Content
- Classification
- Superficial
- Catarrhal
- Phlegmous
- Gangrenous
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Laparoscopic appendectomy
- Open appendectomy
- Potential consequences and complications
- Video about Kocher's symptom
The importance of timely diagnosis of acute appendicitis hard to overestimate. Ignoring the characteristic signs can provoke peritonitis and be fatal. One of the signs is Kocher's symptom.
Classification
The Kocher-Volkovich symptom is important for the diagnosis of appendicitis. Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum can lead to suppuration, peritonitis, sepsis and, in severe cases, death. The name of the symptom was given in honor of the surgeon Theodor Kocher, who first described such a manifestation of appendicitis. The signal refers to the early manifestations of the disease.
Kocher's symptom with appendicitis is the migration of pain. 1-3 hours after the onset of pain, the person notes that they move to the iliac region. As a rule, the pain is localized below, in the right side of the abdominal wall.
To alleviate the condition, patients often take this position: they lie on their right side, their legs are bent at the knees and pulled up to the stomach. The development of the Kocher symptom follows certain stages. In individual cases, some of them may be missing.
Superficial
Primary pain syndrome is localized in the epigastric region and is characterized by a wandering nature of pain throughout the abdominal cavity. Dull or cramping seizures within 2-3 hours intensify and move to the site of localization of the appendix.
In the first hours of the disease, gagging is possible, which has a reflex character. More often, the symptomatology is a feeling of wave-like nausea. Stool is often absent on the day of illness. Violation of urination is rarely observed. The deterioration of the condition is insignificant. The tongue is thickly coated, the pulse can be quickened, the skin retains its normal color.
Catarrhal
At the stage of development of catarrhal inflammation, symptoms of irritation of the peritoneum are not observed. The inflammation process is limited to the mucous membrane and submucosa. There is an increase in body temperature and an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood test. Palpation reveals increased pain in the iliac region.
Phlegmous
Kocher's symptom with appendicitis in the phlegmous stage is marked by intense and constant pain. This is a clinical form, typical for admission to a surgical hospital. The pains are clearly localized in the right iliac region and have a pulsating character. Often accompanied by a feeling of nausea, while vomiting is not typical.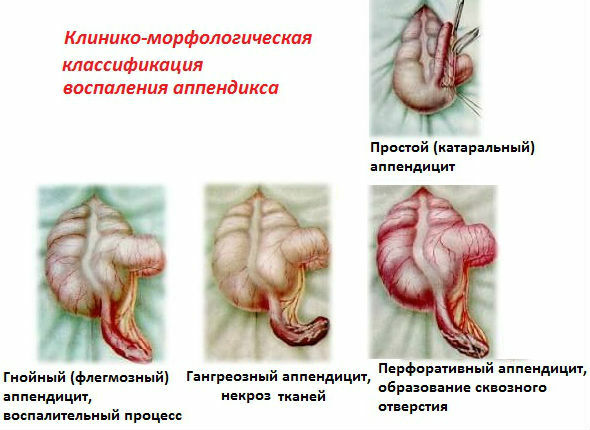
On palpation, hyperesthesia and protective muscle tension are noted, which indicates the spread of inflammation throughout all layers of the appendix.
Gangrenous
Intra-mural venous and arterial thrombosis leads to gangrenous appendicitis. The gangrenous stage is characterized by the onset of necrotic processes in the walls of the appendix. The death of tissues is accompanied by a weakening of pain. At the same time, intoxication increases due to the absorption of decay products into the systemic circulation. As a result, there is a deterioration in health, tachycardia, weakness, blanching of the skin.
Symptoms and Signs
The main symptom is severe pain syndrome. The pain is of low intensity and is initially localized in the epigastrium, the area immediately below the xiphoid process. Subsequently, there is a movement of pain in the right iliac region.
The pain does not go beyond the affected area or organ, occurs for no apparent reason and is not relieved by antispasmodic drugs. In most cases, pain movement occurs during the first 4-6 hours of the disease. However, in some cases, it may be absent or delayed up to 24 hours.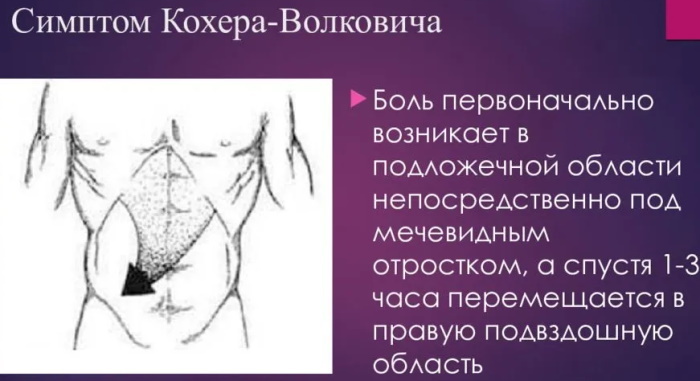
On palpation of the abdomen, pain and tension of the anterior abdominal wall in the right iliac region is noted. To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to lie on the right side, pulling the legs bent at the knees to the stomach.
Causes
There are several reasons for the occurrence of Kocher's symptom. Inflammation can be caused by occlusion of the entrance to the vermiform process of the rectum due to the ingress of a foreign body or feces. It is especially common in young children. Swallowed parts of toys result in mechanical closure and irritation of the appendix.
Main reasons:
| Violation of the process of defecation | Frequent constipation leads to the ingress of feces into the appendix. Unable to clear, the appendix becomes inflamed and leads to pain in the epigastric region. |
| Compression of the upper part of the appendix during the formation of adhesions with cholecystitis or enteritis | The adhesion process leads to a change in the position and mobility of the appendix. The new dense arrangement impairs peristalsis, which entails the formation of stagnation of the contents and the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria. |
| Stagnation of the contents of the appendix | Leads to the creation of a favorable environment for anaerobic bacteria. Actively multiplying pathogenic bacteria contribute to the development of the inflammatory process. The rapid spread of bacterial flora is accompanied by increased pain. |
| Spastic processes in the vessels that provide the appendix with blood | Affect the nutrition of the cells of the appendix. Lack of blood supply leads to a deterioration in the state of cells and the development of necrotic processes. The breakdown of tissue contributes to the intoxication of the body and the rapid deterioration of health. |
| Injuries to the abdomen | Lead to displacement or trauma to the appendix. Violation of the integrity of the structure of the appendix, the formation of extensive hematomas, all this affects the development of pain syndrome. Traumatic situations can lead to rupture of the appendix or extensive hemorrhage. |
| Displacement of the appendix | Promotes its squeezing by surrounding organs. The clamping is accompanied by pain and changes in the processes of defecation and urination. In addition, clamping the appendix can lead to tissue necrosis of both the appendix itself and adjacent organs. |
| The presence of an infectious disease | Contributes to the disruption of the functioning of the appendix. Abundant parasitic invasions lead to blockage of the passages and swelling of the appendix. The presence of an active infectious process leads to the predominance of harmful bacterial flora and the development of an inflammatory process. |
The cause of inflammation of the appendix may be impaired blood circulation due to dysfunction of the regulation of the nervous system. Muscle spasm occurs, accompanied by swelling and the appearance of hematomas. Edema increases intra-abdominal pressure and leads to muscle malnutrition. In this regard, the resistance to harmful flora present in the appendix membrane is reduced.
Kocher's symptom can be triggered with appendicitis by the presence of congenital anomalies in the location or morphology of the appendix.
Diagnostics
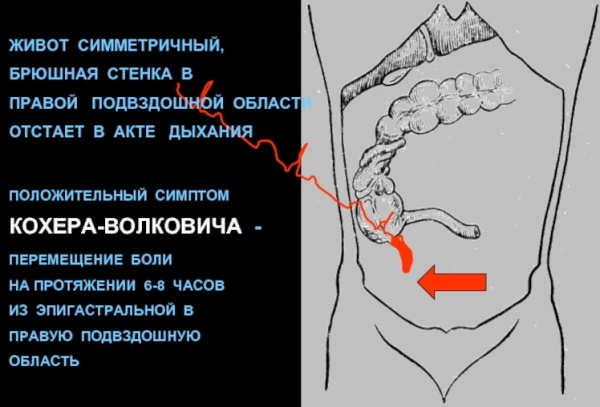
History taking and palpation of the abdominal cavity will help to confirm the presence of a symptom. In 99 cases out of 100, the displacement of pain from the umbilical region to the right side indicates a Kocher symptom.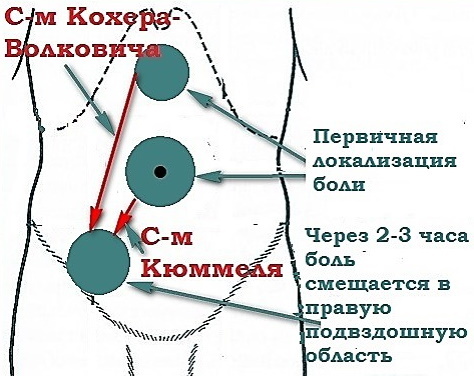
In order to determine appendicitis, it is not enough to know only the Kocher symptom.
There are a number of other signs that can be used to make an accurate diagnosis:
- If the patient cannot sit up from the supine position without assistance, then this is called Bailey's symptom.
- The pain increases when the patient is tilted to the left. This is also a characteristic feature called Volkovich's symptom. The condition worsens if the patient tries to bring the right leg to the stomach.
- Mendel's symptom is manifested by the fact that tapping fingers on the front of the abdomen increases pain in his right iliac region. In 80% of cases, it turns out to be positive.
Kocher's symptom with appendicitis is determined only in the initial stages of the disease. With the further development of inflammation, it is not observed.
Laboratory diagnostics includes:
- General blood analysis. The results will show an increase in leukocytes, an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and a shift in the balance of the leukocyte formula. The appearance of immature forms of leukocytes and an increase in the number of eosinophils are characteristic signs of the symptom. The cost of a general blood test is 150-400 rubles.
- General urine analysis. Characteristic changes in the biochemical analysis of urine are not detected. However, the study is necessary for the differential diagnosis of other abdominal pathologies that are similar in appearance. Analysis for a basic biochemical profile costs 800-1 thousand rubles. 500 rubles, a general urine test will cost 200-400 rubles.
-
Ultrasound. The use of ultrasound diagnostic methods shows high information content. With the help of a sensor on the monitor of the ultrasound machine, the state of the appendix and the presence of a cockade symptom are visualized. The information content of the method is 90%. An ultrasound of the abdominal organs costs 900-2 thousand. rub.
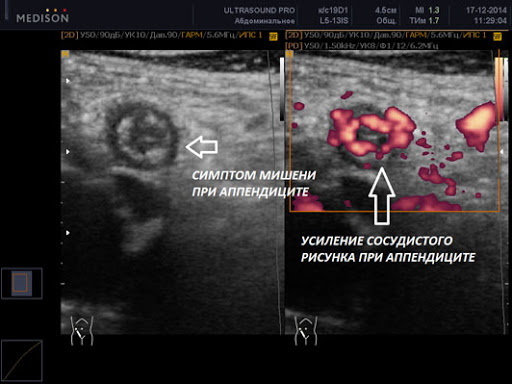
- Abdominal CT scan used for difficult diagnostic cases and differentiation of atypical forms of the disease. The information content is 95%. The cost of the procedure is from 6 to 9 thousand. rub.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy - the most informative diagnostic method. It allows you to directly examine the abdominal organs and provide treatment if a disease is detected. The optical system, which is surgically inserted into the body cavity, makes it possible to assess the macroscopic signs of the disease with minimal intervention and consequence.
The cost of a laparoscopic examination depends on the length of stay of the patient in the hospital, complicating factors and the degree of complexity of the operation. The average cost of surgery varies from 1 thousand to 900 to 30 thousand rub.
Treatment methods
Kocher's symptom with appendicitis, which can be observed in 2 variants: "movement" of pain, and a variant "Residual" pain, in which pain occurs immediately in all parts of the abdomen, should not be left without attention.
Therapy consists in eliminating the inflammatory process formed in the appendix. There is no drug treatment, just like traditional recipes.
Delay in seeking medical attention and self-medication aggravate the disease and lead to a deterioration in well-being. Unwillingness to go to a medical institution contributes to the development of a gangrenous state and can be fatal.
It is possible to stop the inflammatory process only by surgery. Distinguish between the classic surgical method and laparoscopic examination.
Laparoscopic appendectomy
This is the most modern and versatile method. When the diagnosis is confirmed, the procedure allows removing the inflamed process with minimal trauma. The operation to remove the appendix is performed laparoscopic (minimally invasive) under general anesthesia, which means that the patient is sound asleep and does not feel pain.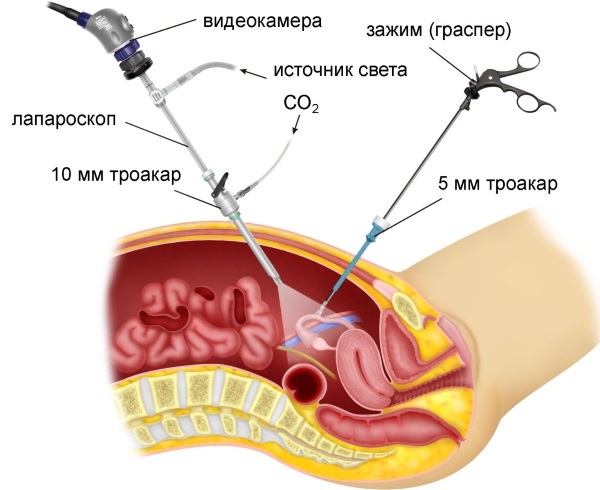
Closer to the beginning of the operation, the patient is given an infusion through which the anesthesiologist administers sedatives to reduce the patient's anxiety. Previously, it was customary to perform this operation from an open access (that is, through a wide incision), which required opening the abdominal cavity, however this method was almost completely abandoned, and today it is customary to perform this operation using laparoscopic (minimally invasive) techniques.
- At the beginning of the procedure, the surgeon makes 2-3 small incisions in the abdominal cavity through which surgical instruments are inserted.
- A laparoscope with a camera at the end is inserted through an incision in the umbilical region. During the operation, the operated area can be seen on the monitor in the operating room.
- To facilitate access to the appendix, the surgeon inflates the abdomen with carbon dioxide. The appendix is cut out and at the end of the operation the incisions are sutured or sealed, then the patient is bandaged.
Despite the advantages of the laparoscopic technique, which include small incisions and therefore leave fewer scars and less pain after surgery, as well as shorter hospitalization and recovery times, surgery is not suitable for every case or for everyone the patient. This method is not suitable for obese patients, as well as for patients who have previously suffered from pelvic infections.
In some cases, open access surgery may be required during laparoscopic surgery, which means a larger incision. The decision to perform an open access appendix removal is made at the time of the operation, depending on the considerations of the surgeon and real situation (for example, if there is massive bleeding or it is difficult to reach the appendix with laparoscopic way).
Open appendectomy
During the first 24-48 hours after the onset of the disease, an operation is performed to remove the appendix. Surgeons usually perform appendectomy surgery under the patient's general anesthesia. During an open appendectomy, the surgeon makes one incision in the lower right abdomen. This procedure allows you to cleanse your abdomen if your appendix has ruptured.
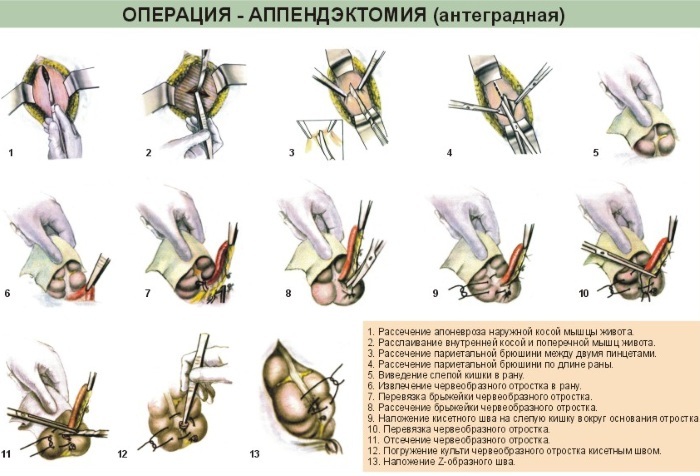
A doctor may choose to have an open appendix removal procedure if it has ruptured and the infection has spread to other organs. It is also the preferred option for people who have had abdominal surgery in the past.
Potential consequences and complications
Failure to seek emergency help leads to the development of complications.
Lack of medical intervention within 2-3 days can cause:
- Peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum. The presence of local peritonitis in the area of the appendix spreads through the abdominal cavity in a phlegmonous form. In the absence of treatment, inflammation spreads to the rest of the peritoneum and becomes purulent in nature. Lack of treatment is fatal.
- Appendicular infiltration - the formation of adhesions of the loops of the small intestine with the abdominal wall around the appendix. The protective mechanism of infiltration formation is to limit acute inflammation of the appendix from other organs.
- Appendicular abscess - the formation of a delimited abscess after rupture of the appendix. It is often a consequence of the appearance of an infiltrate.
- Abdominal abscess - the appearance of delimited intraperitoneal abscesses against the background of developing peritonitis.
- Phlegmon of the abdominal wall - the spread of purulent inflammation of the tissues due to the close location of the appendix to the abdominal wall.
- Pylephlebitis - an extremely serious complication in the form of septic thrombophlebitis of the superior mesenteric and portal veins of the peritoneum. Purulent inflammation spreads from the appendicular vessels throughout the body.
- Sepsis - blood poisoning with harmful microflora or their waste products.
Kocher's symptom is an excellent diagnostic symptom for early detection of appendicitis. A characteristic displacement of intense pain from the epigastric region to the right iliac space develops in the first hours of the disease. The lack of improvement in the condition after taking antispasmodic drugs indicates the development of a symptom. This feature allows at the early stages to carry out differential diagnosis and eliminate the inflammatory process with minimal consequences.
Video about Kocher's symptom
About Kocher's symptom:



