Content
- What is glucose responsible for in a woman's body?
- The norm of blood glucose during pregnancy
- Determination of glucose level
- Are there any contraindications to the test?
- Causes of increased blood glucose during pregnancy
- Who is at risk?
- Symptoms
- Dangers of gestational diabetes to the mother
- Risks to the child
- Treatment during pregnancy, monitoring indicators
- Diet, prohibited foods
- Insulin medication
- Childbirth with GDM
- What to do after childbirth
- Forecasts
- Video about high sugar in pregnant women
Gestational diabetes - a common complication of pregnancy. The pathological condition is characterized by increased blood glucose due to temporary insulin resistance. The metabolic response to the release of a protein hormone is impaired during the growth and maturation of the placenta.
What is glucose responsible for in a woman's body?
The disease does not meet the criteria and signs of a manifest diabetic syndrome, it is due to the physiological state. Glucose uptake is the basic function of cells.
Monosaccharide serves as the main and universal source of energy. Glucose is responsible for the tone of the whole body and individual organs. It regulates metabolic cycles, metabolic reactions.
The products of glucose breakdown by insulin serve as reduced coenzymes in the respiratory chain. Glucose is an essential nutrient for living organisms. In the oxidation or breakdown of the monosaccharide, more than 1/3 of the total energy used is released.
Increased blood glucose during pregnancy is a pathological condition provoked by hormonal changes. The monosaccharide is responsible for the functioning of skeletal muscles. Neurons, including cerebral ones, receive energy for work exclusively from this biological substance. Such cells consume 20-30% of the products of glucose oxidation formed as a result of the metabolic cycle.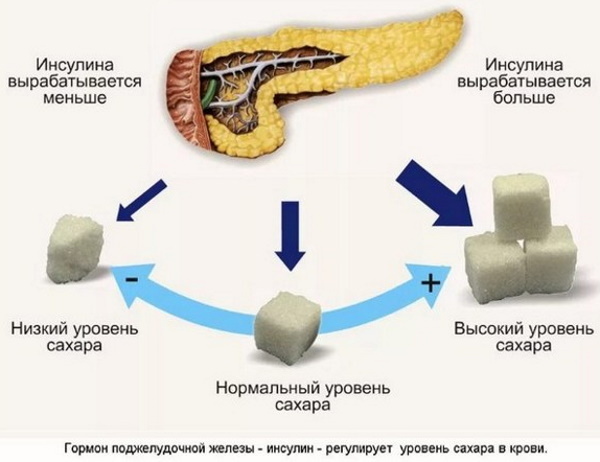
The specific oligosaccharides contained in it form the basis for determining the blood group. The rheological properties of the hematological fluid depend on the key biological energy carrier.
The norm of blood glucose during pregnancy
During the gestational period, the concentration of the monosaccharide is subject to fluctuations depending on:
- trimester;
- diet;
- physical activity;
- taking vitamin complexes or medicines.
During pregnancy, some change in the susceptibility of insulin cells against the background of systemic glucose tolerance is not considered a pathological abnormality. The difference between natural fluctuations and gestational diabetes is the degree of metabolic disorder.
A concentration of 5.8 mmol / L in the analysis of venous blood during pregnancy is considered the norm. The permissible range of the energy monosaccharide content in the biological material obtained by puncturing the skin of the terminal phalanx of the finger is 4.0-6.1 mmol / l.
A slight upward deviation of the indicator is caused by:
- natural hormonal changes, individual for each pregnant woman;
- stress experienced shortly before the laboratory procedure;
- severe physical fatigue;
- a state of emotional excitement.
In the vast majority of women, gestational hyperglycemia occurs between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation. The rate of blood glucose during pregnancy depends on the type of hematological test and related factors.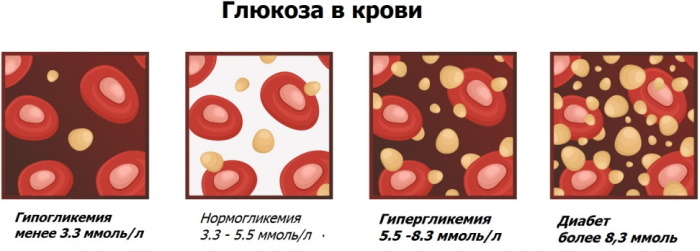
Normal gestational values for different tests are presented in the table:
| Single hexokinase test | ||
| Against the background of a meal | Blood from a vein | Capillary material |
| On an empty stomach | 4.0-5.5 mmol / l | 3.5-5.0 mmol / l |
| Glycemic profile | ||
| On an empty stomach | 4.2-5.5 mmol / l | 4.0-5.0 mmol / l |
| 3-hour oral insulin resistance test | ||
| On an empty stomach | Up to 5.1 mmol / L | |
| After 1 hour. after meal | Up to 10.0 mmol / L | |
| After 2 hours. after meal | Up to 8.5 mmol / L |
For any type of hematological tests, deviations in the direction of decrease or increase by a maximum of 0.5 mmol / L are allowed. The distortions of the results are influenced by the errors of laboratory instruments, daily fluctuations in the concentration of the energetic substance in the blood.
Determination of glucose level
The most accurate diagnostic information can be obtained by laboratory analysis of biological material from the main vein. The composition of capillary blood is subject to daily and situational changes.
The use of vacuum biomaterial sampling systems ensures maximum sterility. When using a butterfly needle, interaction with the environment is excluded.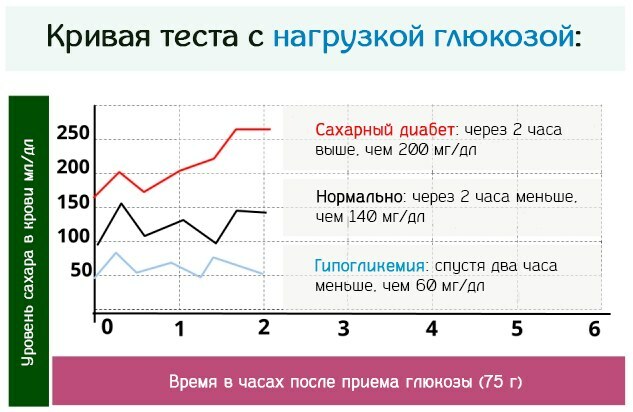
To collect capillary blood from the terminal phalanx of the finger, special microtubes with an anticoagulant located at the bottom of the laboratory vessel are used. The method provides for the free flow of liquid along the walls of the flask.
Such a test is used for express diagnostics for severe symptoms of gestational diabetes or other disorders of carbohydrate balance. When registering a pregnant woman with a antenatal clinic, a comprehensive examination is required.
The standard diagnostic package includes a laboratory test for the concentration of glycated hemoglobin in blood plasma. For accurate detection of GDM, only a glucose tolerance test is used. It can be intravenous or oral.
Increased blood glucose during pregnancy in this way is determined with maximum reliability. The essence of the oral technique is to measure the parameters of the metabolic response to an exogenous monosaccharide.
Women are offered a drink in 5 minutes. 200 ml of warm water with 75 mg of glucose dissolved in it according to Russian rules and 100 mg according to the principles of American diagnostics. Sequentially after 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes. dynamically determine the content of glucose in the venous blood.
The most highly specific method for laboratory diagnostics of hidden metabolic disorders during pregnancy is hexokinase UV study. Radiation does not interact with other components of the plasma blood fraction.
Glucose is recorded with an ultraviolet wave of 340 nm. The diagnostic method is linear up to 50 mmol / l, which allows it to be widely used in obstetric-gynecological and endocrinological practice.
Are there any contraindications to the test?
The use of the laboratory method is limited by absolute clinical prohibitions or relative ones.
Glucose tolerance test is not prescribed for patients with:
- established anaphylactic reaction to saccharides;
- biological intolerance to exogenous glucose;
- any type of diabetes diagnosed before pregnancy - in such a situation, additional research is not required;
- exacerbation of pancreatitis;
- digestive pathologies associated with impaired absorption of saccharides.
Relative contraindications include early toxicosis and preeclampsia, a multisystem disorder that develops after the 5th month of gestation. The disorder is characterized by a spontaneous increase in intravascular pressure, proteinuria, signs of multiple organ failure.
Causes of increased blood glucose during pregnancy
The etiological and pathogenetic factors of gestational diabetes have not been precisely established. Presumably, hormonal compounds responsible for the growth of the embryo inhibit insulin production.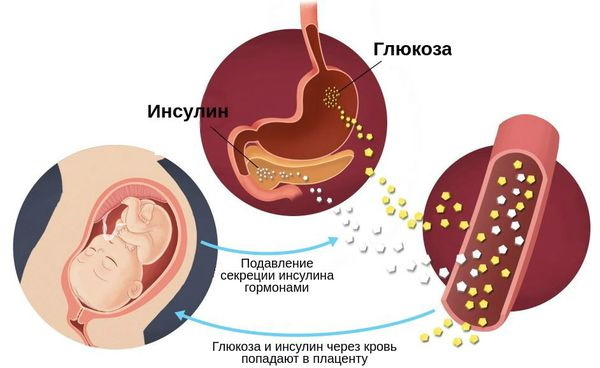
The probable causes of the development of gestational diabetes include:
- infectious hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- systemic neuroendocrine disorders;
- polycystic ovary;
- history of Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome - severe combined regulatory dysfunction of the hypothalamus, pituitary and adrenal cortex;
- hyperthyroidism - excessive secretory activity of the thyroid gland;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- neoplastic processes in the body of the pancreas or in the surrounding lipid membrane;
- hormone-dependent oncological diseases - glucagonoma, pheochromocytoma.
GDM develops due to excessive consumption of carbohydrates against the background of a violation of their assimilation. Among the causes that can lead to an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood during gestation, poisoning with carbon monoxide is called.
A pathological condition in women carrying a child arises from uncontrolled intake drugs based on prednisolone, synthetic estrogens, hormone-containing oral agents contraception.
The injection of monosaccharide into the blood is observed in patients using phenothiazine drugs or beta-blockers. Some endocrinologists believe that the cause of gestational diabetes is autoimmune pathologies that destroy the pancreas or inhibit its functions.
Who is at risk?
Increased blood glucose is more common in women who are overweight or morbidly obese. In the risk group, patients with a body mass index over 30 kg / m2. During pregnancy, diabetic syndrome is often recorded in women under the age of 18 or over 40.
The risk group includes patients with:
- glucosuria - the release of an energetic monosaccharide into the urinary sediment;
- complication of previous pregnancies - intrauterine fetal death, miscarriage, hydramnios;
- bad habits - alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction;
- lack of physical activity;
- polycystic ovary;
- genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- pathological or hereditary short stature.
More often, glucose in blood plasma rises in representatives of the Negroid and Mongoloid races than the Caucasoid. There is a significant risk of developing gestational diabetes with arterial hypertension. Among the factors of current pregnancy, multiple pregnancies are distinguished.
The use of beta-blockers or corticosteroid drugs to prevent premature labor increases the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes by 15-20%.
Symptoms
The endocrine disorder associated with pregnancy has no specific signs and is characterized by a meager or mild clinical picture. General weakness and fatigue are observed, which women attribute to their physiological state.
Severe hyperglycemia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- constant thirst;
- drying out of the lips and mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- frequent urge to urinate characteristic of gestation;
- profuse deurination;
- the development of fungal infections of the genitals;
- decreased visual acuity;
- depressed appetite.
Itching in the perineum, insomnia, and cardiac arrhythmia are nonspecific signs of gestational diabetes. There is swelling of the lower extremities due to a violation of the outflow of lymph.
Dangers of gestational diabetes to the mother
The main risks are associated with impaired rheological properties of blood, accelerated destruction of the vascular walls by increasing pressure, and cardiac dysfunctions.
Excess glucose accumulates in the tissues of organs, introducing destructive changes in their morphological structure.
Against the background of the GDM, the following develop:
- Diabetic retinopathy - defeat of small blood channels, receptor elements of the retina of the optic organ. The complication leads to severe ophthalmic dysfunction.
-
Nephropathic syndrome - complex damage to the glomerular filtration mechanism of the kidneys, tubular ducts. This leads to the development of functional organ failure.
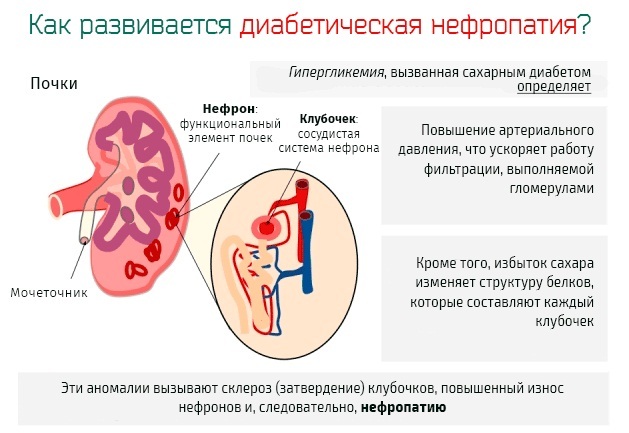
- Increased intravascular pressure. Increases the risk of hemorrhage, spontaneous abortion.
- Metabolic disorders. In 50-60% of women who have had gestational diabetes, obesity occurs within 5-6 years after childbirth.
- Placental abruption. Due to hyperglycemia, the membrane that connects the blood flow of the mother and child is separated from the uterine walls. The pathological process is characterized by bleeding, pain in the pelvic zone.
Increased blood glucose during pregnancy causes a long-term effect in the form of an increase in the likelihood of developing chronic cardiovascular pathologies.
Risks to the child
Gestational diabetes is associated with rapid weight gain by the embryo. This pathological effect is called macrosomia. A child weighing over 4 kg has an increased risk of birth injuries. A caesarean section is often required. Diabetic fetopathy of the mother turns into a violation of carbohydrate metabolism in the neonatal period of the infant's life. The newborn often develops respiratory distress syndrome.
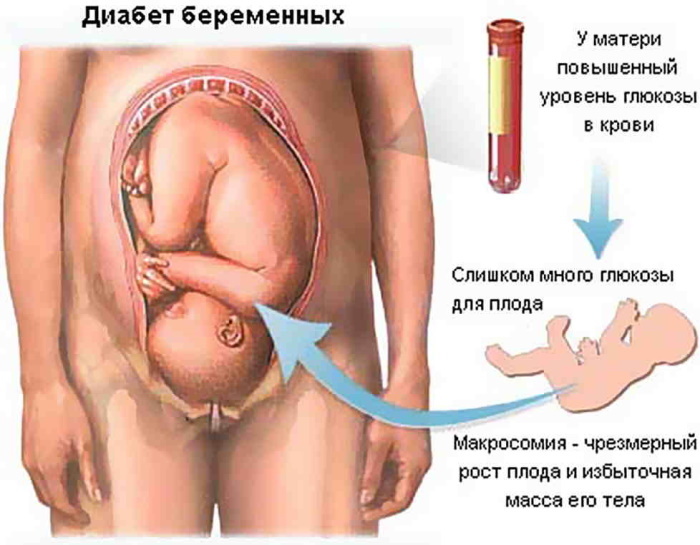
The disorder is characterized by the inability of the lungs to provide blood and body tissues with the required volume of the respiratory mixture. The result is cyanosis, multiple organ failure. An excessive amount of bilirubin is released into the newborn's blood, which leads to postpartum jaundice. Macrosomia causes increased insulin secretion, shoulder dystocia - distortion of body proportions.
Among the long-term consequences of GDM for a child are obesity at the age of 4-5 years, arterial hypertension at 10-11 years. The risk of developing overt diabetes mellitus in adolescents born against the background of such a metabolic disorder is estimated at 20-40%.
Treatment during pregnancy, monitoring indicators
Therapy for gestational diabetes requires an integrated approach. Throughout the entire period of pregnancy, the glycemic index of the woman's blood is monitored. A specialized low-carb diet is prescribed.
The patient is instructed on the principles of a balanced and balanced diet. Treatment for gestational diabetes is carried out on an outpatient basis. Self-monitoring of blood plasma monosaccharide saturation is performed 4-5 times a day using a portable glucometer.
Diet, prohibited foods
Diet correction is an important measure in the management of gestational diabetes.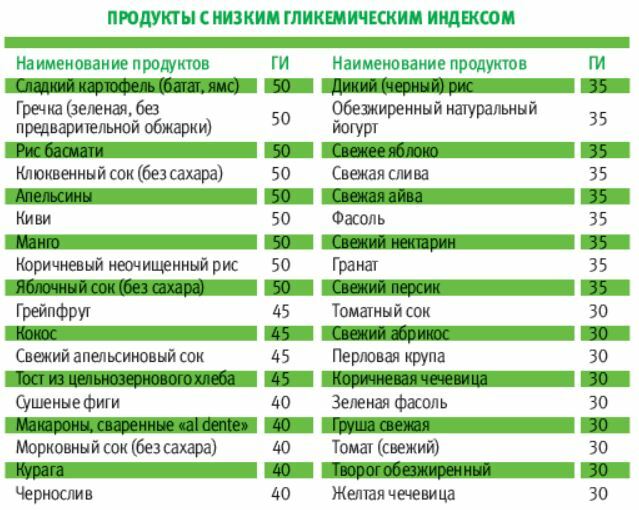
The menu completely excludes:
- confectionery products;
- starchy vegetables and roots;
- flour products;
- homemade yeast baked goods;
- vegetable fats;
- Bee Honey;
- fast food.
Low-carb diets are not suitable for pregnant women. Products with a high glycemic index are replaced with approved counterparts. They eat small portions with an interval of 2-3 hours.
Reducing the intake of starchy foods is combined with an increase in the amount of absorbed protein nutrients.
Exclude from the diet:
- rice;
- White bread;
- pasta;
- cereal porridge;
- potato;
- soy;
- corn.
Complex carbohydrates, which are slowly absorbed, stabilize blood glucose levels. These products are recommended for use during gestation.
These include:
- table greens;
- hazelnuts;
- cottage cheese;
- cucumbers;
- olives;
- pineapples;
- persimmon;
- oranges;
- lentils.
They should be at least 55% of the daily nutritional value. With overweight, calorie content is limited to 1800 kcal / day. The recommended daily fiber intake is 28 g.
The formation of ketone bodies is prevented by breaks between meals lasting 10 hours. Reduce weight gain, improve insulin sensitivity, animal proteins, mono- and unsaturated lipid acids.
Insulin medication
Increased blood glucose during pregnancy is eliminated by hypoglycemic drugs that form the basis of therapy. The endocrinologist or gynecologist prescribes the dosage and frequency of use of synthetic insulin individually.
Such drugs do not possess teratogenic activity and have a high safety profile for the fetus. High-quality control of hyperglycemic state is provided by an insulin pump, which serves as a gentle alternative to daily antidiabetic injections.
The device is used for continuous subcutaneous administration of hypoglycemic drugs. The electronic model is programmed to operate in an automatic mode with constant monitoring of the blood glucose level displayed on the display.
When indicated, oral medications are used to lower blood sugar. Controlling the glycemic state allows the doctor to quickly respond to metabolic changes, adjust the insulin treatment regimen, if necessary.
Childbirth with GDM
Gestational hyperglycemia is not considered an obstacle to vaginal delivery in the absence of fetal macrosomia associated with metabolic disorder. Natural childbirth takes place at 38-39 weeks of gestation.
With a large child, a cesarean section is performed. The surgical procedure is indicated for severe diabetic fetopathy, narrowed pelvic bones of a woman, concomitant pathological conditions or complications of pregnancy.
What to do after childbirth
Gestation is often associated with metabolic disorders and the development of diabetic symptoms. After childbirth, stabilization of hormonal parameters contributes to the disappearance of the signs of GDM.
A woman should be under constant supervision of an endocrinologist to exclude the risk of developing manifest type 2 diabetes mellitus. With subsequent pregnancy, there is a high likelihood of the pathological condition returning. Insulin therapy prescribed during gestation is often canceled after delivery.
In the first week of lactation, the concentration of the energy monosaccharide in the plasma fraction of blood is controlled by laboratory analysis of hematological fluid obtained from the main vein or rapid capillary tests biomaterial.
With normal glucose levels, additional therapeutic measures are not used. A control test for monosaccharide tolerance was recommended 1.5-3 months after childbirth to exclude the development of overt diabetes mellitus.
During the recovery period, they follow a low-carbohydrate diet, use dosed physical activity or a complex of exercise therapy. There are no restrictions on breastfeeding. They work only in the treatment of fungal infections provoked by gestational diabetes with the transfer of the child to artificial milk formulas.
Forecasts
The use of insulin therapy reduces the likelihood of complications by 98%. The prognosis for a woman and a newborn is favorable. The danger is the asymptomatic course of gestational diabetes. The lack of medical intervention leads to numerous intrauterine malformations, complicated childbirth.
Macrosomia, hypoglycemic syndrome, respiratory dysfunction are the most common consequences of increased plasma glucose during pregnancy. Often the infant has a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism, the likelihood of developing obesity in adolescence increases.
Video about high sugar in pregnant women
Doctor about gestational diabetes: