Content
- Clinical and pedagogical classification
- Speaking disorders
- Dislalia
- Rhinolalia
- Dysarthria
- Dysphonia
- Stuttering
- Alalia
- Aphasia
- Tahilalia
- Bradilalia
- Written language disorders
- Disgraphia
- Dyslexia
- Dysorphography
- Psychological and pedagogical classification
- Violation of the means of communication
- Phonetic-phonemic speech underdevelopment (FFNR)
- General speech underdevelopment (OHP)
- Violation of the use of means of communication
- Video about the classification of speech disorders
Speech disorders in children up to 18 years old and in adults, some are a consequence of the incorrect formation of various body systems that perform mental functions during childhood. They can also be the result of the malfunctioning of the already formed structure of speech due to the antagonistic effect on the nervous system in adulthood.
The course of disorders depends on the appearance of dysfunction, its characteristic features and intensity, which affects the symptomatology and severity of pathologies. They are classified according to clinical and pedagogical and psychological and pedagogical characteristics.
Clinical and pedagogical classification
Speech pathologies in the Russian education and health care systems are usually diagnosed according to the clinical and pedagogical classification.
Speaking disorders
The main factors that contribute to the formation of speech disorders are:
- unfavorable external (they are also called exogenous);
- internal (otherwise referred to as endogenous).
Dislalia
Dislalia is characterized by defects in sound pronunciation. In this case, the defeat of the hearing aid is not recorded, and the innervation of the speech apparatus is also preserved.
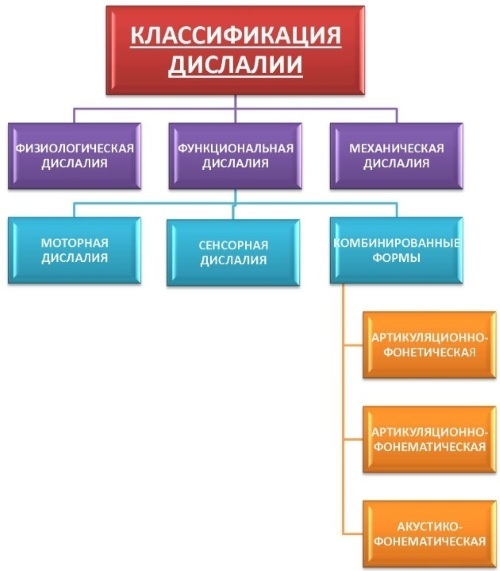
The reason for functional dyslalia is often the lack of corrective exercises that eliminate incorrect sound pronunciation. It can occur in a child with weak immunity or hearing system pathologies. It is characteristic of people who have been diagnosed with developmental delay. Functional dyslalia is often accompanied by incorrect pronunciation of specific sounds.
The mechanical form of the disease can occur due to disorders that are associated with the bite and teeth. She is characterized by a change in the pronunciation of several sounds at the same time. In addition to the very defect associated with the pronunciation of sounds, patients experience difficulties in communication, are shy and often have complexes.
Dyslalia is diagnosed by studying sound pronunciation, determining the specificity of pathology, as well as phonemic hearing.
Preventive actions in this case should be aimed at eliminating anatomical disorders, observed in the system of the articulatory apparatus, the regulation of pronunciation with the help of a visual demonstration correct.
Rhinolalia
Clinical and pedagogical classification of speech disorders includes rhinolalia, which is characterized by incorrect speech functions due to clefts in the upper lip, hard palate. Such violations lead to a distortion of articulation, changes in phonation.
Changes in the timbre of the voice and phonetics are also observed, which is a consequence of the incorrect construction of the articulatory apparatus. With this disease, there is a regular clear nasal tone of voice. Phonetic disorders are characteristic of both consonants and vowels.
The disease has the following types:
| open | in this case, the sound comes through the mouth or nose |
| closed | divided into front and back |
| mixed | this species is characterized by nasal sound, there are also no nasal sounds |
The disease is diagnosed in 2 stages, including research using the speech therapist's instrumentation and the assessment of oral speech.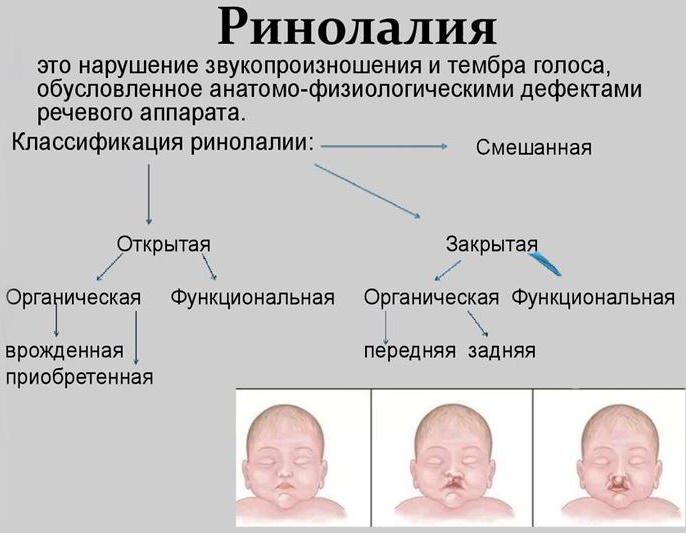
Depending on the type of pathology, patients are prescribed treatment by the following specialists:
- otolaryngologist;
- maxillofacial surgeon;
- neurologist;
- orthodontist.
If a child is born already with clefts of the soft and hard palate, then perhaps surgery will help to get away from more serious violations:
- delayed speech development,
- psychoemotional pathology;
- neurological changes.
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is characterized by a change in speech skills, subsequent lesions of the speech apparatus. Identification of this process is very important, since it leads to disorders that can develop on various structures of the nervous system responsible for the formation of sounds, as well as the logic of the oral speech.
This pathology is classified as spastic and hypotonic forms.
In this regard, the following symptomatic signs are distinguished:
| Muscle spasms | Characterized by tight lips, tongue, and facial muscles. The lips of such patients are often tightly closed. Movement is limited during pronunciation. |
| Muscle hypotension | This condition is characterized by a flaccid form of the tongue, which, at the same time, lies almost motionless on the bottom of the mouth. The lips cannot close, so the mouth is often parted. Experts also note profuse salivation. Since the soft palate is actually motionless, the voice may acquire a nasal tone (that is, nasal tone). |
 With this disease, there are violations of the pronunciation of virtually all sounds. Patients involuntarily soften hard consonants. During the pronunciation of hissing and sibilants, the tongue moves to the side, behind the acting interdental spaces. Normally, it should move forward.
With this disease, there are violations of the pronunciation of virtually all sounds. Patients involuntarily soften hard consonants. During the pronunciation of hissing and sibilants, the tongue moves to the side, behind the acting interdental spaces. Normally, it should move forward.
The voice is characterized by weak and dull tones. Violations can also lead to an imbalance in the breathing act, while the exhalation becomes short, the breathing itself is constantly interrupted and can be frequent during the pronunciation of speech.
Since the patient utters most often slurred speech, he is simultaneously unable to identify specific sounds. This violation can lead to the lack of vocabulary formation, as well as the inability to correctly build the grammar of the sentence. A person suffering from dysarthria with the above symptoms should be observed by a speech therapist and a neurologist.
Doctors may prescribe the following research methods:
- speech therapy, which determines the subject of both oral and written speech;
- electroencephalography;
- electromyography;
- MRI of the brain.
If you follow the recommendations of the gynecologist during pregnancy, take vitamins, observe the daily regimen, then dysarthria can be avoided.
Dysphonia
The clinical and pedagogical classification of speech disorders includes dysphonia, which is characterized by a distorted voice, which is associated with its qualitative change. In this case, he is nasal or hoarse.
And it is also possible to change the timbre and tone, and the last 2 symptoms can be observed both together and separately. The hypotonic type of this pathology is most often diagnosed, which consists in a decrease in the tone of the muscles of the vocal folds, leading to the fact that they cannot close completely.
In speech therapy, the following causes of dysphonia are distinguished:
- Inflammatory pathologies that occur periodically during treatment or are not completely cured.
- Professional singing, especially academic singing, as such vocals can represent a very significant load on the vocal cords.
- Disorders of the larynx, as well as its cartilage, angiomas and other abnormalities. These factors increase the risk of hypotonic dysphonia.

Diagnosis is performed on the basis of complaints of the sick person by oral questioning and examination.
Be sure to carry out:
- laryngoscopy;
- acoustic research of the voice;
- CT scan of the larynx;
- densitometry of the bones of the cervical spine.
Preventive action for such a disease is a gentle voice mode. This is especially true for people whose profession is associated with significant tension in the ligaments. It is recommended to regularly check and treat any infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pharynx and larynx. Chronitization must not be allowed. You should lead a healthy lifestyle, excluding all bad habits.
Stuttering
This pathology is characterized by convulsive movements of the ligaments. At the same time, the rhythm, tempo and fluency of speech are disturbed. It is difficult for the patient to pronounce a particular sound or group, as a result of which he is not able to complete the word.
Stuttering can be caused by stress, as well as uncontrollable fear or anxiety, for example, before exams or when separated from an important person.
In speech therapy, 2 types of diseases are defined:
- Neurotic, caused by mental trauma. Such a disease is possible at any age and is called logoneurosis.
-
Neurosis-like which can be caused by a change in cerebral structures. This disease usually manifests itself no more than 1 time in 3-4 years.

To confirm the diagnosis, consultations are needed:
- neurologist;
- psychologist;
- psychiatrist or psychotherapist.
Moreover, the indicated symptoms of this disease should last more than 3 months. Diagnosis of stuttering is based on clinical presentation. To distinguish between neurosis-like and psychogenic types of stuttering, it is necessary to carry out neurophysiological examinations. Due to the fact that the pathology is formed under the influence of the instability of the functioning of the brain, there are no specific recommendations for the prevention of pathology.
Alalia
Clinical and pedagogical classification of speech disorders includes alalia, which is characterized by severe underdevelopment, and sometimes a complete lack of speech functions, which are caused by lesions of the centers of speech in the cortex brain.
With this disease, they note:
- untimely speech reactions;
- insufficient vocabulary;
- agrammatisms;
- changes and lack of formation of syllabic structure, sound pronunciation and phonemic processes.
The reasons for the formation of alalia are brain damage.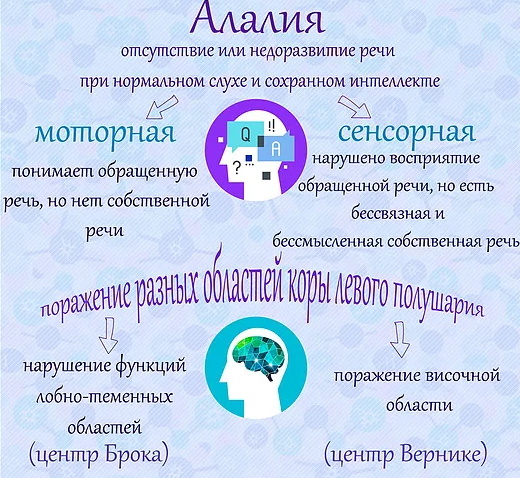
If a patient is diagnosed with this pathology, then he needs to visit consultations:
- neurologist;
- speech therapist;
- otolaryngologist;
- psychologist.
Prevention of this disease in infants should consist in:
- close attention to physical development; protection against all kinds of infectious diseases;
- constant visits to consultations with a pediatrician and a neurologist;
- maintaining a positive microclimate in the family.
Aphasia
Aphasia is characterized by a complete or partial loss of speech functions. The disease is formed due to lesions of the cortical speech centers of the brain.
The causes of this disease are most often the following reasons:
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- traumatic brain injury;
- brain tumors;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- ischemia;
- diseases of an inflammatory nature, for example, meningitis or meningoencephalitis.
In speech therapy, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Motor. This form is associated with damage to the Broca's zone (the lower parts of the premotor region, located in the left hemisphere of the human brain). This type is characterized by impaired pronunciation of words, while maintaining the ability to reproduce specific individual sounds and understand speech as a whole.
| Sensory | This type is also associated with disruptions in the work of the Wernicke center, which is located in the temporal lobe. In this case, the sick person loses the ability to understand speech, but retains the ability to speak. |
| Semantic | This form is characterized by a violation of the functions of the parieto-temporal-occipital region. The ability to understand complex phrases that are interconnected by prepositions or conjunctions is lost. |
| Amnestic | This form is formed as a result of damage to the parietal-temporal zone. The sick person can understand speech, but is not able to remember the definitions and specific names of objects or phenomena. |
| Total | This type is characterized by a complete inability to understand and reproduce speech functions. |
A neurologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all forms of the disease:
- First, the specialist collects complaints, as well as examines the anamnesis.
- Next, he conducts a general neurological examination in order to identify the presence of neurological abnormalities that appear externally. For example, it could be:
- the corners of the lips are lowered;
- tongue deviates when protruding;
- the tone of the limbs decreases.
Prevention of aphasia consists in regularly monitoring the health of the cerebral vessels, undergoing preventive examinations and avoiding various head or neck injuries.
Tahilalia
In addition to the pure form (no mixed disorders), pathologies of rapid speech are diagnosed, combined with phonetic, lexical and grammatical disorders.
These types of pathologies in speech therapy include:
| Battarism (paraphrasia) | This disease appears due to the formed incorrect structures of speech, appearing due to special changes in speech attention or complex speech disorders of the tempo. Such a pathology is sometimes combined with other disorders, the causes of which are somatics, psychogenic factors or habits. |
| Paultern (stumbling) | This form is characterized by accelerated speech, characterized by an intermittent pace. She is characterized by changes in general and speech motor skills. |
The disease often occurs in hyperactive children who have been diagnosed with hyperexcitability.
Diagnosis is carried out by a neurologist and a psychiatrist. During the examination, they find out the neurological symptoms, level and mental abnormalities associated with the disease.
Speech functions are assessed by a speech therapist:
- Examination of the state of speech motor skills.
- Revealing the expressiveness of speech functions, including:
- sound pronunciation;
- vocabulary;
- grammar;
- coherent speech.
- Assessment of specific forms of speech:
- whispering;
- conjugate;
- reflected;
- rhythmic.
The psychologist evaluates the areas:
- sensory;
- cognitive;
- emotional and strong-willed.
Bradilalia
Clinical and pedagogical classification of speech disorders to bradilalia, which is characterized by slow speech, which arises from difficulties in pronunciation, expressed by the inability of the patient to dismember sounds.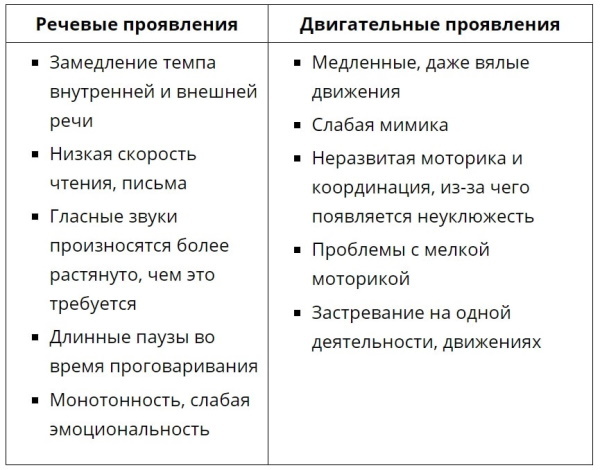
Such a pathology does not affect thinking and intelligence, but lethargy is diagnosed, the person becomes lethargic. Patients who are ill speak slowly, often making long pauses between words. Sometimes they ask again to get more time to respond.
Bradilalia in speech therapy is divided into the following types:
| Separate speech disorder | This kind is characteristic of people belonging to the phlegmatic type, they are slow and lethargic. |
| Consequence of some diseases | For example, this type can be diagnosed after oligophrenia and meningitis, being a concomitant symptom. |
| Cerebellar | This type of pathology is characterized by speech modulation, which becomes chanted. |
When establishing a diagnosis, the patient is upset about the past diseases and brain damage, as well as heredity associated with violations of the rate of speech. This is necessary to study the history.
Preventive actions are expressed in quick treatment:
- neuroinfections;
- perinatal lesions of the central nervous system;
- head injuries;
- asthenic syndrome.
You need to take care of the normalization of the child's speech functions, show him the right examples to follow.
Written language disorders
Difficulties in mastering any discipline taught at school are considered the main reason for maladjustment, as well as a lack of motivation for learning, as a result of which behavioral deviations arise.
Disgraphia
Dysgraphia is characterized by impaired writing skills, manifested in difficulty or complete inability when trying to correlate the sounds pronounced during oral speech and letters, as well as their sound and writing.
For example, the patient can replace letters that are similar to each other when writing, omit and rearrange them in words. Such changes in written language can occur due to the impact of negative factors at various stages of the developing child.
Tokareva O. BUT. the following types of pathology have been identified:
| Optical | It occurs due to the underdevelopment of the visual systems of the cerebral cortex. It is this violation that leads to the lack of stability of visual impressions and representations, therefore, a person does not recognize a number of letters and does not correlate with sounds. |
| Acoustic | The reason for this type of pathology is a violation of phonemic hearing, affecting the differentiation of sounds and changes in sound-letter ratios. |
| Motor | This type appears due to a disorder of fine motor skills of the hands, therefore, a deviation develops when trying to correlate motor images of words with the images of sounds and vision related to them. |
When diagnosing, the following are analyzed:
- written work;
- psychological development;
- formation of speech;
- state of the central nervous system;
- the formation of the organs of sight and hearing;
- development of speech motor skills;
- the quality of the articulatory apparatus.
Preventive actions can include exercises for:
- attentiveness;
- memory;
- thinking processes;
- perception of space;
- differentiation of sight and hearing.
Dyslexia
Dyslexia is characterized by reading impairment. This disease is caused by the fact that some parts of the brain become less functional. There are specific differences in brain tissue from healthy ones. Pathology is also considered hereditary.
When diagnosed, a speech therapist studies:
- long-term and short-term memory;
- does the patient know how to analyze;
- can a person concentrate;
- Attention;
- logical abilities;
- intellectual capabilities.
For prevention, educational games are used, including those aimed at obtaining visual information with adequate and regular supervision of adults.
Dysorphography
Dysorphography is characterized by violations of spelling skills, while changes in the ontogenesis of speech and psychological processes are also observed. With such a disease, a person writes with spelling errors, while he can know the rules very well.
Pathology is diagnosed by studying the level of formation and development of both oral and written speech. Most often this is possible when studying student workbooks.
According to the linguistic characteristic, the following types of the disease are distinguished:
- Morphological, which is characterized by regular multiple errors in compound words.
- Syntactic, in which there are constant errors in the connections of words in a sentence.
- Mixed, which is characterized by both features described above.

Also in speech therapy, the degrees of pathology are distinguished:
- Easy (when there are 15-20% errors in the text).
- Medium (20% to 30%).
- Severe (more than 30% errors).
Psychological and pedagogical classification
Such a classification distributes negative changes from the particular to the general, and also its structure is based on linguistic and psychological criteria. Speech therapists identify generalized manifestations of impairment in various forms of speech development.
Violation of the means of communication
Speech defects with this classification are divided into 2 categories.
Phonetic-phonemic speech underdevelopment (FFNR)
FFNR (phonetic-phonemic speech underdevelopment) is characterized by defects in the formation processes the language system related to pronunciation, subsequently violations of phonemic perception and sound pronunciation. In the case of partial treatment, the disease is transformed into FNR (phonetic speech underdevelopment).
General speech underdevelopment (OHP)
ОНР (general speech underdevelopment) or СНР (systemic speech underdevelopment) differ, first of all, in that the former is characteristic of children with normal development, in the latter - with mental retardation. But both pathologies are characterized by the formation of defects in all components of speech, which relate to sounds and understanding of meaning.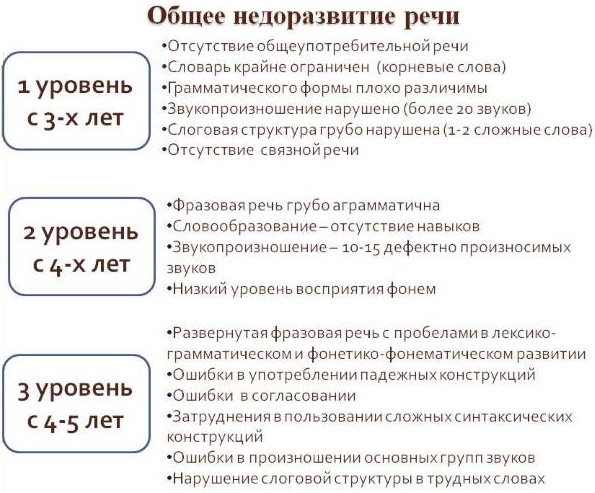
There are 3 degrees of severity of OHP (recently, speech therapists began to distinguish 4). If the pathology can be partially cured, then it is transformed into LHNR (lexico-grammatical speech underdevelopment).
Violation of the use of means of communication
This type of defect is characterized by stuttering. This is a defect in the function of communication, provided that its means are correctly formed. Also in practice, a combined disorder was diagnosed, when logoneurosis is formed together with OHP.
Clinical and pedagogical classification is used more often than psychological and pedagogical in medical institutions, especially by speech therapists and neuropsychologists. This is due to the fact that the first option is based on the causes of speech pathologies.
Video about the classification of speech disorders
Classification of speech disorders. Lecture: