Content
- Description of the device
- The difference between peripheral venous catheters and abdominal
- Use of intracavitary peripheral catheters
- Peripheral catheter classification
- Safety butterfly needles
- By destination
- Diameter and color coding
- Manufacturing materials
- Teflon
- Polytetrafluoroethylene
- Polyurethane
- Vialon
- Vein selection criteria
- Morphological characteristics of suitable veins for catheterization
- Suitable for vein catheterization
- Algorithm for setting a peripheral venous catheter
- Daily catheter care
- Peripheral catheter placement video
To provide quick access to the circulatory system, perform placement of a peripheral catheter. Installation of the device often requires regional anesthesia. The algorithm clearly regulates the criteria for the selection of veins, the diameter of the needle, the rules of antiseptics.
Description of the device
A catheter is a medical instrument in the form of a hollow tube with a needle that provides medicinal or other access to the cavities and canals of the body.
The device is used for:
- supply of medicinal formulations;
- removal of pathological exudate;
- evacuation of urinary fluid;
- conducting intensive drug therapy;
- performing resuscitation procedures;
- transfusion of blood or blood components;
- the use of radiopaque substances for diagnostic purposes;
- parenteral feeding of the patient;
- the introduction of compositions of systemic anesthesia.
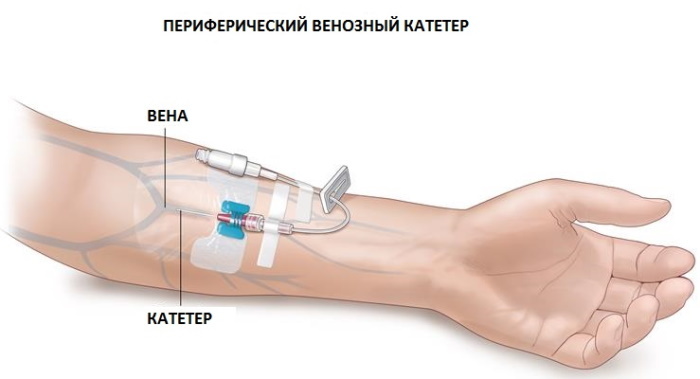
Catheterization is a procedure commonly used in hospitals. An instrument with a needle inserted into the bloodstream, lymphatic canal or other cavity of the body is fixed on the skin with a plaster or special suture material.
Placement of a peripheral catheter (the manipulation algorithm is described in detail in the guidelines for nurses) is used for infusion administration of drugs in acute conditions or long-term medication therapy.
The difference between peripheral venous catheters and abdominal
Vascular instruments are used for the supply of medicinal formulations, blood sampling, and diagnostic procedures. They are distinguished from cavity catheters by length, diameter, design. Vascular cannulas have a different purpose and staging algorithm.
Use of intracavitary peripheral catheters
This category includes the instrument of Foley, Nelaton, and other devices. The design of the first contains an inflatable chamber. Foley's peripheral cavity catheter is used in urological practice to drain fluid from the bladder.
Less commonly, the device is used in:
- radiology;
- obstetrics;
- clinical and minimally invasive surgery;
- traumatology.
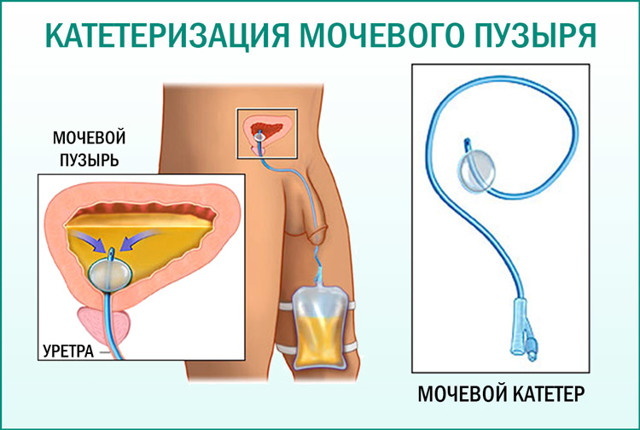
The Nelaton peripheral catheter, installed in patients with difficult or impossible natural urination, has a similar purpose. The device is intended for short-term staging in order to eliminate an acute or life-threatening condition.
Peripheral catheter classification
Intravenous instruments are divided into models with and without an additional port by design type. In the first, the auxiliary hollow chamber is located at the top of the catheter and is equipped with a sealed lid.
The auxiliary port is for bolus injections. Liquid medicine is injected directly into a vein by a jet or infusion method. An additional port is used when the device is flushed with heparin, saline, and antiseptic agents.
The plastic cover ensures the sterility of the instrument. Most modern peripheral vascular catheters have an additional port. There are devices equipped with special wing elements.
The blades of these instruments have holes to facilitate the suspension of the catheter from the skin. Safety peripheral models contain a sterile bullet-shaped capsule in the construction.
It automatically closes the sharp tip of the needle after the injection procedure. The capsule eliminates the risk of injury to the patient or medical personnel when inserting the catheter.
Safety butterfly needles
A special type of peripheral vascular instrument is a butterfly needle. The length of these catheters varies depending on the model and purpose.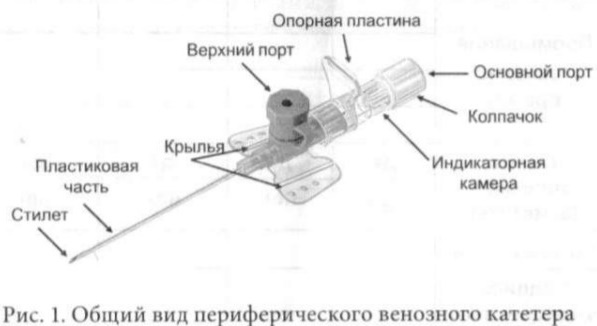
Unlike standard peripheral medical instruments, the butterfly needle is intended for short-term intravenous installation. It is used for taking blood for laboratory analysis, monitoring hemodynamic parameters in critical conditions.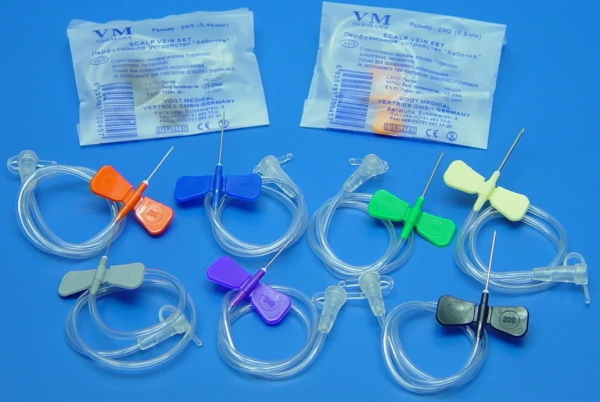
The tool has a relatively small diameter and is set for a maximum period of 24 hours. Such catheters are common in gerontological practice, resuscitation therapy, and neonatology.
Safety butterfly needles contain a key on the body, when pressed, the needle retracts into a sealed capsule. Such instruments are used in the treatment of infectious or urgent patients.
By destination
The classification of catheters by field of application includes peripheral instruments used for a wide range of diagnostic and treatment activities. Despite the similarity in design and size of such medical devices, they are not interchangeable.
The placement of a peripheral catheter, the algorithm of which is clearly regulated by methodological norms, depends on the type of product.
Classification of instruments by purpose:
- Aspiration. Used to cleanse the sinuses, oral cavity, upper respiratory tract from mucus, pathological exudate or foreign particles.
- Epidural. Placed in a cylindrical slit space between the wall of the vertebral trunk and the solid spinal cord a sheath for direct injection of a local anesthetic into the canal or immersion of the patient in a medication dream. Such catheters are used for complex surgical operations, severe skeletal injuries, and painful diagnostic procedures.
-
Urological. Such instruments are used in the treatment or to alleviate the condition of a patient with impaired renal functions, acute difficulty in deurination, and an inflammatory process in the urogenital apparatus.

- Umbilical. Such catheters are used in neonatological practice for blood transfusion to premature infants or newborns with severe intrauterine disorders.
- Gastric. Used for aspiration of the contents of the cavity during stagnation or decompression. With the help of such a catheter, drugs are delivered directly into the gastric cavity for short-term nutritional support of patients in a comatose or unconscious state.
The gastric instruments are equipped with an atraumatic distal tip, which eliminates the risk of damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus. There are trocar catheters.
Such a medical instrument is used for chest drainage, evacuation of fluid and mucus from the pleural cavity. Misuse of the catheter leads to complications.
Diameter and color coding
When selecting a tool suitable for solving medical and diagnostic tasks, the specified speed is taken into account drug composition supply, characteristics of the vascular bed, residence time in the body cavity the patient.
The size of catheters is determined by the Gage scale used to measure the diameter of tubular medical instruments, injection needles, and biopsy devices. Each type of catheter is shaded according to the size according to the international standard ISO 6009.
Sizes, colors and purpose of peripheral intravenous instruments are presented in the table:
| Shade | Purpose | Diameter, mm | Jet flow rate, l / h | ||
| Crystalloids | Plasma | Blood | |||
| Orange | Treatment of urgent patients, elimination of emergency conditions, transfusion of blood or viscous oil-based drugs. | 2,1 | 16,3 | 13,6 | 10,4 |
| Grey | Intensive drug therapy for emergencies, nutritional support, high density drug delivery. | 1,65 | 10,7 | 9,3 | 7,2 |
| White | Blood transfusions, parenteral feeding, stem cell biopsy, transfusion of viscous biological fluids. | 1,5 | 7,4 | 6,6 | 4,7 |
| Green | Blood transfusion procedures, large volumes of intravenous drugs or detoxification solutions. | 1,25 | 4,9 | 4,2 | 2,8 |
| Pink | Blood transfusions, intensive infusion therapy. | 0,9 | 1,8 | 1,6 | 1,2 |
| Blue | Infusional administration of liquid drugs. | 0,7 | 1,9 | 1,7 | 1,1 |
| Yellow | Supply of vitamin complexes, hormonal infusions, blood purification solutions. | 0,55 | 0,8 | 0,7 | 0,5 |
| Violet | Drug support for premature babies, weakened babies, treatment of intrauterine disorders and birth trauma. | 0,45 | 0,7 | 0,6 | 0,4 |
 The use of catheters in accordance with the intended purpose and in compliance with the correct technique for staging the instrument will help to avoid complications in the form of subcutaneous hematomas, phlebitis, and infiltration. The color coding, combined with the highly qualified nursing staff, facilitates the treatment of critically ill patients.
The use of catheters in accordance with the intended purpose and in compliance with the correct technique for staging the instrument will help to avoid complications in the form of subcutaneous hematomas, phlebitis, and infiltration. The color coding, combined with the highly qualified nursing staff, facilitates the treatment of critically ill patients.
Manufacturing materials
The first catheters were made of latex, elastomer, rubber mixture. These tools were reliable, durable, and reusable. Their flexibility left much to be desired, which limited the range of applications. Next generation catheters were made from various modifications of silicone polymer.
The material is distinguished by:
- absolute sterility;
- tensile and tensile strength;
- improved elasticity in comparison with other plastic substances;
- inertness in relation to any biological fluids;
- inability to react with the components of pharmacological substances.
The disadvantages of silicone catheters include increased fragility, vulnerability to temperature extremes. Microscopic particles of the tube are able to remain in the cavities of the bodies, provoking complications and negative consequences.
Inserting a silicone peripheral vascular catheter requires skill, experience, and precautions. The rules for working with such products are detailed in the algorithm for performing therapeutic manipulations.
Teflon
The material characterizes the coefficient of friction, which is reduced in comparison with other polymeric compositions used for the production of catheters. Due to this property, Teflon cannulas provide painless installation and periodic punctures.
The recommended residence time of the instrument in the venous cavity is 48-72 hours. Teflon catheters have low resistance to bending loads. With several repetitive movements, a fracture of the tube with microscopic fragmentation of the Teflon material is not excluded.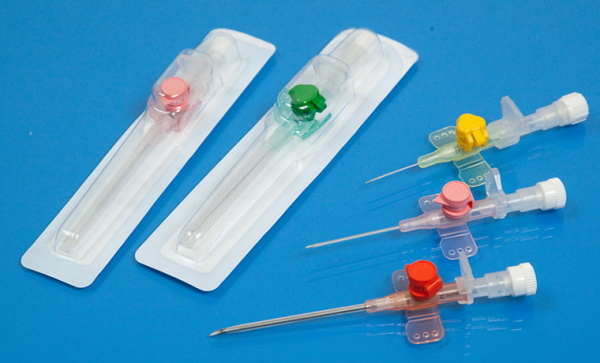
FEP peripheral catheters are suitable for most patients, clinical situations, drug formulations, or therapeutic procedures. The Teflon cannula provides reliable venous access in intensive care settings. The most famous manufacturers of such boats are Vasofix, Romed.
Polytetrafluoroethylene
PTFE material combines high flexibility with a relatively low coefficient of surface friction. Polytetrafluoroethylene catheters are used for blood transfusion, delivery of radiopaque substances, ensuring constant vascular access during resuscitation or intensive therapy.
Such a cannula is inserted into the venous bed for a maximum period of 72 hours. After the specified time, if it is necessary to continue the procedures, the instrument is replaced with a new one. The best polytetrafluoroethylene peripheral catheters are manufactured by the Venflon, Neoflon, KDM brands.
Polyurethane
The soft and thermoplastic material gently interacts with the inner surfaces of the vascular walls. The use of a polyurethane catheter reduces the likelihood of complications such as mechanical phlebitis. Close values of the temperature of the ambient air and the patient's body impedes the comfortable positioning of the instrument.
These situations include:
- summer heat;
- neonatal departments with an optimal microclimate maintained;
- prolonged stay of the catheter in the pocket of the nurse's gown just before installation;
- errors during antiseptic or cleansing procedures.
Such conditions violate the geometric stability of the polyurethane tube and force it to be assembled like an "accordion". Medical device manufacturers and suppliers in hot climates recommend before using soft boats made of this type of polymer, place the instrument in the refrigerator for 3-5 min. The device will acquire the necessary rigidity with softening immediately after intravenous installation.
Polyurethane does not have the smooth texture of Teflon. Therefore, the risk of mechanical phlebitis or blood clots is higher than with an FEP catheter. Delta Ven tools are popular.
Vialon
A modified and improved type of polyurethane material. Thanks to laser treatment of the tube surface, it becomes perfectly smooth, which reduces the risk of complications after the procedure. Such instruments are used in pediatrics and neonatology.
The placement of a peripheral catheter (the algorithm for installing the device from the vial does not differ from the intravenous administration of devices from other materials) is recommended for a maximum period of 72 hours.
The thermoplasticity index is similar to that of polyurethane. The use of a vialon instrument reduces the risk of infiltration. A common complication of catheterization is associated with the introduction of biological substances into an environment unusual for them, the structure of body tissues.
As a result, tumor or inflammatory processes develop. Vialon catheters are used in the treatment of young children, patients with vascular dysfunctions or sclerosed blood vessels. The material is patented by BD. Under license, such tools are produced by Insyte, Adsyte, Venflon Pro.
Vein selection criteria
Distal blood vessels are preferred. For primary catheterization, large, well-visualized vessels are selected. They should be soft and elastic on palpation. These veins have normal patency. It is advisable to place the catheter in a straight lumen corresponding to the length of the needle.
Attention is paid to the following criteria:
- channel diameter;
- the specified feed rate of the medicinal composition;
- the potential duration of the needle's stay in the vein;
- chemical, physiological and rheological properties of the injected therapeutic solution.
For intravenous therapy, the needle material is essential. Steel models and butterflies are used exclusively for single and short-term infusion procedures or for bolus administration of the drug.
Medicinal solutions with blood components, erythrocyte mass are fed into a peripheral vessel using a catheter with a diameter of 18-22 G or thicker. For punctures in the postoperative period, veins are selected from the side of the body opposite the surgical site.
Avoid the use of blood vessels:
- lower limbs;
- articular bends of the legs;
- veins close to the arterial lumen;
- deep-lying channels;
- veins with impaired patency and hematological outflow;
- poorly visualized and superficial vessels;
- places with signs of irritation or complications after previous punctures;
- lymphadenopathic sites;
- infected, inflamed areas;
- areas with compromised skin integrity.
- fragile and sclerotic veins.
When changing the catheter, select a place for staging above the point of the previous installation.
Morphological characteristics of suitable veins for catheterization
The blood vessels direct the hematological fluid towards the heart apparatus. The venous channels are distinguished by thin walls, a minimum volume of elastic connective tissues.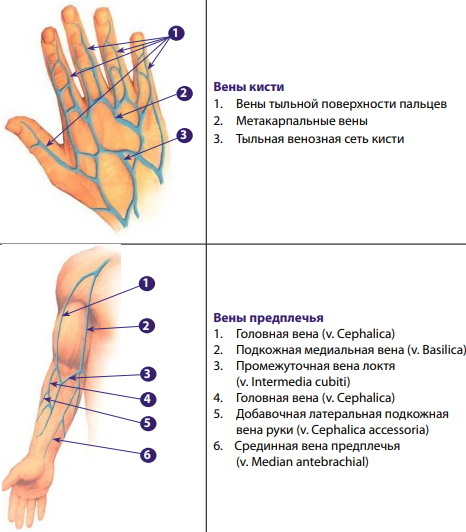
Some channels contain valve elements that prevent the backflow of blood. The inner membrane is the thickest layer of the vascular lumen, consisting of a smooth mucous membrane, flat endothelium, thin muscle fibers.
It is the damage to these structures that provokes the development of mechanical phlebitis or thrombosis. The median membrane of the venous bed is composed of muscle tissues and connective fibers.
Nerve channels pass through it, providing vascular vasoconstriction and vasodilation - reflex narrowing and adaptive expansion of the lumen, respectively.
The placement of a peripheral catheter (the algorithm requires injecting solutions with a neutral pH into such vessels) is used in treatment with isotonic drugs. Alkaline and acidic substances are supplied to the central vessels.
Suitable for vein catheterization
Such tools are used for hydration, hormonal and antibiotic therapy. A peripheral catheter is necessary for the administration of chemotherapy, electrolyte, vitamin drugs. The vein for catheterization is selected in accordance with the type, pharmacological category, and the consistency of the medicinal solution.
Consider suitable:
- subcutaneous medial vessels of the upper extremities;
- similar lateral lumens;
- median vein of the elbow;
- shoulder;
- axillary;
- subclavian;
- internal jugular;
- brachiocephalic.
When choosing a channel for permanent vascular access, the current physiological state of the patient, the degree of fragility and deterioration of the bloodstream are taken into account.
Algorithm for setting a peripheral venous catheter
Before installation, check the integrity of the sterile packaging, the expiration date of the instrument. Manipulation is carried out using a specialized treatment table or in the bed of a heavy patient using a portable stand.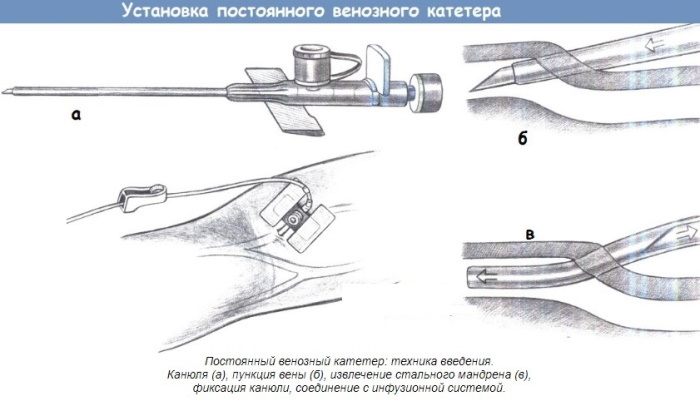
The sequence of actions according to the established algorithm:
- Provide proper illumination of the space and visualization of the area of the upcoming manipulation.
- Prepare a special medical container for the disposal of consumables and sharp accessories.
- Choose the optimal catheter insertion point.
- Apply a tourniquet 10-15 cm above the injection site.
- Ask the patient to quickly clench and unclench the fist several times to build up blood pressure.
- Treat the area where the catheter is placed with an alcohol solution, allowing it to dry.
- Remove the plastic safety cap from the needle and the plug from the auxiliary port.
- Insert the instrument into the venous lumen at an angle of 150 ° to the surface of the skin.
- Monitor the blood filling of the indicator cylinder.
- Securely fix the instrument on the body and remove the tourniquet.
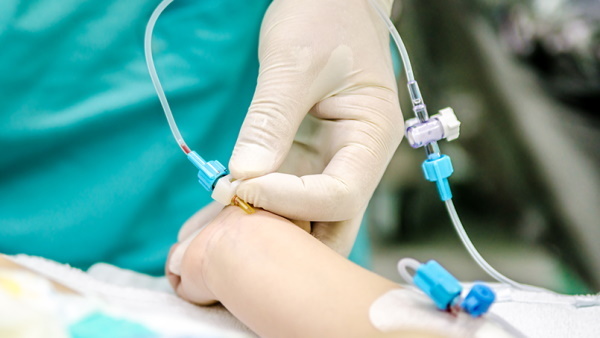
To exclude subcutaneous hemorrhage, the vein is pinched with a finger just above the catheter insertion site. To connect the infusion system, the safety plug is removed from the opposite end of the hollow tube.
Daily catheter care
The place of setting the instrument is inspected at intervals of 6-12 hours. The objects of visual control are the reliability of fixation of the device and the absence of inflammatory symptoms - edema, subcutaneous hematoma, hyperemia.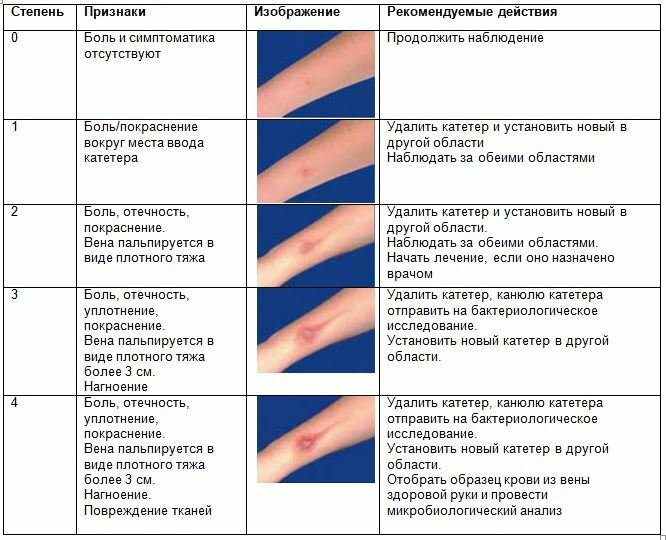
The condition of the catheterization zone is assessed according to the developed phlebitis scale. Touch the installed instrument or infusion set with sterile gloves to prevent infection.
After placement, the catheter is flushed 2 times a day with an antiseptic and before each infusion with saline. The procedure allows you to check the patency of the peripheral vein. The Daily Care Algorithm recommends flushing aids in accordance with a hospital protocol.
Peripheral catheter placement video
Technique for inserting a peripheral venous catheter:



