Content
- What is Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome?
- Causes of WPW Syndrome
- Pathophysiology of the syndrome
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Classification of WPW syndrome
- Latent WPW Syndrome
- WPW Manifest Syndrome
- WPW type B syndrome
- Transient WPW Syndrome
- Intermittent WPW Syndrome
- Atypical WPW Syndrome
- Clinical diagnostic criteria
- How is pathology diagnosed
- Signs of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome on ECG, clinical picture
- Treatment
- Surgery for WPW Syndrome
- Complications
- Course and prognosis, mortality
- Video about Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
With excessive excitation of the ventricular parts of the heart mechanism, WPW syndrome is diagnosed. Congenital or acquired anomaly is due to the presence of an additional atrioventricular pathway for the innervating impulse. ECG signs are considered the basis for a definitive diagnosis.
What is Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome?
The electrocardiographic phenomenon is characterized by spontaneously developing tachycardic paroxysms. The natural rhythm is disturbed by the Kent's bundle - an abnormal innervating plexus located between the left or right atrium and one of the ventricular divisions.
The cardiological phenomenon has been studied insufficiently for the prognostic value and assessment of the risk of life-threatening conditions of the degree.
Scientific evidence base and clarification require:
- etiological factors of WPW syndrome;
- pathogenesis of the disorder;
- options for clinical and electrophysiological course;
- methods of managing patients with overexcitation of the cardiac ventricles.
The history of the study of the cardiological phenomenon is almost 100 years old. The syndrome was first discovered by Paul White, who was approached by a patient on April 2, 1928, complaining of a palpitations. Electrocardiographic examination revealed abnormalities in the QRS complex in combination with a shortened PQ interval.
In 1930, London cardiologists Wolf and Parkinson systematized 11 similar cases in detail. They defined the pathology as a combination of atypical bundle branch block in young patients with healthy hearts.
WPW syndrome ECG signs are in the form of an abnormally short PQ interval - the distance (time interval of contractions) between the corresponding peaks. Normally, this figure is 0.12-0.18 sec.
The diagnostic sign reflects the transit time of the innervating impulse through the atria from the atrioventricular plexus to the ventricular processes of the myocardium. As a result of early excitement, a deltoid wave of tachycardic disorder occurs.
Causes of WPW Syndrome
Congenital arrhythmia is caused by the formation of additional atrioventricular fibers due to incomplete cardiogenesis in the embryonic period. Researchers call the main cause of WPW syndrome a partial regression of muscle tissues during the onset and development of fibrous annular structures.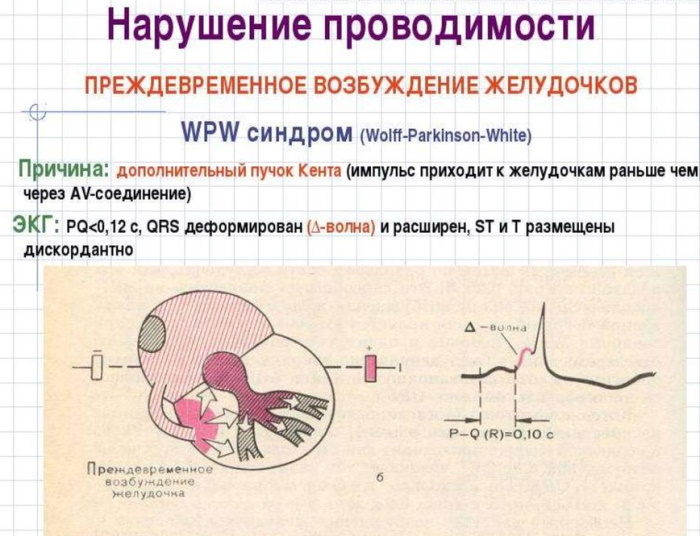
Such tissues are formed in the tricuspid and mitral valve elements of the heart mechanism. Additional innervation bundles develop naturally in the initial phase of embryogenesis.
The excess muscle fibers connecting the atria with the ventricular sections and the channels conducting electrochemical impulses located in them are completely destroyed after the 5th month of gestation. With the disturbed process of nucleation of fibrous rings with atrioventricular pathways, smooth muscle fibers are preserved. The extra innervating lines passing through them provoke an acceleration of heart rhythms in a tachycardic type.
Acquired WPW syndrome develops predominantly in young men or adolescents. The appearance of additional AV channels is considered a genetically determined abnormality. For the family-hereditary form of the cardiological paroxysmal state, a greater number of excess innervating pathways are characteristic than for congenital disorders.
Pathophysiology of the syndrome
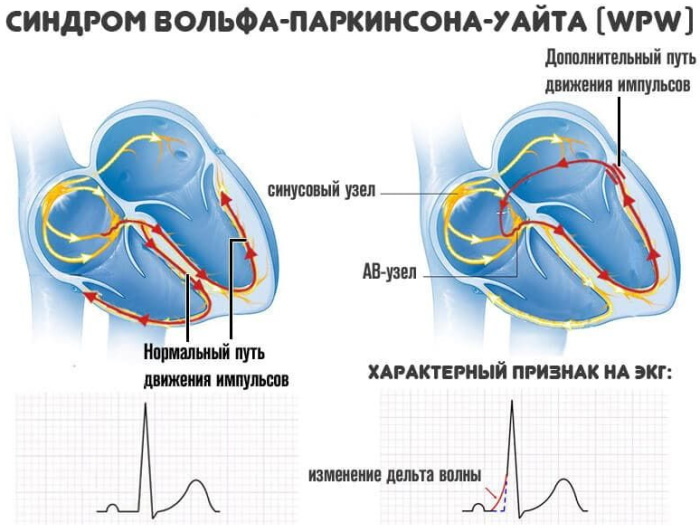
Excitation of the myocardium is carried out through 2 channels, one of which is abnormal. The impulse that innervates the heart muscle originates in the sinus node. During normal functioning of the organ, it spreads through the natural atrioventricular plexuses
Anatomical and morphological changes in combination with pathophysiological disorders lead to the fact that the signal for contraction reaches the myocardium through a shorter Kent bundle. As a result, the heart rate rises. It is fixed on an electrocardiographic tape in the form of a decrease in the PQ interval. After the premature arrival of the innervating impulse, the rest of the ventricles are excited, having received the command through the natural AV channel.
In 30% of clinically reported cases, the pathophysiology of acquired WPW syndrome is complemented by:
- Ebstein's anomaly. Congenital defect of the tricuspid valve with dysplasia and penetration into the space of the right ventricular section.
- Mitral valve prolapse. It is caused by systolic prolapse (protrusion) of the valves into the cavity of the left atrium.
- Anatomical and morphological malformations and physiological dysfunctions of the interatrial or interventricular membrane.
- Fallot's tetrad. Stenosis of the outflow tract is combined with aortic dextroposition and other disorders.
- Dysplasia of connective fibers. It is caused by genetic or congenital inhibition of collagen synthesis.
The pathophysiological picture of WPW syndrome is characterized by hereditary hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The disorder is manifested by an increase in the walls of the right or left ventricle while maintaining the normal volume of the internal space.
Etiology and pathogenesis
WPW syndrome, whose ECG signs show an abnormal slope of the shortened PQ interval, is diagnosed in about 4 patients out of 100,000. In the event of a collision in the ventricular parts of the main impulse with an abnormally accelerated one, the confluent QRS complex is deformed and expanded.
The effect is recorded by the electrocardiogram as a change in the standard slope of the alpha angle of the PQ interval. Excessive excitation of the myocardium accompanies a violation of repolarization. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia occurs, which is the leading pathogenetic feature of WPW syndrome. Atrial fibrillation develops, provoked by a circular wave-like excitation of the atria.
The etiological factors of cardiac disorders have not been precisely established. The relationship between WPW syndrome and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy of hereditary type has been noted - cardiac muscle disease associated with complex specific morphological and functional changes in the structure organ. The development of supraventricular tachycardia is facilitated by neurocirculatory dystonia, hyperthyroidism, or a combination of these pathologies.
WPW syndrome manifests itself in the background:
- cardiac ischemia;
- myocardial infarction;
- rheumatism;
- stigma of dysembryogenesis.
In addition to the Kent bundle, the abnormal impulse into the atria is carried by the Maheim fibers, the James paths, the Brechenmanche tract. They combine different parts of the organ into a single functional mechanism.
Classification of WPW syndrome
WHO has developed guidelines for determining the types of tachycardic overexcitation of the ventricles of the heart. Experts from the World Health Organization propose to separately distinguish between the syndrome and the Wolff-Parkinson-White phenomenon.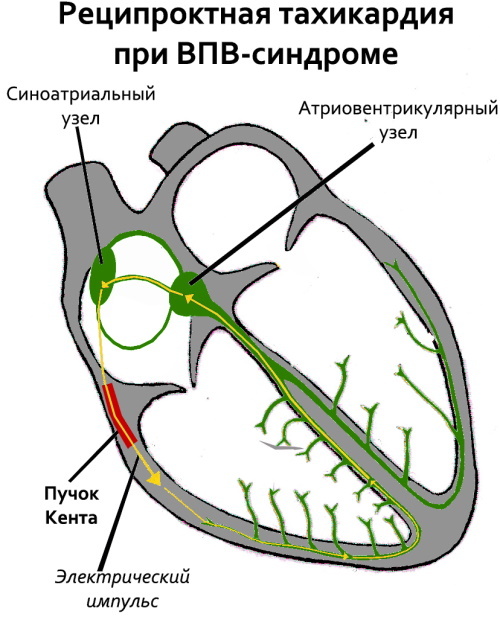
The latter is diagnosed by electrocardiographic signs during the passage of an innervating signal along additional AV pathways and overexcitation of the ventricular sections without accompanying clinical symptoms.
The WPW phenomenon does not have pronounced manifestations of atrioventricular reciprocal tachycardic disorder. The syndrome is understood as a combined overexcitation of the ventricles with arrhythmic symptoms.
According to the presence and distribution of the morphological substrate, the cardiac anomaly is classified into a disorder with additional AV fibers or specific muscle structures.
The first form of WPW syndrome is characterized by the passage of an excess impulse through:
- left or right parietal atrioventricular node;
- mitral-aortic fibrous tissue;
- lateral atrial fibers;
- Valsalva sinus aneurysm or central cardiac vein;
- septal or paraseptal connections.
By the type of conductive muscle fibers, the AV-fascicular and myocardial-right ventricular types of the syndrome are distinguished. Below is the classification of cardiac abnormalities according to clinical symptoms.
Latent WPW Syndrome
The pathology is distinguished by a latent course. Latent tachyarrhythmia is revealed by chance - when examining an organ by an electrophysiological method. A calculated current of strength and voltage is supplied to the ventricles. With such stimulation, excessive excitement is manifested.
Abnormal innervating channels conduct the impulse retrograde. Standard electrocardiographic examination does not record a reduction in the PQ interval, and there are no signs of a change in the delta wave. The latent form is characterized by minor tachycardic paroxysms.
WPW Manifest Syndrome
Such a violation is established in the presence of a permanent delta-wave change on the electrocardiographic recording. The manifesting form of pathology is characterized by the conduction of an excess excitatory impulse both along the retrograde and along the antegrade AV pathway.
WPW syndrome has pronounced clinical symptoms in the form of frequent paroxysmal attacks of reciprocal tachycardia. ECG signs of the manifesting form of the anomaly are due to an increase in the alpha-angle of the delta wave as the ventricular myocardium section expands, which is prematurely innervated from the Kent's bundle.
WPW type B syndrome
Excessive excitation of the right atrium is observed, ahead of the normal transmission of the contractile impulse. Type B of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is characterized by excessive activity of smooth muscle fibers of the right ventricle, which occurs sequentially.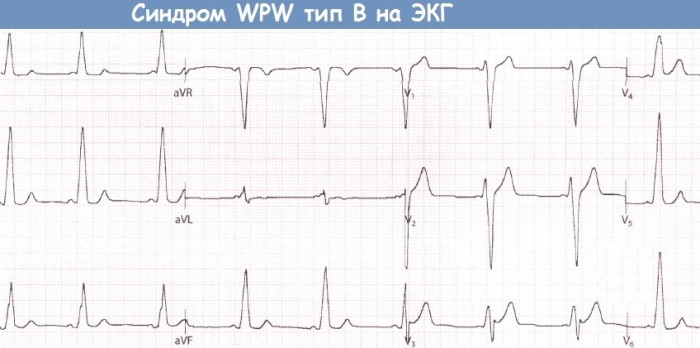
This abnormal effect is due to the time mismatch of the delta wave in both atria. Sequential innervation leads to blockade of the left branch of the His bundle. Clinical cases that do not fully fall under the definition of type B, but also do not correspond to the characteristics of variety A.
Transient WPW Syndrome
Specific abnormalities in electrocardiographic recordings appear sporadically. The intervals between signs can be of significant duration. During this time, ECG indicators remain normal.
The transient form is determined by targeted diagnostic actions to create conditions for excessive excitation of the ventricular sections. These procedures include stimulation through the esophageal canal, intravenous injection of ATP or Finoptin.
Intermittent WPW Syndrome
The form of pathology is characterized by a combination of transient overexcitation of the ventricular sections with sinus arrhythmia and episodic reciprocal AV tachycardia of the verified type.
Intermittent syndrome differs from other forms of cardiac anomaly by alternating changes in the pathways of the accelerated innervating impulse. Outside of a paroxysmal attack, electrocardiographic examination of signs of excessive excitation of the ventricles does not reveal.
Atypical WPW Syndrome
This form of cardiac anomaly is distinguished by the partial presence of ECG signs with a characteristic disorder of the clinical picture. The PQ interval in patients with atypical syndrome has a constant length regardless of paroxysmal seizures.
The main reason for this condition is called the combination of an atrioventricular pause in the transmission of the innervating impulse with abnormal passage of the exciting signal along the Maheim fibers, branched off from the central axis bundle of His.
Presumably, the PQ interval is not shortened due to atrial block. The clinical picture is episodic, implicit and vague. Atypical syndrome is diagnosed in patients with a PQ interval of 120 ms or more with clear signs of tachyarrhythmia.
Clinical diagnostic criteria
Pathological disorders in the work of the cardiac mechanism are determined by objective and subjective signs. The first ones are established according to the results of the initial examination of the patient by a cardiologist, the subsequent set of hardware procedures in combination with the introduction of stimulating substances, if necessary. Subjective clinical diagnostic criteria are based on fixing cardiac arrhythmias.
The following symptoms correspond to WPW syndrome, allowing to suspect the presence of an abnormality:
- paroxysmal acceleration of the heartbeat, not provoked by external factors;
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- increased sweating;
- periodic fainting;
- spontaneous dizziness that occurs;
- feeling of lack of air;
- shortness of breath with minimal exertion or at rest;
- stitching pain in the chest area;
- numbness of the fingers.
These symptoms are not considered precise clinical criteria for WPW syndrome, but they are considered when making a diagnosis. Such manifestations serve as the basis for the appointment of an in-depth examination.
How is pathology diagnosed
Clinical and instrumental activities are carried out. The leading diagnostic method is electrocardiography. Comprehensive examination includes physical examination, laboratory tests, hardware procedures. Some types of cardiac abnormalities are difficult to diagnose.
WPW syndrome ECG signs are often subtle. Such a clinical picture is distinguished by a latent, atypical, intermittent form of the disease. Pathology often has no physical symptoms other than tachycardia.
To make a diagnosis, the following laboratory tests are prescribed:
- biochemical blood test to detect the high content of potassium, sodium, creatinine inherent in WPW syndrome;
- coagulogram, aimed at determining hematological factors that affect coagulation;
- allergic drug susceptibility test;
- lipid spectrum of hematological fluid, shown to patients with a physiological tendency to develop cardiovascular pathologies.
Of the hardware measures, an electrocardiogram is used according to the Holter method, which involves daily monitoring or a longer recording of heart rhythms.
In the case of a latent form of the disease, current stimulation is effective, which makes it possible to activate abnormal pathways for the conduction of the innervating impulse. To induce arrhythmic paroxysms, the esophageal tract is used.
Concomitant cardiac diseases that exacerbate WPW syndrome are detected by ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics is effective when tachycardic disorders are combined with cardiomyopathy.
Endocardial electrophysiological examination is considered an informative method for detecting the latent form of an anomaly. The technology provides for the registration of excess excitation on the internal surfaces of the organ.
Endocardial EPI accurately determines the localization, morphological structure, and the number of abnormal conduction channels of the innervating signal. The method allows you to differentiate pathology and choose an adequate tactics of drug therapy.
Signs of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome on ECG, clinical picture
An abnormal sinus impulse passing through the Kent's bundle excites part of the left ventricular region before the innervation of the remaining sectors of the atria by the signal following the natural atrioventricular paths.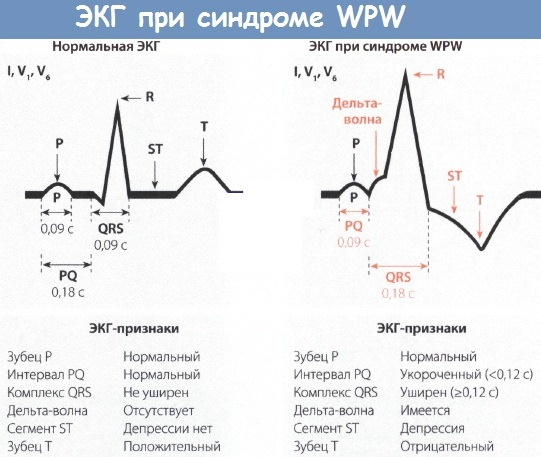
Such a pathological phenomenon is displayed on the electrocardiographic recording by a decrease in PQ. A characteristic ECG sign of an anomaly is the sequential innervation of the muscle layers of the left or right ventricle.
This is reflected on the electrocardiographic tape as a change in the slope of the alpha angle of the exciting delta wave. It acquires jagged and widened peaks in the ascending R-wave knee.
The clinical picture depends on the form of the cardiac anomaly, the number of additional pathways, the type of impulse transmission. The characteristic ECG sign of the syndrome is considered to be sequential excitation of the atria, and not simultaneous, characteristic of a normally functioning organ.
In clinical practice, intermediate forms of the disorder have been recorded with combined characteristics of types A and B. The clinical picture and ECG signs of the anomaly are varied, which does not always allow establishing a cardiac disorder with accurate differentiation.
Treatment
In the absence of pronounced tachycardic paroxysms, the disease does not require medical intervention.
Treatment is prescribed only to patients with hemodynamically significant paroxysms that accompany:
- periodic syncope - fainting;
- paroxysmal and often repeated stabbing pains in the chest area, characteristic of the angina pectoris form of coronary heart disease;
- severe arterial hypertension;
- clear signs of functional organ failure.
WPW syndrome, the EGC signs of which may be absent, with a threatening clinical picture, is symptomatically treated with external or transesophageal electrical stimulation of the heart.
For the relief of arrhythmic and painful manifestations, reflex-vagal manipulations, massage of the carotid sinus, and drug therapy are effective. The drugs used in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are presented in the table.
| A drug | Pharmacological group | Dosage regimen |
| Amiodarone | Class III antiarrhythmic drug | 150-450 mg intravenously in a single dose |
| Propafenone hydrochloride | Class IC antiarrhythmic drug | 150 mg per day in 3 divided doses orally |
| Verapamil | Calcium channel inhibitor | 5-10 mg IV at a rate of 1 mg / min. |
| Diltiazem | Class IV antiarrhythmic agent | 90 mg 2 times a day |
| Sotasol | Antihypertensive drug | 80 mg 2 times a day |
 Patients with an anomaly with severe clinical symptoms are indicated for lifelong supportive antiarrhythmic therapy.
Patients with an anomaly with severe clinical symptoms are indicated for lifelong supportive antiarrhythmic therapy.
Surgery for WPW Syndrome
Surgical intervention is carried out in emergency situations to destroy additional pathways for conducting the innervating impulse. For life-threatening conditions, radiofrequency ablation is performed, which is considered a relatively gentle method. The minimally invasive X-ray surgical procedure involves the installation of an endovascular catheter that conducts high-frequency pulsed electrical waves. The method allows you to fully restore the natural sinus rhythm.
Complications
The consequences of a cardiac anomaly include an increase in tachycardic paroxysms with age. The disease with severe clinical symptoms with frequently recurring seizures significantly reduces the quality of life. Possible sudden death due to acute heart failure.
Course and prognosis, mortality
The dynamics of the development of the pathological condition depends on the patient's age, the form of the anomaly, and multiple accompanying and influencing factors. With an asymptomatic course of the abnormal process, the prognosis is favorable.
The mortality rate from WPW syndrome does not exceed 4%. Patients with abnormal cardiac conduction require regular preventive examinations. If there are no pronounced ECG signs, and the clinical symptoms do not progress, the violation is considered a physiological phenomenon that does not require treatment.
Video about Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
SVC syndrome: