Content
- Causes of temperature in osteochondrosis
- Complications causing fever, associated symptoms
- Which doctor should I go to?
- What to do?
- Video about spinal osteochondrosis
Increased body temperature for any degree of osteochondrosis may indicate a gradual development of the inflammatory process. But this symptom is not associated with all diseases. Temperature rarely accompanies osteochondrosis, usually it appears against the background of the development of complications.
Causes of temperature in osteochondrosis
A person's temperature will rise for many reasons. Mainly due to infectious or inflammatory processes. Most often, it is not higher than 37 degrees and returns to normal in 1-2 days.
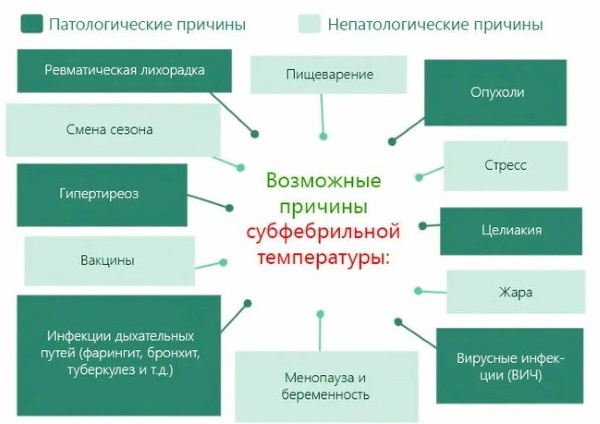
If it is higher or lasts longer, then this may indicate the development of additional diseases:
- protrusion of discs;
- pinching of nerve fibers;
- stenosis of the spinal cord canal arising from injuries, degenerative-dystrophic processes, natural wear of cartilage;
- main vertebral artery syndrome;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- neurological disorders;
- pneumonia;
- myofascial cervico-cranial syndrome;
- fiblomyalgia;
- intracranial inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- hernia of the spine.
Frequent stress, depression, spinal injuries can provoke an increase in body temperature.
Depending on the severity of the symptoms of complications, the values can rise to certain limits:
- subfebrile, with osteochondrosis it is usually not higher than 38 °;
- febrile - 38-39 °;
- high - 39-40 °;
- excessive - from 40 °.
In the latter case, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. A temperature above 40 degrees is a threat to health, raising it by 1-3 degrees can result in the death of a person
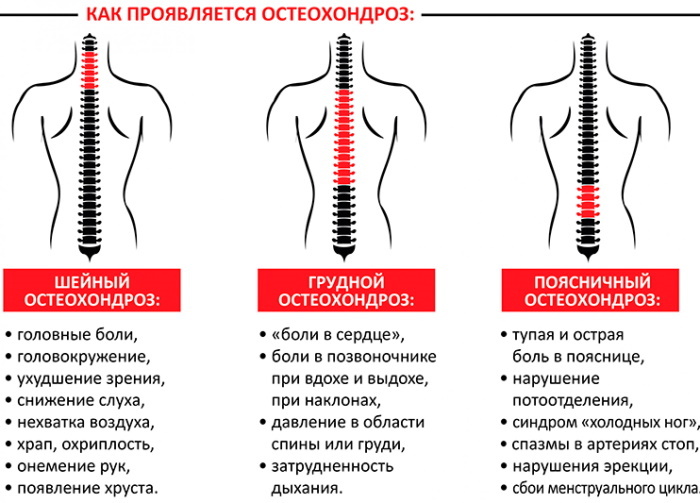
In terms of duration, it can be:
- Acute (up to 14 days). In this case, degenerative lesions of the spine are observed.
- Subacute (2-6 weeks). It lasts all the time while osteochondrosis is slowly developing.
- Chronic (from 6 weeks). It occurs in the absence of treatment for osteochondrosis.
Temperature in osteochondrosis often occurs if the disease has affected the cervical region. Less commonly, when the deformity appears in the lumbar or thoracic region. Then the temperature rises by 1-2 degrees, but decreases to normal values during the day.
Complications causing fever, associated symptoms
The temperature in osteochondrosis does not appear immediately. With this disease, degenerative changes occur in the cartilage, intervertebral discs, which is reflected in the condition of the bones. However, the temperature does not rise. It appears against the background of other diseases that appear as a complication of osteochondrosis.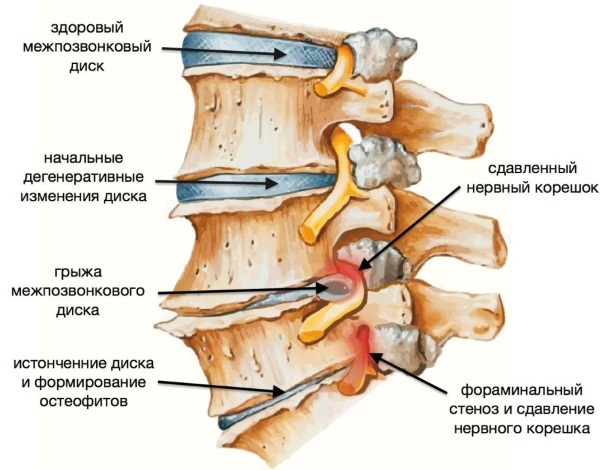
| Disease | Brief description, reasons for the rise in temperature | Additional symptoms |
| Protrusion, hernia | This is the protrusion of individual discs of the spine. But the fibrous ring remains intact. Compression of nerve fibers occurs, and then the inflammatory process begins. It is also typical for a hernia. An increase in temperature is not provoked by diseases, but by inflammation. |
Compression of nerve fibers occurs, radicular syndrome develops. Pain appears between the ribs, shoulder blades, in the arms and legs. |
| Cerebral stenosis | It appears with advanced types of osteochondrosis. There is a slow narrowing of the lumen of the spinal cord canal. This is often caused by age-related changes, microtraumas. In this case, there is a regular increase in temperature to a subfebrile value or above 38 degrees. |
There are degenerative and dystrophic disorders in the spine, wear of cartilage, bulging discs. Stenosis is accompanied by pain, inflammation, and impaired limb movements. |
| Vertebral artery syndrome | It occurs due to spasms or compression of an artery. The syndrome appears with cervical osteochondrosis. The arteries are surrounded by nerve fibers, and damage to them causes inflammation and swelling. The temperature rises due to a violation of the blood supply, but does not reach 38 degrees. If other symptoms are additionally present, then this can provoke an irreversible process - tissue necrosis and stroke. |
|
| Neurological disorders | They often arise due to discomfort and pain, restriction of movements that accompany osteochondrosis. The person begins to get nervous, against this background, the temperature may slightly rise. |
|
| Myofascial cervico-cranial syndrome | First, there are spasms, pain in the head, pressure in the skull increases. The temperature increases if the pathology is additionally accompanied by inflammation. | Headaches in the back of the head, lumbago in the neck and shoulder blades. |
| Fibromyalgia | At the same time, the strength of the connective tissue decreases, and the state of health deteriorates sharply. In addition to the main symptoms, the temperature rises. |
|
| Extrusion of vertebral discs | In this case, the correct anatomical position of the discs is violated. The temperature can rise up to 40 degrees. | Symptoms depend on the affected area, sometimes accompanied by signs of intoxication |
| Radiculitis | It is accompanied by inflammation of the spinal endings. The temperature rises to 38 degrees. | Among the main symptoms are pain, limitation of movement. Additional signs are weakness, drowsiness, redness of the skin at the site of the lesion. If sciatica is accompanied by a hernia, then the symptoms become stronger, more pronounced. |
| Myositis | This is inflammation of the muscle tissue. The development of degenerative processes enhances the pathological process and an increase in temperature. |
|
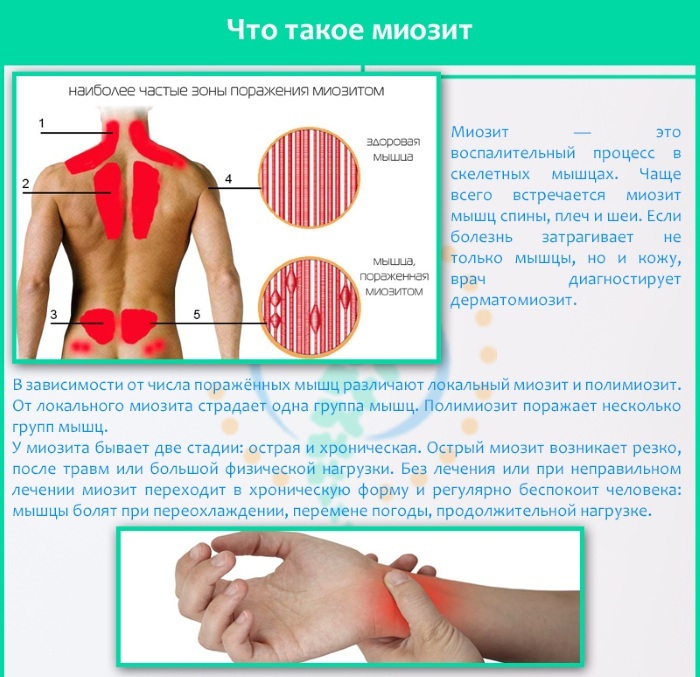 The temperature appears if an inflammatory or infectious process has begun. Then the person at first feels a slight malaise, weakness, loss of strength. Only then does the temperature rise. With inflammation - up to 37 °, with infectious processes it can reach 38 °.
The temperature appears if an inflammatory or infectious process has begun. Then the person at first feels a slight malaise, weakness, loss of strength. Only then does the temperature rise. With inflammation - up to 37 °, with infectious processes it can reach 38 °.
Which doctor should I go to?
The temperature in osteochondrosis is first measured by a therapist. He then refers the patient to a specialist physician. Usually, consultation with a traumatologist, vertebrologist or neurologist is required. Since the temperature accompanies many diseases, it is necessary to determine whether the symptom refers to osteochondrosis or is it a sign of another disease.
Therefore, they first turn to a therapist. Be sure to do a general blood test and biochemistry (if necessary, urine), examination by instrumental methods (X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MRI). It is imperative to take fluid from the spinal cord. To exclude heart disease, an electrocardiogram is prescribed. But if the cause of the increase in temperature cannot be established, then a more complete examination is prescribed.
What to do?
The temperature can be brought down with antipyretic drugs, for example, Paracetamol. But if with osteochondrosis it has not reached 38 degrees, then it is not recommended to take medications - the body must cope on its own. If this does not happen, then they take antipyretic drugs.
When symptoms are caused by an inflammatory process, NSAIDs will be more effective. These are non-steroidal drugs of a wide spectrum of action that relieve several symptoms at once (for example, Nise, Analgin, Ibuprofen). They are released in the form of tablets, suppositories, gels. Topical agents may be less effective than oral agents, but are safe for the gastrointestinal tract.
To make the drug work faster, an intramuscular injection is given. Also, injections are prescribed if due to diseases it is impossible to take medications orally. If the temperature rises during osteochondrosis, then it is important to determine the cause of the symptom. Otherwise, antipyretic drugs will only have a short-term effect.
Also, treatment is supplemented with vitamin complexes, antispasmodics (No-Shpoy, Spazmolgon), muscle relaxants and chondroprotectors. Sometimes it is necessary to take medications to improve blood supply, increase vascular tone. If the temperature is accompanied by swelling, then the patient is additionally prescribed antihistamines.
In any case, exceeding the normal values indicates a deterioration in the patient's condition. If you do not pay attention to this, it will lead to the progression of osteochondrosis and related complications. Antipyretic drugs can only help temporarily. But if they are taken uncontrollably, without a doctor's prescription, then this can aggravate the situation and worsen the patient's condition.
After elimination of symptoms, in particular pain and temperature, the patient is sent for massage, physiotherapy, and therapeutic exercises. At the initial stage of the development of complications, electrophoresis with calcium and iodine, acupuncture, and spinal traction help.
Surgical operation is performed only if the inflammation progresses, it is not possible to eliminate the symptoms with medication. Then an operation is performed, replacing the damaged discs of the spine, removing neoplasms and hernia.
Temperatures up to 37 degrees with osteochondrosis do not need to be brought down, the body itself will cope with this task. But you need to consult a doctor in any case, especially if there are additional negative symptoms (pain, lumbago, restriction of movement).
Video about spinal osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis - symptoms, diagnosis, treatment:



