Content
- Causes of foamy stools with and without fever in children 1-6 years old
- Infectious causes
- Non-infectious causes
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- What symptoms accompany diarrhea with foam in different pathologies
- Survey
- Symptomatic therapy
- Dysbacteriosis
- Intestinal infection
- Celiac disease
- Lactase deficiency
- Complications of pharmacotherapy
- The use of medicines
- Appointment of proper nutrition
- Video about diarrhea in a child
Foam diarrhea often occurs in children and adults against the background of various provoking factors. Symptoms occur in a child at the age of 3 more often as a result of dietary changes that occur when visiting a preschool. The appearance of foam in the feces is considered a reason for immediate medical attention, as it may indicate the progression of a serious illness.
Causes of foamy stools with and without fever in children 1-6 years old
Changes in the consistency and color of stool is considered a fairly common symptom, especially in childhood. Changes in diet and some other reasons provoke the disorder. Foamy stools are not typical for a child and are often accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Depending on the predisposing factor, the pathology treatment regimen is determined.
Infectious causes
Diarrhea in a child can be triggered by infectious pathologies. Most often, the disorder acts as a complication in the multiplication of bacteria in the intestines of various forms and types. Less commonly, the violation is associated with the activity of certain viruses that can multiply in the digestive tract and disrupt its work.
In some cases, diarrhea is triggered by infectious and viral diseases of the liver and intestines. Usually, with such violations, the patient's body temperature additionally rises, symptoms of intoxication of the body are present.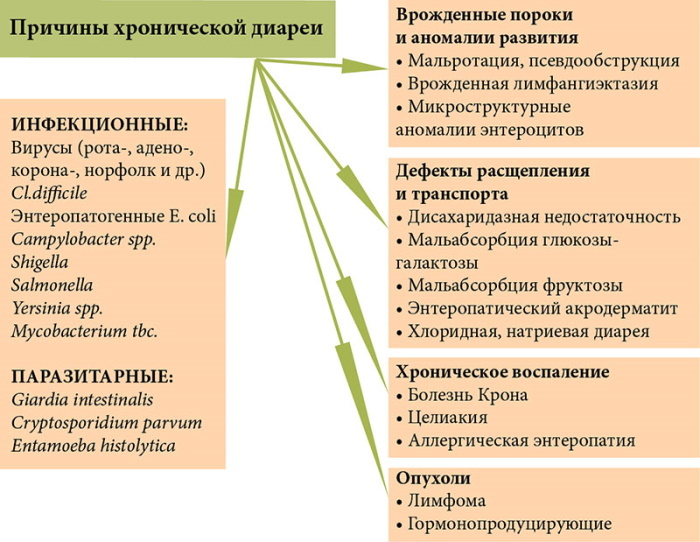
It is not so easy to recognize the infectious origin of a pathological condition. Usually several diagnostic methods are required.
Non-infectious causes
Foamy diarrhea in a 4-year-old child can be triggered by non-infectious causes. Usually, with such disorders, not only diarrhea is present, but also some other manifestations.
The most common non-infectious causes of stool disorder are:
- Eating atypical foods that were not previously included in the child's diet. For example, when attending a preschool institution, a temporary stool disorder is possible against the background of a change in diet.
- A stressful condition that affects the work of the intestines and can provoke increased peristalsis.
- Chronic pathology of the digestive tract. Some children are diagnosed with gastritis, enteritis, or colitis. These pathologies are not provoked by bacteria and viruses, but can lead to intestinal disorders.
- Poisoning of the body with toxins and harmful substances. For children, this reason is not considered typical, but it cannot be ruled out when examining a patient.
- Violation of the intestinal microflora as a result of the death of a large number of beneficial bacteria and the reproduction of pathogens.
- Abuse of foods that provoke increased peristalsis. Excessive consumption of fruits, vegetables, dried fruits and fermented milk products can provoke temporary diarrhea.
- Intolerance to any food components. For example, a child may have an intolerance to cow's milk proteins and cereals. With the introduction of complementary foods in the form of cereals into the child's diet or eating them in large quantities, celiac disease develops.
- Parasitic diseases.
These and some other reasons can provoke negative reactions from the intestine. In most cases, the symptoms disappear on their own over a period of time, sometimes it is necessary to prescribe medications to improve the condition.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Foamy diarrhea can occur in a child at the age of 3 against the background of frequent stressful conditions, as well as with a history of chronic intestinal diseases. This is commonly referred to as irritable bowel syndrome.
The disorder can occur against the background of the use of ordinary foods, as well as minor emotional excitement. In most cases, diarrhea bothers the patient for no longer than 1 day, sometimes symptoms may persist for 2-3 days.
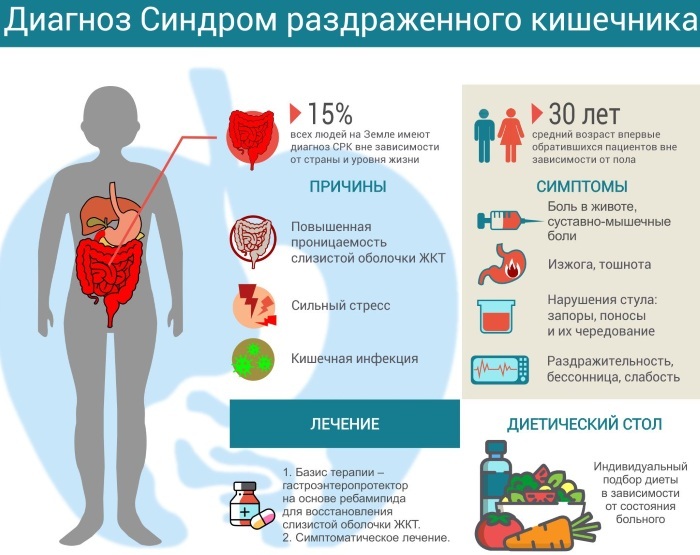
Medical treatment for irritable bowel syndrome does not always help to improve the condition, which is associated with the origin of the disorder.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
When using medicines with antibacterial properties, a child often develops dysbiosis, which provokes frequent loose stools. Adults also often suffer from such disorders, but in children, they manifest themselves in an acute form and significantly worsen the general condition.
Some groups of antibiotics do not cause stool disorder, but many lead to changes in the bacterial composition, which is accompanied by stool disorder. Children are less likely to take long-term antibiotics, but short-term use can also lead to diarrhea. Symptoms arise as a result of the effect of antibacterial components on the intestinal microorganism. At the same time, the funds destroy not only pathogenic, but also beneficial bacteria, which leads to the development of dysbiosis and stool disorder.
What symptoms accompany diarrhea with foam in different pathologies
Foamy diarrhea in a 2-year-old child and in patients of a different age is often accompanied by other symptoms that depend on the underlying cause of the disorder.
The most common accompanying deviations:
- Increased body temperature. Indicators in the acute stage are high, they can persist for several days. Usually, antipyretic medications do not significantly improve the condition. The symptom is observed with an infectious or viral lesion of the digestive tract.
- Muscle and joint pain occurs with fever. The child speaks of severe weakness, his activity is significantly reduced.
- Decreased appetite or no appetite at all.
- Thirst and dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- Pain in the abdomen. Discomfort occurs with an infectious and non-infectious origin of the disorder, but if an infectious pathology is diagnosed, the pain is expressed in an acute form.
- Flatulence and bloating are common symptoms.
- Pain in the stomach area may be present when the child has a history of chronic pathology.
- Vomiting can be observed with an infectious origin of pathology or poisoning of the body.
- Headache, dizziness acts as a concomitant symptom of intoxication with fever.
- Nausea and heartburn. These symptoms are less common, but can occur over a short period of time.

Foamy diarrhea in a child
If diarrhea develops against the background of intolerance to any products, the symptoms appear some time after they are consumed. It is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature, and the manifestations disappear within a short period of time.
With an infectious origin of the disorder, the symptoms gradually worsen in the absence of treatment, which only worsens the patient's condition. Depending on the clinical picture and the conditions for the occurrence of disorders, not only the treatment regimen is determined, but also the most effective diagnostic methods.
Survey
Foamy stool in a child is considered a reason to see a doctor if it is observed several times and is accompanied by concomitant disorders. Diagnostics involves the use of several effective methods to obtain a complete picture of the child's condition.
| Method | Features of the |
| General examination and questioning | The first stage of diagnosis, which involves examination of the patient and a survey. If the child is unable to talk about the symptoms on his own, parents are interviewed, observing his condition. The doctor palpates the abdomen, examines the skin and mucous membranes, notes possible symptoms that may indicate the development of an infectious disease. After the examination, a further diagnostic scheme is determined. |
| Clinical blood test | The standard method, in which the child's blood is examined under laboratory conditions, reveals signs of inflammation and possible complications from the internal organs. Based on the data obtained, the expediency of prescribing certain medications is determined.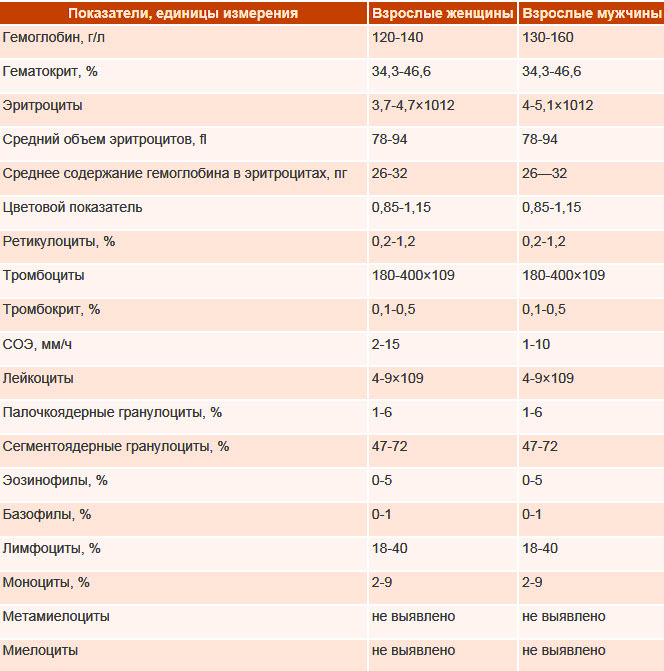
|
| Coprogram | A method involving the study of feces for the presence of parasites in them, as well as other reasons that can provoke a pathological condition. The feces are examined in the laboratory, after which the doctor determines the presumptive cause of the disorder. |
| Ultrasound diagnostics | An additional research method in which the organs of the digestive system are studied using a special device. As a result, it is possible to determine the presence or absence of pathologies of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas. |
| Bacteriological culture | Sowing is necessary for the bacterial origin of the disorder. Its result allows you to determine to which antibacterial agents microorganisms are sensitive. Through research, the most effective antibacterial drug can be prescribed. |
Additionally, a blood test may be needed to determine if the child has an intolerance to a particular product. After receiving the diagnostic results, the specialist determines the cause of the violation, prescribes drugs, if necessary.
Symptomatic therapy
Foamy diarrhea in a 1-year-old child, as well as the onset of symptoms in children older than this age, requires the prescription of medications to improve the condition and prevent progression disease. Different remedies can be used depending on the origin of the disorder, but the decision is made only by the doctor. It is strongly discouraged to give the child any medications without an appointment.
Dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis is a pathological condition in which there is a change in bacterial intestinal composition, provoking stool disorder and concomitant manifestations from internal organs.
When diagnosing diarrhea against the background of this violation, medications are prescribed to normalize the microflora:
-
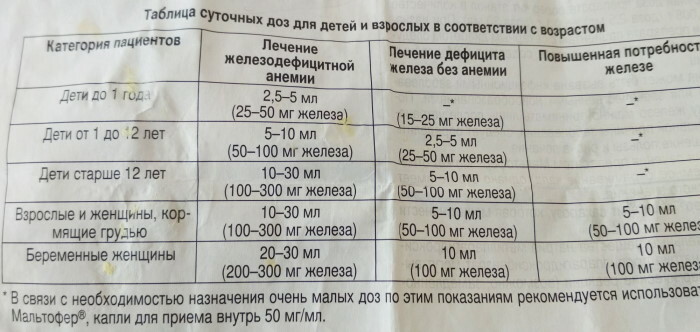
Bifidumbacterin is considered an effective tool for the treatment of dysbiosis. It is prescribed simultaneously with other medicines to achieve a pronounced effect. The drug normalizes the intestinal microflora by populating it with beneficial bacteria. Children under 1 year old take 2.5 doses 2 times a day, children over 1 year old take 5 doses 3 times a day. It is better to give the child a powder in the form of a powder, which must be diluted with water and taken orally. The treatment lasts up to 10 days.
- Espumisan often indicated for the purpose of eliminating flatulence, bloating and discomfort in the abdomen with prolonged diarrhea. It is recommended for children to take it in the form of drops. The drug is prescribed simultaneously with medications based on beneficial bacteria, which increases the effectiveness of treatment. Children under 1 year old take 25 drops of the medicine 2-3 times a day. Patients over 1 year old are shown taking 25 drops up to 4 times a day. The treatment lasts up to 7 days.
- No-shpa can be used to eliminate spasms of intestinal smooth muscles. Such symptoms are often present with dysbiosis in a child. Children over 2 years old are allowed to take tablets at a dosage of 40-80 mg per day. It is imperative to divide the daily rate by 2-3 times during the day. Taking pills is indicated for 3-6 days.
If the patient does not have flatulence and spasms of intestinal smooth muscles, only preparations containing beneficial bacteria can be used. Depending on the symptoms, the doctor determines the dosage of the medication, taking into account the age of the child, the severity of the manifestations of dysbiosis.
Intestinal infection
When diagnosing an intestinal infection in a child, 3 groups of medicines are used to eliminate symptoms of the disease - antibacterial agents, enterosorbents and drugs to avoid dehydration.
- Regidron refers to products that are designed to restore water balance. With an intestinal infection, loose stools are often observed, vomiting is often present, which leads to dehydration. The powder helps to restore balance and prevents the development of complications due to the loss of a large number of important components. The powder is dissolved in water at the rate of 11.95 g per 500 ml of boiled water at room temperature. Take the finished product in different dosages depending on the body weight. For 1 kg of weight there is 30 ml of solution. The duration of use is 3-4 days.
- Polysorb is an absorbent and detoxifying agent, it is prescribed to eliminate the symptoms of intoxication and prevent the progression of disorders. The powder is dissolved in water before use. For 1 reception, a child is enough 1 tsp. l. powder and 100 ml of water. Reception is carried out 2-3 times a day, depending on the severity of manifestations. In combination with other drugs, the drug helps to significantly improve the condition. The duration of its admission is 3-5 days.
- Antibacterial agents are always assigned on an individual basis. There is no standard method of application, which is associated with the need to select a dose and a specific drug on an individual basis. Depending on the type of infection, Kanamycin, Tetracycline, Gentamicin, and others may be used.
Celiac disease
In celiac disease, there is an intolerance to the components of cereals, which leads to repeated loose stools during the day. Some parents note that the frequency of bowel movements reaches 10 times throughout the day. In the case of the development of such violations, it is worth excluding various cereals from the child's diet.
Additionally, children may be prescribed medications to combat loose stools. For example, Smecta helps to improve the condition, prevents prolonged diarrhea. It is taken orally after preliminary dilution in 100 ml of 1 sachet of powder. The treatment lasts no more than 2 days.
Loperamide is prescribed for children over 2 years of age, 1 tablet 2-3 times a day, depending on the frequency of bowel movements. The treatment lasts up to 2 days. If there is no effect from the use of medicines, it is necessary to place the child in a hospital and identify the cause.
Funds from other groups are usually not used, since celiac disease most often provokes frequent loose stools.
Lactase deficiency
Foamy diarrhea in a 1 year old child may be associated with lactase deficiency and lactose intolerance. If a specialist detects such a deviation, it is necessary to exclude from the menu products that provoke loose stools, for example, milk and all dairy products. This is usually enough to eliminate all symptoms.
Lactase deficiency is accompanied by bloating, so it is possible to use drugs to eliminate manifestations. Often, Espumisan and other drugs based on simethicone are prescribed.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
If loose stools are provoked by taking antibacterial medications, the child is prescribed medications based on beneficial lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. They normalize the intestinal microflora, which allows you to get rid of diarrhea and associated manifestations of the disease.
In addition to Bifidumbacterin, specialists can prescribe Linex to the child in the form of drops, which is approved for use for patients from the first weeks of life. Drops are taken once a day, but the dosage depends on the age of the child. The duration of use can be up to 2-4 weeks, if necessary.
Bifiform also has pronounced properties and contains a large number of microorganisms that are beneficial for the intestines of the child. Take it 1 capsule 2-3 times a day, depending on the severity of manifestations. The duration of the therapeutic course depends on the patient's condition, usually 10 days is enough.
In each case, the doctor makes a decision on the appointment of certain medications based on the data of the diagnostic examination.
The use of medicines
Sometimes the child does not have concomitant symptoms of the disease, therefore, only medications are required to eliminate diarrhea.
The most effective medicines for children:
- Imodium has a pronounced antidiarrheal effect, but it is allowed to use it only in the therapy of patients over 6 years old. Capsules are taken orally 1 piece no more than 2 times a day. The medication helps to quickly eliminate the manifestation and prevents the profuse loss of fluid against the background of frequent loose stools. The duration of the use of the medication usually does not exceed 2 days.
- Lopedium is also considered to be an effective remedy for diarrhea. It is prescribed in short courses of 1-3 days with a daily intake of 1 to 3 tablets of the medicine. The medication is indicated for patients over 6 years old, but in some cases the doctor may prescribe it to a child under 6 years old according to individual indications.
If loose stools are not repeated many times during the day, special medications may not be prescribed. In this case, the child's diet is changed, some foods are excluded and the amount of liquid consumed during the day is increased. Each case requires an individual approach to each child.
Appointment of proper nutrition
A prerequisite for the treatment of diarrhea in a child is considered to be a change in the diet and the exclusion from it of foods that can aggravate the condition or provoke its re-development.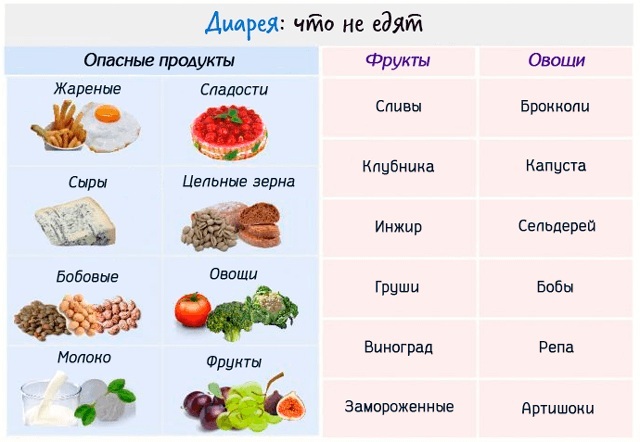
Experts recommend giving up the use of the following products:
- Fatty meat and dairy products.
- Nuts.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Freshly squeezed juices.
- Porridge should also be excluded in the case of diagnosing an intolerance to some components of grain products.
The child's diet should consist of boiled or stewed dishes. Vegetables are allowed to be steamed, apples and some other fruits are also better baked. It is allowed to use jelly, jelly, biscuit biscuits. Certain foods may be excluded based on individual indications.
Compliance with such dietary rules during the period of therapy and after its end allows you to avoid the development of complications and speed up the healing process. After the elimination of diarrhea and associated symptoms, it is recommended to adhere to the diet for another 1-2 weeks. The absence of symptoms during this period is considered a reason for the gradual inclusion of familiar products in the menu, if their intolerance is not observed.
Foamy diarrhea can occur in a child of 1 year of age, as well as in older children. The symptom is considered a reason for contacting a doctor who will determine the cause and prescribe the most effective remedies.
Video about diarrhea in a child
Komarovsky about diarrhea in children: