Content
- Determination of heart rate and respiratory movements
- The importance of indicators in children
- Relationship between NPV and heart rate
- Norms of NPV and heart rate in children by age
- How are indicators measured?
- Heart rate
- Respiratory rate
- The specificity of the respiratory system in newborns
- What does the baby's heart rate depend on?
- What does a fast or slow heart rate indicate?
- Rapid pulse
- Slow heart rate
- Possible deviations in heart rate and respiratory rate
- Causes of pathological violations of NPV and heart rate in a child
- Rapid breathing
- Holding your breath
- High heart rate
- Slow heart rate
- What to do if the child's pulse and breathing do not correspond to the average values?
- Video about heart rate in children
NPV and HR (respiratory rate and contractions of the heart) largely depends on the age of the child. In newborns, the norm of these physiological indicators is 2 times higher than in an adult. Chronic and acute diseases of the lungs, bronchi, as well as the cardiovascular system slow down or sharply increase the pulse rate, force the child to take a large number of breaths for 1 min.
Determination of heart rate and respiratory movements
The norm or deviation of indicators of NPV and heart rate in children can be established during a routine examination by a pediatrician, or determined independently by one of the parents. In this case, the child is diagnosed at home.
Counting the frequency of the performed acts of respiration and rhythmic contractions of the heart requires compliance with the following rules:
- NPV and heart rate must be calculated during the period of physical calmness of the child (laughter, enthusiasm for the game or crying contribute to the distortion of physiological results);
- the number of breaths and heart beats should be counted for exactly 1 minute;
- the most objective data for determining the frequency of respiration and heart rate are obtained at the moment when the child is asleep;
- fixation of the total number of breaths is carried out by visual observation of the contraction of the muscle tissues of the chest;
- A child's heart rate is determined by counting the number of pulsations in a blood vessel located in the wrist.
To carry out this diagnosis, you will need a calm environment and a watch with a stopwatch. If, after the examination, slight deviations of the NPV and heart rate indicators are found in the direction of their increase or decrease, then this is the basis for an additional examination at a pediatrician.
The importance of indicators in children
NPV and heart rate in children (the norm for the number of acts of respiration and rhythmic contractions of the heart is higher in newborns) is an important biological marker of the general health of the child. Any deviations from physiologically normal values may indicate diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory system.
Pathologies of the bronchi, lung tissue, heart muscle and blood vessels can have an acute and chronic course. Early diagnosis allows you to start timely treatment of diseases at the initial stages of their development. Compliance with this approach minimizes the risk of serious complications and the occurrence of negative consequences for the child's body.
Relationship between NPV and heart rate
The frequency of respiratory movements and the rhythmic activity of the heart are closely related. For a stable and full-fledged work of the cardiovascular system, a sufficient amount of air must enter the child's body. Oxygen is carried along the tissues of the internal organs and musculature of the musculoskeletal system along with the blood flow. Slowdown of respiratory activity, spasm of the bronchial lumen or inflammatory lung diseases lead to oxygen starvation.
Against the background of the pathological state of the lungs and bronchi, the activity of the heart, blood pressure automatically decreases, all metabolic processes slow down. At the same time, dysfunctional disorders in the work of the heart muscle also negatively affect the performance of the bronchopulmonary tissue.
Norms of NPV and heart rate in children by age
NPV and heart rate in children (the norm of the total number of acts of respiration and rhythmic contractions of the heart is determined by pediatricians based on multiple clinical trials) changes at different stages of their physical development. The table below lists the main physiological indicators of heart rate for a child of the appropriate age.
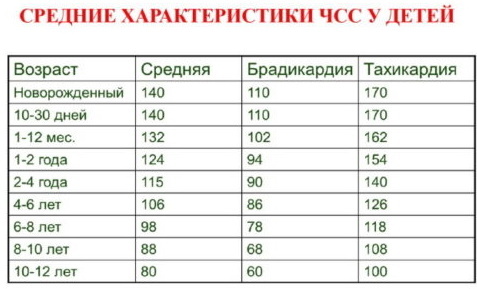
| Child's age | Heart rate norm (number of beats within 60 s) |
| From the first days after birth to 1 month | 110 to 170 |
| 1 month to 1 year | from 102 to 162 |
| 1 to 2 years | 94 to 154 |
| 2 to 4 years old | 90 to 140 |
| 4-6 years old | 86 to 126 |
| 6-8 years old | 78 to 118 |
| 8 to 10 years old | 68 to 108 |
| 10 to 12 years old | 60 to 100 |
| 12 to 15 years old | 55 to 95 |
For children over 15 years old, adult heart rate norms apply. This is a sinus rhythm with a heart rate range of 60 to 90 beats per minute, when the child's body is in a state of physical calm.
The table below lists the norms for the frequency of acts of breathing for children from the first days after birth until adolescence.
| Child's age | The rate of the frequency of acts of respiration for 1 min. |
| The first 14 days after birth | 40 to 60 |
| 2 weeks to 3 months | 40 to 45 |
| 4 to 6 months | 35 to 40 |
| 7 to 12 months | 30 to 35 |
| 2 to 3 years old | 25 to 30 |
| 5 to 6 years old | Within 25 |
| 10 to 12 years old | 20 to 22 |
| 14 to 15 years old | 18 to 20 |
For children over 15 years old, adult norms of NPV apply, which range from 16 to 20 breaths per 1 minute. When measuring the frequency of acts of breathing, it is necessary to take into account the fact that in a state of emotional arousal, the contractile activity of the muscles that are responsible for filling the lungs sharply increases air.
How are indicators measured?
Fixation of indicators of NPV and heart rate is not a difficult diagnostic procedure. It does not require any special hardware.
Heart rate
Measurement of the heart rate is carried out by a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist using the following methods: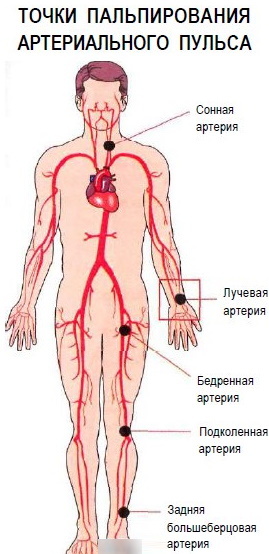
- the number of pulse beats in the wrist is recorded;
- the frequency of contractions of the walls of the carotid artery in the neck is calculated;
- the number of beats of the heart muscle is determined.
In the latter case, the doctor uses a phonendoscope. The frequency of rhythmic contractions of the child's heart muscle is fixed for 60 seconds. Based on the results of the examination, appropriate conclusions are drawn about the functional state of the child's heart and blood vessels.
Respiratory rate
Determination of the frequency of respiratory movements is carried out using the method of visual observation of the chest. The doctor records the numerical number of inhalations and exhalations that are made within 1 min.
In this case, the child should be in a horizontal position in a state of physical and psycho-emotional rest.
Even minor physical activity, laughter, or sudden mood swings are immediately reflected in the results of calculations of NPV. After the examination, the pediatrician confirms the fact of normal functioning of the respiratory organs, and if signs of pathology are found, then additional diagnostic methods are prescribed.
The specificity of the respiratory system in newborns
NPV and heart rate in children (the norm of the number of acts of respiration and rhythmic contractions of the heart decreases as the child grows up) have their own specific differences.
The features of the respiratory system of newborns are as follows:
- the opening of the baby's lungs occurs immediately after his birth at the time of the first breath;
- the volume of the bronchopulmonary tissue of the newborn is significantly less than the general parameters of his chest;
- in the first 30 days after birth, there is an increased number of blood vessels in the baby's lungs, which compensate for the small size of the respiratory system;
- newborn children are forced to make 2 times more respiratory movements than adults;
- in infants, the main amount of oxygen enters the lungs through the nasal canals (the slightest irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa leads to disruptions in the respiratory system).

During breathing, a newborn child practically does not use the oral cavity, since this skill has not yet been developed. In this regard, parents need to ensure that their baby's nasal passages always remain clear of mucus.
What does the baby's heart rate depend on?
The decrease or increase in heart rate in children of different age groups depends on the general state of health, as well as the environmental conditions in which he spends most of his time.
There are the following factors that affect the heart rate in a child:
- the quality of the diet (in children who systematically do not get enough vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats, carbohydrates and essential amino acids, depletion of the body develops, blood pressure indicators decrease and Heart rate);
- the presence of concomitant diseases of the heart, arterial and venous vessels;
- the air temperature in the room where the newborn child is;
- psycho-emotional state of the infant (in children who develop in a favorable environment, heart rate indicators remain stable almost all the time without sharp drops to increase or decrease rhythm);
- the ratio of periods of wakefulness and sleep;
- hereditary predisposition to heart rhythm disturbances;
- the level of blood pressure (a sharp increase and decrease in blood pressure affect the frequency of heart contractions);
- the state of health of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- birth trauma and anomalies of intrauterine development;
- infectious diseases of the heart muscle.
There is a close relationship between the work of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs. Concomitant diseases of the lungs and bronchi disrupt the stable functioning of the child's cardiovascular system. Depending on the type of pathology, an increase or a periodic decrease in heart rate indicators is possible.
What does a fast or slow heart rate indicate?
A slow or rapid pulse is not always a sign of pathology. In the presence of such indicators of the work of the heart and blood vessels, the accompanying factors that are present in the life of the child are taken into account.
Rapid pulse
The physiological reasons for the occurrence of a rapid pulse include excessive physical exertion, which is present in the life of a child. Also, stressful situations and too high air temperature can cause similar symptoms.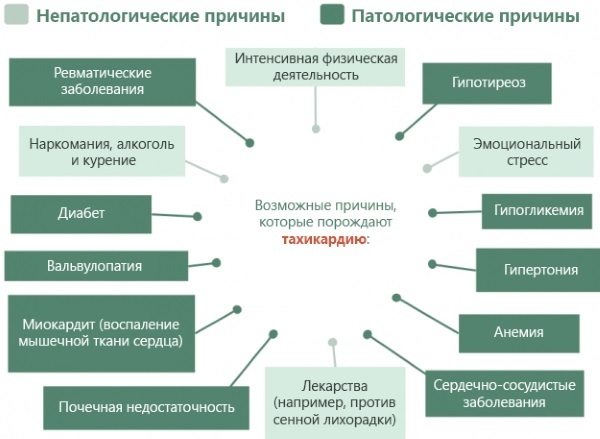
If the child is constantly in comfortable conditions, does not show hyperactivity, and his pulse still remains speeded up, then there may be pathological factors. First of all, versions of excessive fatigue, concomitant diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as respiratory dysfunctions are considered. A child with a fast heart rate should be examined immediately by a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist.
Slow heart rate
A too slow pulse in a newborn baby almost always indicates concomitant pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, or bronchopulmonary tissue. In older children with a low heart rate, who feel satisfactory, such signs indicate a good training of the heart muscle.
Cases are considered pathological if a slow pulse in a child is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- physical weakness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- dry barking cough that occurs suddenly when there are no signs of an infectious or inflammatory disease of the body;
- unstable blood pressure with its periodic increase and decrease;
- headache attacks;
- cyanosis of the skin;
- loss of consciousness or light-headedness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- spasm of the respiratory system.
The above symptoms, combined with a slow pulse, are signs of a painful condition of the heart and blood vessels. A child with similar symptoms should be admitted to the inpatient department of the pediatric department for a comprehensive diagnosis with the appointment of further treatment.
Possible deviations in heart rate and respiratory rate
NPV and heart rate in children (the norm changes under the influence of external environmental factors) can deviate in the direction of increase and sharp deceleration. The range of violation is completely different. In pediatrics, there are cases when a child has only a deviation in the frequency of rhythmic contractions of the heart, and the number of breaths remains relatively stable.
In children with bouts of bronchial spasm of an allergic nature, a violation of the respiratory rate is possible, but the heart rate remains within the normal range. Deviations in the rate of contraction of the heart and the rate of respiration are individual in nature, depending on what factors have created an additional load on the child's body.
Causes of pathological violations of NPV and heart rate in a child
The most dangerous are pathological causes that violate the respiratory rate and heart rate in children of different age groups.  These are diseases with an acute and chronic form, which can go into a latent state, or progress within a very short period of time. Most pathologies of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs are dangerous for the life and health of the child.
These are diseases with an acute and chronic form, which can go into a latent state, or progress within a very short period of time. Most pathologies of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs are dangerous for the life and health of the child.
Rapid breathing
Rapid breathing in a child of any age occurs under the influence of the following disease states of the body:
- spasm of small bronchi, when there is a sharp reduction in their lumen (in this case, frequent, but shallow breathing is observed);
- diffuse inflammation that has affected the mucous membrane of the bronchial tree (this pathology is also known by the definition of bronchiolitis);
- insufficient saturation of the alveoli with the required volume of air;
- viral pneumonia with croupous lesions of the lung tissue;
- collapse of the right or left lung, when there is a decrease in respiratory potential;
- pleurisy with the release of a large amount of exudative fluid, which compresses the organs of the respiratory system;
- local or extensive pulmonary infarction;
- hydrothorax;
- thrombosis of an arterial vessel, which provides blood supply to the lung tissue;
- pneumothorax;
- emphysema of the lung;
- an attack of bronchial asthma of an allergic nature of origin;
- a benign or malignant tumor that is located in the mediastinal region;
- concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system, causing pulmonary edema, as well as overflow of their vessels with excess blood volume;
- intercostal neuralgia of various etiologies;
- dry pleurisy, when inflammation of the pleural membrane proceeds without the release of serous exudate;
- metastasis of a cancerous tumor from other parts of the body into the structure of bronchopulmonary tissue;
- chest and rib injuries;
- a sharp increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- acute form of myositis;
- flatulence caused by various reasons;
- exacerbation of neurological disorders triggered by an attack of hysteria.
Rapid breathing can occur in a child who has experienced a stressful situation. The presence of a pathologically high NPV is the basis for hospitalization of the child and a comprehensive examination. Delay in providing medical attention can be fatal.
Holding your breath
Bradypnea (holding your breath) is the result of the following pathological conditions of the child's body:
- cerebral stroke;
- high intracranial pressure;
- a condition close to diabetic or hepatic coma;
- renal failure;

- intoxication of the body with biological poisons or chemicals of toxic etiology;
- the consequences of acute infectious diseases with the preservation of a high body temperature and an extensive inflammatory process (in the presence of such a symptom, there is a likelihood of septic shock);
- tumor neoplasms in those parts of the brain that are responsible for the function of respiration;
- meningitis;
- edema of the lining of the brain of various etiologies.
In a child with healthy bronchi and lungs, there is a synchronous rise of the right and left side of the chest. Dysfunction of a specific area of the sternum is a sign of pathology.
High heart rate
Too high pulse in children can be caused by the following pathological factors:
- an attack of a panic attack or the negative consequences of a stressful situation;
- intoxication of the body;
- hyperfunction of thyroid tissues, in which an excess amount of thyroid group hormones enters the child's blood;
- acute lack of magnesium and potassium;
- side effects from taking medications;
- ischemia of myocardial tissue;
- endocrine disorders with the simultaneous release of too much norepinephrine and adrenaline into the general blood flow.
Children who have a too high pulse may complain of a feeling of compressive chest pain, dizziness, physical weakness, and migraine. In 80% of cases, such conditions are accompanied by unstable blood pressure in the direction of its increase.
Slow heart rate
The occurrence of a slow heart rate is associated with the negative effects of the following pathologies:
- cardiomyopathy;
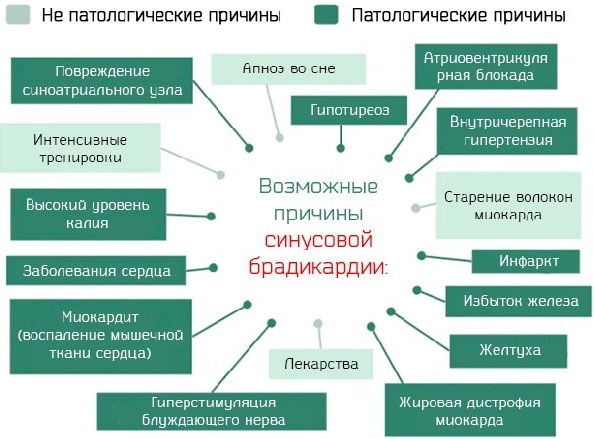
- congenital defects of the heart and great vessels;
- blockade of the heart muscle;
- weakness of the sinus node;
- myocarditis;
- bradycardia;
- angina pectoris.
In medical practice, there are occasional cases when a slowdown in heart rate in children causes heart failure. The tendency to the occurrence of most of the above pathologies can be transmitted from parent to child along with genetic information.
What to do if the child's pulse and breathing do not correspond to the average values?
The pulse rate and the number of breaths in the child should correspond to the average values. The presence of deviations from the indicator of the norm is the basis for seeking medical help. It is strictly forbidden to make independent attempts to restore normal respiratory rate and heart rate with the help of drug therapy. These actions can aggravate the general condition of the child.
NPV and heart rate are interrelated physiological indicators that are biological markers of a child's overall health. The rate of heart rate and the number of breaths changes as children grow up. Diseases of the heart, blood vessels and bronchopulmonary tissue cause violations of the respiratory rate and heart rate upward or downward.
Children who have symptoms of tachycardia, slow heart rate, frequent but shallow breathing should be examined by a pediatrician, cardiologist, or pulmonologist. Determination of indicators of NPV and heart rate provides for counting the number of breaths and pulse contractions. To perform this diagnosis, a phonendoscope and a stopwatch are used.
Video about heart rate in children
Violation of the heart rhythm in a child: