Content
- Diagnostics of the depth of the lesion
- First aid
- First aid for chemical eye burns
- First aid for burns of the esophagus
- What is forbidden to do
- Burn treatment options and medications used
- Treatment of 1st degree burns
- Treatment of 2nd degree burns
- Treatment of 3rd and 4th degree burns
- Care for burn-damaged skin
- Possible complications and prevention
- Video about chemical burns of the skin
Complex damage to the skin, underlying tissues, mucosa as a result aggressive effects of chemicals make up 3-5% of all types of burns, provoking not only tissue damage, but also the appearance of various skin problems, including dermatitis and eczema. Wounds on the skin resulting from the action of acids and alkalis require urgent rehabilitation. activities, including actions to cleanse and bandage them, and in some cases, lavage the stomach or organs vision.
Diagnostics of the depth of the lesion
Actions in the event of chemical burns must be clear and aimed at preventing further traumatic effects of reagents that can lead to irreversible consequences. Most often occurring at work, chemical burns can be the result of neglect of safety regulations, as a result of a domestic injury or suicide attempt.
The classification of chemical burns according to the International Classification of Diseases is based on:
- reactions of reagents;
- concentration of toxins received on and under the skin;
- the duration of exposure and the depth of penetration of chemicals.
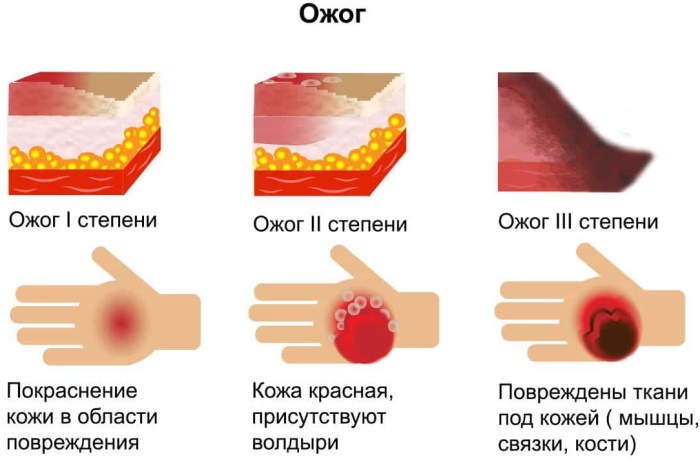
There are 4 degrees of burns:
| Degrees | Description |
| I degree. | It occurs with a mild, short-term lesion of the skin and is accompanied by the appearance of red spots, swelling and soreness on the injured part of the body. |
| II degree | It occurs when the inner layers of the skin are affected and manifests itself, in addition to puffiness and the appearance of red spots, by the formation of bubbles filled with a transparent liquid on the surface of the skin. |
| III degree | In this case, the burn affects the deep layers of the epidermis, accompanied by the appearance on the injured surface blisters with cloudy liquid or bloody filling, as well as destruction of nerve endings (loss of pain skin). |
| IV degree | The most severe lesion affecting not only the skin, but also muscles and tendons (up to bone tissue). |
 Experts agree that burns with chemicals are mostly characterized by III and IV degrees of damage.
Experts agree that burns with chemicals are mostly characterized by III and IV degrees of damage.
- For acid burns, the appearance of a dry scab (crust) is characteristic, with clear boundaries with superficial tissue damage.
- Under the action of alkalis, a white scab (crust) is formed on the skin surface, soft to the touch, with blurred boundaries, easily spreading to neighboring areas. A feature of alkalis is also their ability to quickly penetrate deep into tissues, causing a strong, destructive effect.
Depending on the type of reagent, the shade of the scab also differs:
- with nitric acid, a light yellow-green or brown crust appears;
- with sulfuric acid, a white scab appears first, and then it acquires a gray-brown tint;
- for damage with hydrochloric acid, the yellow color of the burn is characteristic;
- with acetic acid, the affected tissues become off-white;
- carbolic acid stains the skin scab in a white-brown color;
- a high concentration of hydrogen peroxide creates a gray burn on the surface of the skin.
A feature of burns is the negative effect of acid or alkali on the damaged surface and after completion of direct contact with them, which invariably leads to severe injury to all layers of the skin cover. For this reason, doctors are not able to immediately assess the extent of tissue damage.
A full diagnosis of a chemical burn is possible only for 7-10 days. It is at this moment that the scab begins to fester, making it possible to assess the degree of skin damage. The peculiarity of a chemical burn is not only in its depth, but also in the area of the affected tissue, since the wider it is, the greater the danger threatens the victim's life.
First aid
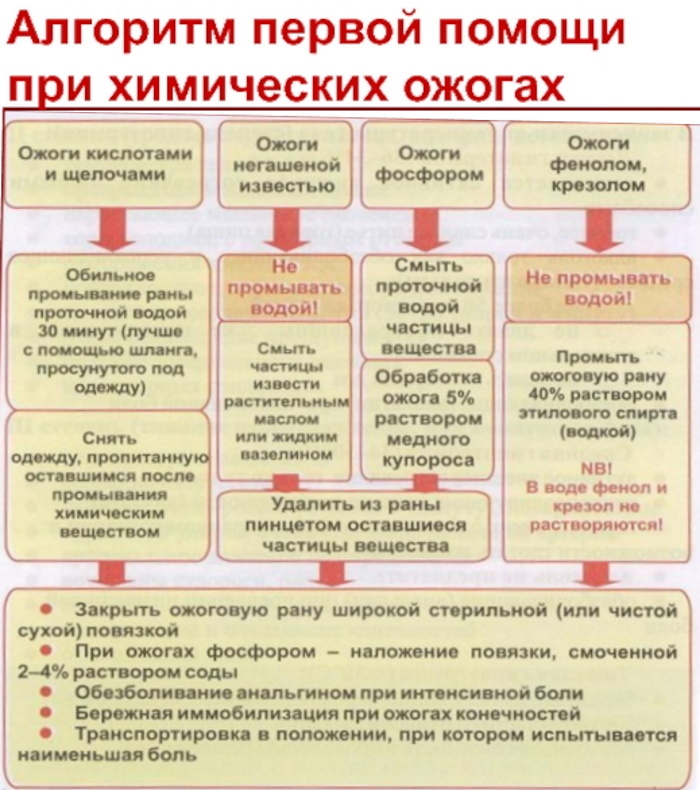
Actions in the case of chemical burns include copious cleansing of the damaged tissue with water, the application of an antidote and the application of a cold compress that relieves pain.
The first aid algorithm is described in the Interdisciplinary instruction on labor protection and in the Federal Clinical Guidelines of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and requires:
- Immediately take off the victim's clothing that has gotten on it with alkali, acid or other corrosive liquid.
- Remove reagents from the skin surface with running water for at least 25 minutes. If help does not come immediately, it is necessary to rinse the burn site for at least 30-40 minutes. It is necessary to wash the wound until the victim ceases to feel a burning sensation. If the first cleaning is not enough, the procedure should be repeated.
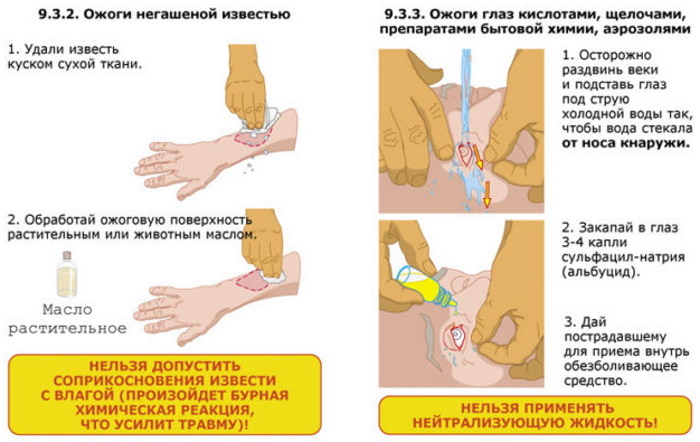
- If the reagent causing the burn is a dry, powdery substance (such as lime), it should first be removed from the surface of the skin with a cotton pad, and only after cleansing, start washing. Exceptions for exposure to water are burns caused by aluminum or its derivatives, which instantly ignite on contact with liquids.
- After rinsing, a cold cloth compress (towel) should be applied to the injured skin to reduce pain, and then the affected area should be placed under a dry and sterile bandage.
After rinsing with water, experts recommend using a neutralizing solution that differs depending on the type of reagent:
| Reagent | Neutralizing solution |
| Lime. | Gauze napkins with sugar dissolved in water are applied. |
| Chromic acid | It is recommended to apply gauze napkins moistened with 5% sodium thiosulfate solution. |
| Hydrofluoric acid | Shows the use of dressings with 5% aluminum carbon dioxide or magnesium oxide mixed with glycerin. |
| Borohydride compounds | Compresses with ammonium hydroxide or nitrilotriethanol are used for neutralization. |
| Selenium oxide | A gauze bandage is applied with a 10% solution of sodium salt and thiosulfuric acid. |
| Aluminum and its derivatives | The burned area must be wiped with gasoline, kerosene, alcohol solution (use of water is unacceptable). |
| White phosphorus | First, it is necessary to remove the hazardous substance, then rinsing with water and the use of compresses with 3-5% copper sulfate solution or 5% potassium permanganate solution are shown. |
| Other acids | Compresses with sodium bicarbonate are used to cleanse the skin. |
| Alkalis | It is shown by washing the affected area in a 1% solution of monocarboxylic or boric acid. |
| Phenol | Compresses with 40-70% ethanol are used as an antidote. |
| Chromium iron ore | Shows rubbing the affected area with 1% hyposulfite solution. |
| Mustard gas | It is recommended to use compresses with a 2% solution of chloramine, calcium hydrochloride. |
With light chemical burns, according to doctors, a simple cleansing of the skin will be enough and in the future they will heal on their own. If the victim has shock, fainting, pallor, or chemical the substance has affected the area of the eyes, the mucous membrane of the mouth or esophagus, an urgent need to seek medical attention help. You also need to go to the hospital if the pain is so strong that it does not go away under the influence of painkillers (Nurofen, Baralgin).
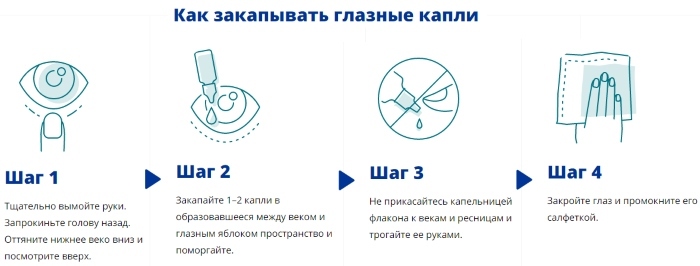
First aid for chemical eye burns
In case of chemical damage to the eyes, it is necessary to immediately and abundantly (at least 20-30 minutes) rinse the organs of vision with water. Since this lesion is serious and, in addition to photophobia and tearing, can lead to loss of vision, the victim should be taken to the hospital as soon as possible. You should not waste time looking for a neutralizer, since tap water is much more effective than any chemical agent.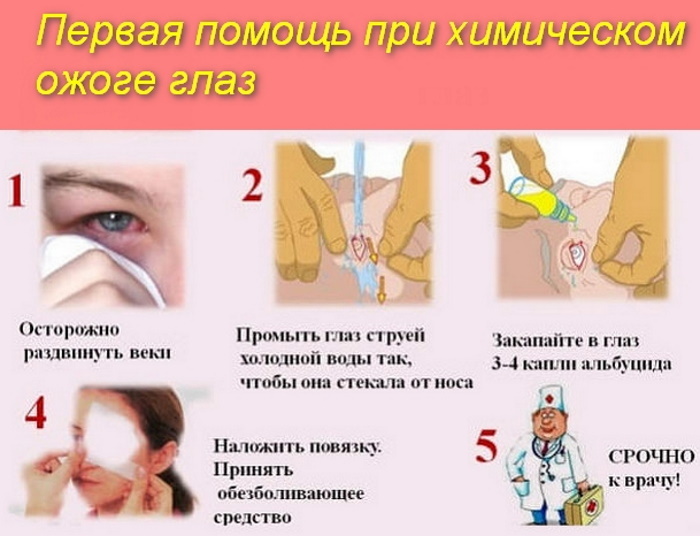
Doctors of the burn center recommend that you also take a bottle of the reagent that caused the burn with you before going to the hospital, as this will help the doctor more quickly determine the depth and extent of tissue damage.
First aid for burns of the esophagus
In case of burns of the esophagus and stomach, arising from ingestion of acetic acid or alkali, it is necessary to rinse the esophagus with a neutralizing solution in large quantities, and then call an ambulance help. Since the ingestion of chemicals can be associated with attempted suicide, experts advise the person first aid provider, do not pay attention to the possible resistance of the victim and forcibly deliver the patient to hospital.
What is forbidden to do
Actions in case of chemical burns should in no case be postponed until the arrival of an ambulance, because with every minute, acid or alkali penetrates deeper into the skin tissue, expanding the lesion. Doctors strongly recommend using distilled water to rinse the skin and eyes, since it is this water that most effectively removes alkali. It is strictly forbidden to use cotton pads or wet wipes to cleanse liquid poisonous substances, since they do not remove the reagent, but only rub it harder into the skin.
Powdered substances must be removed from the surface with a napkin before washing the skin.
Rinsing with running water is necessary in all cases, except for burns with aluminum, its compounds or lime. The former, on contact with liquid, ignite, and the latter begins to foam, which leads to more severe damage.
Burn treatment options and medications used
In the event of mild chemical burns, in accordance with the Rules for the provision of the first help, with the correct carrying out of cleaning actions in the future, no specific treatment. More serious skin lesions can lead to hospitalization and surgical treatment.
Treatment of 1st degree burns
Burns of the first degree do not affect the deep layers of the skin, therefore, they only need timely cleansing of the skin and the appointment of restorative drugs. In this case, experts recommend using an ointment or spray to accelerate skin healing. Dexpanthenol (Bepanten) relieves inflammation, moisturizes, soothes and accelerates cellular regeneration.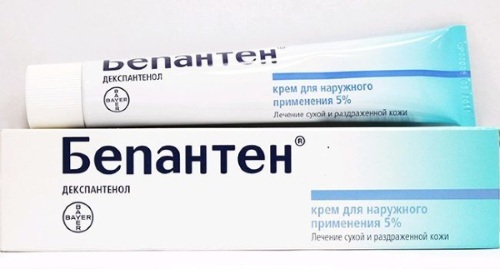
On contact with the surface of the skin, it turns into pantothenic acid, which is involved in:
- regenerative processes of the skin and mucous membranes;
- normalization of cell metabolism;
- acceleration of cell division;
- increasing the strength of collagen fibers.
Treatment of 2nd degree burns
In accordance with the Federal Clinical Recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, when burns of the II degree, first of all, the opening of the blisters is shown, followed by their antiseptic processing. With the correct procedure, the skin will take 1 to 2 weeks to heal. Otherwise, in addition to scars, an infection may join the burn, provoking suppuration of the surface.
In the first few days, the victim should use antimicrobial ointments: Argosulfan and Levomekol, and then the use of healing ointments with dexpanthenol is allowed.
Medicines are used in the form of gauze compresses applied every 2-3 days. The course of treatment is selected individually, depending on the degree of skin lesions. To prevent infection, antibiotic therapy can also be prescribed, including Flemoxin Solutab or Amoxiclav.

For several days, the victim will be disturbed by a fairly strong pain sensation. In this case, it is permissible to use Nurofen, 1 tablet every 8 hours.
Treatment of 3rd and 4th degree burns
According to the rules established by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, treatment of third and fourth degree burns is carried out only surgically. At grade III, skin transplantation from other, intact areas of the patient's body is indicated. With a grade IV lesion involving muscles, bone tissue and tendons, the medical prognosis is poor.
In this case, the following are shown:
- decompression surgery or necrectomy with excision of dead tissue;
- excision of a scab, including complete or partial amputation of the limbs;
- dermatoplasty to compensate for a cosmetic defect.
Decompression measures are carried out primarily at the stage of burn shock and are aimed at reducing the severity of the manifestation and to prevent subfascial edema, leading to impaired blood flow in the nerve trunks and muscles.
After stabilization of the patient's condition, necrectomy is prescribed, aimed at excising dead tissue that can cause the release of a large amount of toxins. The third stage of treatment is skin grafting aimed at eliminating the cosmetic defect.
Experts from the Moscow Burn Center note that in no case should be used for the treatment of chemical burns:
- oil;
- honey and propolis;
- ice;
- Toothpaste;
- chemicals.
Care for burn-damaged skin
To restore the skin after burns caused by toxic reagents, timely first aid, the use of healing ointments and hygiene requirements will help. Blisters formed after burns in no case should be pierced on their own, since this is the only way to avoid suppuration and inflammation of the tissues.
After a few days, the skin over the burn will be covered with a crust, under which new tissue will gradually form. The trouble with this process is that the skin under the crust itches a lot, which gives unpleasant moments, but in no case should you comb the injured place, since you can infect and provoke scarring of tissues.
To prevent scarring possible after severe chemical burns, it is recommended together with healing drugs, the use of anti-scar gels and silicone-based ointments, as well as moisturizers.
It is possible to wash injured skin only under running water, and after cleansing, it is imperative to apply a compress with healing ointment to its surface.
Grade II and III burns often lead to scarring and scarring. Experts note that it will not be possible to cope with them on your own and you will need to resort to the help of a beautician. Here, both the use of the scar excision technique, followed by the application of several cosmetic sutures, and laser resurfacing, which allows to smooth out a rather large skin surface, are permissible.
After scar removal, tissue moisturizing preparations are also prescribed.
Possible complications and prevention
Actions in case of chemical burns are clearly regulated by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and spelled out in by-laws. According to statistics, the majority of chemical burns are associated with professional activities, therefore, workers employed in work with harmful and hazardous working conditions is strongly shown to strictly adhere to the rules of labor protection and technology security.
The poyarok prescribed by the legislation and norms of SAN-PIN includes not only the employee's observance of a certain algorithm actions in the performance of their official duties, but also the use of personal protective equipment: suits, glasses, gloves. Of particular importance is also the work of labor protection specialists with employees of the enterprise, prescribed in the norms SAN-PIN and Interdisciplinary OSH instructions, and aimed at preventing occupational injury.
Chemical burns received in everyday life, according to doctors, are more associated with negligence and inattention. adults and their inadequate supervision of children, which leads to the accidental use or spill of chemical substances. In this case, experts strongly recommend that parents do not leave toxic drugs in the accessible for children. places and conduct educational work with them, with a mandatory story about the dangers of using unknown substances.
Exposure to acids and alkalis is dangerous not only for its mechanical damage to the skin, but also for its deep impact, capable of having a destructive effect on tissues even after the termination of contact of the skin with an aggressive liquid. This ability of acids and alkalis is dangerous not only for its rapid penetration, but also for its wide cavity. girth of damage, leading to the appearance of large burn surfaces, often incompatible with life.
Danger of chemical burns in the depth and width of damage to the skin, mucous membranes or organs of the eyes, which can cause serious damage within a few hours, in some cases incompatible with life. Timely actions of others in the event of chemical burns, prescribed in the Interdisciplinary Occupational Safety and Health Manual and in medical manuals for first aid, not only alleviate the condition of the victim, but also allow, by reducing the depth and width of the damage, to prevent the occurrence of burns of 3 or 4 degrees, which can lead to amputation of limbs or lethal outcome.
Video about chemical burns of the skin
First aid for chemical burns: