Content
- Indications for the appointment of antibiotic therapy
- Types of antibiotics
- Drug selection mechanism
- What antibiotics can pregnant and lactating women take?
- Antibiotics for the treatment of various diseases of the throat and respiratory tract
- Angina
- Pharyngitis
- Laryngitis
- Features of the use of antibiotics
- Throat Antibiotic Videos
Antibiotics are widely used for the treatment of many infectious diseases in adults and children. Often, patients try to resort to antibiotic therapy for sore throat or upper respiratory tract.
Indications for the appointment of antibiotic therapy
Some patients tend to start using antibiotics as soon as the first signs of a disease appear. However, do not forget that this is not always appropriate. Moreover, such an approach to the problem can lead to the development of complications.
For example, antibiotics do not have the following properties:
- destruction of viruses;
- decrease in body temperature;
- prevention of complications of bacterial infection.
Antibiotics for the treatment of throat in adults or children can only be prescribed if there is an accurate diagnosis, results analysis on the tank culture from the microflora of the throat, as well as in cases where the doctor considers it necessary to prescribe this group drugs. The fact is that unreasonable antibiotic therapy leads to a number of consequences.
Among them:
- Reproduction of microflora resistant to drugs. That is, microorganisms become resistant to the effects of the antimicrobial drug. This is dangerous because the next time the antibiotic may be powerless.
- Disruption of the healthy microflora of the body, including the intestines. Antibiotics cannot work topically, acting only on the lining of the throat. They act systemically, destroying not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microorganisms. It is for this reason that indigestion is the most common adverse reaction to antimicrobial treatment.
- Increased risk of developing adverse symptoms.
- Increase in the cost of treatment.
In view of all of the above, antibiotics should not be considered a panacea for all diseases.
The main indications for antibiotics are bacterial infections. body systems such as:
- respiratory system (bronchitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia);
- genitourinary system (cystitis, urethritis, bacterial prostatitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, some sexually transmitted infections);
- skin (purulent wounds, abscesses);
- organs of hearing (otitis media of any location);
- organs of vision (conjunctivitis, keratitis);
- systemic blood poisoning (sepsis);
- dental infections (periodontitis, deep caries, flux);
- other infections (bacterial meningitis).
The list of diseases does not end there. The range of use for each antimicrobial drug is different. The use of antibiotics is advisable in cases where the patient has a bacterial infection, accompanied by prolonged manifestations of fever, pain and edema.
The doctor should study the patient's CBC, which should indicate such abnormalities as:
- An increase in the number of leukocytes (neutrophils).
- A shift in the leukocyte formula.
- Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
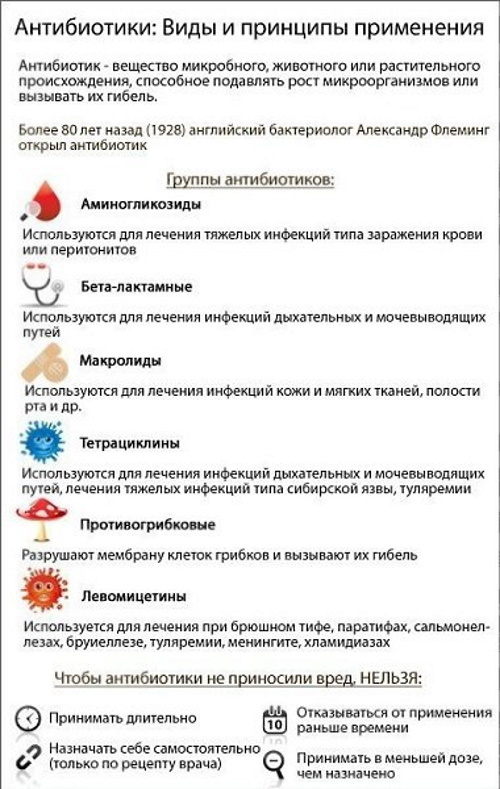
Types of antibiotics
Antimicrobial drugs include several classes of antibiotics. They differ from each other in origin (natural or synthetic), mechanism of action (bacteriostatic or bactericidal), chemical structure, indications and contraindications for use, a list of undesirable side reactions.
Among specialists, the classification of drugs according to their chemical structure is most often used: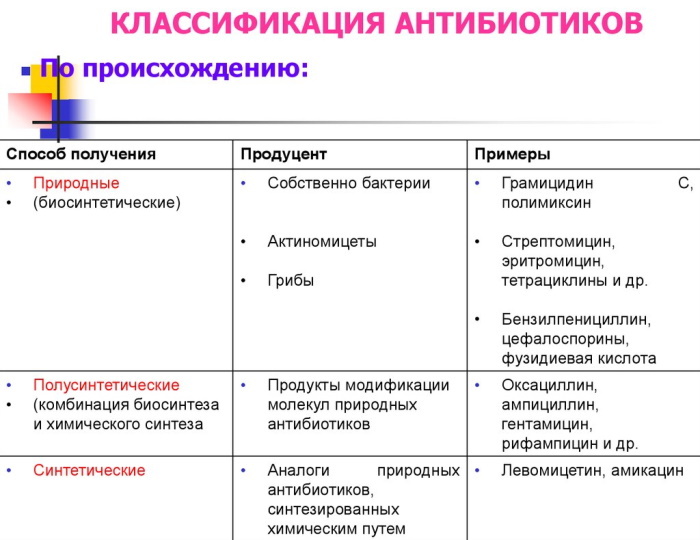
| Antibiotic group | Short description |
| Beta-lactam antibiotics | |
| Penicillins | Synthesized by the flexible genus Penicillinum. |
| Cephalosporins | They have a similar structure, but a wider range of applications. |
| Carbapenems | Less commonly, cause microbial resistance. |
| Monobactams | The only representative is called Aztreonam, it is active against some aerobes. |
| Antibiotics other than beta-lactam | |
| Macrolides | They do not kill microbes, but do not allow them to move and multiply (bacteriostatics). |
| Tetracyclines | Bacteriostatics, effective against tuleria and anthrax. |
| Aminoglycosides | They kill bacterial cells, are effective in sepsis, but are highly toxic. |
| Amphenicols | They are prescribed in extreme cases, as they can affect the bone marrow. |
| Glycopeptide antibiotics | They have both bactericidal and bacteriostatic mechanisms of action. |
| Lincosamides | Bacteriostatics, but in high dosages can have a bactericidal effect. |
Drug selection mechanism
Antibiotics for throat treatment in adults and children can only be prescribed by a specialist, given many features of the patient's body, data from analyzes and diagnostic procedures, as well as diagnosis.
When choosing a drug, attention is paid to factors such as:
- The microorganism that caused the inflammation (established using microbiological tests).
- The ability of the drug to penetrate the epicenter of the infection and provide its therapeutic effect in it.
- The state of the patient's excretory organs (kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract). During treatment, the main principle is always “do no harm”. Therefore, the doctor must take into account the patient's condition, the ability of his organs to excrete, so that antibiotic metabolites do not harm these systems.
- Determination of the likelihood of developing unwanted side reactions.
- Age and gender of the patient.
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
It is important to follow a number of principles with antibiotic therapy.
Namely:
- Early initiation of treatment.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of therapy after 2 days from the start of the course.
- Compliance with the dosage regimen and course duration.
- Control of side effects of the antibiotic (patient interview, clinical observation, laboratory monitoring).
- Tracking the likelihood of developing antibiotic resistance.
What antibiotics can pregnant and lactating women take?
Antibiotic treatment should begin with taking into account all the characteristics of the patient, both in adults and in children. This is especially true for pregnant and lactating women. For the treatment of inflammatory processes of the throat in this category of persons, antibiotics, as a rule, are not used. The fact is that any antimicrobial drug has a systemic effect, which increases the risk of side effects and complications.
During the period of childbearing or during lactation, a woman's immune system is usually weakened and prone to the development of diseases such as bronchitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis. In such cases, the question arises of choosing an antibiotic for a woman.
As a rule, before 12-16 weeks of pregnancy, specialists try to avoid prescribing antimicrobial drugs to the patient. The fact is that in the early stages the fetus is not protected by the placenta, and also during this period there is an active laying of the organs and systems of the unborn child. Therefore, if possible, in the first 3-4 months of pregnancy, any medications should be excluded.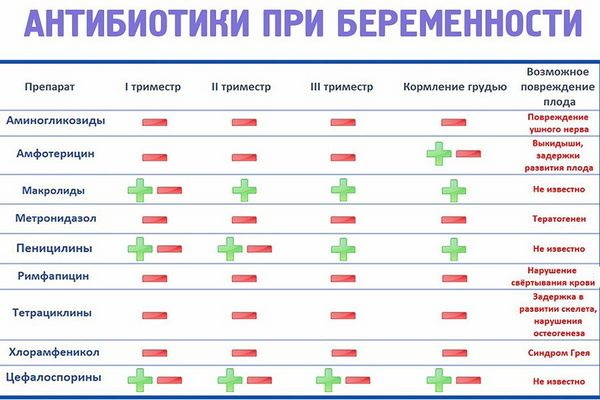
In later stages of pregnancy, antibiotics such as:
- semi-synthetic penicillins;
- macrolides;
- many representatives of cephalosporins.
Regardless of the duration of pregnancy, any antibiotic should be prescribed only by a doctor and taken under his strict control, clearly according to the prescribed scheme.
However, there are drugs that are unacceptable to take in any trimester, as they are toxic action on the fetus, causing a violation of the formation of the organs of hearing, skeletal system, nervous system, and so on Further.
Antibiotics that are strictly prohibited during pregnancy include:
- tetracyclines;
- aminoglycosides.
Also, many antibiotics are incompatible with lactation, so they can penetrate into breast milk, changing its quality and composition.
Medications that can be taken during breastfeeding include:
- penicillins (ampicillin, amoxicillin, amoxiclav, flemoxin;
- aminoglycosides (gentamicin, netromycin);
- cephalosporins (cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefazolin).
In case of emergency, with extreme caution, when deciding whether to stop breastfeeding, it is permissible to take macrolides (Azithromycin, Sumamed, Macropen, Erythromycin).
It is strictly forbidden to use medications for nursing mothers such as:
- tetracycline;
- tinidazole;
- metronidazole;
- sulfonamide;
- levomycin;
- clindamycin.
Antibiotics for the treatment of various diseases of the throat and respiratory tract
Antibiotics for throat treatment in adults and children can only be used after consulting a doctor and establishing an accurate diagnosis. The fact is that such a disease as "sore throat" does not exist. As a rule, inflammation, redness, pain when swallowing, discomfort in the throat are symptoms of a medical condition.
Far from always, it will be of bacterial origin. Often, such symptoms indicate the penetration of the virus into the human body. In this case, antibiotics will be powerless and only harm. Therefore, if you experience discomfort in the throat area, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Angina
The second name is acute tonsillitis. The disease can be caused by viruses, fungi and bacteria. Therefore, antibiotics should be used only after the etiology of the disease has been determined and the doctor has made an accurate diagnosis. As a rule, bacterial tonsillitis leaves a characteristic white thick coating on the surface of the tongue and tonsils, as well as enlargement and swelling of the uvula.
Most often, with bacterial angina, doctors prescribe drugs such as:
-
Amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid (to protect the gastrointestinal mucosa). Produced under such trade names as Amoxiclav, Flemoxin Solutab. The drugs belong to the group of penicillins, have a destructive bactericidal effect on microbial cells, and have a wide spectrum of action. The standard dosage regimen involves ingestion of 1 tablet 3 times a day for 5-7 days.

- Ceftriaxone, cefotaxime. Refers to cephalosporins, injected intramuscularly or intravenously. They have a quick effect in the treatment of sore throats. Assign, as a rule, 1 injection per day for 5.7 or 10 days.
- Azithromycin based medicines (Azitrox, Sumamed) have a high therapeutic effect and are used once a day for 3-5 days, however, they have a more pronounced manifestation of side effects. For example, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. In addition, these drugs have many contraindications.
In the treatment of angina, local use of antibiotics is also relevant. Most often, these drugs are available in the form of lozenges or lozenges. These forms of release act more quickly in the throat area, relieving unpleasant symptoms.
Such means include:
- Furacillin solution. It is a synthetic antibacterial agent. However, when combined with systemic antibiotics, the risk of developing vomiting and allergies increases.
- AntiAngin, which is an effective remedy with a complex composition. The drug includes tetracycline, chlorhexidine and ascorbic acid.
- Gramidin neo. The composition includes an antiseptic gramicidin and an anesthetic component.
Pharyngitis
This disease is manifested by symptoms such as:
- sore throat and dryness;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- dry, painful cough without sputum discharge;
- pain when swallowing.
In the inflammatory process of the pharyngeal mucosa, first of all, preference is given to drugs of the penicillin series (amoxicillin) or cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, cefotaxime). If this patient is prohibited from prescribing these funds, treatment is carried out with macrolide antibiotics (azithromycin, erythromycin).
Laryngitis
The disease has symptoms such as:
- pain when swallowing and while talking;
- hoarseness of voice or its complete disappearance;
- attacks of "barking" cough;
- feeling of lack of air at night.
The antibacterial regimen for the treatment of laryngitis is similar for pharyngitis. Penicillins or cephalosporins are preferred. In severe cases, macrolides (azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin) may be prescribed.
Features of the use of antibiotics
Antibiotics for throat treatment in adults should be prescribed to the patient when all the rules of antimicrobial treatment are explained to him.
In order for the effect of taking the drug to be maximum, and the risk of side effects to be minimal, the patient must follow a number of recommendations:
- Antibiotics are permissible to drink only as directed by a doctor. Drugs in this group have a detrimental effect on the beneficial microflora of the body, which can lead to the development of a number of complications. Infections often have similar symptoms. Only a specialist can determine the cause of the disease. Antibiotics are effective only against bacteria, but they are powerless against viruses. Therefore, it is unacceptable to prescribe the drug on your own and be treated with it.
- Do not adjust the dosage of the drug. Some patients, wanting to recover quickly, double the dose of the antibiotic. Others, on the contrary, are afraid of the toxicity of the drug and reduce the dosage. In any of these cases, negative consequences may develop. With an increase in dosage, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain may occur. With a decrease, the development of microbial resistance to the drug is manifested, the lack of effect. Also, many patients complete the course earlier than expected, immediately after the disappearance of symptoms. However, the course of antibiotic treatment must be complete, otherwise the infection may "return".
- When treating with antibiotics, it is recommended to keep a diary of the drug intake. This will prevent unwanted consequences, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. Doctors recommend indicating the time of drug use, dosage, dietary characteristics during therapy, symptoms of the disease, and possible side effects.
- It is important to strictly observe the time of using the drug, the number of doses per day, the duration of the course of treatment. The dosage regimen is set by the doctor on an individual basis for each patient. It is necessary to maintain a constant concentration of the antibiotic in the blood, so you should not skip the appointment or take the pill in advance.
- You should drink the drug correctly. A glass of clean drinking water at room temperature is optimal for these purposes. Juices, carbonated drinks, tea and coffee cannot be used for these purposes, since the absorption of the active substance may be disturbed.
- Any amount of alcohol is incompatible with antibiotics. Otherwise, severe intoxication of the body is possible, disruption of the liver and kidneys.
- Compliance with a diet. Diet during antibiotic treatment directly affects the effectiveness of treatment. It is important to exclude fatty, smoked, salty and fried foods, as well as pickles and sweets. It is better to give preference to foods that are rich in fiber (vegetables, fruits, wholemeal bread, bran). This will help with normal digestion.
- Taking probiotic complexes. Typically, antibiotics cause side effects in the digestive system. For this reason, doctors try to prescribe probiotics that will restore the intestinal microflora. If, when prescribing an antimicrobial drug, the doctor does not prescribe such a complex, you should clarify about the possibility of taking probiotics.
Many medications can be used to treat throat in adults. Preference should be given to antibiotics only in cases where the doctor, during the examination, accurately established the presence of a bacterial infection. Self-medication with antibacterial drugs is strictly prohibited.
Author: Olga Orlova
Throat Antibiotic Videos
Komarovsky about why antibiotics are needed for angina:
