Content
- Hemoglobin
- Erythrocytes
- The width of distribution of erythrocytes in the general blood test
- The average volume of red blood cells in the general blood test
- Average hemoglobin content in erythrocyte
- Average concentration of hemoglobin in erythrocyte
- The erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the general blood test
- Leukocytes
- Platelets
- Hematocrit
- Granulocytes
- Monocytes
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Video about blood tests in children
Blood is a mobile connective tissue in the human body. Her analysis can tell about any changes occurring in a particular organ or system. The most common analysis is considered a general clinical one, because it is accessible, simple and sufficiently informative. The study of the basic parameters of blood allows not only to correctly diagnose, but also to correctly prescribe therapy.
Some diseases (especially in children), such as neuropenia or anemia, begin to develop gradually and do not even a pediatrician with experience will always be able to recognize their development, and a general blood test will help to find the cause of anxiety child. But to recognize the changes, it is important to know the rate of blood counts.
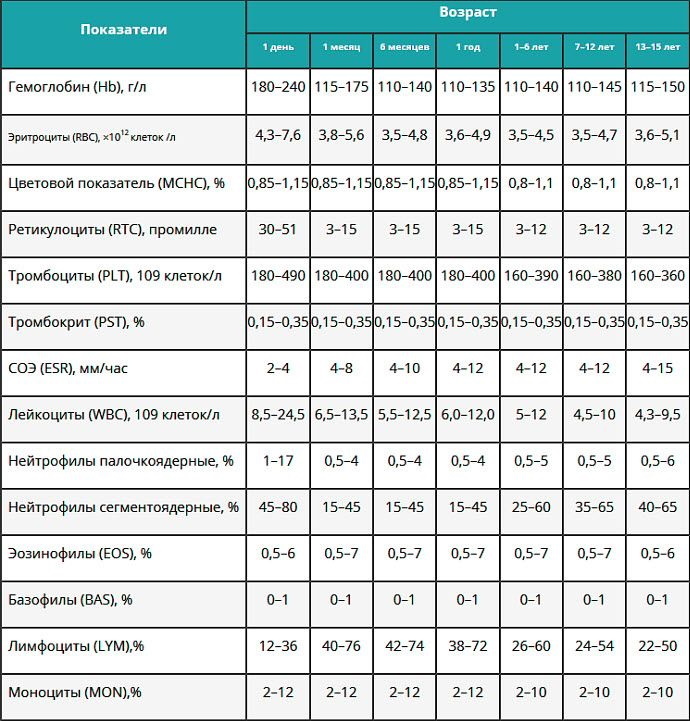
The rate of indicators for its most important components for children under one year and older is described in the table below:
| Indicators | Child's age | |||
| On the 1st day of life | 30 days after birth | At the age of six months | 1st year | |
| Hemoglobin, g / l | 180-240 | 115-175 | 110-140 | 110-135 |
| Erythrocytes, 1012 cells / l | 4,3-7,6 | 3,8-5,6 | 3,5-4,8 | 3,6-4,9 |
| Reticulocytes,% | 30-50 | 3-15 | 3-15 | 3-15 |
| Platelets | 180-490 | 180-400 | 180-400 | 180-400 |
| Leukocytes | 8,5-24,5 | 6,5-13,5 | 5,5-12,5 | 6-12 |
| Neutrophils, stab | 1-17 | 0,5-4 | 0,5-4 | 0,5-4 |
| Neutrophils, segmented | 45-80 | 15-45 | 15-45 | 15-45 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5-6 | 0,5-7 | 0,5-7 | 0,5-7 |
| Basophils | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 |
| Lymphocytes | 12-36 | 40-76 | 42-74 | 38-72 |
| Monocytes | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-12 |
Blood indicators in children (the norm is described in the table) are deciphered in several stages, during which the main criteria of blood are assessed. Today, thanks to modern technology and new equipment, automatic determination of basic parameters can be easily performed.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein from red blood cells that helps transport the mineral iron throughout the body. And iron helps to retain oxygen, which is indispensable for the work of all body systems. Various factors can affect the level of hemoglobin, including age, gender of the child, and various pathologies.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood of children is significantly different from that of an adult. Normally, in newborns, it is in the range of 130-190 g / l, but as they grow older, its level changes, but insignificantly, so for example, in children at 2-6 months it is 90-140, and from one year to 18 years old it averages 100-150 g / l.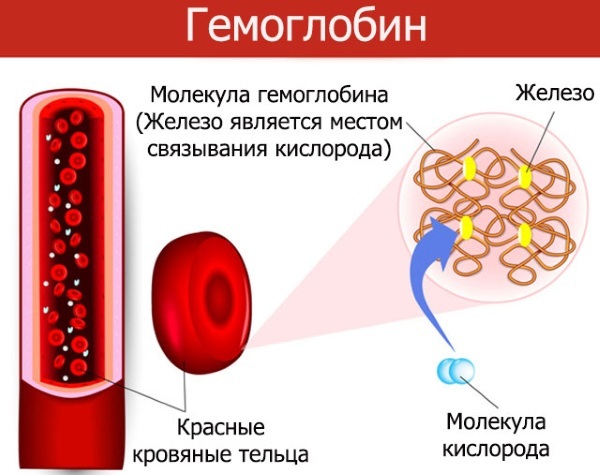
If the hemoglobin level exceeds the norm, then this may indicate the presence of such pathologies:
- Congenital heart defect;
- dehydration;
- kidney disease;
- respiratory disease;
- polycythemia vera.

Also, the norm can be exceeded in people who abuse smoking, recent blood transfusions. Low levels may indicate bone marrow abnormalities, kidney failure, conditions that trigger the destruction of red blood cells.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells or red blood cells are the most abundant blood cells. Formally, they cannot be considered cells, since in the process of maturation they lose their cell structure. They completely lack nuclei, and they do not synthesize protein molecules, unlike other blood cells. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow and constantly circulate through the blood throughout the body, transferring oxygen from the respiratory system to tissues and organs, and removing carbon dioxide.
In children under one year old, the level of red blood cells is constantly changing, and after a year there are some deviations from the norm in adults, but by adolescence the level of red blood cells levels off.
If the level of red blood cells is elevated, then this may indicate:
- dehydration;
- lack of oxygen in the body;
- Congenital heart defect;
- genetic failures;
- polycythemia vera.

If the level of red blood cells is lowered, then a similar condition may indicate the development of such pathologies:
- unbalanced diet with iron deficiency;
- bone marrow damage;
- any pathologies that have affected the bone marrow;
- chronic inflammation;
- bleeding in the organs of the digestive system;
- profuse menstruation;
- trauma with severe bleeding;
- kidney failure.
The width of distribution of erythrocytes in the general blood test
This indicator helps to assess the condition of red blood cells. With its help, it is possible to determine the index of the presence of erythrocytes of different volume in the blood, the area of their distribution, the difference between large and small blood cells. Most often, red blood cells in the blood are homogeneous and equal in volume, but changes may be observed with age or in the presence of certain pathologies.
Erythrocytes and hemoglobin perform the same function in the body - to saturate organs with oxygen, maintain acid and alkaline balance, and remove carbon dioxide. But hemoglobin is part of the red blood cell. That is why, when passing the analysis, not one of the erythrocyte indices is checked, but several, and one of them is the distribution width of erythrocytes.
Blood counts in children (the norm of the width of distribution of erythrocytes at the age of up to six months is in the range of 14-18%, and after six months 11-14%), can be reduced, which indicates:
- oncology;
- the occurrence of myeloma or leukemia;
- destruction of red blood cells with the release of hemoglobin: lack of iron, vitamins, large blood loss, pathological decay.
If the level is above the norm, then this may indicate development:
- kidney disease;
- lack of vitamin A and B12;
- anemia;
- leukocytosis;
- oncology.
Also, an overestimated indicator can be in case of lead poisoning, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
The average volume of red blood cells in the general blood test
This indicator displays the number and size of red blood cells in a general blood test. Thanks to this indicator, it is possible to determine the state of health of the human body.
Blood counts in children (the norm depends on gender and age) should be as follows:
- the first 7 days after birth - 88-126;
- on the 30th day after birth - 88-124;
- in children at 2 months, the indicator normally varies within 77-115;
- from 3 to 6 months - 77-108;
- from 1 year to 5 years - 73-85;
- 5-10 years old - 75-87.

Blood counts in children (normative data are given for informational purposes) can be increased, which indicates the development of such ailments:
- heavy metal poisoning;
- malfunctions of the thyroid gland;
- lack of iodine or iron in the body;
- hepatitis or cirrhosis;
- oncology;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- liver failure.
If the indicator is below normal, then this indicates the development of anemia, leukemia, thalassemia, oncology, metal poisoning, profuse blood loss.
Average hemoglobin content in erythrocyte
This indicator helps to assess the significant content of hemoglobin in one erythrocyte. This indicator is measured in picograms. The norm of this indicator is for people of any age and sex 28-32 picograms in one erythrocyte. This indicator may indicate the severity of the course of the anemia.
Average concentration of hemoglobin in erythrocyte
This indicator makes it possible to determine with what density the red blood pigment filled the cell. Its norm in the body varies between 32-36 g / dl or 320-360 g / l.
If the indicator is below normal, then this indicates such health problems:
- anemia of all types;
- hypoosmolar state of water-electrolyte metabolism.
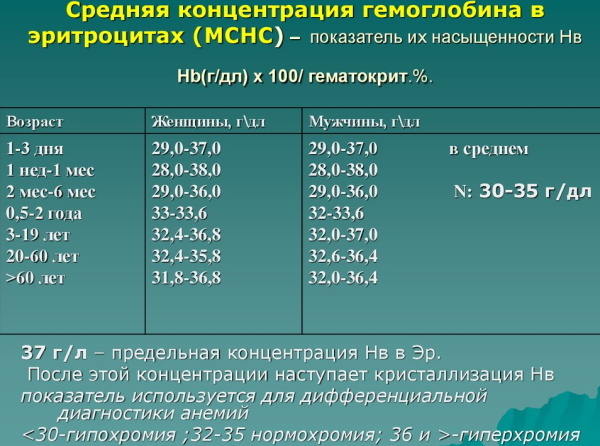
An increased rate may indicate such pathological conditions:
- lack of vitamin B12 in the body;
- ovalocytosis;
- spherocytosis;
- anemia caused by a lack of folic acid;
- violation of water-salt metabolism.
For a person, a very high level of this indicator is very dangerous.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the general blood test
In a general blood test, this indicator is abbreviated as ESR. The sedimentation rate must be checked during a general blood test. The ESR test is carried out during the diagnosis of any pathologies, as well as during dispensary examination and prevention. This nonspecific test helps to identify the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in a particular organ or system, but its cause is not revealed.
The rate of ESR in children who are just born varies between 0-2 mm / h, and in babies from 1 month to six months - 12-17 mm / h. By the age of eight, the level of ESR in children corresponds to the level of an adult.
The level of ESR can increase in children during a cold, as well as other pathologies:
- fractures and injuries that have occurred more recently;
- period after surgery;
- collagenoses;
- anemia;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- tuberculosis;
- neoplasms;
- malfunctions of the kidneys and liver.
But a low level of ESR often appears due to an increase in blood viscosity, an increase in red blood cells in the blood, a decrease in the pH level in the blood.
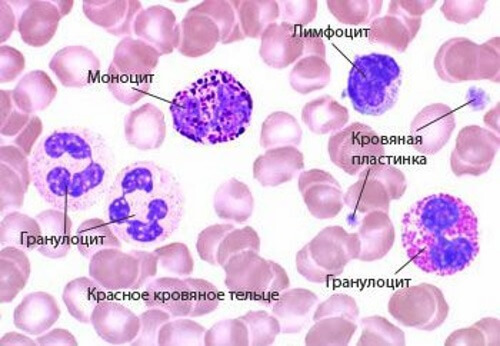
Leukocytes
These are white blood cells that belong to a heterogeneous group of blood cells in the human body that differ in appearance and function. Leukocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Also monocytes and lymphocytes. The general function of the entire leukocyte group is a reliable defense of the body. Normally, the content of leukocytes to peripheral blood is 4-10 x 109 for 1 liter of blood.
Leukocytes help protect the body from external and internal pathogens. If the level of leukocytes in the blood is below normal, then this is called leukopenia in medicine.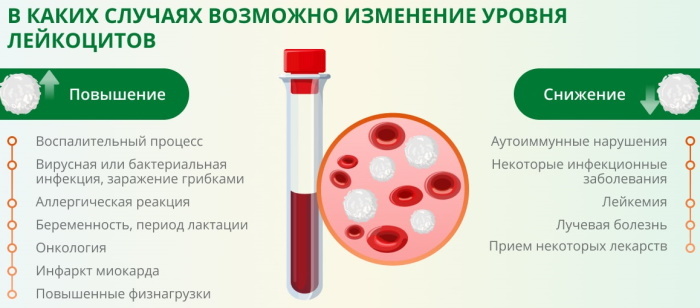
If such a problem is observed, then this may indicate that such pathologies are developing in the body:
- congenital aplasia or hypoplasia of the bone marrow;
- bone marrow neoplasm;
- toxic effects of drugs used in oncology;
- HIV AIDS;
- viral infections;
- tuberculosis;
- metabolic disorders.
If the level of leukocytes in the blood is higher than normal, then in medicine, this condition is called leukocytosis.
It is observed in the presence of such pathologies:
- bacterial infections;
- aseptic inflammatory process;
- paresis, burns and injuries;
- poisoning with toxins;
- the initial stage of radiation sickness;
- blood loss;
- oncology.
Platelets
These are small platelets that are responsible for the main function of blood - its clotting. For the circulatory system to function correctly, it is simply necessary that the platelets fully cope with the functions assigned to them.
The platelet count in children depends on age:
- in the first month after birth, the platelet level varies between 208-410 thousand U / μl;
- from a month to a year - 199-395 thousand U / μL;
- from a year to 5 years - 196-362 thousand U / μl;
- from 5 to 7 years old - 205-360 thousand U / μL.
If the level of platelets is elevated, then this may indicate such diseases:
- tuberculosis;
- leukemia;
- liver or kidney cancer;
- acute infection;
- anemia;
- hemolysis.
Reduced platelets warn of the development of such ailments:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- bone marrow damage;
- hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism;
- anemia.
Also, a low platelet count can be observed with uncontrolled drug intake.
Hematocrit
Hematocrit is a measure of the number of red blood cells in total blood volume. The average value of this indicator can be determined even with the naked eye, if you take an analysis and let the blood settle. Red blood cells that have settled to the bottom will indicate the level of hematocrit as a percentage of the rising plasma.
Each person's body contains about 5 liters of blood. It is composed of red blood cells and light plasma. If you leave the blood taken for analysis to settle, then the red bodies settle to the bottom, and the plasma rises to the top.
Normal hematocrit in children depends on age:
- in newborns - 0.44-0.62;
- from 1 to 3 months - 0.32-0.44;
- from 3 months to a year - 0.36-0.44;
- from one year to 10 years - 0.37-0.44.
A hematocrit level below normal may indicate that the body is observed:
- bleeding;
- anemia;
- leukemia.
Also, its decrease can provoke the introduction of a large volume of fluid into the human body through a vein, overhydration of the body with water intoxication.
Increased hematocrit provokes erythrocytosis, erythremia, the inclusion of compensatory mechanisms on the part of the cardiovascular system.
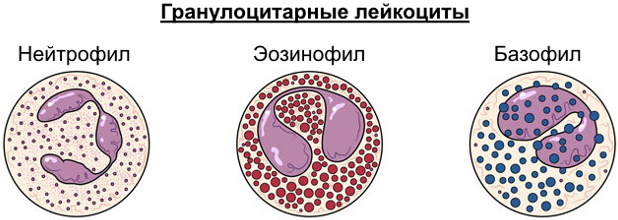
Granulocytes
As already mentioned, leukocytes are of two separate classes - granulocytic and agranulocytic. The group of granulocytes includes neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
Granulocytes are the guardians of the human body, which reliably protect the body from microbes. They are the first to detect pathogenic microorganisms.
In granulocytes, nuclei of irregular shape are present. It is these nuclei that are divided into 2-5 parts, it is for this reason that in medicine they are often called polymorphonuclear cells. About 75% of all leukocytes are granulocytes. These cells are present not only in the blood, but also in the cells of the body.
If you look at the blood test, then the granulocytes in it are presented in the following quantity:
- eosinophils - 1-5%;
- basophils - 0-15;
- neutrophils - 40-70%.
There can be up to 7000 cells in 1 ml of blood of granulocytes.
If the level of this indicator is higher than normal, then this indicates that there is an infection in the body, the inflammatory process is actively developing. It can also increase in the second half of pregnancy, in the first days of the menstrual cycle, after a heavy meal.
If the indicator is below the established norm, then this may indicate a viral infection, liver pathology or collagenosis.
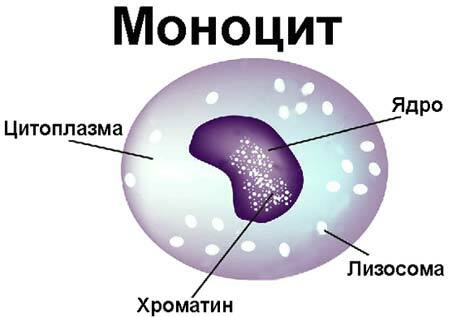
Monocytes
Monocytes are white blood cells. They are formed in the bone marrow and live in the body for three days. It is in the blood that they reach their maximum active state. It is in the blood that they grow, work and are reborn into macrophages, after which they penetrate into the tissues.
Their main function is protective and cleansing. Moving along the bloodstream, they find foreign bodies, which can be cancer cells, viruses, infections or parasites, and try to destroy them with all their might. They also fight bacteria and dead cells, removing them from the body.
The norm of monocytes in children from the first days until reaching the age of 16 changes:
- in a newborn - 3-12%;
- the first 14 days of life - 5-12%;
- by the year - 4-10%;
- by 2 years - 3-10%
- from 3 to 16 years old 1-3%.
When the level of monocytes in the blood rises, this may indicate that the body is developing:
- chronic bowel ailments;
- the most severe chronic pathologies of the joints;
- poisoning with phosphorus or chlorine;
- infection: tuberculosis, syphilis, rubella, influenza, whooping cough;
- rheumatological ailments;
- infestation with helminths.
A low level of monocytes in children is a very dangerous condition, because it can indicate depletion of the body and poor resistance to harmful factors.
Neutrophils
This is one of the largest groups of white blood cells. It is they who are entrusted with the main protection of the body against pathogenic microorganisms. If an infection suddenly enters the body, the neutrophils absorb it, preventing it from developing.
In a blood test, neutrophils are tested in two categories: stab and segmented. In children, these two indicators change with age.
So segmented normally should be:
- per year - 45-65;
- from 4 to 5 years old - 35-55;
- from 6 to 12 - 40-60.
With a low level of neutrophils in the blood, the development of:
- viral pathologies;
- severe anemia;
- infections.
Also, their level rises after taking drugs with antibacterial action.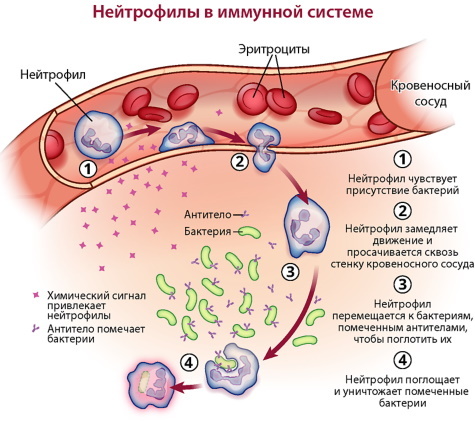
A high score indicates development:
- poisoning with cardiac glycosides;
- oncology;
- gout;
- viral pathologies;
- viral pneumonia;
- bacterial and parasitic ailments.
Eosinophils
These are blood cells, which are entrusted with the function of protecting the body from pathogenic microflora. They are part of the leukocyte formula. These cells penetrate into the focus of the inflammatory process and stimulate cellular receptors in it, which are responsible for antiparasitic immunity.
The rate of eosinophils in the blood in children depends on age:
- in the first 2 weeks of life - 1-6%;
- from 2 weeks to a year - 1-5%;
- from one year to two years - 1-7%;
- 2-5 years old - 1-6%;
- From 5 years old - 1-5%.
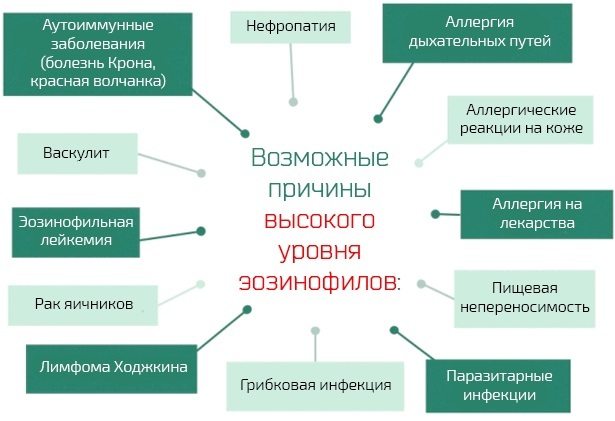
If the indicator in the analysis is overestimated, then this may indicate:
- an allergic reaction;
- helminthic invasions;
- the recovery period after an infectious disease;
- connective tissue pathology;
- administration after antibiotics.
A low score indicates the development of an infection or after injury.
Basophils
These are the components of the leukocyte formula. Normally, in a general blood test for children and adults, it is 1%. Basophils are detected in the body if there is a suspicion of inflammation or an allergic reaction. Basophils themselves are one of the varieties of leukocytes, which are blood cells and are obtained from a granulocyte germ.
A high level of basophils may indicate colitis, enterocolitis, gastritis, peptic ulcer disease. As well as acute blood diseases, liver inflammation, diabetes, hypothyroidism, allergies.
Decrease may indicate an acute infection, hyperthyroidism, leukemia, mental disorders.
The norm of blood counts is a must for all adults. It often happens that the analysis fell into the hands of one of the parents before visiting the doctor, and it is very important to accurately determine whether there are any changes in it in order to help your child in a timely manner. In children, many indicators often vary depending on age, so many laboratories indicate the norm on the form, and it will not be difficult to determine deviations.
Video about blood tests in children
Komarovsky about a clinical blood test: