Content
- What is blood sugar and why is it needed?
- Norms of indicators by age, time of the test
- How blood sugar levels are determined
- Why does the sugar indicator "jump"?
- What does a steady 18-18.9 sugar level mean, the reasons for the increase
- How does a rise in blood sugar to 18 feel?
- Why is a sugar level over 18 dangerous?
- What to do if your sugar level is above 18
- Drugs
- Diet food
- Sugar substitutes
- Can sugar levels be stabilized permanently?
- Video about high blood sugar
Sugar enters the human blood along with food. The carbohydrates contained in food are the main source of energy, which is necessary for the vital functions of the whole organism. However, glucose should not be allowed to rise to 18 mmol / l. A high concentration of sugar in the blood will provoke the development of diabetes mellitus or other diseases, against the background of which complications arise without timely diagnosis and therapy. Treatment is selected by a physician or endocrinologist, taking into account the person's condition and the present complaints.
What is blood sugar and why is it needed?
Sugar is a simple carbohydrate. In the body of a living being, 80% of this substance belongs to glucose, thanks to which its normal vital activity is maintained.
The sugar contained in human blood is necessary to maintain the following functions:
| Name | Description |
| Energy | As a result of glucose metabolism, adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP) is produced. It provides the human body with the necessary energy by 60%. |
| Plastic | Glucose oxidation products synthesize amino acids, lipids and enzymes. |
| Structural | Glucose is part of polysaccharides. They are the backbone of ligaments, hair and cartilage. |
| Detoxification | Sugar disinfects poisons and toxins that pathogenic microbes produce during reproduction and development. |
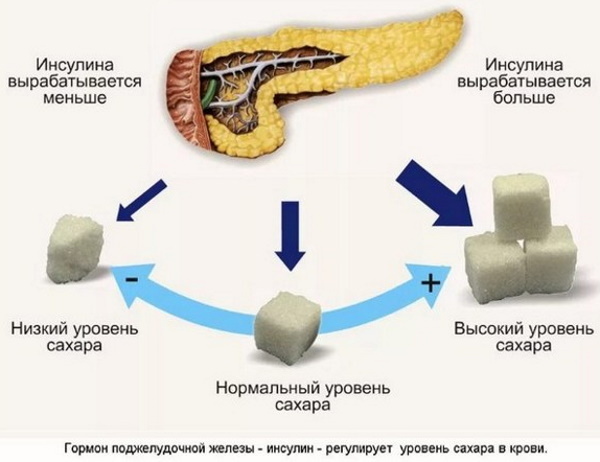 A person's blood sugar is controlled by insulin. We are talking about a certain hormone that the pancreas synthesizes.
A person's blood sugar is controlled by insulin. We are talking about a certain hormone that the pancreas synthesizes.
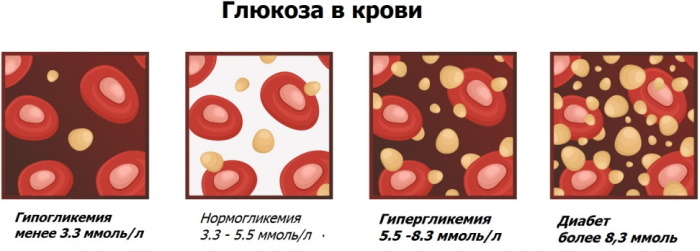
Norms of indicators by age, time of the test
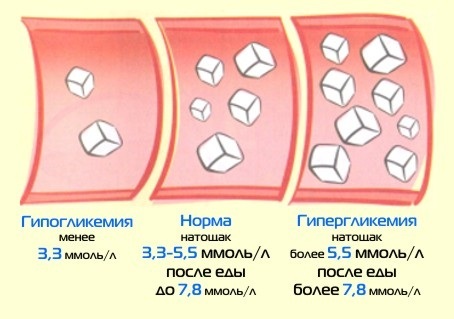
Sugar readings indicate the concentration of glucose in a person's blood. These data depend on numerous factors, including the weight and age of the patient, as well as the individual characteristics of the organism.
The standard indicators of blood sugar levels in men and women differ slightly and rarely, in most cases the norms are the same:
|
Human age (years old) |
Indicators on an empty stomach (mmol / l) | Indicators after meals (mmol / l) |
| 15-40 | 3,3-5,5 | <7,8 |
| 41-50 | 3,3-5,5 | <7,8 |
| 51-60 | 3,3-5,7 | <8,0 |
| 60 and older | 3,5-6,1 | <8,0 |
In women, a slight increase in blood sugar levels occurs during gestation. The same goes for hormonal changes.
For children, blood glucose levels differ:
| Child's age | The rate on an empty stomach (mmol / l) | The rate after meals (mmol / l) |
| Newborn | 2,77-4,0 | 7,0-11,00 |
| 6-12 months | 2,77-4,4 | 7,0-10,5 |
| 2-3 years | 3,2-4,4 | 7,0-10,5 |
| 4-5 years old | 3,5-5,0 | 7,0-10,0 |
| 6-7 years old | 4,5-5,5 | 7,0-10,0 |
| 8-14 years old | 3,5-5,5 | 6,0-9,0 |
Glucose levels in children change when puberty begins.
How blood sugar levels are determined
Blood sugar 18 mmol / L requires a thorough medical examination to determine the cause of the pathological condition and differentiate the disease. Based on the results of the study, an individual treatment regimen is selected, which is important to strictly adhere to. The tactics and effectiveness of therapy directly depend on the information received after a comprehensive diagnosis. Therefore, it is important to properly prepare for testing in order to reduce the likelihood of biased results.
Preparatory recommendations:
- It is not recommended to eat 10-12 hours before blood sampling. Testing is performed on an empty stomach.
- Before donating blood, you need to give up physical activity, avoid overwork.
- Patients should also avoid taking hormone-containing and sugar-reducing drugs.
- For several days before the analysis, adhere to a specially formulated diet. The diet will be helped by a physician or nutritionist.
- A week before testing, you must completely stop drinking alcohol.
A study of the blood sugar level is prescribed to a person in the event of the appearance of indicative symptoms (constant thirst, dry mouth, blurred vision, decreased performance). Diagnostic tests will help differentiate the disease, since many pathological processes occur along with high levels of glucose concentration in the blood.
Why does the sugar indicator "jump"?
Elevated blood sugar levels are the result of not only external provoking factors.
Many pathological processes and diseases cause disturbances:
- obesity of varying severity;
- diabetes;
- pancreas cancer;
- acute pancreatitis;
- high levels of thyroid hormones;
- malignant processes in the human body.
When the liver is damaged, blood sugar levels rise. The same applies to diseases of the digestive system, trauma to the hypothalamus, hormonal imbalance. A physician will help determine the cause of high blood sugar levels. It is important to go to the hospital when the first symptoms appear, undergo an examination and, if necessary, begin treatment.
What does a steady 18-18.9 sugar level mean, the reasons for the increase
Numerous factors trigger high blood sugar levels. Some reasons are associated with disrupted work of internal organs and systems. Other sources contribute to the launch of a pathological mechanism, against the background of which glucose indicators change.
Blood sugar 18 mmol / l is provoked by the following external factors:
- unhealthy diet, abuse of fatty and sweet foods, junk food, fresh baked goods;
- frequent stress, emotional outbursts and overexcitement;
- chronic lack of vitamin B in the human body;
- bad habits (abuse of tobacco products, alcoholic beverages);
- treatment with certain drugs (corticosteroids, beta blockers, antidepressants, and birth control pills).
Indicators of 18 mmol / l and above indicate a severe course of pathological processes. This condition is especially dangerous for the elderly, since there are irreversible changes in the work of the brain. The risk of complications is high. For this reason, the first symptoms of high blood sugar cannot be ignored; you should immediately go to the hospital.
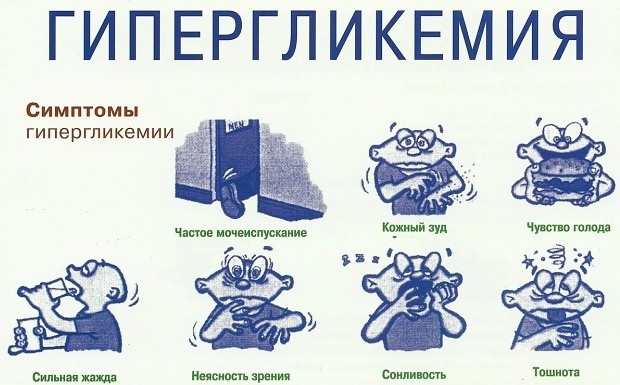
How does a rise in blood sugar to 18 feel?
The clinical picture with a high concentration of glucose in the blood will help the specialized doctor determine the stage diseases, establish a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe to the patient the most informative examination.
Blood sugar is 18 units higher than standard values, while a person exhibits the following clinical signs:
- there are sharp fluctuations in body weight;
- a person is tormented by constant thirst and hunger;
- dryness appears in the mouth;
- the urge to urinate becomes more frequent;
- wounds, abrasions and other injuries on the body heal slowly;
- a person gets enough sleep, but he is constantly drowsy;
- chronic fatigue syndrome develops;
- the smell of acetone is heard from the mouth;
- hair thinning and falling out;
- vision problems appear;
- the work of the heart is disrupted, arrhythmia develops;
- worried about itching.
 High sugar levels are also associated with dizziness, cephalalgia, and bouts of nausea. A person becomes lethargic, his performance deteriorates, apathy to the world around him, nervousness and irritability appear. The skin is peeling. There is discomfort and pain in the lower extremities.
High sugar levels are also associated with dizziness, cephalalgia, and bouts of nausea. A person becomes lethargic, his performance deteriorates, apathy to the world around him, nervousness and irritability appear. The skin is peeling. There is discomfort and pain in the lower extremities.
Why is a sugar level over 18 dangerous?
A high blood sugar level indicates the development of serious diseases in a person. The same applies to disturbed material exchange. It is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner, undergo an examination and start treatment.
Lack of therapy and progressive pathological changes will lead to the development of serious complications:
- diabetic gangrene;
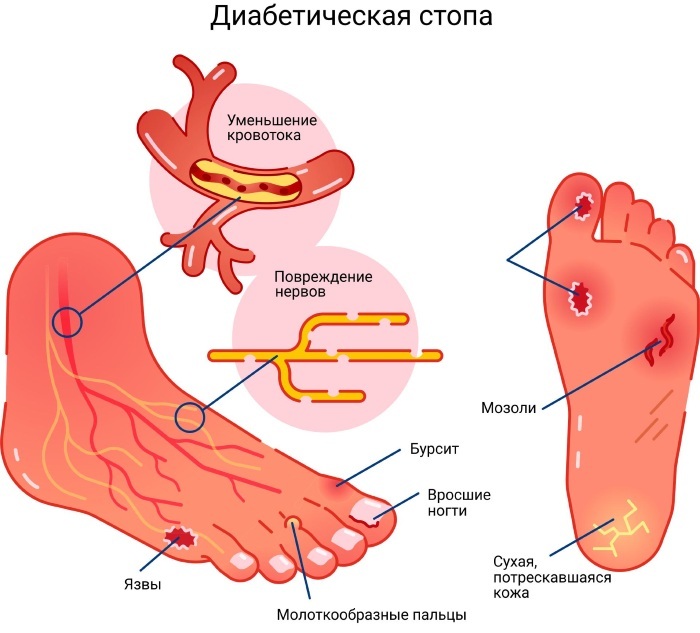
Diabetic foot - the development of concomitant pathologies against the background of a strong decrease in immunity;
- decrease in skin sensitivity;
- renal failure develops;
- the functioning of the visual organs is disrupted;
- problems appear in the work of the central nervous system;
- sexual dysfunction occurs in women and men;
- the risk of stroke, heart attack increases.
A chronic increase in blood glucose levels will lead to the destruction of the vascular and central nervous system, against which a person will also have serious complications. Among such dangerous consequences, not the last place is occupied by ketoacidotic coma. In this situation, 5-15% of patients die.
What to do if your sugar level is above 18
Blood sugar 18 mmol / l is an elevated indicator, therefore, requires complex therapy. Patients are prescribed medications, special food is selected. The therapy regimen for each patient is compiled individually. Patients are advised to strictly adhere to dosages and medical prescriptions.
Drugs
Medication helps restore blood glucose levels. Medicines are selected by an endocrinologist or therapist, taking into account the patient's condition and the course of pathological processes.
To reduce the concentration of sugar in the blood, patients are prescribed the following drugs:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Biguanides | Metformin, Glucophage | The drugs increase the sensitivity of the body's cells to insulin. Adult patients are prescribed 500-850 mg 2-3 times a day. The medicine should be taken orally after a meal or during a meal. The medical dosage, if necessary, is adjusted by the doctor every 10-15 days. |
| Sulfonylurea derivatives | Glibenclamide, Amaryl | Medicines increase the release of insulin, thereby lowering blood sugar. The drug is taken orally before breakfast or 2 times a day. The initial dosage for an adult patient is 1-1.5 mg per day, it is gradually increased to 15 mg. |
| Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) | Trajenta, Galvus | The drugs restore insulin synthesis. Adults are recommended to take 1 tablet 1 time per day. |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 (arGPP-1) receptor agonists | Lyxumia, Victoza | Adult patients are prescribed 10 mcg 1 time per day. The course of treatment lasts 14 days. The dosage is gradually increased to 20 mcg per day. |
| Alpha glucosidase inhibitors | Acarboza, Glucobay | The drugs block the absorption of carbohydrates through the digestive tract. It should be taken before meals, 50 mg 3 times a day. The dosage is slowly increased to 100-200 mg 3 times a day every 4-8 weeks. |
| Glyflozins (NGLT-2 inhibitors) | Canagliflozin, Forsiga | Medicines remove glucose in the urine. The tablets should be taken before meals. The adult dosage is 100-300 mg once a day. |
Complex treatment of diabetes mellitus involves not only taking medications, but also changing the way of life. The patient will have to monitor daily blood glucose levels. Additionally, it is recommended to engage in physical activity, eat right, and walk more and more in the fresh air.
Diet food
A diet with elevated blood sugar levels will prevent critical situations and maintain a satisfactory state of human health.
| Featured Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|
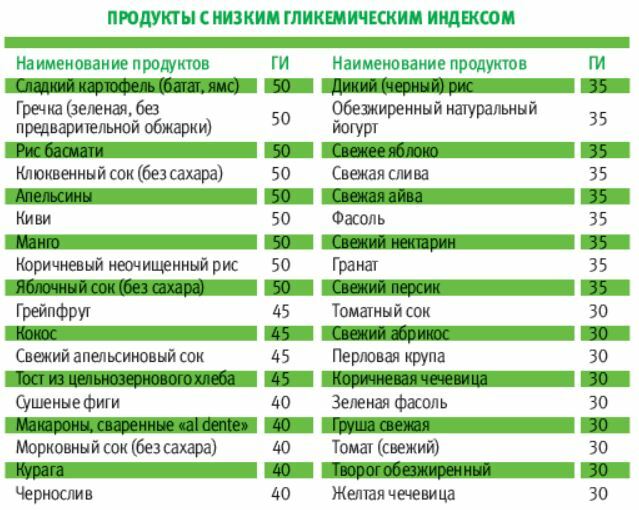 A nutritionist advises patients with high blood sugar to bake, boil, and steam. You need to eat small meals throughout the day. Drink plenty of clean, still water. Replace tea and coffee with herbal decoctions.
A nutritionist advises patients with high blood sugar to bake, boil, and steam. You need to eat small meals throughout the day. Drink plenty of clean, still water. Replace tea and coffee with herbal decoctions.
Sugar substitutes
Blood sugar at the level of 18 mmol / l is treated in a comprehensive manner. In addition, sugar substitutes are prescribed to patients. These are substances that do not affect glucose levels, but allow diabetics to feel sweetness.
Patients are offered sugar substitutes:
| Name | Description |
| Natural sweeteners |
|
| Artificial |
|
Any sweetener should be selected with a healthcare professional. Each substance has its own advantages and disadvantages, as well as contraindications. A negligent attitude towards one's health will provoke the appearance of serious complications.
Can sugar levels be stabilized permanently?
A high concentration of sugar in a person's blood in most cases provokes diabetes mellitus. The disease belongs to the category of chronic pathologies, therefore it cannot be treated. There is a possibility of coping with the disease at an early stage of development, but only on condition that a person monitors his health throughout his life. A prophylactic visit to a doctor and the delivery of all tests will prevent violations of material exchange.
If the diagnosis is established and there are still complications, it will not be possible to stabilize the sugar level forever. These patients are prescribed insulin for life. Patients are registered with an endocrinologist, since diabetes mellitus can lead to dangerous consequences, up to and including death.
You can prevent an increase in blood sugar up to 18 mmol / L if you carefully monitor your health. It is better to prevent the development of diabetes than to control it for life and are afraid of serious complications. To do this, it is enough to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, eat right, consult a doctor in a timely manner if any disorders in the body appear.
Video about high blood sugar
Malysheva about high sugar, but not diabetes:



