Content
- Pathogenesis, causes of the development of esophagitis
- Symptoms
- Reflux esophagitis
- Infectious esophagitis
- Eosinophilic esophagitis
- Classification of the disease, distinguishing features
- Acute form
- Chronic form
- Development stages
- Diagnostics
- Esophagitis treatment
- Medication for reflux esophagitis
- Drugs and treatment regimens for an infectious form of pathology
- Medicines for eosinophilic esophagitis
- Diet for different forms of the disease
- Complications of esophagitis
- Forecast
- Esophagitis video
In gastroenterology, one of the most common diseases is esophagitis, which is characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The pathology is inflammatory. The gastroenterologist prescribes effective treatment of esophagitis taking into account the etiology of the disease.
In 98% of cases, patients are shown diet, physiotherapy, and the use of medications. Only in isolated situations, to eliminate painful symptoms and normalize the patient's condition, surgical intervention is required to narrow the lumen of the esophagus. For example, bougienage, dissection of cicatricial structures.
Pathogenesis, causes of the development of esophagitis
Esophagitis (symptoms and treatment medicinal inflammatory disease of the esophageal wall, chronic or acute course, should be known to all patients who have previously been diagnosed pyloroduodenal stenosis, since in this case the likelihood of the stomach contents being thrown into the esophagus significantly increases) in 40% of all cases proceeds without a characteristic symptoms.
With the classic development of esophagitis, the patient is worried about burning pain behind the chest, heartburn and increased salivation. A violation of swallowing is possible. If effective drug treatment is not prescribed in a timely manner, then the patient may be diagnosed with various kinds of complications. For example, Barrett's disease, peptic ulcer, stenosis, esophageal perforation. For a correct diagnosis of the disease, esophagoscopy, radiography of the esophagus and endoscopic biopsy should be performed.
Pathology can develop as a result of damage to the mucous membrane or if there is a history of gastritis. Medical statistics indicate that the chronic form of the disease can occur against the background of the presence of inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and stomach. In some cases, a lesion of the esophageal wall is diagnosed in those patients with a history of tuberculosis or syphilis.
In people with achalasia of the cardia, stenosis of the esophagus, the stagnant form of esophagitis occurs due to stagnation and subsequent decomposition of food in the esophagus. This condition is extremely dangerous for the patient's life, since in the absence of effective drug treatment, the disease progresses, rapidly deteriorating the quality of human life. The most common cause of the development of pathology is the reflux of gastric juice into the esophageal cavity, which is due to cardia insufficiency. In such a situation, the patient is diagnosed with peptic esophagitis or reflux esophagitis.
Pathogenic microorganisms can provoke damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. For example, herpes viruses (HSV, HSV-1, HSV-2) and fungi of the genus Candida. The infectious form of the pathology is characteristic of patients with weakened immunity. The risk group also includes people who take steroids for a long time for the complex treatment of bronchial asthma.
Esophagitis can occur under the influence of acids and certain medications:
- Potassium chloride possesses hyperosmolarity, which is why it can affect tissue destruction and damage to blood vessels. It should be borne in mind that osmolarity is possessed by those solutions that, even through semipermeable membranes, attract the solvent to themselves.
- Ferrous sulfate, Tetracycline, Doxycycline. These substances are characterized by high acidity, which can cause damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
- Provoke irritation and the subsequent inflammation of the esophagus can be drugs from the acetylsalicylic acid group.
Esophagitis can occur due to careless insertion of the probe, as well as as a result of radiation therapy. Inflammation of the esophagus is diagnosed by gastroenterologists in 80% of those patients who have previously been diagnosed with Behcet's disease.
Symptoms
Esophagitis (symptoms and drug treatment directly depend on what stage of the disease was diagnosed in the patient) in acute form accompanied by pronounced discomfort in the epigastric region, heartburn, as well as painful passage of food through the digestive path. If the patient does not promptly seek help from an endocrinologist, then the pathology will turn into a chronic form, due to which periods of exacerbation will alternate with remission.
Esophagitis in catarrhal form can be asymptomatic, only in rare cases can the patient complain of an increased sensitivity of the esophagus to cold or hot foods. In the absence of complex treatment, acute pain occurs behind the chest, which radiates to the back and neck. The patient's condition worsens against the background of dysphagia, heartburn and increased salivation.
In severe cases, vomiting of blood occurs, which can shock the patient. Even severe esophagitis after 7-9 days can be replaced by a sudden improvement in the patient's condition, but without complex treatment after 3-12 weeks, the wounds on the mucous membrane of the esophagus will heal, and in their place scars and stenosis form, which is fraught with the progression of regurgitation food.
Reflux esophagitis
This form of the disease is characterized by inflammation of the esophagus, which is associated with the reflux of gastric contents. The prevalence of reflux esophagitis among patients over 18 years of age reaches 46%. The main symptom is heartburn, which rapidly intensifies after drinking coffee, fatty and spicy foods, carbonated drinks. Overeating significantly increases the symptoms of the disease.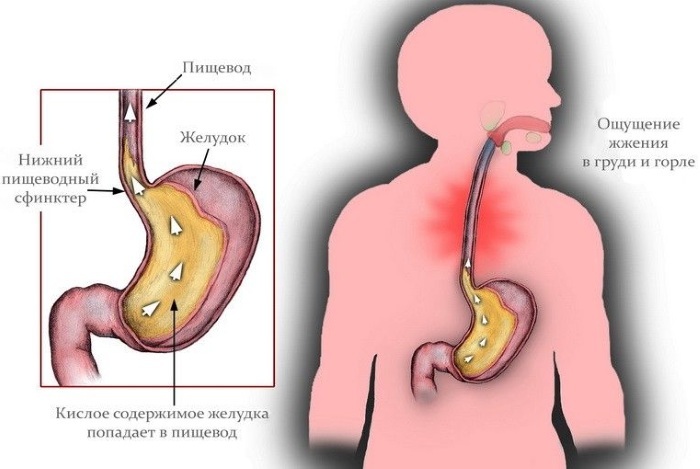
The patient may be disturbed by acute chest pain, which can be easily confused with pain in the heart. The occurrence of a swallowing disorder may be associated with the transition of pathology to a more severe form, when cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus occurs.
Infectious esophagitis
The disease develops as a result of damage to the esophagus by fungi of the genus Candida, which is associated with a decrease in the protective functions of the immune system. Infectious esophagitis is most common among people who have acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or diabetes mellitus.
The disease is accompanied by heartburn, increased salivation, difficulty swallowing and acute pain in the chest, which increases significantly during physical activity and after eating. Additionally, the body temperature may rise to 38 C.
Eosinophilic esophagitis
It is a chronic form of inflammatory disease of the esophagus. Eosinophilic esophagitis can occur when exposed to a variety of allergens. Statistics confirm that every year out of 150,000 people, this pathology is diagnosed in 8-12 patients.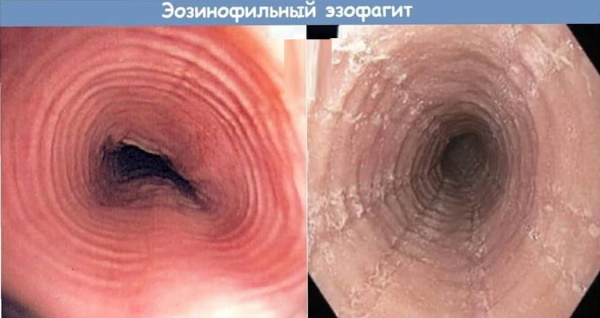
In 98% of cases, patients complain of nausea, vomiting, respiratory failure and severe pressing / bursting pain throughout the esophagus, which occurs immediately after eating. Dysphagia worries constantly, because of which the patient may have difficulties with the use of even semi-liquid food. Painful symptoms provoke increased irritability.
Classification of the disease, distinguishing features
In gastroenterology, it is customary to distinguish between acute, subacute and chronic esophagitis. The classification of lesions of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract largely depends on the severity and nature of the inflammatory process.
For example, there are the following forms of esophagitis:
- Necrotic.
- Phlegmonous.
- Hydropic.
- Catarrhal.
- Erosive.
- Hemorrhagic.
- Pseudomembranous.
- Exfoliative.
In 95% of patients, edematous or catarrhal esophagitis is diagnosed, when the pathological condition is limited to hyperemia of the mucous membrane and tissue edema. The development of erosion can be associated with the presence of an acute infection in the body, as well as with chemical or thermal burns of the esophagus.
In the absence of an effective complex treatment and a severe course of the disease, esophagitis is accompanied by internal bleeding. But with the pseudomembranous form of pathology, the fibrous exudate is not fused with the submucous tissue (in contrast to exfoliative esophagitis). If the wall of the esophagus is damaged by a foreign object, there is a high probability of developing phlegmon.
Depending on the prevalence and localization of the inflammatory process, esophagitis can be proximal, distal or total. The exact classification of pathology according to the degree of damage to the esophagus has significant differences for the acute and chronic course of the disease. In the latter case, the Savary and Miller technique is used in traditional medicine.
Acute form
Acute esophagitis can bother the patient for 3 months, but in 90% of cases, painful symptoms appear within 7 days, after which the ulcers on the walls of the esophagus heal, and scars form in their place (provided that the patient did not seek medical help). This form of inflammatory disease is diagnosed by gastroenterologists in 3-5 out of 100 patients. It is possible to reduce the likelihood of further progression of the pathology and avoid possible complications only in if, at the first manifestations of the disease, consult a doctor who will prescribe a medication treatment.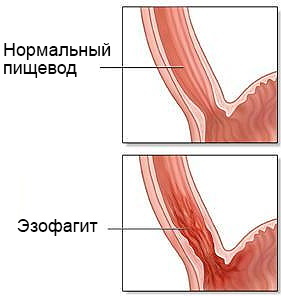
Gastroenterologists divide acute esophagitis and esophageal burns into 3 categories:
- Superficial damage to the mucous membrane, when the patient did not have erosion and ulcers.
- The defeat of the entire thickness of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. In this case, the patient's condition rapidly deteriorates against the background of the development of ulcers and subsequent tissue necrosis.
- In a severe case, the pathology extends to all submucosal layers, due to which deep wounds are formed with possible perforation of the esophagus and internal bleeding. After undergoing complex treatment, there is a high probability of the formation of scar structures.
With a catarrhal form of pathology, characteristic symptoms may be absent. The patient can only be concerned about the hypersensitivity of the digestive tract to hot and cold foods. In severe cases, the patient complains of acute chest pain, diarrhea, migraine, lack of appetite, dysphagia, heartburn and increased salivation. Only 1 patient out of 100 has bloody vomiting, which is fraught with the development of shock.
Chronic form
For esophagitis in a chronic form, the manifestation of heartburn is characteristic, which intensifies after consuming smoked and fatty foods, carbonated drinks, strong coffee. Even a single overeating can intensify the symptoms of the disease. Chronic esophagitis is also accompanied by respiratory distress, frequent belching and regurgitation. The patient may experience discomfort in the xiphoid process. In chronic esophagitis, the symptoms are less pronounced than in the acute form of the disease. Painful symptoms can bother the patient for more than 6 months, then the period of exacerbation is replaced by remission.
Development stages
Esophagitis (symptoms and drug treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease are primarily of interest to those patients with diagnosed with acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, since with the help of diet alone it is possible to normalize the condition only with a mild form of pathology) has several stages of development, each of which is accompanied by painful symptoms different intensities.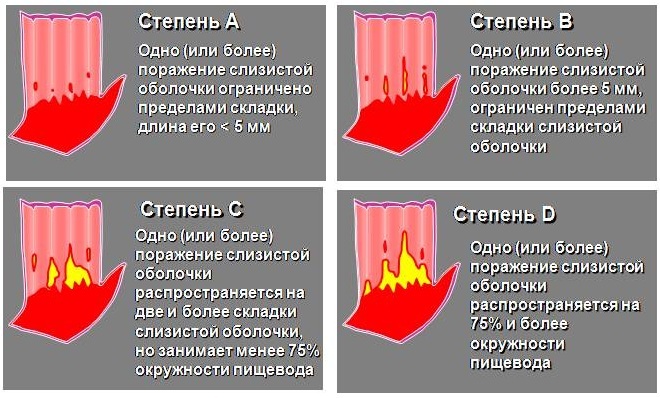
With a comprehensive examination of the patient, gastroenterologists classify the endoscopic signs of chronic esophagitis, which has 4 stages of development:
- Hyperemia of tissues without ulcers in the distal esophagus.
- Scattered small erosive defects appear on the mucous membrane.
- The existing erosion and ulcers merge with each other.
- The mucous membrane of the esophagus undergoes total defeat with ulcers, stenosis develops.
If the patient self-medicates, then there is a high likelihood of developing Barrett's disease, which is characterized by degeneration of the epithelium of the esophagus, which significantly increases the risk of oncological neoplasm of malignant character.
Diagnostics
Correct diagnosis of inflammation of the esophageal mucosa is not difficult, since the patient is worried about the characteristic localization of the pain syndrome. Interviewing the patient allows the gastroenterologist to establish the likely cause of the development of esophagitis.
To confirm the suspected diagnosis, qualified doctors use the following diagnostic methods:
- Manometry. With the help of esophagomanometry, it is possible to accurately determine disorders of esophageal motility.
-
Esophagoscopy. The procedure helps to identify all changes in the state of the mucous membrane. It is advisable to carry out esophagoscopy at least 6 days after the first manifestation of symptoms of the disease. If necessary, specialists perform an endoscopic biopsy of the mucous membrane and histologically examine the collected samples.
- X-ray. Radiography can help diagnose changes in esophageal contours, excessive mucus accumulation and tissue swelling.
Only on the basis of the collected anamnesis, the gastroenterologist can prescribe an effective treatment. Self-medication is fraught with further progression of the disease, the development of complications and concomitant pathologies.
Esophagitis treatment
Esophagitis (symptoms and drug treatment depend on the form of the disease, which the attending physician must determine at the initial stage so that the prescribed therapy is not only effective, but also safe) requires urgent gastric lavage to get rid of the chemical agent only if the disease has arisen as a result of a chemical burn. If the patient is diagnosed with an acute form of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, then for 2-3 days you should refuse to eat, focusing on taking antacids and drugs from the Famotidine group.
With a severe course of the disease, refusal of enteral nutrition is indicated. Enveloping antacid drugs are highly effective. To normalize the patient's condition in case of intoxication of the body, doctors carry out infusion therapy, using detoxification solutions for this. You can fight infectious processes with antibiotics.
Medication for reflux esophagitis
For effective treatment of esophagitis, it is recommended to take medications that help reduce the acidity of gastric juice. Anesthetic antacid gels, histamine H2 receptor blockers, and proton pump inhibitors are best. Medicines that increase the tone of the lower sphincter and accelerate the movement of the food coma from the stomach into the duodenum help to improve the patient's condition. For example, cholinomimetics, dopa receptor blockers.
Drugs and treatment regimens for an infectious form of pathology
A safe regimen of drug treatment for infectious esophagitis can only be prescribed by a gastroenterologist, guided by the collected analysis and the current condition of the patient. In 97% of cases, therapy for lesions of the esophageal mucosa lasts within 1-2 months. In severe pathology, treatment can be extended up to 5-6 months.
The following drugs are most effective:
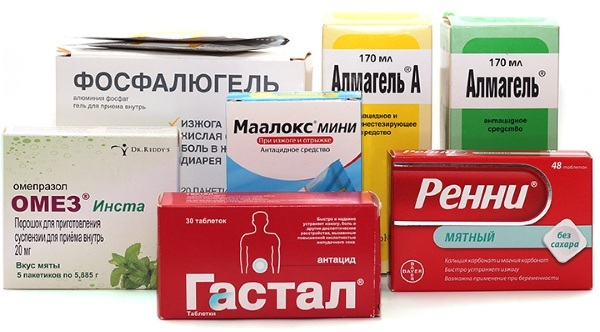
- Maalox, Gaviscon, Almagel. These drugs belong to the category of antacids, which are responsible for blocking the excess secretion of gastric juice, and also reduce the likelihood of a negative effect of hydrochloric acid on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal path.
- Prokinetic Motilium must be taken within 4 weeks. In severe cases of the disease, the therapeutic course can be extended up to 12 weeks, but only with the permission of the attending physician. The drug helps to eliminate attacks of nausea, vomiting. To achieve a positive therapeutic effect, it is recommended to take Motilium 10 mg (1 tablet) in the morning, at lunchtime and in the evening. The maximum daily dosage is 30 mg. The drug should be taken before meals. The optimal course of treatment is determined individually by the attending physician.
- Vitamins B5 and U (methyl-methionine-sulfonium) can help the body to cope with the disease much faster and accelerate the regeneration of the esophageal mucosa.
To achieve a positive therapeutic effect, it is important not only to take medications, but also to follow the diet prescribed by the gastroenterologist.
Treatment of the infectious form of esophagitis should be aimed at suppressing the causative agent of the disease:
| The nature of the disease | Recommended medicines (drug therapy) |
| Esophagitis, which is triggered by the herpes virus | Foscarnet, Acyclovir, Famciclovir. |
| Esophagitis in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) | Antiretroviral therapy in combination with high quality corticosteroids. |
| Fungal esophagitis | Oral, external, and parenteral antifungal medicines. |
| Bacterial esophagitis | Aminoglycosides, B-lactam broad-spectrum antibiotics. |
| The negative effect on the digestive tract of the Epstein-Barr virus | Acyclovir is highly effective and is recommended to be taken 5 times a day (every 4 hours). |
| Tuberculous esophagitis | To normalize the condition, the patient is prescribed standard anti-tuberculosis therapy. |
Effective treatment of other types of esophagitis directly depends on the nature of the underlying pathology, which triggered the development of the inflammatory process.
Medicines for eosinophilic esophagitis
The principle of the development of eosinophilic esophagitis is poorly understood in modern medicine, since this disease does not affect the occurrence of oncological neoplasms. The symptomatology of the disease gradually decreases after the use of inhaled steroids for 3 months. Most often, gastroenterologists prescribe Fluticasone to patients, which should be taken 2 times a day at 440 mcg. In order for steroids to enter the esophagus and not into the lungs, it is forbidden to use a spacer with an inhaler.
If inhaled steroids did not help achieve the desired result, then in the combined drug therapy includes leukotriene D4 receptor antagonists, which are recommended to be taken at 10-40 mg per day. Oral steroids are equally effective. For example, Prednisone. You need to take the drug at 30 mg per day for 14 days. The patient may also be prescribed proton pump inhibitors followed by bougienage of the esophageal structures.
Diet for different forms of the disease
With esophagitis, patients must definitely adhere to proper nutrition, excluding all prohibited foods from the diet.
Additionally, the following rules should be observed:
- The food consumed should not increase the acidity of the gastric juice.
- It is necessary to abandon products that can injure the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus, thereby provoking the development of the inflammatory process.
- Food should not increase gas production, which increases the likelihood of flatulence.
- It is not recommended to cook large portions of food for several days at once, since fresh dishes are the most useful for the body.
You need to have dinner at least 3 hours in advance. before sleep. If the patient is hungry, then you can drink a glass of milk or kefir.
| Allowed Products | Prohibited foods |
| Potatoes, beets, spinach, carrots, cauliflower. | Cucumbers, onions, tomatoes |
| Lean meats. | Chili, curry |
| Basil, oregano, garlic, fennel, sage, tarragon, rosemary, dill, parsley. | Processed cheese, as well as camembert and brie cheeses. |
| Yeast dough confectionery (in small quantities). | Fast food (fast food). |
| Herbal teas, still water. | Alcoholic drinks. |
| Soufflé, marmalade | Strong tea, coffee. |
| Soft-boiled chicken eggs, omelet | Fatty meats. |
| Porridge cooked in milk (for example, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, semolina). | Dishes with the addition of vinegar. |
| Kissel, low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, low-fat cheese, yogurt, milk. | Chocolate and all dishes with the addition of this product. |
| Banana, watermelon, pear, melon, raspberry, apricot, peach, strawberry. | Juices: grapefruit, lemon, orange, tomato. |
| Vegetable, butter |
Soups should be present in the daily diet, which are best cooked in vegetable or meat second broths. In the cooking process, you need to use cereals and vegetables, which should be simmered over low heat. Casseroles that need to be cooked in the oven are equally useful. As a side dish, you can use grated vegetables and fruits. It is allowed to use pumpkin, during the preparation of which you can add honey. For dessert, it is recommended to prepare a soufflé, to which you can serve weak green tea, jelly, homemade compote or a decoction of dried fruits.
Complications of esophagitis
Most often, complications are encountered by those patients who have been diagnosed with acute esophagitis.

With an untimely appeal to a gastroenterologist, you may experience:
- Internal bleeding, which is associated with damage to a large blood vessel in the lining of the esophagus.
- Perforation with the subsequent development of mediastinitis. For this pathological condition, purulent fusion of adipose tissue is characteristic. Negative changes also affect the lymph nodes of the mediastinum. This complication occurs as a result of the destruction of the esophageal wall.
- The formation of strictures. During this process, the damaged areas of the esophagus are replaced with scar connective tissue, which cannot contract and stretch.
With a long course of the chronic form of pathology, there is a high probability of developing laryngitis, aspiration pneumonia, bronchospasm. The patient may also be diagnosed with a disease such as Barrett's esophagus.
Forecast
With a timely visit to a gastroenterologist and the passage of the necessary drug therapy, the prognosis is positive. With the development of an acute form of esophagitis and the absence of treatment, the patient will have complications. As a result of the development of Barrett's esophagus, there is a risk that at the next examination the patient will be diagnosed with adenocarcinoma.
If there is a history of stenosis and strictures of the esophagus, the flow of consumed food into stomach, which is fraught with depletion of the body, as well as a rapid decrease in body weight with an outcome of hypotrophy. That is why gastroenterologists recommend knowing the main symptoms of esophagitis in order to timely recognize the disease and start drug treatment, since in an advanced form, pathology can significantly reduce the duration life.
Esophagitis video
Reflux esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus: