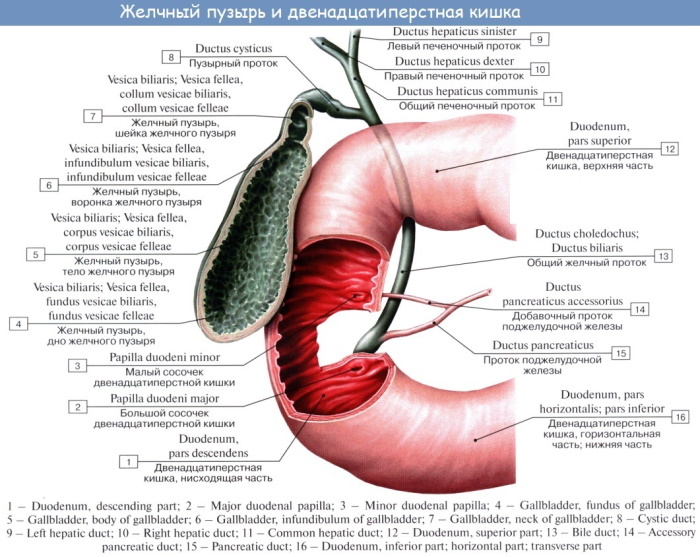
This organ is connected by a single bile duct, the blockage of which leads to the development of painful conditions. liver, directly the gallbladder itself, and also causes a disorder in the work of the entire digestive systems.
Functions
The human gallbladder is located in close proximity to the liver tissue. The table below describes the main functions that this body performs.
| Functions of the gallbladder | Characteristics of the physiological process |
| Cumulative | The basic function of this organ is to accumulate bile secreted by the liver. Within 24 days, this reservoir accumulates from 500 to 1200 ml of bile content, which is subsequently consumed for the needs of the digestive system. |
| Concentration | The human body has the ability to increase or decrease the concentration of bile depending on the diet. The walls of the bladder pull water from the bile secretion, replacing it with the biologically active substance mucin. Due to this process, the concentration of bile increases from 5 to 10 times. A digestive secretion is formed, enriched with bile acids, which are further redirected to the intestines to break down fats. |
| Transportation | After the completion of the accumulation stage, a reflex contraction of the bladder walls occurs, which redirects bile through a single channel into the duodenal cavity. The release of digestive secretions is regulated by the sphincter system. |

Between successive meals in the bladder cavity, a continuous accumulation of bile continues. Poor nutrition, abuse of diets that exclude the use of fats, leads to functional disorders in the work of this organ.
Histological structure
The human gallbladder is located in the right hypochondrium.
The histological structure of this organ is as follows:
- Serous membrane from the peritoneal side.
- Superficial epithelial cells, cambial and goblet cells.
- The mucous membrane with multiple folds, covered with a single-layer columnar epithelium.
- Cholecystocytes with microvillous border.
- Own mucosal lamina, composed of fully elastic fibers.
- Plasma, fat and fatty cells.
- Alveolar-tubular glandular tissue.
- Smooth myocytes that form the muscular layer.
- Adventitia, composed of high-density connective tissue.
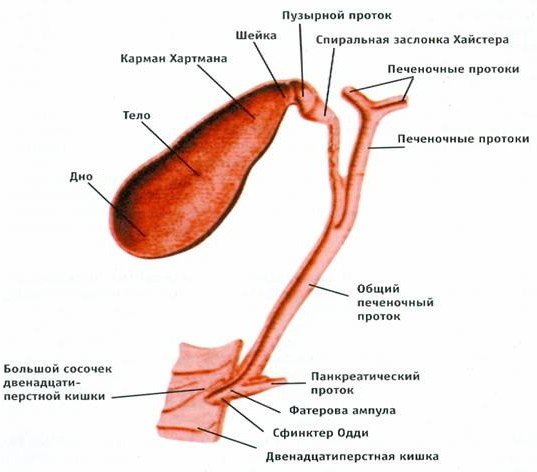
Human gallbladder
The innervation of the gallbladder is provided by peripheral nerve branches located in the liver capsule. Here are concentrated the vessels that provide blood supply to this organ.
How does the gallbladder work and what is it responsible for?
The gallbladder works on the principle of a physiological reservoir. After the accumulation of a sufficient amount of bile secretion, this organ ensures its further transportation into the intestinal cavity to maintain a stable functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of pain in the gallbladder
Pain in the gallbladder area is an alarming symptom that indicates a painful condition of this organ.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder may occur, which develops due to displacement of its anatomical position, squeezing of the walls, temporary changes in hormonal balance.
Cholecystitis associated with bearing a child is accompanied by additional symptoms in the form of:
- severe toxicosis;
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- stool disorders;
- frequent vomiting.
During pregnancy, the manifestation of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder is acute or chronic with periodic exacerbations.
Biliary dyskinesia
Violation of the patency of the bile ducts is a serious and dangerous disease that can lead to the loss of the gallbladder. This pathology develops as a result of tumor processes, helminthiasis, intestinal infections, blockage of the ducts with stones.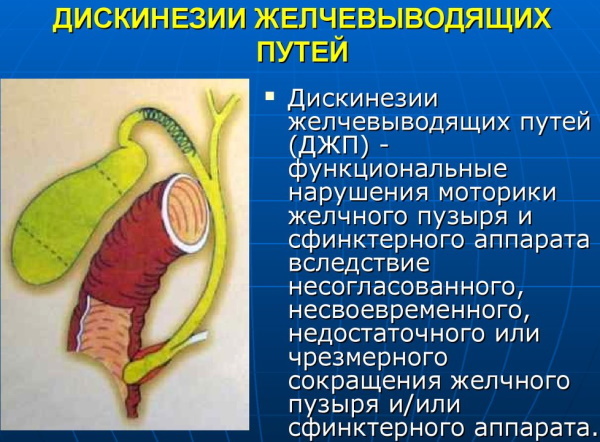
A patient suffering from biliary dyskinesia will experience the following symptoms:
- paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- uncomfortable sensations extending to the tissues of the right shoulder;
- heaviness in the abdomen;
- clarification of feces;
- bitterness in the mouth.
There is hyperkinetic dyskinesia of the bile ducts, when the walls of the bladder contract, they try to remove the accumulated bile, but the channel along its outflow is blocked. The second type of this disease is hypokinetic. In this case, the musculature of the organ is completely relaxed and does not function.
Chronic cholecystitis
This type of cholecystitis is a chronic inflammation of the gallbladder walls. This type of disease develops gradually, accompanied by periodic bouts of pain in the right side.
Chronic cholecystitis is manifested by additional symptoms in the form of:
- chills;
- active gas formation;
- nausea;
- deterioration in appetite;
- frequent belching.
The main danger of chronic cholecystitis is that over time, against its background, a serious complication develops in the form of cholelithiasis. This disease requires the use of medical and surgical treatment.
Acute purulent cholecystitis
Inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder, proceeding in an acute form with an accumulation of purulent contents, is an extremely dangerous pathology. In most cases, this disease is caused by organ trauma, autoimmune disorders, infectious and parasitic invasions.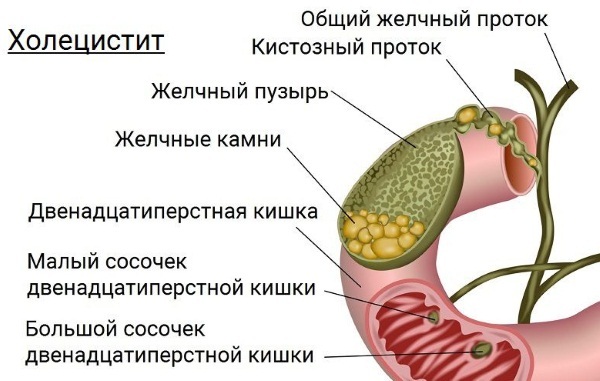
Acute suppurative cholecystitis can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- cutting pain in the right hypochondrium;
- vomit;
- an increase in body temperature up to 38-39 degrees;
- yellowing of the skin;
- aversion to food;
- fever.
Cholecystitis of this type is dangerous by the spread of the infectious and inflammatory process to the liver tissue and other organs of the digestive tract.
Cholangitis
Angiocholitis or cholangitis is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the bile ducts. This pathology is of an infectious origin. The main causative agent of the disease is Toxoplasma parasitic microorganisms, and their main carrier is cats.
Cholangitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- acute or chronic pain in the right hypochondrium with spread to the shoulder and scapula;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- fever;
- general breakdown;
- decrease in body temperature;
- vomit;
- confusion of consciousness.
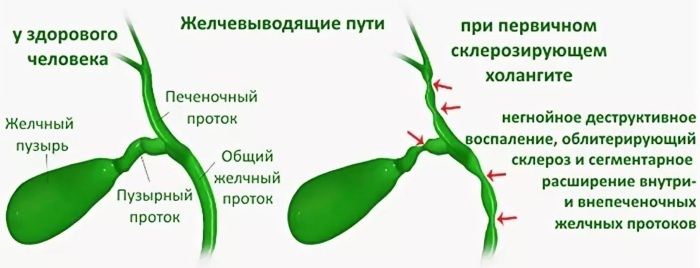
A prolonged course of cholangitis without the use of effective therapy leads to obstruction of the bile ducts with a violation of their patency. This disease can cause septic shock and severe intoxication of the patient's body with the onset of death.
Cholelithiasis
The human gallbladder is located inside the abdominal cavity. The reason for the development of gallstone disease is the accumulation of extraneous calculi inside this organ.
This disease is accompanied by attacks of severe pain of varying intensity, as well as the following symptoms:
- colic in the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of heaviness inside the abdominal cavity;
- an increase in body temperature from 37 to 39 degrees;
- lack of appetite;
- violation of the stool towards constipation or diarrhea;
- yellowing of the skin.
In most cases, gallstone disease is a complication of chronic cholecystitis, when the person suffered from this disease for a long period, did not take action on its timely treatment.
Parasitic invasions
Infection of the gallbladder with parasites causes acute or chronic cholecystitis. The inflammatory process inside this organ is provoked by the pathogenic microorganisms of lamblia. These are the simplest parasites that are able to penetrate under the membrane of the muscular layer of the gallbladder, migrate along its ducts into the tissue of the liver and pancreas. In terms of symptoms, parasitic infection of the gallbladder is identical to cholecystitis.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome
The gallbladder in humans is located in close proximity to the liver. Postcholecystectomy syndrome is a disorder that manifests itself after a complete resection of the gallbladder. The appearance of pathological symptoms is associated with functional disorders in the work of the sphincter of Oddi.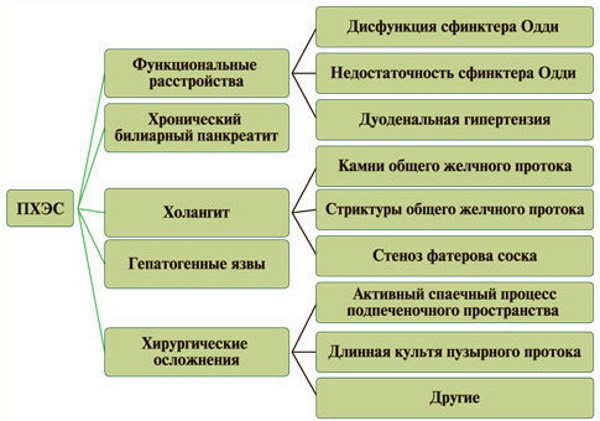
This disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased gas formation;
- frequent belching;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- bitterness in the mouth.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome is accompanied by repeated bouts of aching pain in the right hypochondrium. Systemic disturbances in the work of the gastrointestinal tract join the uncomfortable sensations.
Tumors of the gallbladder
Distinguish between benign and oncological tumors that are localized inside the gallbladder, or grow through its walls. The nature of the pathological symptoms depends on the type of extraneous neoplasm. As the tumor grows, the patient develops painful signs resembling cholecystitis.
Diagnosis of pathologies of the gallbladder
The table below shows the main diagnostic methods that are used to determine the pathologies of the gallbladder.
| Diagnostics type | Purpose and cost of the survey |
| Clinical analysis of capillary blood | Displays the possible presence of an inflammatory process. The average cost of this study is 480 rubles. |
| Biochemical analysis of venous blood | Allows you to determine the functional state of the tissues of the pancreas and liver, the level of lipid metabolism in the body. The average price of the analysis is 800 rubles. |
| Immunological test for tumor markers | It is carried out to detect cancer cells. The average cost of diagnostics is 950 rubles. |
| Coprogram | Analysis of the patient's feces reflects the functionality of his digestive system, and also allows you to detect the simplest parasites of lamblia. The price of this study is 590 rubles. |
| Ultrasound |
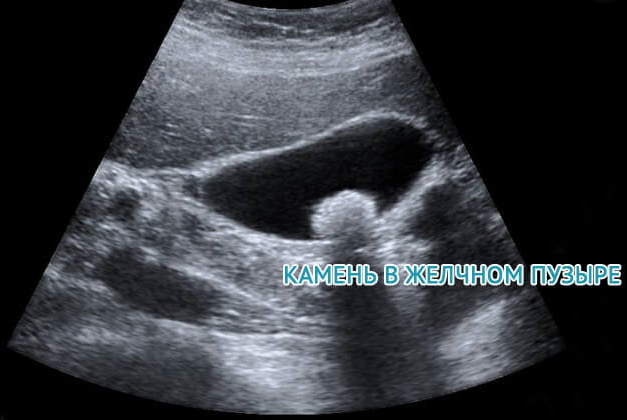 This method for diagnosing the gallbladder is considered one of the most informative. An assessment of the shape, size, position, wall thickness of the investigated organ is carried out. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to detect the presence or absence of tumor neoplasms, stagnation of bile secretion, to measure the physiological parameters of the pancreatic and bile ducts. The average cost of this examination is 1100 rubles. This method for diagnosing the gallbladder is considered one of the most informative. An assessment of the shape, size, position, wall thickness of the investigated organ is carried out. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to detect the presence or absence of tumor neoplasms, stagnation of bile secretion, to measure the physiological parameters of the pancreatic and bile ducts. The average cost of this examination is 1100 rubles. |
Patients who have signs of a tumor neoplasm in the structure of the gallbladder are prescribed an additional study in the form of CT or MRI diagnostics.
Methods used for treatment
The method of treating the pathological condition of the gallbladder depends on the reasons that provoked its occurrence.
First aid for acute pain
Acute pain in the gallbladder occurs due to the fact that inside this organ there is a sharp change in pressure due to the growing spasm.
To alleviate the suffering of a person with a similar symptom, you must do the following:
- Remove outer clothing from the patient that squeezes the abdomen.
- Place the person on their right side.
- Apply a cold cloth or ice pack to the surface of the patient's abdomen in the right hypochondrium.
- Call an ambulance.

In some cases, taking a warm bath can help relieve an attack of acute pain caused by gallbladder disease. The use of painkillers is contraindicated, since they mask the pain syndrome, but are not able to eliminate the cause of the pathology.
Conservative therapy
The method of conservative therapy involves the use of drugs of the following pharmacological groups:
- antibiotics;
- choleretic agents;
- antispasmodics;
- digestive enzymes;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The selection of the drug is carried out by the doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient's body. The type of disease that affected the walls of the gallbladder affects the construction of the therapy regimen.
Lithotripsy
Non-contact lithotripsy is considered a modern method of crushing stones inside the gallbladder without surgery. For this, an ultrasound apparatus is used. With the help of ultrasound waves of high frequency, stones in the gallbladder are crushed to the state of sand. This method of treatment does not cause damage to healthy tissues and does not require post-therapeutic rehabilitation. The average cost of lithotripsy of gallstones is from $ 25,000. rub.
Surgery
Therapy of pathologies of the gallbladder using a surgical operation involves the complete removal of this organ. After cholecystectomy, bile continues to be released into the intestinal cavity, but directly through the bile duct without reservoir accumulation. Because of this, its quality indicators and density decreases. 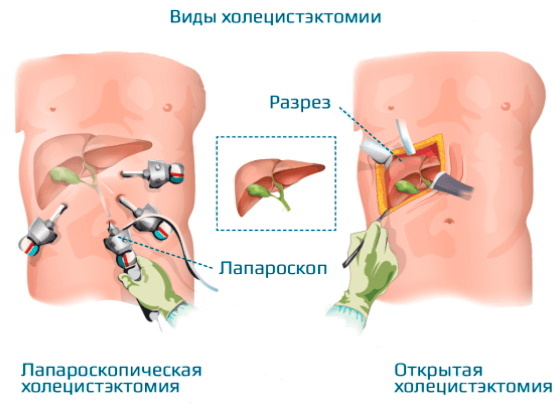 People who have undergone surgical removal of the gallbladder require a lifelong diet. Cholecystectomy is performed under general anesthesia with penetration into the abdominal cavity.
People who have undergone surgical removal of the gallbladder require a lifelong diet. Cholecystectomy is performed under general anesthesia with penetration into the abdominal cavity.
Treatment methods for specific pathologies
Therapy for gallbladder disease includes the use of drugs and surgery.
Cholelithiasis
Patients diagnosed with cholesterol calculi are prescribed a course of therapy with litholic drugs for drug dissolution of dense fatty deposits. Depending on the size of the stones, the attending physician may prescribe a lithotripsy procedure with their crushing using high-frequency ultrasound waves. The gallstone disease that causes the blockage of the duct is treated with surgery. In this case, the surgeon performs a complete removal of the gallbladder together with stones that disrupt the stable outflow of bile.
Cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis is treated using the following methods:
- taking antibiotics in case of infectious invasion;
- therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- removal of spasm of the walls of the organ with antispasmodic drugs;
- stimulation of the outflow of bile with drugs with choleretic properties.

Acute cholecystitis with signs of increasing inflammation requires complete removal of the gallbladder. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia by opening the abdomen or using laparoscopy.
Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
A distinctive feature of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis is the thickening of the walls of the gallbladder, formation of concretions of cholesterol and mixed type inside the organ, as well as multiple yellow granulomas colors. The tactics of treating this pathology is determined on an individual basis, but in most cases the method of cholecystectomy with complete removal of the gallbladder is used.
Gallbladder polyps
Benign neoplasms in the form of polyps, which are located on the surface of the gallbladder, can be removed without injury to the organ. In the case of their germination through the walls of the physiological reservoir, cholecystectomy is performed. The removed polyps are sent for histological examination for laboratory confirmation of their benign origin.
Gallbladder cancer
Oncological lesion of the gallbladder requires a surgical operation to remove the organ. In this case, the use of chemotherapeutic and cytostatic drugs is not advisable, since there is a risk of spreading cancer cells in the liver tissue, pancreas and gastrointestinal tract. After the successful completion of the surgical operation, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination of all digestive organs in order to exclude the factor of metastasis of a malignant tumor.
Nutrition with a diseased gallbladder
People suffering from chronic gallbladder disease must constantly adhere to dietary norms.
The diet of patients in this category should include the following food:
- lean vegetable and milk soups;
- low-fat varieties of fish and meat, cooked in a steam bath or baked in the oven;
- dairy products with a minimum concentration of fat;
- protein omelets from chicken eggs;
- Dill;
- cereals and pasta;
- sweet jam;
- fresh fruits and vegetables that do not have a high level of acidity;
- bread;
- dried fruits;
- parsley.
Patients with cholecystitis are strictly prohibited from eating the following types of food and drinks:
- mayonnaise;
- alcohol;
- hot ketchup and adjika;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- dairy products with a high level of fat content;
- hot spices and vegetables;
- too sour greens;
- chicken egg yolks.
Fatty, sour, pickled, spicy, overly salty food can exacerbate chronic cholecystitis, which entails the development of severe complications.
The gallbladder is an important organ of the human body, which is located in the area of the right hypochondrium in close proximity to the liver tissues. The main purpose of this structural unit of the digestive system is the accumulation, thickening and transportation of bile secretion into the intestinal cavity. The pathological condition of the gallbladder in adults and children leads to the development of acute or chronic inflammation of its walls. Cholecystitis, cholangitis, polyposis, as well as gallstone disease are those diseases that can lead to the complete removal of the gallbladder.
Video about the gallbladder
Gallbladder Anatomy: