Content
- Characteristic
- Symptoms
- In children
- In the elderly
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Basic methods
- Duplex ultrasound doppler
- In children
- Treatment
- Basic methods
- Surgical intervention
- Possible consequences and complications
- Carotid Coiling Video
Deformation of the internal arteries is defined as coiling, where the internal carotid arteries acquire irregular shapes, the disease can be congenital or acquired, as a result of which nodes are formed that lead to a change or blockage of blood flow, which in turn causes cerebrovascular failure.
Characteristic
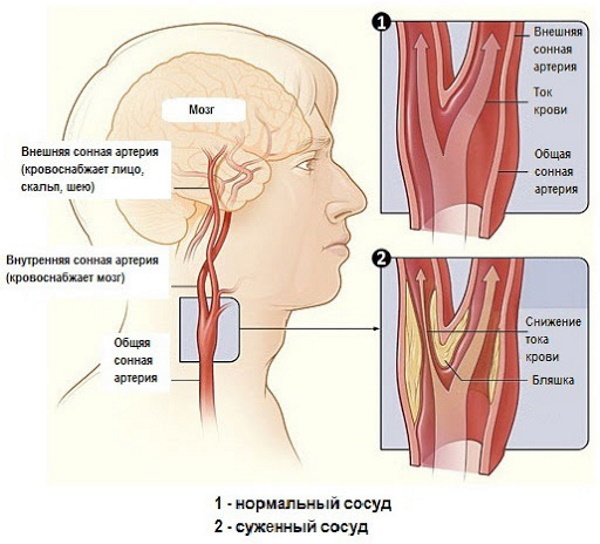
Internal carotid artery - one of the terminal branches of the common carotid artery. Its importance lies in the blood supply to most of the brain, therefore, any change in its structure or flow has adverse consequences for the body.
The position of the nodes of the arteries change due to an increase or decrease in blood pressure and the position of the human body. The blood flow becomes chaotic, due to which the blood pressure decreases in the segment where the node was formed, and the blood supply to the brain decreases accordingly. Cervical arteries, which are of particular diagnostic value, lose the elasticity of the vessel wall with age.
Loops of the carotid artery that do not coexist with arteriosclerotic lesions are characterized by the presence of neurological symptoms. The link between tortuosity of the carotid artery and cerebrovascular insufficiency was first discovered in 1951.
Anomalies of the carotid artery are a well-known phenomenon since the beginning of this century, but the etiological and clinical role and possibilities of surgical correction remain controversial. When symptoms of cerebral circulation insufficiency appear, this indicates that blood flow is impaired and there is an urgent need to conduct a detailed examination. Anomalies are divided into several types, which depend on the shape and structure of the pathology of the arteries.
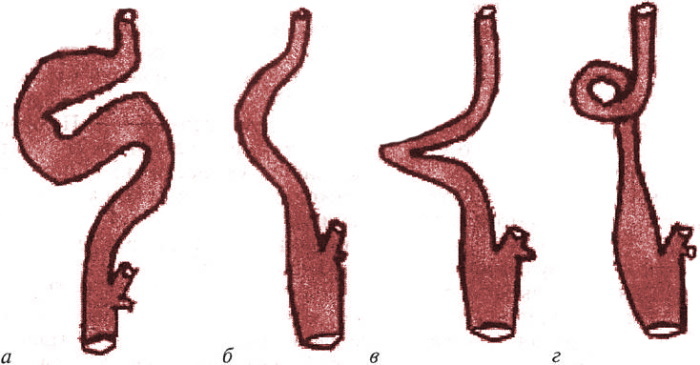
The most common types of carotid artery deformities are considered to be:
| Kinking | Arteries bend at an acute angle | Acquired or congenital form of pathology |
| Coiling | Loop formation | Acquired pathology |
| Lengthening of the artery | Length is not correct | Congenital pathology |
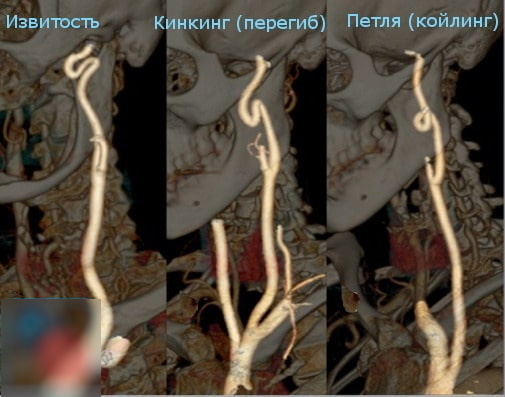
The course of cerebrovascular insufficiency during coiling can be both acute and chronic. On the one hand, this pathology is described as the cause of progressive impairment of cerebral hemodynamics, the development of neurological symptoms, transient ischemic attacks, manifestations of discirculatory encephalopathy and is a risk factor for the development of ischemic infarction brain. On the other hand, as a variant of the norm when conducting instrumental research methods, which does not affect cerebral hemodynamics and does not cause acute cerebrovascular accident.
With age, acquired hypertension aggravates the pathological state of tortuosity of the internal carotid artery, the vessels are deformed, but they adapt to the pathological state and function, providing a uniform blood flow. Research shows that not only adults, but also children who have congenital vascular anomalies are at risk.
Coiling is an anomaly of the internal carotid artery associated with a low prevalence of hemodynamic changes, in accordance with the anatomical structure. There is a significant prevalence of more frequent recurrence of episodes of transient ischemia in subjects with severe headache, in addition to other less specific symptoms such as dizziness, lipothymia, and amaurosis.
Symptoms
Clinical indications of neurological manifestations of cerebral insufficiency caused by coiling of the carotid arteries account for up to 16% of all cases caused by extracranial vascular pathology. Symptoms of the manifestation of coiling are quite diverse, they include signs of circulatory disorders, both in the carotid and in the vertebrobasilar basin. The absence of pathognomonic symptoms characteristic of the disease makes it difficult to make a diagnosis based on neurological manifestations.
Coiling of the internal carotid artery may be asymptomatic. To date, the results of randomized and single-center studies show that it is impossible to divide patients into those who show symptoms and who do not.
But there are cases when symptoms manifest as:
- ischemic attacks (temporary interruptions in the blood supply to the brain);
- the appearance of migraines, noises in the ears and head;
- the appearance of temporary blindness;
- frequent dizziness;
- short fainting;
- migraine attacks;
- the appearance of temporary paralysis of the upper limbs;
- violation of coordination of movement;
- speech disorders;
- loss of consciousness.
It should be noted that for various reasons, about 20% of patients with coiling disease remain undiagnosed. Patients do not focus on the symptoms of short-term focal neurological deficits or do not remember their history. It is also necessary to consider the possibility of a transient ischemic attack during sleep.
An important point is the dependence of the severity of symptoms of cerebrovascular accident on the position of the head. In the presence of carotid coiling, tilting or turning the head to one side or the other can cause the formation of a more pronounced bend, which can serve as a trigger for the development of cerebral insufficiency blood circulation.
In children
In children, the symptoms are difficult to recognize, often the disease goes unnoticed and unrecognized.
But you should pay attention if the child:
- Lags behind in school performance (with good performance earlier).
- Has frequent headaches.
- Refuses physical activity.
- Avoids sports activities.
- Not interested in mental and physical play.
There is also a possible link between damage to the carotid artery and cerebrovascular disease. Detected in connection with the appearance of clinical symptoms such as hemiplegia and cerebrovascular insufficiency, they are associated with anatomical variations in the carotid arteries.
In the elderly
Since the anomaly is often detected for the first time in a clinical study, symptoms, and their frequency is manifested to a greater extent in older age groups. If symptoms of neurological deficit appear during research, the suspicion of injury to the internal carotid artery is generally confirmed.
Elderly people often complain of neurological symptoms, even in the absence of stricture with the results of hemodynamic changes in the carotid artery, abnormalities can be the result of vessel aging, due to which the artery becomes wider and lengthened, arteriosclerotic damage to the wall makes it more susceptible to hemodynamic stress.
Causes
Cerebrovascular insufficiency occurs as a result of the actions of certain mechanisms, such as:
- Hemodynamic mechanism - associated with a decrease in pressure and energy subsequently reduction of blood flow during the passage through an area with loops and tortuosity, leading to a deficiency in the supply of nutrients and oxygen to brain.
- Embolic mechanism - due to the appearance of turbulent flows, causing damage to the walls and leading to formations of microemboli (platelet aggregates) with subsequent embolism of intracranial vessels brain.
According to the results of the study of the etiology of morphological variants, visible in 4-45% of angiograms, coiling, mainly acquired in connection with atheroma, aging of the body, deterioration of the internal carotid arteries of a person and hypertension. These disorders are considered asymptomatic in 80% of cases. In 4-20% of cases, patients have ischemic, neurological symptoms secondary to thromboembolism or hemodynamic mechanisms.
The thromboembolic mechanism is secondary to endothelial lesions. It is determined by impaired blood flow, but the most important mechanism is hemodynamics, when the angle of deflection reaches a high degree.
Also, the reasons for the acquired coiling are considered to be the weakening of the elastic frame of the arterial walls, changes cervical spine, which has an anatomical age character, atherosclerosis, plaque bending atherosclerotic.
In an adult, vascular disease acquires a pathological character mainly due to a number of indicators, such as:
- atherosclerosis;
- high blood pressure;
- smoking;
- diabetes;
- inflammatory diseases;
- age-related changes in the body.
In children, the disease is caused by congenital anomalies, where the vessels and arteries do not straighten properly and take a tortuous position. In such cases, in the kinks, the blood does not move correctly and because of this, the vessel wall thickens and acquires a narrow lumen or is completely clogged with a thrombus.
Diagnostics
Loops and curves of the carotid artery often do not manifest themselves in symptoms, so it is important to sometimes diagnose vessels to varying degrees, especially if the cause is ischemic disease and to assess their condition, in order to avoid stenosis. In most cases, clinical examination gives satisfactory results. Sometimes pulsating mass or noises appear.
Basic methods
Diagnosis is carried out using instrumental examination methods: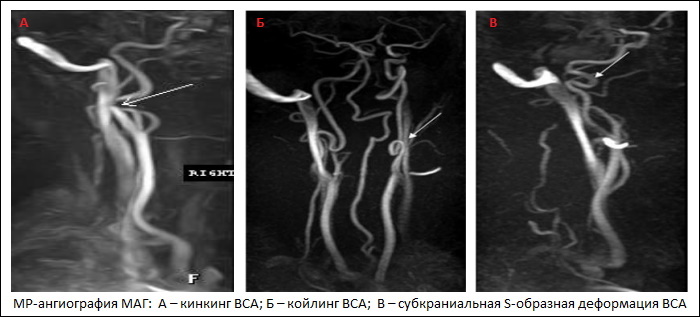
| Doppler ultrasound | Examines the vessels of the neck, head | Reveals early asymptomatic vascular lesions. |
| Arteriography | Examines the carotid arteries, vertebral and cerebral arteries | Reveals disorders in the arterial and venous circulation system. |
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Tomography) | Examines internal organs and tissues, muscles, nerves | Allows you to get high-quality images in three-dimensional image inside the body. |
| Computed tomography angiography | Radiological X-ray contrast study of the brain, blood vessels, arteries | Provides an image of the vascular system of the body in 3D slices and layers. |
| Computed angiography of axial tomography | Examines blood vessels, the degree of damage to arteries, arterial walls | Provides accurate information about vessel pathway, degree of bend and presence of stenosis, and characterization on the walls of blood vessels and arteries, for example, coexistence with atherosclerotic lesions or calcifications. |
| Doppler ultrasonography | Examines the internal carotid arteries | Facilitates the identification of loops and convolutions in the extracranial internal carotid artery. |
| Angiography | Examines the aortic arches, carotid axes and vertebral arteries | Helps to assess the presence of other anatomical changes or bilateral lesion, shows changes in position and lumen in the vessels. |
Duplex ultrasound doppler
The advent of duplex Doppler ultrasound made it possible to make a correct assessment of non-invasive morphology and blood flow in carotid arteries and the ability to study in more detail the changes in hemodynamics and the approximation to a more accurate diagnosis, however, the role carotid abnormalities in the onset of ischemic symptoms are difficult to determine due to the frequent association with atherosclerotic lesions walls of arteries.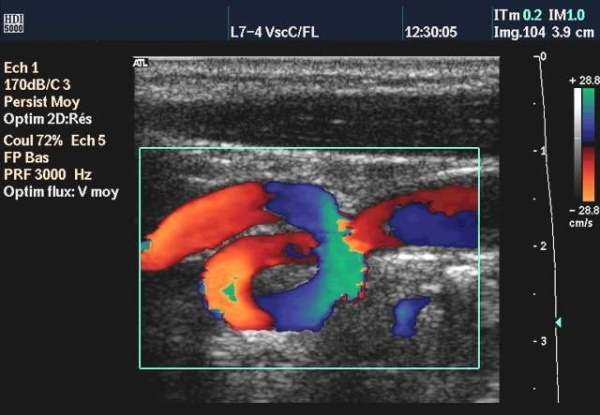
In children
In children, the disease is difficult to determine, since studies using high-tech equipment that can determine the pathology of the vascular system, abnormalities of internal and external arteries using ultrasound and angio scanning ultrasonic.
Coiling of the internal carotid artery in its manifestation has different clinical pictures and needs further research on this pathology, standardization of the diagnostic algorithm, establishment of indications for surgical intervention and optimization of the choice of the method of surgical treatment.
Treatment
The therapeutic options to ensure the correct treatment of patients with curves and loops of the internal carotid arteries remains a challenge for vascular surgeons. Carotid abnormalities are observed with different frequencies and require a different approach to diagnosis and treatment. Treatment directly depends on the degree of arterial damage, the presence of symptoms and the general health of the person.
Basic methods
The main types and methods of treatment are divided into:
- Controlling risk factors: lowering cholesterol levels, controlling diabetes and hypertension, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking.
- Taking antiplatelet drugs: acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel, dipridamole and others. Taking antiplatelet drugs that prevent platelets from clumping together, forming clots in the carotid arteries and thereby reducing the risk of stroke.
- Surgery. With a high risk of getting a heart attack due to coiling, a high degree of carotid artery stenosis.
Surgical intervention
Coiling of the internal carotid artery is associated with episodes of coronary artery disease, hemodynamic or embolic origin. This can lead to symptomatic cerebrovascular disease. In this case, surgery will be justified. The goal of treatment is to prevent stroke and cerebral ischemia.
Symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial is performed in patients who have had coiling symptoms subsequently diagnosed with cerebral infarction, in this case, surgical intervention is superior drug treatment.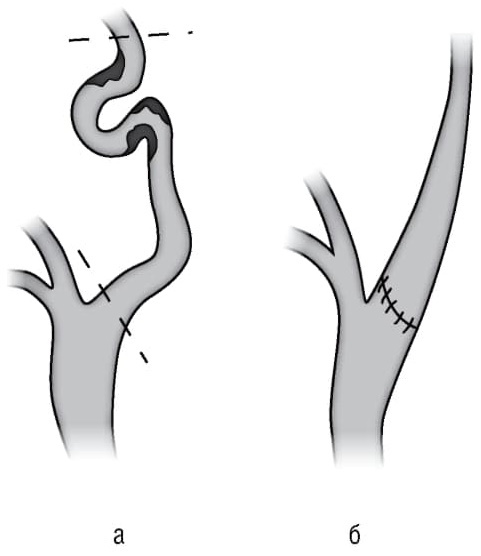
A study conducted in patients with the disease (in the absence of cerebral infarction in history), showed that surgery reduces the risk of stroke compared to treatment medication. Also, surgical intervention is indicated for patients with stroke and stenosis of more than 50% and asymptomatic patients (without a previous stroke).
Most studies comparing surgery with a carotid stent show that today surgery remains the best option for patients because it poses a lower risk of death and perioperative stroke. But one should take into account the postoperative complications in the near and distant period after the operation, such as: intraoperative stroke, which can be fatal.
In asymptomatic patients, studies were carried out much less frequently, therefore there are not enough indications for the placement of a carotid stent as the main treatment.
Today, there are practically no results of randomized studies in angiosurgery, dedicated to determining the choice of the method of surgical treatment in this category of patients. The decision on the method of surgical intervention is made by the surgeon depending on the indications and symptoms of the disease.
Possible consequences and complications
Coiling of the internal carotid artery leads to cerebrovascular insufficiency, as a result of which apoplexy can occur (cerebral stroke). Deformation of the internal carotid artery, leads to uneven blood flow, forming thrombosis of the cerebral and cervical vessels.
In people with pathology of the internal carotid artery with concomitant arterial hypertension, there is also an increased risk of transient ischemic attacks. Pathological tortuosity of the internal carotid artery or coiling, today takes the second step after the disease atherosclerosis, these diseases are the main causes leading to the development of acute and chronic cerebrovascular failure. If symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist and conduct the necessary research.
Carotid Coiling Video
What does the tortuosity of the vessels of the neck mean:
