Content
- Etymology and types of pathology
- Causes
- Signs
- How is it diagnosed
- Giving help
- Basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Specialized assistance
- After the rhythm is restored
- "Chain of survival"
- Early recognition of pathology and request for help
- Early start of resuscitation.
- Early defibrillation
- Early transition to advanced resuscitation
- Complications
- Prophylaxis
- Video about circulatory arrest
Stopping blood circulation - a sudden cessation of the pumping function of the heart (blood circulation) caused by a violation of the ability of the heart muscle to emit electrical impulses or its mechanical damage.
The cessation of blood circulation instantly provokes the transition of the body to a state of clinical death, accompanied by a potentially reversible loss of vital functions organs (brain, heart, lungs) and manifested by such clinical signs as coma, accompanied by a temporary cessation of breathing and pulse, on sleepy arteries.
Without emergency resuscitation actions for 10-15 minutes, constantly progressive hypoxia of all cellular structures will lead to biological death - irreversible damage to the functions of the brain and other vital organs.
Etymology and types of pathology
Cessation of blood circulation (clinical signs of pathology are given below in the article) is one of the main causes of death of people around the world. According to medical observations, only in the USA and Europe a day from a similar pathology that occurred out-of-hospital walls, about 2,000 people die (this figure is more than 700,000 per year Human). In the Russian Federation, this figure is equivalent to 250,000 people per year, most of which fall on people over the age of 50 who do not suffer from previously identified cardiac pathologies.
With the development of sudden cardiac arrest in out-of-hospital conditions, the percentage of survival, with the timely initiation of resuscitation measures, is about 10-11%. In a hospital setting, this figure reaches 18-20%, which is associated with the availability of resuscitation equipment and the availability of qualified medical personnel.
It is possible to classify sudden cardiac arrest (or sudden cardiac death) due to the pathologies that caused it, as well as by the presence of signs preceding the condition.
In the latter case, there are:
- Asymptomatic cessation of blood circulation - not accompanied by visible signs and arising suddenly in a perfectly healthy person.
- Having previous signs - such as short-term loss of consciousness, dizziness, severe chest pains that occur about an hour before the blood circulation stops.

By the type of cardiac abnormality, which is important for resuscitation measures, they are distinguished:
| Circulatory arrest caused by ventricular fibrillation | It is recorded in approximately 80% of all cases of sudden cardiac death and is associated with an irregular contraction of individual myocardial fibers that are unable to provide full coronary blood flow. The condition is reversible and is well controlled by a number of resuscitation measures (chemical or electrical defibrillation). |
| Circulatory arrest caused by asystole | In this case, there is a complete cessation of heart contractions, accompanied by the cessation of the bioelectric activity of the myocardium. The condition can develop as a result of fibrillation, and without any reason, asymptomatic. In most cases, it provokes death, and resuscitation measures, as a rule, are not effective. |
Circulatory arrest, which occurs in 80% of all pathological cases, is caused by a violation of ventricular fibrillation and is prone to occur in older men (from 50 to 75 years old) suffering from alcohol or nicotine addiction, as well as a violation of lipid-fat exchange. Due to physiological reasons and a more active lifestyle, women are less likely to suffer from this pathology.
Causes
Circulatory arrest (clinical signs such as sudden fainting and chest pain are considered one of the main precursors of the soon development of pathology) most of it is associated with a violation of cardiac activity and in about 80% of cases it is provoked by myocardial ischemia caused by the pathology of the coronary blood circulation.
In addition, sudden cardiac death can be caused by:
- cardiomyopathy (dilated or hypertrophic);
- heart valve pathology;
- myocarditis;
- hereditary canalopathies.

The factors that provoke a violation of the electrical impulse activity of the myocardium, which causes circulatory arrest, include:
- ischemic disorders of coronary blood flow;
- hypokalemia, hypercalcemia and hypokalemia associated with electrolyte imbalance;
- metabolic disorders such as acidosis and hypoxemia;
- disorders of the function of the autonomic nervous system;
- intoxication with cardiotoxic substances;
- taking proarrhythmogenic drugs;
- mechanical injury;
- suffocation;
- reflex cardiac arrest that occurred during surgery;
- electric shock;
- complications after diagnostic measures.
The causes of sudden cardiac death can also include:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- eating a lot of fatty foods;
- arterial hypertension;
- insufficient intake of vitamins.
Pathology can also arise under the influence of external factors:
- excessive power loads;
- diving into icy water;
- insufficient concentration of oxygen in the ambient air;
- under the influence of acute psychological stress.
In young children, circulatory failure can occur due to injury or respiratory failure, in as a result of drowning, a foreign body entering the windpipe, with asthmatic syndrome, and wearing a secondary character.
Signs
Clinical signs of sudden circulatory arrest, in some cases, can be observed for 40-60 minutes. before the development of a pathological condition, these include:
- sudden fainting, lasting 30-40 seconds;
- severe dizziness;
- lack of coordination;
- a strong rise or vice versa a fall in the physical indicators of blood pressure.

A person may also complain of sudden and very severe chest pain, as if, according to survivors, the heart is tightly squeezed into a fist.
Harbingers of sudden cardiac death can not always be observed, and most often a person simply falls while doing some work or exercise. It is also possible that the blood circulation stops at the moment of awakening.
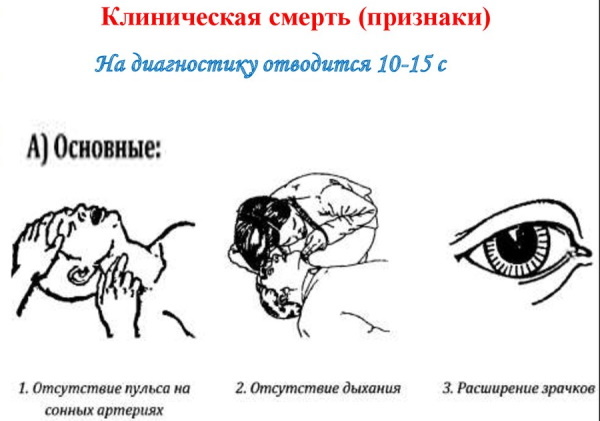
By itself, the cessation of blood circulation is accompanied by a sudden loss of consciousness with a lack of breathing and pulse in the carotid artery. Sudden cardiac death provokes a sharp fall of a person with a transition into unconsciousness, within the first 15 seconds from the moment of its development. At the same time, breathing in a lying person can persist for 1-2 minutes, but since it is superficial, it is not can fully provide vital organs with oxygen, which leads to a gradually progressive hypoxia.
An abrupt cessation of blood flow to the brain also contributes to the onset of seizures. Within 1 minute after the cessation of blood circulation, the pupil dilates.
The skin of an unconscious person takes on a pale, bluish appearance, with visible cyanosis of the lips, earlobes and nail plate. The pupils are dilated and do not respond to light. The pulse is not felt not on the radial, not on the main artery, and Korotkov's tones are not heard on the tonometer.
In primary cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia is observed on the electrocardiogram. As hypoxia progresses, this state is replaced by pulseless electrical activity. In case of secondary circulatory arrest due to respiratory failure or severe shock, asystole or ventricular fibrillation can be observed on the screen.
If, when the circulation is stopped, the electrocardiogram shows ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, urgent resuscitation can save a person's life and has an almost 100% chance of restoring cardiac circulation. When asystole appears, the survival rate will be no more than 5%.
How is it diagnosed
Cessation of blood circulation (clinical signs of pathology need to be known to everyone, for timely help to loved ones) is diagnosed by a resuscitation doctor or other specialist with a medical education. Sudden cardiac death can also be determined by representatives of emergency services (Ministry of Emergency Situations, firefighters, police) or bystanders, based on the totality of signs of pathology.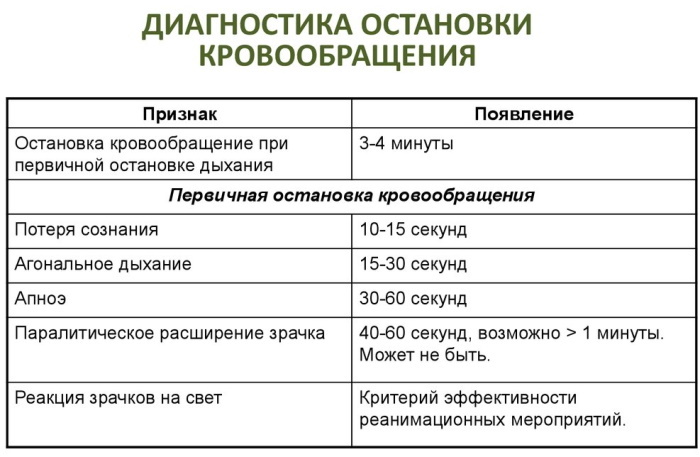
Additional techniques are used only in a hospital setting, including:
| Hardware manual | On the monitor to which the victim is connected, the onset of large- or small-wave ventricular fibrillation is noted. If the saturation indicators sharply decrease at the same time, it is possible that not flickering, but an asystolic isoline with the impossibility of determining blood pressure, may appear. If the patient is on the ventilator at this moment, a signal is also heard about the absence of attempts to breathe on his own. |
| Laboratory diagnostics | It is assigned simultaneously with measures to restore cardinal activity and consists in conducting blood tests for acid base balance and electrolytes, showing a shift towards the acid side and biochemistry blood. |
Giving help
Assistance in stopping blood circulation to the victim is provided on the spot. It is possible to transport a patient to a medical institution only after the restoration of the heart rhythm.
Basic resuscitation is performed outside the hospital walls. In a hospital or in an ambulance, they are supplemented with chemical or electrical defibrillation.
Basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation
When resuscitating, the victim should be laid with his back on a flat surface, cleansed the oral cavity from mucus, raise his head and extend the lower jaw. Having pinched the victim's nose, a tissue napkin should be put on his lips, and then the rescuer should clasp his lips with his lips and take a deep breath. In this case, at least 30 resuscitation compressions are performed, in which the sternum should be pressed by at least 4-5 cm. The ratio of compressions and inspirations should be 30: 2 and carried out until breathing is completely restored.
In this case, at least 30 resuscitation compressions are performed, in which the sternum should be pressed by at least 4-5 cm. The ratio of compressions and inspirations should be 30: 2 and carried out until breathing is completely restored.
Specialized assistance
In a hospital setting, care is provided in accordance with the ECT data. With ventricular tachycardia, defibrillation is performed with discharges of 200 and 360 J. It is also possible to administer antiarrhythmics. When diagnosing asystole, injections are performed with adrenaline, atropine, sodium bicarbonate and calcium chloride. The victim is incubated without fail and connected to a ventilator.
After the rhythm is restored
When the heart rhythm is restored, the patient's condition is continuously monitored, while assessing the damage to the nervous system. If necessary, the victim remains on the ventilator, and in accordance with the results of the blood test, the electrolyte balance is corrected and the pH level is restored.
After the normalization of the state, depending on the situation, the following are prescribed:
- dopamine injections;
- treatment with antidepressants and antioxidants;
- taking vascular drugs;
- soda and nootropic substances.
"Chain of survival"
Cessation of blood circulation (clinical signs of pathology allow you to provide assistance to the victim before arrival ambulance crews) in some cases can be recognized in advance, with the correct interpretation of it harbingers. In medical practice, a certain "survival chain" has been developed to help people suffering from cardiac pathologies or those at risk to recognize the primary signs of sudden cardiac death, thereby saving their a life.
Early recognition of pathology and request for help
Here is a patient suffering from cardiovascular pathology, due to sudden severe pain in the chest, a violation coordination and dizziness suggests an early arrest of blood circulation and asks the people around him to call an ambulance help.
Early start of resuscitation.
In case of sudden circulatory arrest, resuscitation measures should be started as early as possible, since gradually developing hypoxia leads to irreversible death of brain cells within 3-4 minutes after the cessation of cardiac activities. Since the ambulance team cannot reach the victim so quickly, eyewitnesses of the incident should carry out resuscitation measures.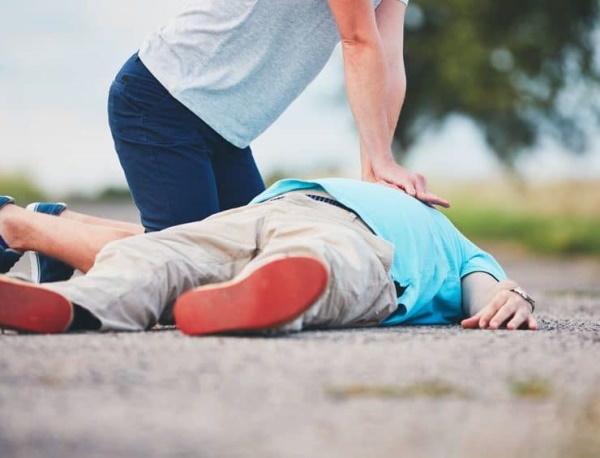
Since every minute the chances of successful restoration of blood circulation are reduced by 10%, eyewitnesses should recognize pathology by clinical signs and proceed with the implementation of the basic complex of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Only in this case the chance of complete recovery of the victim increases by 2-4 times.
Unfortunately, in the modern world, in most cases, eyewitnesses do not start resuscitation, even if the victim is a person close to them, due to ignorance of basic actions or fear of harm sick.
Early defibrillation
Early defibrillation (within 3-5 minutes) increases the likelihood of a person's survival by 50-70%. At the same time, delaying defibrillation with each subsequent minute reduces the chances of the victim by 10%
Early transition to advanced resuscitation
In most cases, this option is possible only with out-of-hospital circulatory arrest, and significantly increases the victim's chances of restoring normal cardiac activity.  Supplementing basic resuscitation with an extended complex of cardiopulmonary resuscitation will allow stabilize and optimize the work of vital organs, as well as prevent repeated shutdown hearts.
Supplementing basic resuscitation with an extended complex of cardiopulmonary resuscitation will allow stabilize and optimize the work of vital organs, as well as prevent repeated shutdown hearts.
Complications
Cessation of blood circulation (clinical signs of pathology, such as cessation of pulse and respiration should be the impetus for emergency resuscitation measures) never goes unnoticed. A metabolic storm is one of the complications caused by successful resuscitation. A change in the pH level associated with hypoxia leads to a violation of the hormonal background, and in the absence of timely correction, to the development of renal failure.
Poorly performed cardiopulmonary resuscitation provokes brain death, in which the human body continues to function. The restoration of consciousness in this case is impossible. Posthypoxic encephalopathy, accompanied by a decrease in mental activity and social adaptation of a person, is considered a relatively easy variant of this condition. Also, this condition is characterized by the appearance of paralysis, paresis and disruption of the internal organs.
Prophylaxis
Since for any course of circulatory arrest, the prognosis remains unfavorable, the most effective method of prevention here will be timely identification and correction of cardiovascular pathologies, smoking and alcohol cessation, regular moderate physical activity and maintaining a healthy lifestyle life.
Cessation of blood circulation is a severe pathology associated with a sudden cessation of cardiac activity due to myocardial pathologies, suffocation or mechanical injury. The most common sudden death in men from 50 to 75 years old, accompanied by clinical signs, a sharp loss of consciousness, cessation of breathing and pulse requires urgent resuscitation, and in the absence of them provokes an early lethal Exodus.
Video about circulatory arrest
Stopping blood circulation in the operating room:
