Content
- Characteristics and properties
- The table is ok
- Symptoms of abnormalities
- Reasons for rejection
- How is it determined
- General blood analysis
- Detailed blood test
- How to increase your platelet count
- Diet changes
- Drug treatment
- Prednisalone
- Etamsilat
- Immunoglobulin
- Traditional methods
- Rose hip
- Nettle
- Methods for lowering platelet count
- Change of diet
- Medicines
- Aspirin
- Anagrelide
- Thromboreductin
- Warfarin
- No-shpa
- Curantil
- Traditional methods of treatment
- Donnik
- Grape
- Platelet Videos
Platelets are thin blood cellsthat are formed in the bone marrow. They help to carry out the basic processes of hemostasis and thrombosis, therefore, in children, their indicator of the norm should always be according to age. Platelets not only help stop any blood loss in case of damage, but also dissolve the resulting thrombi and blood clots, contribute to the preservation of its liquid qualities and even strengthen the blood vessels of the child's body. If the process of platelet production is disrupted, the child develops a sharp change in character, increased tearfulness, weakness and poor health.
Characteristics and properties
Platelets, the norm in children by age is always correlated with the general state of health child, are non-nuclear blood cells that contain trace elements inside that determine it quality. Platelets are 1–2 micrometers in size and have a smooth cell surface.
Platelets are formed in the bone marrow from megacarcytes and live in human blood for no more than 12 days. After this time, all platelets are destroyed in the child's liver and spleen, and new cells are produced instead. Every day, a child forms about 60,000-70000 new cells of this type, therefore, a change in their number in the blood can occur in 1-2 days.
Platelets have several basic functions in the blood:
- form blood clots when a small vessel is damaged to stop blood loss;
- when combined with plasma coagulation factors, they help to stop bleeding in case of damage to large vessels;
- form blood clots with rupture of blood vessels inside tissues;
- contribute to the restoration of the walls of blood vessels and strengthen their walls;
- nourish the child's epithelium with vital substances;
- contribute to the maintenance of the fluid state of the blood.
For children at every age, a platelet level has been established, which is systematically checked by a doctor through a referral for a blood test. This procedure is carried out from the birth of the baby until he reaches the age of majority. An excess of the platelet norm or its decrease is fraught with significant disorders in the health and well-being of the child, the causes of which are important to identify and eliminate in advance.
The table is ok
Platelets, the norm in children of which by age is established systematically according to the results of analyzes by a doctor, must be indicated in the general blood test as the main indicator of health. As a result of the analysis, this indicator is designated as Plt or Platelets, which translated from English means platelets. The indicator is measured in 109/ l, which means that to obtain an accurate value, the resulting number of bodies must be multiplied by 109. The resulting platelet size will be present in 1 liter. child's blood.
Depending on the age, the child produces a different number of platelets, which maintain their level, therefore, the rate of platelets for a child changes as they grow older and is:
- on the 1st day after birth from 180 to 500 units;
- from 2-10 days after birth from 95 to 420 units;
- from 11 to 30 days of life from 140 to 420 units;
- from 2 months up to 6 months from 180 to 435 units;
- at the age of 7-12 months from 165 to 400 units;
- at the age of 1 to 5 liters. from 153 to 500 units;
- aged from 5 to 10 liters. from 175 to 430 units;
- at the age of 10 to 12 y. from 160 to 385 units;
- at the age of 12-15 years. from 160 to 435 units, while in girls this indicator may be lower at this age due to the establishment of the menstrual cycle;
- in 16 liters. and older from 175 to 315 units.
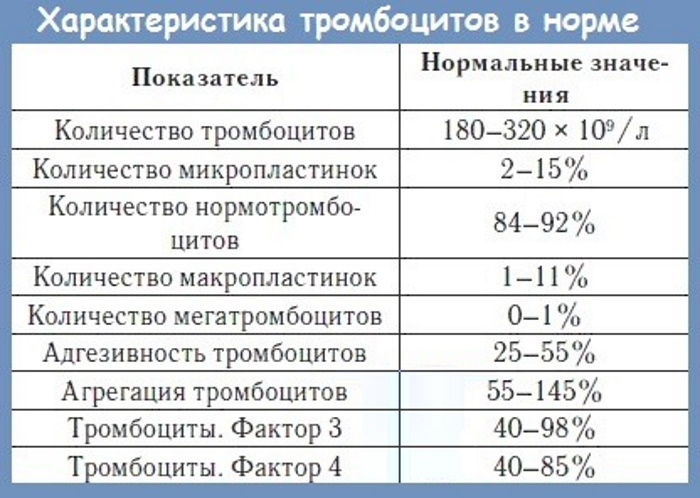
The results of the analysis can be influenced by many factors: the condition of the child, lack of drink before undergoing the analysis, the use of medications. To get the most accurate result, it is recommended to take a blood test for a child only during a period when he is completely healthy. On the eve of the test, it is important to follow the diet and give the child a sufficient amount of clean water.
| Age, l. | Platelet count, 109/ l |
| 1 | 135-435 |
| 2-5 | 150-490 |
| 5-12 | 165-425 |
| 12-15 | 155-425 |
| 16 and up | 177-325 |
Symptoms of abnormalities
Platelets, the norm in children by age, which can fluctuate depending on the state of health of the child, change their value in the blood quickly enough. Within a few days or weeks, the number of platelets in a baby can decrease or grow by almost half without medication. At the same time, the increased production of platelets and their shortage manifest themselves in different ways.
If the number of platelets increases, the child's blood becomes thick. There is a threat of thrombophlebitis and blockage of small vessels, including the brain.
In this case, the child has:
- fatigue and physical weakness;
- a sharp drop in vision, the child begins to constantly squint;
- the limbs of the child become pale and cold;
- causeless hematomas of various sizes of a saturated dark color (which sometimes have the character of compaction) appear on the child's skin;
- the child may experience unreasonable bleeding (from the nose, mouth).
With a low level of platelets, on the contrary, there is a high probability of a violation of the blood coagulation process, in which uncontrolled prolonged bleeding is possible, sometimes for no reason.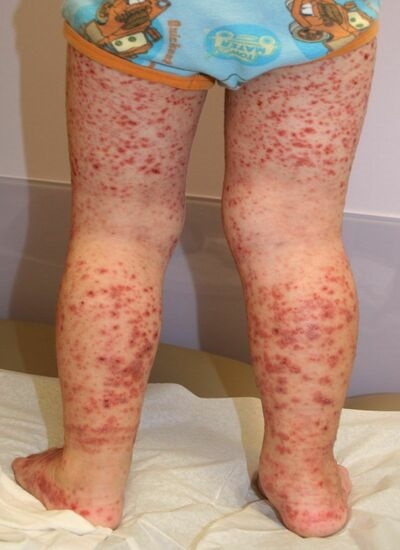
With a low level of platelets in a child, the following are observed:
- systematic and prolonged nosebleeds;
- increased bleeding of the gums, including during teething;
- permanent large bruising with minor injuries and trauma;
- in rare cases, a child may have blood inclusions in the urine.
In both cases, the child feels increased discomfort, therefore, becomes whiny, weakened and passive. His character changes and his level of activity decreases.
Reasons for rejection
In children, platelets normally change as age changes and concomitant factors appear. Since the change in the number of platelets produced depends on various factors, the reasons for the increase and decrease in the number of platelets in the blood may be different.
The main reasons for an increase in platelet levels are:
- inflammatory processes, including in the postoperative period;
- infectious diseases occurring in acute form in children (measles, rubella);
- in rare cases, neoplasms in the bone marrow;
- extensive injuries and blood loss;
- blood diseases (leukemia, thrombocytosis);
- stress and strong emotional stress;
- avitaminosis;
- dehydration;
- heart failure.
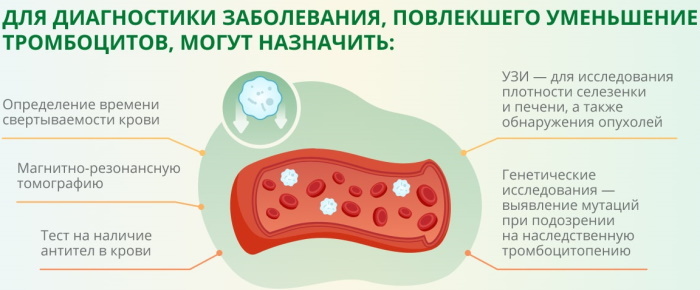
The reasons for the decrease in platelet levels include:
- disorders in the work of the bone marrow;
- large blood loss after injuries;
- blood transfusion;
- disorders of the immune system;
- blood diseases
- changes in the work of the thyroid gland;
- infectious hepatitis.
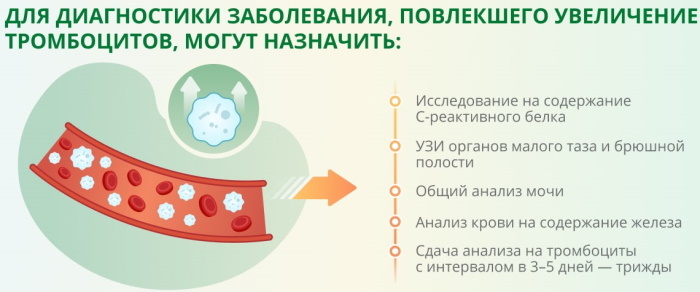
When diagnosing a disease associated with a change in the rate of platelets in the blood, the doctor needs to assess the presence of concomitant diseases and the state of health of the child. If there is a suspicion of the temporality of the changes that have occurred or a medical error, the doctor should prescribe a second blood test after a few days.
How is it determined
Platelets, the norm in children by age, is determined as a standard every 3-6 months, are established on the basis of a venous blood sample. For this, the child is assigned a general blood test or a detailed blood test.
General blood analysis
Capillary blood is suitable for testing platelet counts. A blood test in a child to study the level of platelets is taken from the finger, and in newborns from the heel.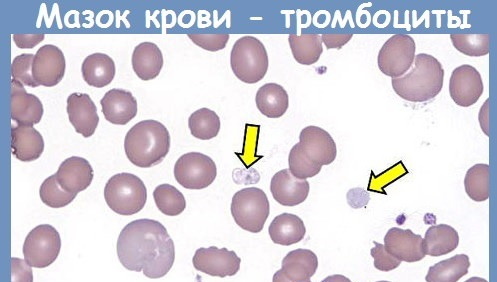
After the baby is born, a complete blood count is taken every 2-3 months in the first year of life. If a deviation from the norm in the number of platelets is detected, a blood test is taken monthly to monitor the state of health.
A blood test can be done at any clinic or medical laboratory. During the procedure, the child is treated with an antiseptic compound on the ring finger of the left hand. Then this finger is pricked with a special game and the required amount of blood is obtained with the help of a sampling pipette for examination. The biomaterial is carefully packed and labeled, and then sent for analysis.
A blood test is taken on an empty stomach or in children under the age of 3 liters. after 3 hours. after the last meal. No special preparation is required for the analysis.
Detailed blood test
The level of platelets in the blood is shown by a detailed blood test taken from a vein. Such an analysis is not done in young children, since it can be difficult to find a suitable vein in a child. The study is most often assigned to children over 10 years of age. Research is being conducted in medical centers.
The analysis is done in the following order:
- First, the nurse examines the baby's veins. For children, blood is most often drawn from a vein in the elbow or wrist.
- Then a tourniquet is attached to the child's hand and the puncture site is treated with a disinfectant solution.
- A needle is inserted into the vein and the required amount of blood is drawn with a syringe. Blood can be drawn directly into a sterile tube.
- Then the puncture site is healed with a cotton swab and the needle is removed. For better fixation, the puncture site with a cotton swab is fixed with a bandage or adhesive plaster.
The collected blood is stored in a special refrigerator for 1-2 hours. submitted for analysis, the result of which is ready within 1 day. A blood test from a vein determines the level of platelets in a child.
How to increase your platelet count
Platelets, the norm in children according to their age, depends on pathological disorders and many related factors, are constantly produced by the child's body. To restore their level, 2 different therapies are used.
Diet changes
For increased production of platelets, the child is recommended to eat foods rich in iron. The kid is advised to give more often plain and seaweed, nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, almonds), buckwheat and oatmeal. From the diet, you should completely exclude salted and smoked foods, remove semi-finished products and fast food. It is recommended to reduce the amount of sugar in the child's diet. During this period, it is important for a child to be more outdoors and actively move.
Drug treatment
As a drug treatment in children, medications are used that affect the level of platelets, increasing it. These include:
Prednisalone
Prednisolone has an immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory effect, and promotes an increase in the number of platelets in the blood. The drug removes manifestations of an allergic nature. You can use the medicine with 3 liters. For children, the drug is prescribed at 1 mg / g per day, divided into 3-4 doses, in courses of 1-2 weeks.
You can use the medicine with 3 liters. For children, the drug is prescribed at 1 mg / g per day, divided into 3-4 doses, in courses of 1-2 weeks.
Etamsilat
The drug effectively restores the state of the blood, increasing the production of platelets. The medicine can be used in children from birth. It is prescribed at a dose of 8 mg / kg per day for 2-3 times. The treatment period is 10-14 days.
Immunoglobulin
With an acute lack of platelets, immunoglobulin injections are prescribed. The drug contains antibodies that increase the level of platelets up to 60-70% in any conditions of the course of the disease. The drug has an effect even in cancer of the bone marrow, without negatively affecting the body. Injections are given to children 2-3 times at intervals of 3 days. After 1-2 months. the course of injections can be repeated.
Traditional methods
To raise the level of platelets in children, folk remedies are used only in the absence of contraindications. These are used as:
Rose hip
Rosehip infusion contains vitamins and microelements that enhance immunity and restore blood condition.
- For the preparation of the infusion 2 tbsp. rose hips (preferably chopped) are cooked with 1.5 tbsp. boiling water.
- The infusion is left for 1-2 hours, and then filtered and given to the child to drink 50-100 ml 3 times a day, sweetening with sugar or honey. The course of admission is 20-30 days.
Nettle
Nettle has properties to improve blood quality and blood clotting. However, due to possible allergic manifestations, it is recommended to give it only to children of 8 liters. and older, injecting in small portions.
- For the preparation of the broth 2 tbsp. nettle leaves are poured with 2 tbsp. boiling water, mix thoroughly.

- The broth is kept warm and filtered.
- The solution is drunk in 3 tbsp. 3 times a day after meals for 1-2 months.
If skin rashes, redness and other manifestations of an allergic nature appear, it is recommended to refuse taking the drug and immediately consult a doctor.
Methods for lowering platelet count
The following methods are used to lower the platelet count:
Change of diet
Children with high platelet counts are advised to eat a diet. Eliminate fatty, salty, fast food and sweets. Reduce sugar, amount of baking and drink to 1.5 liters. water every day. Such children need to include in their daily diet a lot of greens, fruits and vegetables, as well as ginger, celery, and garlic.
Medicines
Medication is taken exclusively as directed by a pediatrician.
Aspirin
Aspirin lowers blood viscosity by preventing platelets from binding to each other. Aspirin is recommended for children after 3 liters. 1-2 tab. per day depending on age and weight. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Anagrelide
Anagrelide helps to reduce the level of platelet production in the blood by suppressing the activity of transcription factors. The drug is prescribed for children at 0.5 mg / day for 7-10 days.
Thromboreductin
The drug reduces the production of platelets in the blood and has a mild effect. The medicine is prescribed for children with 7 liters. approximately 0.5 mg per day for 7 days.
Warfarin
Warfarin lowers blood viscosity and helps reduce the likelihood of platelet clots in the blood. The drug is prescribed in 1 tab. children to receive 2 servings within 10 days.
No-shpa
To relieve spasms and vasodilation, children are prescribed no-shpa. It is recommended to take it in 0.5-1 tab. 1-2 times a day for 7-10 days.
Curantil
To improve local blood circulation and effectively reduce the likelihood of blood clots, courantil is prescribed. The medicine is recommended for children over 10 liters. 1 tab. 25 mg 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional therapies are used only as a supplement for children and after receiving approval from the attending physician. As such, children are used:
Donnik
Melilot leaves have a unique composition that affects the reduction of platelet production, gently restoring the normal composition of the blood.
- For the preparation of infusion 1 tbsp. l. dry grass you need to pour 1 tbsp. boiling water.
- The infusion is filtered and given to children 1-2 tbsp. 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks.
Grape
Grapes actively contribute to the restoration of the normal state of blood and reduce platelet levels.
- For the preparation of the medicine 2 kg. fresh grapes are passed through a juicer or meat grinder and squeezed thoroughly.
- Then the resulting juice must be boiled for 2-3 hours. until it decreases in volume by 2 times.
- The resulting thick liquid is given to children 2-3 tbsp. 3 times a day for 3-4 weeks.
In children, the platelet count changes every day. With a slight change in nutrition and drug therapy, the number of platelets can be established within a week at the level that is needed normally by age. However, in case of pathological disorders in the work of the body, the lack of treatment can cause a deterioration in the child's health, therefore it is important systematically undergo examination and treatment when any discomfort appears in the well-being of the baby, in order to avoid possible complications for health.
Platelet Videos
Malysheva about the analysis of platelets:



