Content
- Classification of diseases
- Angina
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Flu
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Scarlet fever
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Diphtheria
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Epiglottitis
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Laryngitis
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Phlegmon
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Videos about diseases of the throat and larynx
Diseases of the throat and larynx - this is a large list of pathologies, photos and descriptions of which are presented in more detail below. They are caused by inflammation, colds, infections, and other factors. Often, throat diseases are secondary pathologies that have formed as a complication of the main one. Some are mild and heal quickly, while others can pose serious health risks and cause death.
Classification of diseases
Diseases of the throat and larynx are presented in several classifications. Photos and descriptions of the most common pathologies are described separately below. Most often they are infectious.
| Group | general description |
| Viral | Such diseases include ARVI, influenza, chickenpox and measles. When the inflammation spreads to the throat, it feels sore and painful. This group also includes infectious mononucleosis, which occurs due to the herpes simplex virus type IV. It is dangerous by the spread of inflammation to the liver or spleen. All viral diseases have common features. In addition to sore throat, there is a loss of strength, migraine, general weakness in the body. If the temperature rises, it is usually insignificant. With acute respiratory viral infections or flu, a cough, a runny nose, and measles, smallpox are accompanied by a rash on the skin. |
| Bacterial | The most common disease in this category is sore throat. Many pathogens can provoke it. Angina has a separate classification:
Also, bacterial diseases include diphtheria, scarlet fever, which, in addition to sore throat, are characterized by perspiration, swelling of the tonsils, an increase in temperature to 40 ° C. Epiglottitis is diagnosed before 4 years of age, and leads to severe respiratory failure. |
| Fungal | This group includes diseases that are triggered by the multiplication of yeast-like fungi. Such pathologies include tonsillitis, pharyngitis. Laryngitis has a separate classification. Acute - catarrhal, edematous, phlegmonous. Infiltrative-purulent has two types - infiltrative, abscess. Chronic laryngitis can be:
If they have a fungal nature, then a white bloom appears on the mucous membranes of the throat, pain occurs, but the temperature is kept within normal limits. Mycosis occurs due to vitamin deficiency, weakened immunity, hormonal drugs. The disease can cause prolonged antibiotic treatment or gastrointestinal disturbances. |
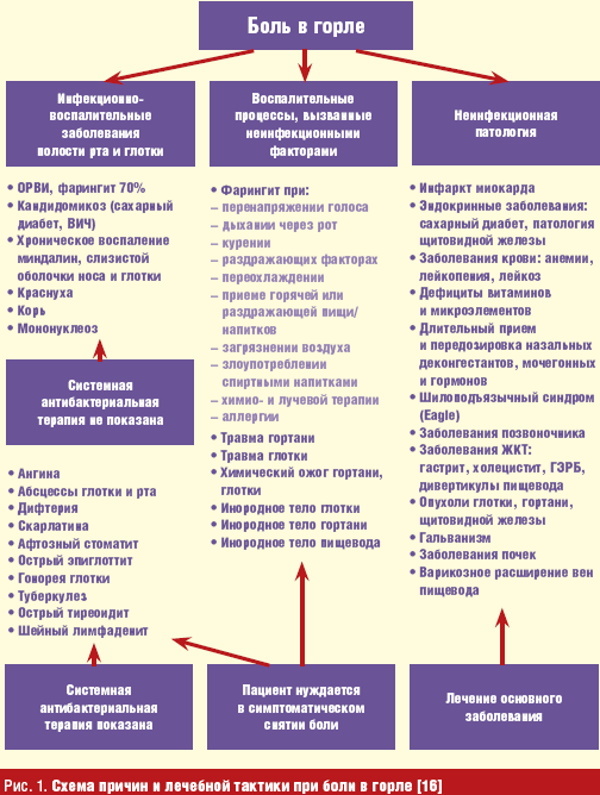 Also, diseases of the throat and larynx are divided into separate groups depending on the reasons caused by:
Also, diseases of the throat and larynx are divided into separate groups depending on the reasons caused by:
- benign neoplasms;
- malignant tumors and metastases;
- diseases;
- a foreign body entering the throat;
- laryngeal injuries.
Classification of diseases caused by inflammation:
- laryngitis;
- chondroperichondritis;
- epiglottitis;
- pharyngolaryngitis;
- perichondritis;
- laryngotracheitis.
Diseases of the throat and larynx (photos and descriptions of common pathologies are presented below) can appear immediately at birth - due to the abnormal structure or improper intrauterine development of the fetus.
Angina
Angina is an infectious pathology, which is accompanied by inflammation of the tonsils in the pharyngeal ring. More often affects the palatine. Angina is transmitted by food or airborne droplets, hematogenous (through the bloodstream). Appears after trauma, as a complication of other diseases.
Symptoms and Signs
The first symptoms appear 10 hours after the pathogen enters the body. The patient's temperature rises to 38-40 ° C, severe weakness and chills appear. The feverish state becomes permanent. 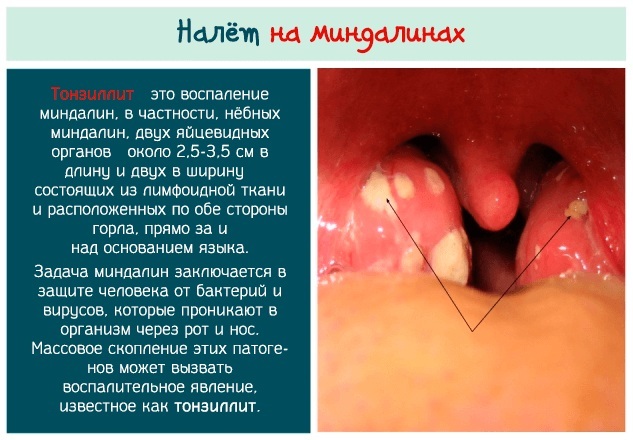 Then there is a sore throat and when swallowing, aching joints, muscles. The peri-maxillary lymph nodes are enlarged. The palate, tonsils and uvula become red, hyperemic. On the third day, a purulent plaque may appear on the mucous membranes.
Then there is a sore throat and when swallowing, aching joints, muscles. The peri-maxillary lymph nodes are enlarged. The palate, tonsils and uvula become red, hyperemic. On the third day, a purulent plaque may appear on the mucous membranes.
Causes
More often, the cause is the penetration of microorganisms by airborne droplets, less often - as a result of other pathologies.
The main pathogens:
- diplococci;
- enteroviruses;
- staphylococci;
- pneumococci;
- streptococci;
- Candida fungi.
The appearance of sore throat causes hypothermia, weakened immunity, vitamin deficiency. The tonsils are negatively affected by tobacco smoke. Other causes are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and ENT organs, alcohol abuse.
Treatment methods
For angina, drink plenty of fluids, antibiotics of the group of penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins. Additionally, rinse the mouth and tonsils with antiseptic solutions, decoctions and infusions with medicinal herbs (for example, with chamomile). They give drugs to strengthen the immune system, antihistamines, pain relievers. With severe intoxication, detoxification parenteral infusion therapy is prescribed.
Flu
Diseases of the throat and larynx (photo and description give a general idea of the pathology) include influenza. It is a respiratory viral infection that affects the upper respiratory tract. It is transmitted by airborne droplets. The patient is contagious for the first 5-6 days. The incubation period is 12-48 hours. Influenza is of two forms - typical and atypical, in severity - four degrees, it can be complicated.
Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms appear in the first hours of the disease. A person's temperature rises to 40 ° C, chills, headaches occur.
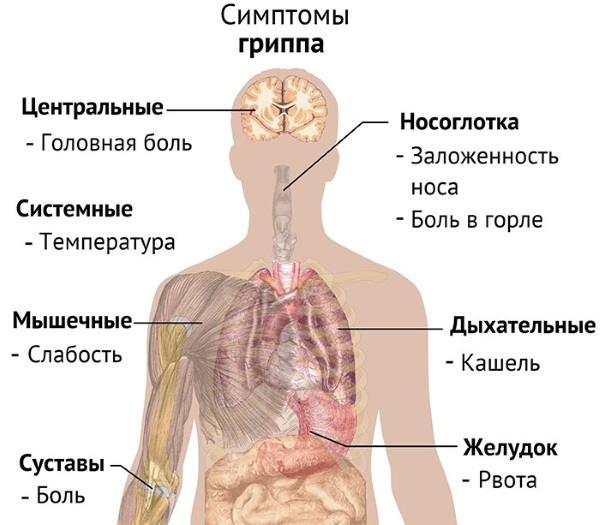
Other symptoms:
- severe weakness;
- sore throat;
- confusion of consciousness;
- tachycardia;
- pain when moving the eyeballs;
- dry cough;
- runny nose, nasal congestion;
- pain in the nasopharynx and throat.
The intensity of the symptoms depends on the severity of the course of the disease. In difficult cases, vomiting is observed, the temperature rises to a delusional state. Influenza is dangerous for its complications (for example, difficulty breathing, pulmonary edema). When the infection joins, pneumonia develops.
Causes
Influenza is caused by seasonal viruses A, B and C. The first two cause epidemics, moderate or severe in severity. Virus C has been little studied, but the disease is mild and does not cause severe symptoms. Influenza is transmitted by airborne droplets, the infection zone around the patient is up to 3 m.
Treatment methods
The patient is immediately prescribed antiviral drugs. For example, "Oseltamivir", "Zanamivir", "Peramivir". You need to drink more liquid, especially with a high concentration of vitamin C (for example, cranberry juice), milk with honey. From the temperature give "Paracetamol". Gargle daily with infusions of chamomile, sage or eucalyptus. You can bury "Pinosol" in the nose.
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (Filatov's disease) is a viral infection that affects the mouth and larynx, spleen, and liver. He is diagnosed only up to 40 years, after - rarely, mostly HIV-infected. In early childhood, mononucleosis proceeds like a common respiratory infection, and by the age of 35, immunity is formed.
Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms increase gradually. At first, a person feels a slight malaise, a breakdown, a slight nasal congestion appears. Gradually, the symptoms become more intense. 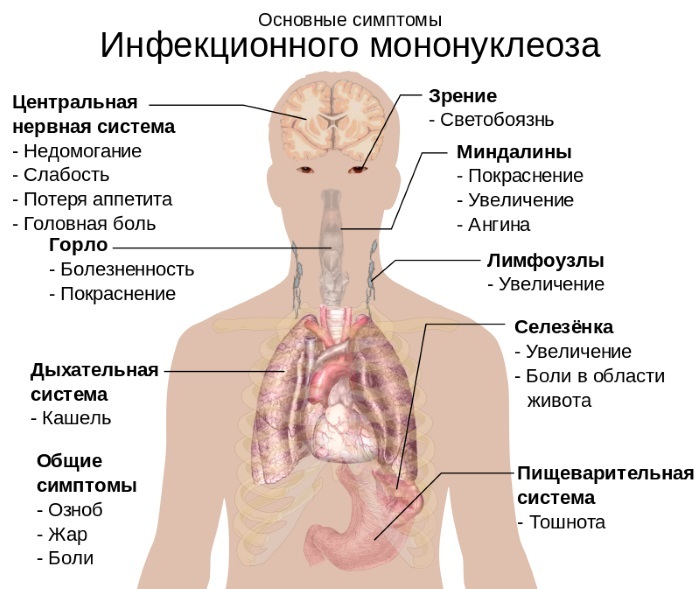 A sore throat, enlarged tonsils and lymph nodes are added to them, the temperature rises to 37.7 ° C. Then there is a strong fever, body aches, headaches, soreness occurs during swallowing. A yellow bloom is observed on the walls of the pharynx, sometimes slight bleeding.
A sore throat, enlarged tonsils and lymph nodes are added to them, the temperature rises to 37.7 ° C. Then there is a strong fever, body aches, headaches, soreness occurs during swallowing. A yellow bloom is observed on the walls of the pharynx, sometimes slight bleeding.
Causes
The causative agent of mononucleosis is the Epstein-Barr virus from the herpesvirus family. It does not destroy, but stimulates the host cells, multiplies in B-lymphocytes. It is transmitted by airborne droplets, affects the epithelium of the upper respiratory tract. In patients, the virus begins to stand out in the last days of the incubation period. The pathogen can pass to a healthy person during blood transfusion, from mother to child.
Treatment methods
Infectious mononucleosis is treated on an outpatient basis, with the exception of a severe course of the disease. The patient must comply with bed rest, if the liver is impaired, table No. 5 is prescribed according to Pevzner. From drug treatment, antiviral and pain relievers are given.
During attacks of compression of the larynx, they are removed with "Prednisolone". Glucocorticosteroids are used only in short courses. Antibiotics are prescribed only in case of bacterial infection or complications. The therapeutic regimen includes drugs to enhance immunity.
Scarlet fever
This is an acute infectious disease, more common in children, less often in adults. It is mainly transmitted by airborne droplets, but infection can occur through touch, poorly washed dishes, toys, or the use of shared towels. The patient is contagious for 22 days from the first day of the disease. The peak of infection occurs in September-October.
Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms appear suddenly. The temperature rises sharply, headaches, weakness and aches in the muscles, tachycardia occur. With severe poisoning, vomiting appears. It is painful for a person to swallow; on examination, a pronounced hyperemia of the tonsils, palate, pharynx and uvula is visible. In the first days of the disease, the tongue becomes covered with a gray-white bloom, on days 4-5 it becomes bright crimson, with pronounced hypertrophy of the papillae.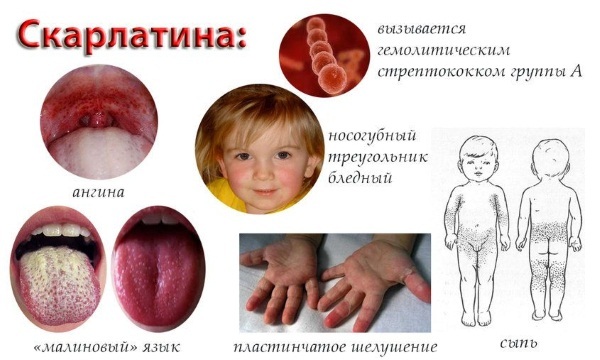
With a severe course of scarlet fever, the lips become the same color. A pale nasolabial triangle appears. The body becomes covered with a small rash (from the face and neck goes down), which eventually merge into large spots. The skin becomes rough, flaky, itchy. Then it comes off the feet and palms in layers.
Causes
Diseases of the throat and larynx (photo and description of the pathology are presented for your reference) can occur due to different pathogens. In scarlet fever, it is a beta-hemolytic streptococcus from group A, which belongs to the gram-positive bacteria Streptococcus.
It secretes Dick's toxin, which is toxic to the body and causes rashes. Streptococcus is located on mucous membranes, mainly in the nasopharynx. With active reproduction, the pathogen forms large colonies. The development of scarlet fever is provoked by stress, weak immunity, hypothermia.
Treatment methods
With scarlet fever, antibiotics must be prescribed.
Additionally give:
- antihistamines (Cetrin, Loratadin);
- antipyretic ("Ibuprofen", "Paracetamol");
- strengthening vessels ("Galascorbin", "Askorutin").
To cleanse the nasopharynx, daily rinses with "Furacilin" or "Chlorophyllipt" are performed. In severe cases of scarlet fever, glucose and saline solutions are administered intravenously. To accelerate recovery, physiotherapy is prescribed - UHF, KUF, magnetic and laser effects.
Diphtheria
It is an acute infectious disease that affects the pharynx in 95 percent of cases. The danger is not the pathogen itself, but the toxin secreted by it, which is one of the most dangerous. If diphtheria is not treated immediately, then the poison will cause serious poisoning, the nervous system, kidneys and heart will be affected. Severe intoxication is fatal.
Symptoms and Signs
Signs of diphtheria appear suddenly - with fever, headaches. Then a plaque appears on the tonsils, appetite is lost, the pulse quickens. A person feels general weakness, a sore throat, and the skin turns pale. Fever persists for 2-3 days. Then the plaque on the tonsils becomes smooth, with a pearlescent sheen.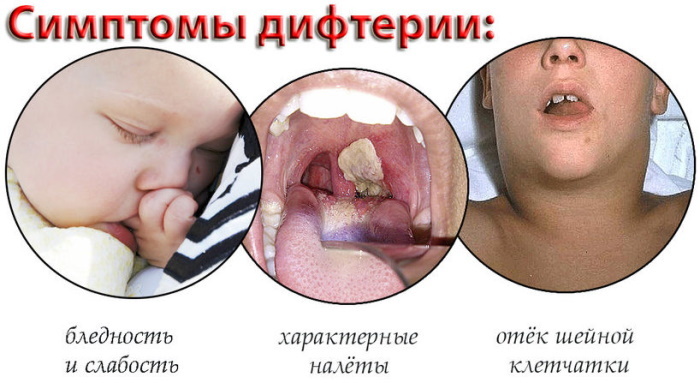
It is removed with difficulty, after which the mucous membrane begins to bleed and again becomes covered with a film. Some symptoms may be absent or supplemented, depending on the type of disease. For example, with diphtheria of the nasopharynx, plaque covers not only the tonsils, but also the mucous membrane of the mouth and pharynx.
Causes
The causative agent of diphtheria is an immobile gram-positive bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae (Klebs-Loeffler). Outwardly, it looks like a stick, it remains in dust and on objects for up to two months. In terms of toxicity, it is second only to botulinum or tetanus exotoxin. Infection occurs by airborne droplets, with saliva. Less commonly, infection occurs through objects, products, and physical contact.
Treatment methods
In case of diphtheria, the patient is injected with a special serum according to the Bezredki method. In severe cases of the disease, it is given intravenously. With toxic diphtheria, detoxification treatment with vitamin C, glucose and cocarboxylase is prescribed. Sometimes Prednisolone is prescribed for a short course, antibiotics - with the development of a secondary infection. In some cases, plasmapheresis, intubation, tracheostomy are performed.
Epiglottitis
This is a disease of the larynx that leads to acute respiratory failure. The inflammation of the epiglottis progresses rapidly. Affects surrounding tissues. As a result, breathing becomes very difficult, edema occurs, which can be fatal.
Symptoms and Signs
Epiglottitis develops rapidly - in 2-5 hours the airways can be completely blocked due to edema.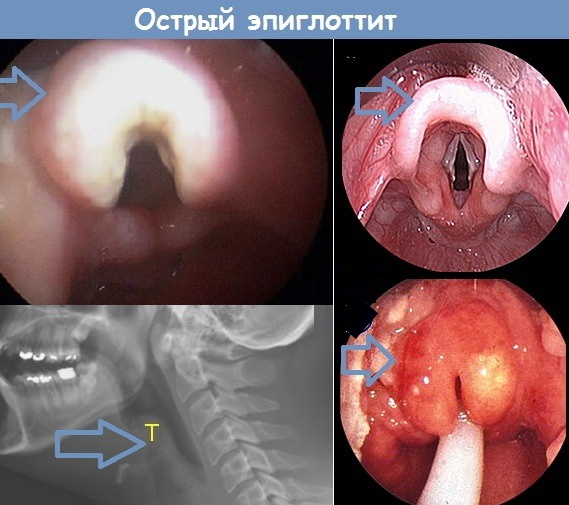
The first symptoms of the disease:
- wheezing difficulty breathing;
- heat;
- a sore throat;
- irritability;
- general weakness, exhaustion;
- difficulty swallowing;
- sore throat;
- fever;
- blue lips;
- muffled voice;
- salivation.
In the abscessed form, painfulness occurs during palpation, hyperemia of the epiglottis mucosa, and pain during swallowing increases. Pus is visible through the edematous membrane. With other types of epiglottitis, the patient's condition is more severe. The sore throat becomes unbearable, which causes grimaces, severe shortness of breath. The tongue is covered with a dark gray coating, swelling of the soft tissues quickly spreads through the larynx.
Causes
Epiglottitis is mainly caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus influenzae), type b. It enters the body by airborne droplets. Sometimes the bacillus is in a latent state for a long time until it is activated by conditions favorable for the bacteria.
Other causative agents of epiglottitis:
- varicella zoster;
- streptococci A, B, C;
- Pneumococcus;
- fungus Candida.
Other causes are trauma, respiratory tract burns, and hot liquids. Drugs, weakened immunity can provoke the development of the disease. Pathology is more common in dark-skinned people and men.
Treatment methods
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital. First, an x-ray of the larynx is taken. A plastic tube is inserted into the patient's airways. The operation takes place under general anesthesia. Antibiotics and nutrient solutions are administered intravenously. The patient is under constant supervision. Usually the patient is in the hospital for 5-7 days. But the course of antibiotics is 10-14 days, so the patient is treated at home.
Laryngitis
Diseases of the throat and larynx (photos and descriptions of laryngitis are not the basis for treatment) often occur due to the inflammatory process. It can be acute or chronic. The disease is seasonal, often of a viral nature, affecting the mucous membrane of the larynx and vocal cords. As an independent pathology, it rarely develops, usually secondary, arising against the background of other pathologies.
Symptoms and Signs
The first signs of the disease are sore throat, dry cough. Sometimes the temperature rises to 37 ° C. With the subsequent development of the disease, the vocal cords are involved in the process, so the voice becomes hoarse. The cough becomes moist, the larynx narrows and breathing becomes difficult
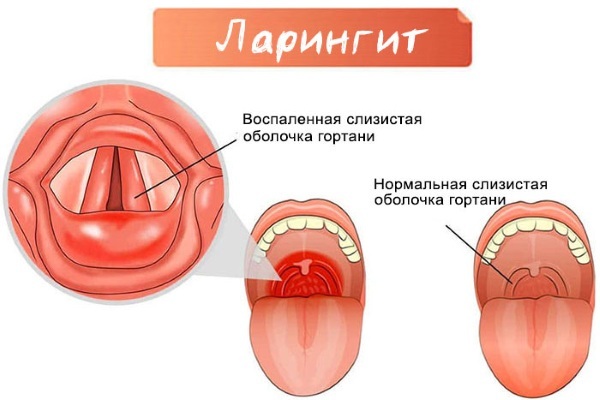
In children, the symptoms are more specific, the course of the disease is paroxysmal. One of the varieties (false croup) is accompanied by a barking cough, wheezing, blue nails. The attacks last for half an hour, then the swelling subsides.
Causes
Causes - pathology of the upper respiratory tract, viral or bacterial nature.
Also, laryngitis can be provoked by:
- chronic inflammation of the nasopharynx;
- flu;
- excessive tension of the vocal cords;
- bronchitis;
- dusty or dry air;
- pneumonia;
- mechanical damage to the larynx;
- colds;
- burns of mucous membranes with chemicals;
- allergy;
- viral infections.
To provoke the development of laryngitis can be a strong emotional stress, stress, overwork.
Treatment methods
With laryngitis, antihistamines and antispasmodics are prescribed. The lumen of the larynx helps to expand inhalation with mineral alkaline water or saline solution. For 5-7 days, only warm drinks and food can be given.
Drug treatment:
- in the first days of the disease, "Berodual" is prescribed, which improves the discharge of sputum;
- local antiseptic "Lizobakt";
- the throat is lubricated or sprayed with "Lugol";
- "Pulmicort" helps to relieve swelling;
- "Geksoral" has antifungal and antimicrobial effects.
With laryngitis, inhalations with sage, chamomile can be done daily. If necessary, antibiotics from macrolides, cephalosporins or penicillins are prescribed.
Phlegmon
This is a purulent process in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, gradually spreading to the surrounding tissues. It can be an independent disease or secondary, developing against the background of other pathologies.
Symptoms and Signs
A characteristic feature of phlegmon is that it has no clear boundaries. Cellulitis is visible as redness, swelling, or swelling. The temperature rises to 37 ° C, with palpation of the affected area of the throat, pain occurs, regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
With the development of inflammation, its contents break out. A fistula is formed, pus flows out or spreads through the surrounding tissues, the nasopharynx. For deep phlegmon, signs of severe intoxication are characteristic. The temperature rises to 40 ° C, headaches, chills, thirst appear. Sometimes there is a decrease in blood pressure, the pulse quickens and at the same time is weakened.
Causes
The main reasons are pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the damaged skin. The risk of developing the disease is increased in people with weakened immune systems.
The main pathogens:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae;
- streptococcus;
- hemophilic bacteria;
- Pasturella multocida.
Other reasons are soft tissue injuries, purulent-inflammatory processes, foreign bodies (for example, splinters) or chemical aggressive substances getting under the skin. Phlegmon is caused by improperly performed injections, ingestion of hypertonic solutions into the fiber. The risk group includes people with bad habits (drug or alcohol abuse).
Treatment methods
The main treatment is medication, aimed at relieving symptoms. Anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic drugs are prescribed. The phlegmon is opened, the purulent contents are cleaned out, drainage is placed. If possible, a gauze envelope soaked in antibiotic ointment is applied to the wound.
Antibiotic therapy is a must. Or they are prescribed intramuscularly, in tablets. When the healing process begins, phlegmon can be lubricated with sea buckthorn or rosehip oil.
Of the methods of physiotherapy, UHF, thermal procedures (compresses, heating pads, sollux) are prescribed. If necessary, "Urotropin" (to normalize the blood state), a solution of calcium chloride (to increase vascular tone), glucose (to nourish the heart muscle) are injected intravenously.
Diseases of the throat and larynx make up an extensive list, photos and descriptions of the most common are briefly presented in the article. Less common is hemangioma, papilloma, stenosis. Abscesses and paralysis often develop secondarily, against the background of other diseases. You cannot engage in self-treatment; at the first symptoms, you must consult a doctor.
Videos about diseases of the throat and larynx
Throat and larynx diseases:



