Content
- What is fetal distress?
- Intrauterine fetal distress
- Acute (birth) distress
- Reasons for the appearance
- Diagnosis of pathology and management of pregnancy
- Causes and management of labor
- Signs of fetal distress and postpartum activities
- Possible complications
- Prophylaxis
- Fetal Distress Videos
The term fetal distress in medicine refers to the poor condition of a child in the womb associated with in most cases with oxygen deprivation, which can cause the appearance of pathologies of the cardiovascular, nervous or respiratory system.
The pathology that occurs during pregnancy or during labor is characterized by a violation heart rate of the fetus and can threaten its further full life, causing premature birth and detachment placenta.
What is fetal distress?
In gynecology and pediatrics, "distress" is understood as the development of fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation of the child) in which insufficient the amount of oxygen supplied through the placenta can cause disruption of the cardiovascular system, kidneys or head brain. The development of hypoxia can also cause premature birth or spontaneous miscarriage in late pregnancy.
Fetal distress can occur both during labor and pregnancy, and is associated with it pathologically long course, chronic pathologies of the mother's health or other accompanying complications.
Depending on the moment of detection, fetal distress in gynecology is subdivided into intrauterine (chronic) or generic (acute):
Intrauterine fetal distress
Fetal distress that has arisen during pregnancy can be talked about if the child's process of producing a surfactant, which is necessary for lubricating the alveoli, is disturbed. This process begins at 20-21 weeks of pregnancy and ends just before the very birth of the baby.
A lack of surfactant production is associated with a woman's chronic pathologies or problems that arose during pregnancy and can lead to:
- the appearance of pulmonary edema in the fetus or their malfunction;
- a decrease in the volume of the bronchi in a child.
Acute (birth) distress
Fetal distress in an acute form occurs at the time of childbirth and is associated with insufficient labor activity of the mother, stimulation of labor or the outpouring of meconium into the amniotic fluid. A sharp oxygen starvation of the fetus can also develop due to the umbilical cord entwining the baby's head, pinching it or falling out.
This condition is considered dangerous to the health of the mother and her baby and is fraught with detachment of the placenta and the development of uterine bleeding.
Reasons for the appearance
Dangerous pathology requires immediate measures necessary to prevent or minimize the consequences of oxygen starvation of the child. Medical practice has many reasons that can provoke intrauterine hypoxia in a child, part of which is associated with the state of health and behavior of the expectant mother during pregnancy, and the other with pathologies of the generic activities.
Among the reasons associated with the health of a young mother, and provoking the development of fetal hypoxia during pregnancy, experts include:
- metabolic disorders and obesity;
- dysfunction of the biliary system;
- heart failure;
- anemia;
- hypertension;
- viral hepatitis;
- diabetes.

For reasons beyond the control of the young mother, the development of distress during pregnancy is possible due to the occurrence of:
- late gestosis;
- placental infarction;
- multiple pregnancy;
- infection with viral or bacterial pathologies;
- genetic pathologies of the fetus;
- teratogenic factors.
The onset of distress at the time of delivery can lead to uterine bleeding and premature placental abruption and is associated with:
- protracted course of pregnancy;
- stimulation of labor activity;
- entwining the baby's head with the umbilical cord, pinching it or falling out;
- getting meconium into the amniotic fluid.
Diagnosis of pathology and management of pregnancy
You can determine the pathology, starting from 20-30 weeks of pregnancy, using:
| Method of determination | Description |
| Listening to fetal heart activity | The procedure is performed by an obstetrician-gynecologist starting from the 20th week of pregnancy. Normally, the child's heart rate should be in the range of 110-170 beats per minute and with deviating it to a greater or lesser extent, doctors may suspect the appearance of oxygen failure. |
| Evaluation of the child's biophysical readings | The procedure is carried out starting from the 30th week of pregnancy and includes an assessment of the condition of the fetus by: heart rate, respiratory activity, as well as the amount of amniotic fluid. |
| Doppler sonography. | It makes it possible to assess the work of the placenta and the movement of its blood flow. |
| Assessment of the child's motor activity | Starting from the 28th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother needs to count the number of movements of the baby every day. Normally, a child must move 10-12 times per day, and with an increase or decrease in this indicator several times, the likelihood of fetal hypoxia is high. |
| Visual examination, allowing you to notice the child's lag in growth and development | At each examination, the gynecologist measures the circumference of the pregnant woman's abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus, allowing time to notice possible deviations in the development of the fetus. |
When diagnosing intrauterine fetal hypoxia, the developed and approved a pregnancy management protocol by specialists from the Ministry of Health, consisting of:
- Treatment of concomitant diseases of a pregnant woman, leading to fetal distress.
- Step-by-step dynamic monitoring of the fetus.
- Outpatient follow-up and prolongation of pregnancy to full-term, which is possible with normal indicators of biophysical methods for diagnosing the state of the fetus.
With a slowdown in diastolic blood flow in the arteries of the umbilical cord, a study of the biophysical profile of the fetus (BPP) is prescribed. If the study does not reveal pathological values in the development of the child, repeated dopplerometry is performed with a difference from the previous study of 5-7 days. If pathological abnormalities of BPP are detected, dopplerometry should be performed within 1-2 days to monitor the general condition of the child.
The detection of deviations in the values of the BPP and unsatisfactory indicators of fetal Doppler measurements are the basis for hospitalization of a woman in the department of pathology of pregnant women.
Treatment in this case will be directed to:
- Until the 30th week of pregnancy - for the prevention and treatment of concomitant diseases of the young mother that caused fetal distress.
- After the 30th week of pregnancy - operative delivery.
A sharp deterioration in fetal blood flow indicators (to zero or negative blood circulation in arteries of the umbilical cord) requires the appointment of an emergency operative delivery regardless of the term pregnancy
Causes and management of labor
Fetal distress during childbirth requires an emergency caesarean section and is associated with a too long delivery process or:
- stimulation of labor;
- preeclampsia;
- the appearance of an impurity of meconium in amniotic birth;
- lack of water.
In a situation where a woman cannot give birth on her own after the water has passed, doctors resort to artificial stimulation of labor. This process takes quite a long time, during which the child is forced to be inside the mother without water, which leads to the appearance of distress.
With oxygen starvation, lasting for a long time, there is a danger of the development of various pathologies of the cardiovascular, nervous system or brain. In this case, the mother and baby should be under the supervision of doctors for some time.
Specialists cannot visually determine fetal distress during childbirth, therefore, special devices are used to diagnose the process and monitor the condition of a young mother and baby.
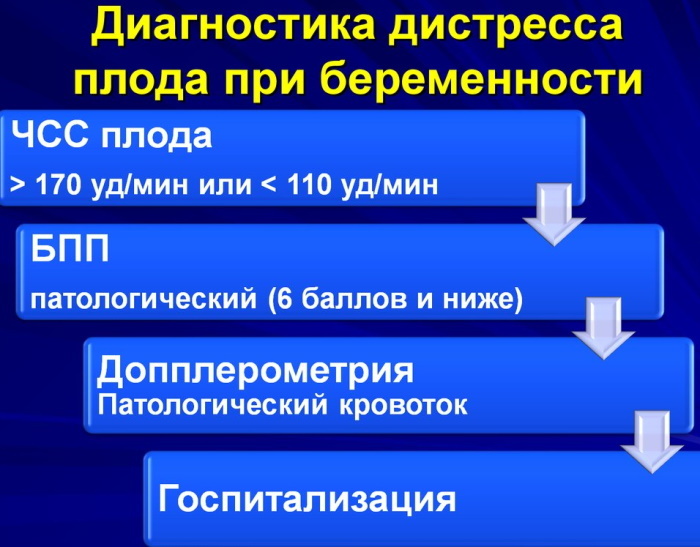
It is possible to talk about the appearance of hypoxia in a child at the time of childbirth if:
- his heart rate is above 170 or below 110 beats per minute (except for the moment of contraction of the uterus);
- The amniotic fluid is green or gray due to the ingress of meconium.
Doubts about the normal state of the fetus require auscultation and cardiography, which make it possible to assess the condition of the baby:
| Fetal heart rate ascultation is necessary to determine the heart rate (HR) of the child in 1 min. | The fetal heart rate is calculated within 1 min:
|
| Cardiotocography (CTG) is performed to fix the child's heart rate and uterine contractions for 10-15 minutes. | When analyzing CTG, the following is assessed:
|
In the normal course of labor, the baby's heart rate will be in the range of 110-170 beats per minute.
With fetal distress, there is:
- tachycardia or bradycardia;
- persistent monotony of rhythm;
- instability of the heart rhythm, characterized by the appearance of early or, conversely, later strokes.
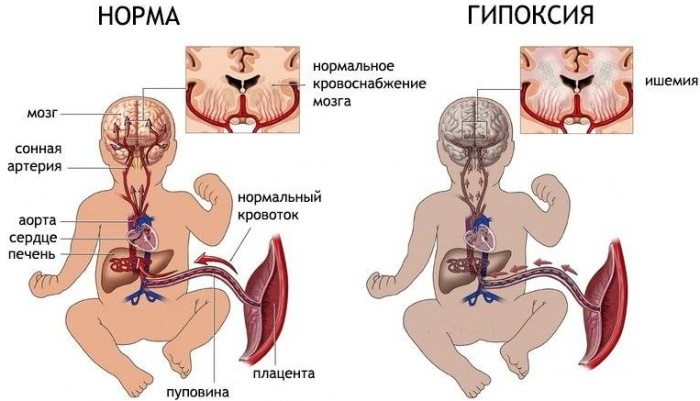
With an abnormal heartbeat of the child, detected at the very beginning of labor, the doctor can pierce the fetal bladder to speed up labor and assess the state of the amniotic fluid. If they are colored green or dark, we can talk about the ingress of meconium into them, which requires an immediate caesarean section.
With an increase or slowdown in the child's heartbeat, with a normal heart rate of his mother and the absence of contractions, doctors suggest the development of hypoxia, which requires:
- stop intravenous administration of oxytocin to a woman;
- moving the mother to the left side, avoiding the supine position
- conducting an internal obstetric study necessary to assess the condition of the child and the possible determination of the causes of hypoxia;
- application of an oxygen mask.
If the reason for the increased fetal heart rate is associated with the condition of its mother, the woman is injected intravenously with drugs to normalize the heart rate.
When fetal distress appears in the second stage of labor, caesarean section is prohibited, therefore, the process of childbirth is accelerated:
- for cephalic presentation - using obstetric forceps or vacuum extraction of the fetus;
- with breech presentation - extraction of the fetus at the pelvic end.
The use of such methods is quite risky and can lead to fetal injury.
Signs of fetal distress and postpartum activities
Fetal distress during childbirth, according to statistics, occurs in about 20 cases out of 100, but not always in further accompanied by the appearance of any violations of a physical or psychological nature on the part newborn.
With timely diagnosis and preventive treatment, the likelihood of a child developing cardiovascular, nervous pathologies or disruption of the brain can be prevented and subsequently the child will not differ from his peers.
A newborn who has given birth with a diagnosis of fetal distress has:
- acute respiratory syndrome with respiratory failure;
- retraction of the chest on inspiration;
- cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes, their paleness;
- crepitus.
In order to prevent the serious consequences of hypoxia, the treatment of the baby begins immediately after birth. Measures taken in the first hour of a child's life can not only reduce the severity of damage to vital organs and systems, but also completely prevent the possible occurrence of complications.
With the development of distress, the fetus of the newborn, extracted from the woman's uterus, is warmed and measures are taken to stabilize breathing. To do this, it is necessary to help the child's lungs to turn around and support them in an expanded state, preventing the alveoli from collapsing.
As the lungs inflate, the child is constantly supplied with oxygen and supportive medications. In severe cases, a child born with hypoxia is transferred to a ventilator or an oxygen mask is used.
Possible complications
Fetal distress during childbirth, lasting for a long time, is dangerous by the appearance of pathologies of all vital important organs and systems, but most of all the heart muscle, vascular and nervous system suffer from a lack of oxygen (CNS). As a result of hypoxia in a child, the process of adaptation to an independent life and subsequent physical and mental development can be significantly disrupted.
When hypoxia occurs in the first period of pregnancy, the process of laying the fetal organs is disrupted, which leads to spontaneous miscarriage and death of the child.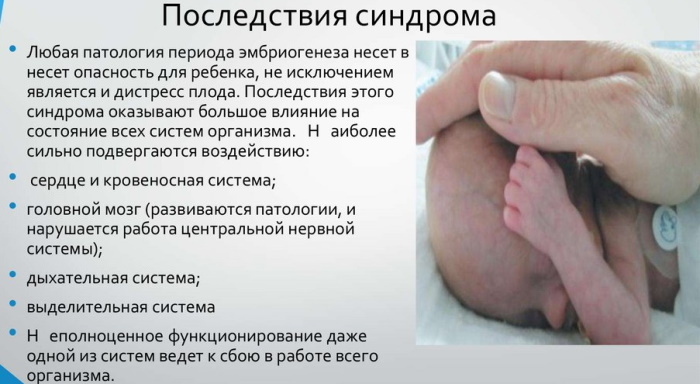
The distress of the second stage of pregnancy, which occurs after the end of the 30th week, does not pose a danger to the life of the fetus, but often becomes the cause of intrauterine growth retardation of the child. It is also possible the onset of premature birth, accompanied by uterine bleeding and placental abruption.
Oxygen starvation that occurs during childbirth poses a danger to the child's life and requires an immediate emergency caesarean section. After the operation is completed, the mother and her baby should be in the hospital for 1-2 weeks under the supervision of a doctor. At this time, the newborn is carefully examined, and special medications are injected into his body to prevent the negative consequences of distress.
After stabilization of the child's condition, he is discharged from the hospital under the supervision of a local pediatrician.
Prophylaxis
Fetal distress during childbirth, resulting from insufficient labor activity of a young mother, is largely associated with a woman's behavior during pregnancy. Obstetricians-gynecologists agree that a timely visit to a doctor, as well as compliance with all his recommendations in within a 9-month period is the key to the birth of a healthy child without the negative consequences of oxygen fasting.
The expectant mother needs to pay attention not only to her physical, but also to her emotional state, and, if possible, avoid stress.
A woman should carefully take care of her health not only during pregnancy, but also at the stage of preparation for it, namely:
- Healthy food;
- quit smoking and alcohol abuse;
- do not abuse sweet, fatty and fried foods;
- take medications necessary to prevent the recurrence of chronic diseases;
- lead an active lifestyle, but not get carried away with strength physical exercises.
If distress occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, doctors advise the young mother to remain calm and completely trust them, because the use of drugs and timely medical assistance can prevent the negative impact of oxygen deprivation on health child.
Fetal distress - intrauterine oxygen deficiency, leading to impaired physical development of the child, the appearance of cardiovascular pathologies, disruption of the brain and kidneys.
Caused by chronic diseases of a young mother, pathologies of pregnancy, childbirth, or entanglement with the umbilical cord the neck of the child, oxygen deficiency requires doctors to strictly adhere to the protocol pregnancy. With timely medical measures and prophylactic administration of drugs, it will not have a negative impact on the health of the child.
Fetal Distress Videos
Acute fetal distress in labor during full-term pregnancy: