Content
- Characteristics and properties
- The table is ok
- Increase symptoms
- Reasons for the increase
- Ovalocytosis
- Spherocytosis
- Folate deficiency anemia
- Sickle cell anemia
- B12 deficiency anemia
- Hemoglobinosis C
- How is it determined
- How to bounce back
- L-Glutamine
- Voxelotor
- Diet therapy
- Video about ICSU in the blood test
Analysis at the ICSU level in the blood of a child is carried out in private and public laboratories to determine the total concentration of hemoglobin in each individual erythrocyte. An increase in this indicator indicates the possible presence of congenital and acquired hematological diseases.
Characteristics and properties
MCHC in a blood test is the quantitative number of hemoglobin that is contained inside red blood cells - erythrocytes. Depending on the general state of health of the child, this indicator may increase or change downward.
A laboratory test for determining the numerical amount of MCHS in the blood allows one to diagnose the processes of the generation of hemoglobin protein compounds in the patient's body. The main advantage of this study is that during the analysis, scientists manage to obtain the most reliable information regarding the density of red blood cells filled with hemoglobin.

It is believed that, unlike other methods of laboratory blood tests, the analysis for the concentration of MCHS is more objective. This is due to the fact that the density of hemoglobin inside erythrocyte cells belongs to the category of stable indicators of the hematological health of the body. In medical practice, the ICSU index is used to conduct control diagnostics of patients with severe blood diseases. This research method is also used in laboratories for test detection of errors in the operation of ultra-precise equipment.
The table is ok
MCHS in the blood test is increased in a child if his hematopoietic system works with obvious disorders. The table below lists the indicators of the norm of this substance in the composition of erythrocytes of children of different age groups.
| Child's age | Normal concentration of MCHS (unit of gram per 1 liter of venous blood) |
| From the first days of birth until the age of 14 days | 280 to 350 g |
| 14 to 30 days | 280 to 360 g |
| 1 to 2 months | 280 to 350 g |
| 2 to 4 months | 290 to 370 g |
| 4 to 12 months | 320 to 370 g |
| From 1 year old until the child reaches 3 years old | 320 to 370 g |
| From 3 to 12 years old | 320 to 370 g |
| 12 to 15 years old | 320 to 370 g |
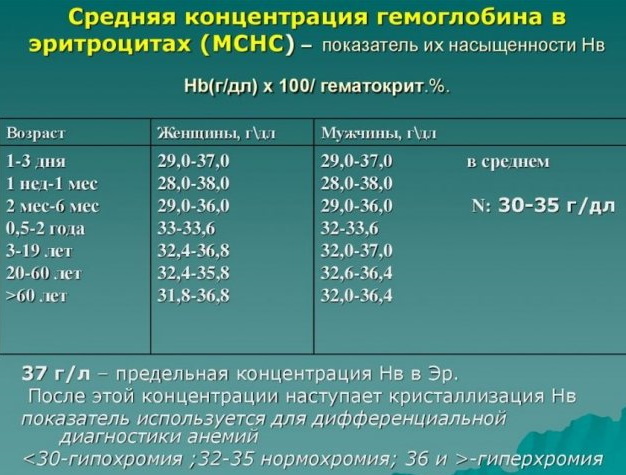
After the end of puberty, the level of MCHS in the blood of boys and girls remains stable and unchanged, as in most adults. This indicator remains in the range of 320-360 g per 1 liter of venous blood. Violation of the density of hemoglobin inside erythrocyte cells upward in 95% of cases indicates a developing blood disease.
Increase symptoms
Signs of an increased level of MCHS in the blood of a child depend on what kind of disease triggered the change in the density of hemoglobin inside the erythrocytes.
In most cases, a high concentration of this indicator is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- decreased attention level;
- memory impairment;
- violation of local blood circulation, which is manifested by blue tips of the fingers, constantly cold extremities;
- increased irritability;
- lack or significant deterioration in appetite;
- constant sleepiness;
- decreased visual acuity;
- recurrent nosebleeds;
- dizziness;
- attacks of muscle pain that occur for no apparent reason when the musculoskeletal system was not subjected to physical exertion;
- constant fatigue and fatigue.
A child with an increased level of MCHS in the blood seems to be lethargic, constantly tired, sleepy, sedentary and moody. The presence of the above symptoms is the basis for immediate medical attention to a pediatrician.
Reasons for the increase
MCHS in the blood test is increased in a child who has concomitant diseases of the endocrine or hematopoietic system. Most of the reasons causing an increase in the concentration of this indicator are pathological.
Ovalocytosis
Ovalocytosis is a genetic blood disorder that is manifested by an irregular shape of the structure of red blood cells. Under conditions of partial carriage, about 40-50% of the cells of this group have an irregular elliptical shape. Children who have inherited most of the mutated genes show signs of complete carriage of modified erythrocytes. In this case, the number of modified red blood cells reaches 96%. An increase in the level of MCHS is associated with an abnormal and physiologically abnormal structure of the cells of the erythrocyte group.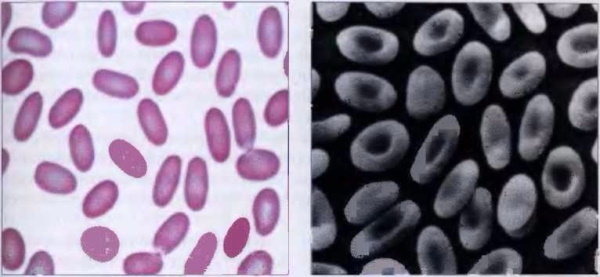
The danger of ovalocytosis is that this pathology becomes not only the cause of an increase in the level of MCHS in the blood, but can also be accompanied by the development of hemolytic anemia. This reason for the increase in the density of hemoglobin inside erythrocytes always has a family-hereditary etiology. Mutated genes can be passed on through the mother and father. The first signs of the disease associated with an increase in the numerical indicator of the ICSU appear in the first 1-2 weeks after the birth of the child. As the baby develops, pathological symptoms only intensify.
In children with a high concentration of MCHS in the blood, patients with ovalocytosis, additional signs of a painful condition of the blood may be present, namely:
- defects in the cell wall of erythrocytes, in which there are obvious damage to their membrane (this symptom is determined after a laboratory study of the cellular structure of red blood cells);
- severe yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- enlargement of liver and spleen tissues (occurs in children with severe ovalocytosis, which is accompanied by hemolytic anemia).
Ovalocytosis, as one of the reasons for the increased level of MCHS in the blood of children of different age groups, is an incurable genetic disease. The prognosis for the child's further vital activity depends on how many malformed erythrocytes he carries.
Spherocytosis
Spherocytosis is a hereditary disease that is passed on to newborns through the paternal and maternal lines. This pathology causes a consistently high increase in the level of MCHS in the blood. Spherocytosis is characterized by abnormalities in the formation of the cytoskeleton of erythrocytes. The result of the pathological process is a decrease in the total area of the cell membrane.
Against the background of a decrease in the surface of the outer membrane of the erythrocyte, its plasticity decreases, which is necessary to maintain normal blood functions. Due to this, the density of hemoglobin in red cells sharply increases with a simultaneous increase in the level of MCHS.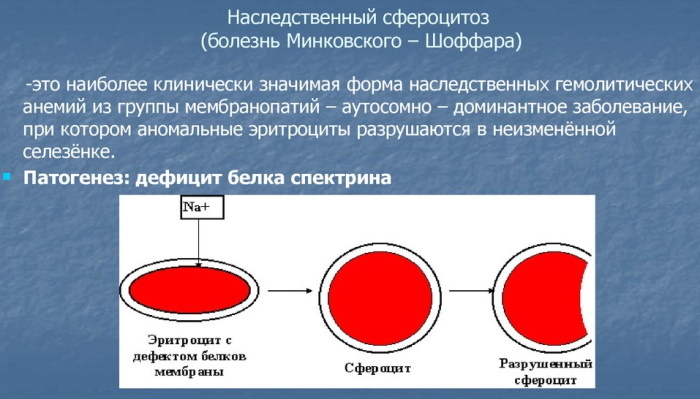
Severe forms of spherocytosis are accompanied by concomitant pathological processes in the form of destruction of erythrocytes in the tissues of the spleen. In this regard, the child's skin acquires a rich icteric shade, the biochemical composition of the blood changes. The prognosis for the recovery of children with signs of spherocytosis depends on how much they are deformed red blood cells, whether the complications of this pathology have spread to the tissues of the internal organs. Hereditary spherocytosis, accompanied by total hemolysis of erythrocytes, can cause death.
Folate deficiency anemia
MCHS in the blood test is elevated in a child who has folate deficiency anemia. It is an acquired disease that occurs in children of different ages. This pathology develops against the background of chronic vitamin B9 deficiency. In order for a significant increase in the level of MCHS in the blood of a child to occur, his body must suffer from a lack of folic acid for a long period of time.
Under normal conditions, this biochemical substance is produced by the children's own microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, and also enters their body along with the following food products:
- legumes;
- spinach;
- boiled cattle liver;
- asparagus;
- fresh lettuce leaves;
- baked goods made from wholemeal flour;
- citrus;
- beetroot.
In children with folate deficiency anemia, the process of producing nucleic acids, which are responsible for the active division of hematopoietic cells, is disrupted. Against the background of a deficiency of red blood cells in a child, there is a simultaneous increase in the density of the protein compounds of hemoglobin located inside the red blood cells. Eliminating the conditions that predispose to the development of folic acid deficiency allows you to completely get rid of this pathology, as well as restore the previous level of MCHS in the child's blood.
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is one of the most common causes of elevated MCHS concentration, which is congenital in origin. This pathology can be transmitted along with genetic information from the mother and father. If sickle cell anemia is inherited from only one of the parents, then such a child suffers the disease in mild or moderate form with the presence of a moderately elevated level of MCHS. This pathology, which was transmitted immediately from the mother and father, is always difficult, accompanied by complications in the work of the hematopoietic system of children.

With sickle cell anemia, the structure of the hemoglobin protein changes, which acquires signs of crystallization. Red blood cells, which take part in the transport of oxygen, have a sickle-like appearance. An incorrect structure of red blood cells leads to the fact that the child's blood tests are found stably high indicators of the level of ICSU, the reduction of which is possible only under the condition of a well-formed complex scheme therapy.
Sickle cell anemia, as one of the most common causes of an increase in MHCS in children, manifests itself in additional symptoms in the form of:
- periodic thrombosis in the tissues of the liver and spleen;
- anemia;
- an increased tendency to infect the body with bacterial infections;
- inflammatory processes in the joints of the upper and lower extremities;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- aseptic necrosis;
- ulcerative formations on the legs;
- pathological damage to the structure of the eyes.
Sickle cell anemia is characterized by the fragility of the structure of red blood cells. In this regard, a child with an increased level of MCHS always looks tired, has pale skin with a yellowish tinge. Severe forms of this disease can be fatal.
B12 deficiency anemia
B12 deficiency anemia is a pathological condition of the blood that is caused by a systematic lack of vitamin B12 the child's body, or the presence of concomitant diseases of the body that impede the full assimilation of this substances.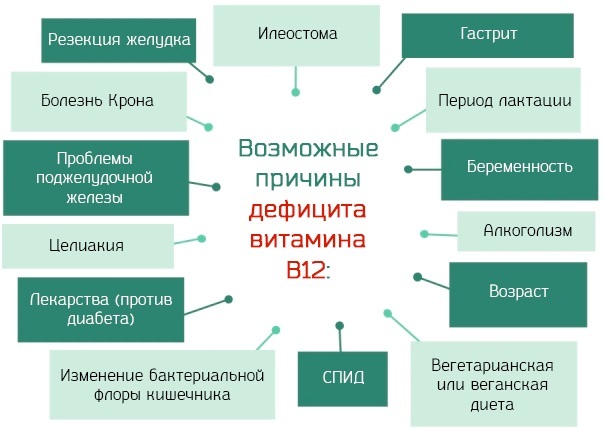
The emergence of this cause of an increase in the level of MCHS in the blood is facilitated by the influence of the following factors:
- inflammatory processes in the digestive tract, as well as damage to their tissues by malignant neoplasms;
- total or subtotal excision of the stomach;
- resection of most of the small intestine;
- chronic enteritis;
- the child's diet is completely free of food of animal origin (for example, when parents deliberately, or because of a difficult financial situation, do not include meat, fish, poultry in the children's diet);
- enteropathy caused by individual gluten intolerance;
- a prolonged decrease in the functional activity of the pancreas, which led to a disruption of the process breakdown of protein substance R (without the presence of this protein, vitamin B12 is not able to build a strong bond with mucopolysaccharide);
- long-term therapy with drugs, the side effect of which is a violation of the digestibility of cyanocobalamin.
B12-deficiency anemia, which caused an increase in the level of MCHS in the blood, can be hereditary and acquired in origin. This reason for the high density of hemoglobin proteins inside erythrocytes is eliminated with the help of drugs, containing a daily dose of vitamin B12, as well as by daily consumption of foods with a high concentration cyanocobalamin.
Hemoglobinosis C
MCHS in the blood test is increased in a child who is sick with hemoglobinosis C. This disease is transmitted to newborn babies along with genetic information. Pathology is characterized by the acquisition of mutated genes responsible for the synthesis of red blood cell proteins. In addition to an increase in the level of MCHS in the blood, the disease manifests itself as a state of chronic anemia, saturation of the skin with yellow pigment. A complication of hemoglobinosis C is the concomitant development of cholelithiasis.
The mechanism of increasing the level of MCHS in the blood of children, which is caused by hemoglobinosis C, is as follows:
- The child's body initially synthesizes a defective form of the hemoglobin protein.
- The improper structure of the protein substance acts as a physiological stimulus that triggers the process of producing even more hemoglobin.
- The defective protein does not fully cope with the function of transporting oxygen through the tissues of the internal organs, which triggers the process of increasing the MCHS index.
Hemoglobin C, like most other hereditary blood diseases, is incurable. The quality of life of a child depends on the degree of pathological changes in the structure of hemoglobin proteins.
How is it determined
The concentration of MCHS is determined by performing a general analysis for clinical blood parameters. The average duration of a laboratory test is 1-2 days. As a biological material, venous blood is used, which in general will require from 3 to 5 ml.
To get the most reliable examination result, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- Come to the clinic before 10-00 o'clock on an empty stomach, since the last meal should take place 8 hours before the test.
- 24 hours before the visit to the laboratory, fatty and fried foods are completely excluded from the child's diet.
- It is impossible to donate blood to determine the level of MCHS after X-ray and physiotherapy.
- Before undergoing the examination, the child must be in a satisfactory emotional state.
Upon arrival at the diagnostic center, the child's parents must notify the pediatrician about what medications the patient is taking. Some types of medications can skew blood test results.
How to bounce back
The method of reducing the level of MCHS to normal values depends on what kind of disease caused the change in the quality indicators of blood. In this case, the means of drug therapy and the norms of dietary nutrition are used.
L-Glutamine
Glutamine is a glutamic acid-based drug. It has been approved for the treatment of sickle cell disease. L-Glutamine is available in the form of tablets coated with a protective film, as well as granules for the preparation of a drinking suspension.
This medication is taken orally with the following dosage:
- children under the age of 12 months. drink 0.1 g;
- a child of the age category from 1 to 3 years old takes 0.15 g;
- children from 3 to 4 years old use 0.25 g of the drug;
- a child aged 5 to 6 years should take 0.4 g of L-Glutamine;
- patients of the age group 7-9 years old drink 0.5-1 g of this medication;
- children from 10 years old take 1 g of the drug.
The above-mentioned single doses of the drug L-Glutamine should be consumed 2-3 times a day. The duration of the therapeutic course is from 1 to 12 months. The therapeutic effect of L-Glutamine is realized due to its pharmacological properties of activating metabolic processes in the body, improving the quality of protein bonds. The average cost of this drug is 1,095 rubles.
Voxelotor
Voxelotor is a potent drug developed in the USA. With the help of this medication, it is possible to achieve a decrease in the level of MCHS in the blood by inhibiting the processes of polymerization of hemoglobin molecules damaged by sickle cell anemia.
Voxelotor is approved for use in children over 12 years of age. This medication is taken orally 1 time per day at a dosage of 1.5 g. This drug is contraindicated in children who have been diagnosed with signs of an allergic reaction to its constituent substances.
Voxelotor can cause the following side effects:
- headache attacks;
- feeling tired;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- cramping abdominal pain;
- allergic rash on various parts of the skin.
Children who show signs of hypersensitivity to Voxelotor should stop taking this drug. The average cost of this medication is $ 10,900.
Diet therapy
Compliance with dietary norms is necessary for children who have been diagnosed with high levels of MCHS in the blood, caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid.
The following food products are included in the diet of a sick child:
- beef liver;
- chicken eggs;
- broccoli;
- citrus;
- celery;
- avocado;
- walnuts;
- beetroot;
- sunflower seeds;
- onion;
- parsley;
- peanut;
- milk;
- beef kidney;
- turkey meat;
- mutton;
- shrimps;
- hard cheese;
- mackerel;
- mussels.
The main diseases causing an increase in the ICSU indicator are:
- sickle cell anemia;
- acute deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid;
- hemoglobinosis C;
- ovalocytosis;
- spherocytosis.
An increase in the level of MCHS in a blood test in a child is a sign of a pathological state of erythrocyte cells. Most diseases that provoke an increase in the density of hemoglobin proteins are congenital in origin. These pathologies are manifested by various disorders in the structure of the cytoskeleton of erythrocytes, which leads to the synthesis of defective hemoglobin proteins.
Video about ICSU in the blood test
Doctor about MCHS in a blood test: