Content
- Characteristics
- Features of the classification
- Indicators are normal
- Causes
- How is it determined
- How to bounce back
- Getting rid of the underlying pathology
- Fundamentals of drug therapy
- Magnesium-potassium complexes
- Beta-blockers
- Antiarrhythmic line
- Video about supraventricular extrasystole
The most common type of arrhythmia is signs of extrasystole, they are manifested by extraordinary contractions of the heart (the entire organ) or its different parts. Based on the location of the source of extrasystoles, cardiac arrhythmias have different causes.
If there is a supraventricular type of extrasystole (supraventricular), then the impulse provoking extrasystoles in this case is located above the ventricular chambers. For a person who does not suffer from cardiological pathology, the rate of premature heart contractions per day is up to 300 episodes. Exceeding the limit value is life-threatening and therefore requires immediate treatment.
Characteristics
The heart, in fact, performs a pumping function, providing blood to the systems and organs. For the distillation of blood through the vessels, the heart muscle contracts due to the constant (internal) electrical pulsation generated by the sinus node. As a muscular organ consisting of cardiomyocytes, the heart functions in a state of constant spontaneous excitement without external stimulation. The brain controls the rate of contractility along with a set of hormonal substances.
Extrasystole is an extraordinary or replacement contractile impulse due to the activity of not a sinus, but another generator. Most often these are the atria. The fact of an early contraction of the heart can be empty and ineffective due to the insufficient volume of blood ejected into the vessels. The appearance of extrasystoles belongs to the category of arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances), the signs of which are found on the cardiogram in the form of teeth.
Episodes of premature contractions of the heart caused by impulses generated by the atria, pulmonary or vena cava, AV connections are called supraventricular extrasystoles (SVE). Simply put, active pulsation is triggered not only by the sinus node, but also by a number of additional (abnormal) foci located above the location of the ventricles.
Additional contractions caused by excessive pulsation deprive the heart muscle of rest, filling it with blood at the moment of relaxation.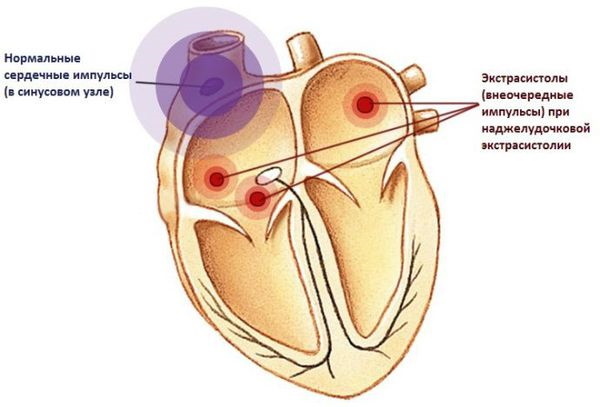
With frequent supraventricular extrasystoles (more than 5-6 episodes per minute), there may be no obvious symptoms, but the following disorders can form:
- redistribution of systemic blood flow;
- the development of heart failure due to impaired blood circulation;
- depletion of the myocardium due to its overstrain.
The frequent occurrence of extrasystoles contributes to a deterioration in the quality of life, episodes are not so easy to diagnose, but their multiple occurrence in groups is attributed to the precursors of atrial fibrillation. The main task of treating extrasystole of the supraventricular type is to eliminate provoking factors, but it will not be possible to achieve this with folk methods.
Features of the classification
Supraventricular extrasystoles (the norm per day of several additional impulses does not pose a threat to health) not dangerous, especially if accelerated rhythm is diagnosed in young people without signs of disease hearts. There are several methods for classifying extraordinary abbreviations.
Focusing on a wide range of characteristic features, the main types of NLE can be typified:
| Options for extrasystoles | a brief description of |
| Atrial | Activation of contraction from the upper chambers of the heart, until a normal impulse appears. The violation is common, although it is of an episodic nature, but it can be a sign of cardiac pathology. |
| Atrioventricular | The focus that induces contraction is located in the atrioventricular septum separating the ventricles and the atria. The contractile process in this case is significantly different from the norm. |
| Supraventricular | Early appearing atypical contractions are considered the most common variant of extrasystole. Deviation poses a great health hazard. |
| Solitary | The appearance of single extrasystoles is not life-threatening, does not cause changes in the body, and is asymptomatic. However, a deviation can transform with an increase in risks. |
| Plural | The characteristic traces are recorded on the cardiogram in the form of areas that signal excessive excitation of the heart. Nonspecific symptoms manifest themselves brightly, threatening the development of atrial fibrillation. |
 The appearance of single supraventricular extrasystoles is one of the most benign variants of ELE if it occurs in healthy people. Diagnosis of frequent and multiple failures requires an immediate response - adequate therapy in a hospital. In the absence of timely assistance from a cardiologist, in more than half of cases, complications develop that lead to insufficiency or coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and may result in cardiac arrest.
The appearance of single supraventricular extrasystoles is one of the most benign variants of ELE if it occurs in healthy people. Diagnosis of frequent and multiple failures requires an immediate response - adequate therapy in a hospital. In the absence of timely assistance from a cardiologist, in more than half of cases, complications develop that lead to insufficiency or coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and may result in cardiac arrest.
Indicators are normal
In the course of large-scale clinical studies of the problem of supraventricular extrasystoles, their daily rate was established - up to 100 episodes. A range of 200-300 extraordinary cardiac impulses is not considered a threatening disorder.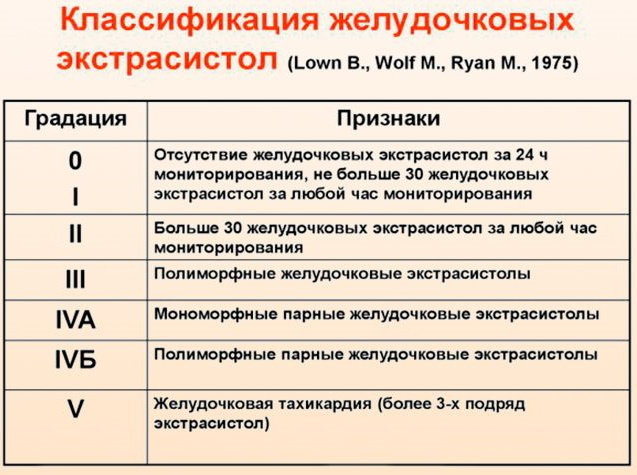
To determine the presence of cardiopathology in a particular patient, doctors use the normative (daily) indicators of the frequency of extrasystoles:
- 600-950 episodes is considered an indicator of a conditionally normal state;
- 1000-1200 pulses are also not life-threatening if they are polymorphic;
- more than 1200 extraordinary contractions during the day pose a threat to health.
Supraventricular extrasystoles (the norm per day is not the same for all categories of patients), manifested by a sinking heart, frighten people, because this is an unsafe symptom. The rate of registered extrasystoles per hour for healthy people is 30 impulse bursts in 60 minutes. In children, the appearance of extrasystolic strokes does not depend on age, but on the presence of various diseases. Adolescents 12-14 years old with signs of extrasystole on the ECG are put on a cardiac record when confirming the presence of arrhythmia.
Registration of extrasystoles in pregnant women is due to increased stress due to hormonal changes. Frequent episodes disrupt the blood supply to the fetus, and the paired appearance of extraordinary bursts is dangerous for the development of complications. In women who are not pregnant, extrasystole increases by the beginning of the second half of the menstrual cycle, then the heart rate returns to normal. With the onset of menopause, rhythmic disruptions with the appearance of at least a single extrasystole are noted in 95% of women who do not even suffer from arterial hypertension.
In men of working age, registration of ELE is more often due to signs of obesity, aggravated by the development of arterial hypertension. In such a situation, the likelihood of arrhythmia, threatening atrial fibrillation, increases. The feeling of a rapid heartbeat in patients of any age and gender requires a visit to a cardiologist for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes
Most patients do not complain of signs of supraventricular rhythm disturbances or have rather poor symptoms. The severity of signals of cardiac pathology depends on a wide range of reasons, and not only of a cardiological nature. After all, the result of even a banal sneezing or fear may be the appearance of extraordinary contractions of the myocardium.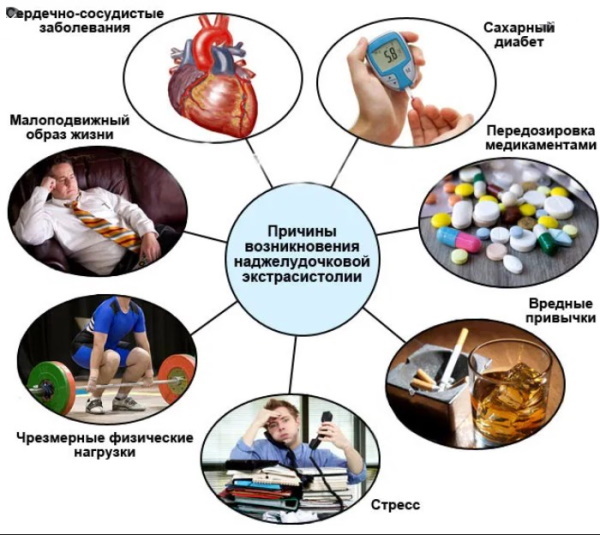
Among the pathogenic factors that provoke extrasystole are the following pathological conditions:
| Causal factor | Explanation |
| Heart diseases | Cardiac pathologies of various types - any types of myocardial diseases (cardiomyopathy), inflammation in the tissues of the heart muscle (myocarditis). ELEs are often the result of a recent heart attack, heart failure, chronic ischemic heart disease. |
| Medication load | A heart rhythm failure with the appearance of extrasystoles is often the result of an overdose or uncontrolled intake of drugs to lower blood pressure, treat arrhythmias, and diuretics. |
| Metabolic disorders | Supraventricular extrasystoles (the norm per day is no more than 100 episodes) are the result of insufficient levels of potassium, as well as, to some extent, magnesium. The problem is solved quickly by saturating the blood with the necessary trace elements. |
| Exposure to hazardous substances | A dangerous type of extrasystole provoke poisoning with ethyl alcohol (alcoholic beverages), the action of salts of heavy metals and toxic substances, nicotine. The harm of starvation, infectious diseases, oxygen deficiency (hypoxia) is not excluded. |
| Systemic diseases | Symptoms of ELE provoke autonomic nervous disorders, especially the course of neurocirculatory dystonia. Among the endocrine pathologies that cause heart rhythm failure, in addition to diabetes mellitus, an excess of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism), decreased or increased activity of the adrenal glands. |
In addition to diseases of various etiologies, the cause of premature supraventricular impulses is the consequences of nervous shocks - both fleeting and long-term.
The appearance of episodes of additional myocardial contractions may be due to the lifestyle:
- the level of excessive physical activity exceeds the capabilities of the body, which is manifested by tachycardia, and ends with interruptions in the heart rhythm;
- with a lack of mechanical stress (physical inactivity), the muscular organ weakens from the limited physical training.
To diagnose the degree of a cardiac problem and the causes that caused it, patients with signs of extrasystole are sent by the cardiologist for examination.
How is it determined
It will not be difficult for an experienced doctor to detect extrasystoles while probing the pulse after reviewing the patient's complaints and taking anamnesis. In the process of listening to heart sounds (auscultation), unnaturally loud beats are muffled, but rhythmic. The task of general research methods is to record the presence of an irregular pulse and an irregular heartbeat. To determine the type and confirmation of ELE, it is necessary to make an electrocardiogram, and by the method of regular screening.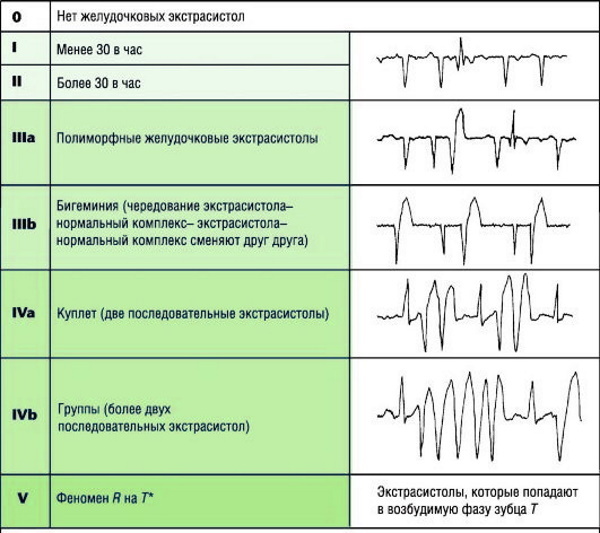
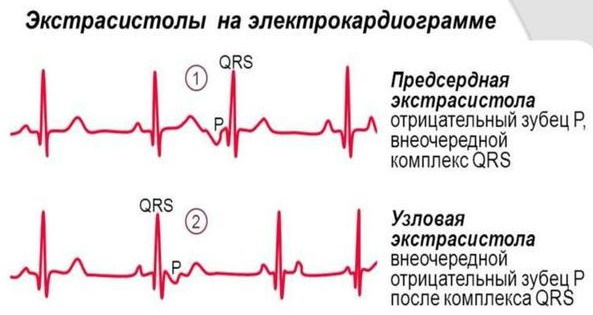
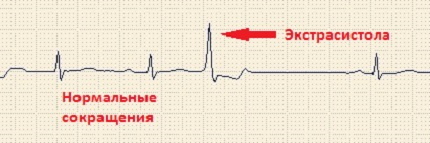
Supraventricular, as well as ventricular extrasystoles are clearly visible on the ECG. The statistical rate of both types of atypical myocardial contractions should not exceed 200-300 impulses per day.
However, the results of these studies are not informative enough to establish an accurate diagnosis, since interruptions in the rhythm of heartbeats are of a periodic nature.
Therefore, the patient needs a more accurate diagnosis by the following methods:
- Holter monitoring - the possibility of daily fixation of rare single extrasystoles, unregistered by the cardiogram;
- load samples - testing of the heart with a dosed increase in physical activity under the control of an ECG;
-
Ultrasound technique - obtaining additional information about possible damage to the myocardium or valves that provoke extrasystole.
To identify violations of an organic nature, echocardiography is used, the results of angiography are no less important. The patient may need to undergo an MRI or CT scan for early detection of life-threatening pathologies.
How to bounce back
A benign type of ELE, which proceeds without noticeable sensations of a disturbed rhythm, does not require specific treatment in all cases.
If possible, it is enough to eliminate the etiological factors to normalize the condition:
- rejection of bad habits (mainly smoking), high physical activity, as well as drugs that provoke arrhythmia;
- normalize blood pressure, sleep, thyroid functioning, replenish potassium reserves in the blood;
- get rid of physical inactivity using feasible physical activity, balance the diet and daily regimen.
With poor tolerance of supraventricular episodes of rhythm disturbance, the presence of concomitant diseases, a high frequency of ELE (more than 1000 failures), a comprehensive treatment strategy is indicated. The systemic approach consists in the treatment of diseases provoking arrhythmia, the prescription of antiarrhythmic drugs, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Getting rid of the underlying pathology
A severe type of ELE is usually a symptom of another more serious medical condition. For example, after successful treatment of ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy or thyrotoxicosis, extrasystole usually subsides. Therefore, the complete cure of the main pathology eliminates the cause of the arrhythmia, stopping the premature contractile activity of the myocardium.
Fundamentals of drug therapy
Supraventricular extrasystoles (the norm per day reaches 100 failures) do not require antiarrhythmic drugs, and their uncontrolled use can only harm health, causing complications. If the symptoms of ELE are increasing (tachycardia, atrial flutter), antiarrhythmic therapy is indicated to eliminate the frequency of sudden attacks, as well as to reduce their number.
Magnesium-potassium complexes
Preparations containing a combination of potassium together with magnesium, when injected, demonstrate a moderate antiarrhythmic effect.  The tablet form of Asparkam or Panangin is much weaker.
The tablet form of Asparkam or Panangin is much weaker.
Beta-blockers
Medicines in this group are available only in pill form. Their appointment is relevant for patients suffering from symptoms of hyperthyroidism, sinus-type tachycardia, provoked by stressful situations. The use of a group of beta-blockers is justified in ischemia, hypertension, and the presence of sympatho-adrenal crises.
The following medicines are most popular:
- Bisoprolol - the drug acts quickly, you need to wait 2 weeks for a stable therapeutic effect. The minimum dosage capsule (5 mg) is taken once a day sutra (on an empty stomach). The decision to increase the dosage is made by a specialist.
- Metoprolol - selective type beta-blocker stably lowers blood pressure, has anti-ischemic and antianginal effects. The dosage is chosen by the doctor, you need to take the medicine 2 times a day.
- Nebival - has a double pharmacological property. It is a selective β1-adrenergic receptor blocker with a slight vasodilatory effect. Suitable for both monotherapy and in combination with drugs that reduce blood pressure.
In this group of drugs there is also a calcium channel antagonist (blocker) - Verapamil. This is the first choice drug for patients with bronchial asthma, variant angina pectoris, intolerance to the use of nitrate-containing drugs. Treatment with Verapamil does not affect the level of calcium in the blood, and the dosage is selected individually, but the drug should be discontinued gradually.
Antiarrhythmic line
Antiarrhythmic drugs quickly restore adequate activity of the heart muscle. However, in this regard, therapy should not be canceled immediately, since the treatment course is designed for weeks, or even months. If there is a history of episodes of atrial fibrillation, antiarrhythmic treatment of ELE will be lifelong.
-
Cordaron is a universal antiarrhythmic agent. The drug stops stable signs of supraventricular rhythm failure, as well as a violation of the type of seizures, without changing the intraventricular conduction.
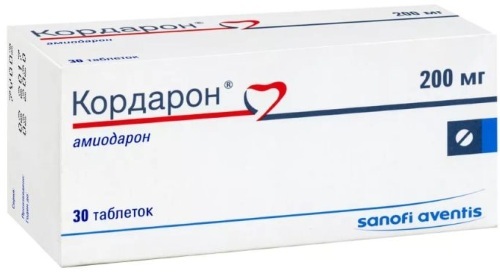
- Propanorm - despite the moderately pronounced β-adrenergic blocking effect, the drug not only prevents the appearance of extrasystoles. Propanorm eliminates arrhythmia, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial flutter.
- Etatsizin - the antiarrhythmic effect of the tablets is long-term, pronounced. An important feature of the drug in the absence of an effect on heart rate in the case of short-term administration. However, a long course of Etacizin reduces the heart rate.
Treatment of ULE is a trial and error method, the doctor evaluates the effectiveness of a short-term intake (3-4 days) of an antiarrhythmic drug prescribed in an average dose. The functioning of the organ is monitored by the results of the ECG. If necessary, a combination of drugs is permissible, and the criterion for the effectiveness of the therapeutic scheme is the disappearance of interruptions in the heart rate against the background of an improvement in the patient's general well-being.
If severe extrasystole (more than 15 failures per minute) does not respond to the complex effects of drugs, the patient needs surgery. The operation to eliminate foci of abnormal rhythm is performed by the endovascular method - ectopic foci of extrasystole are destroyed using radio frequency waves (catheter ablation method). The open method of intervention is more traumatic, accompanied by an incision of the sternum to remove part of the atrium.
Despite the relative safety of supraventricular supraventricular extrasystoles, their frequent the occurrence can provoke dangerous symptoms, manifested by a sinking heart, interruptions in its work, dizziness. Even in the case of a norm of frequent heartbeats per day, it is recommended to visit a cardiologist to find out the cause of the violation, undergo an examination to identify cardiological or other diseases.
Video about supraventricular extrasystole
Supraventricular extrasystole:



