Content
- Why does discoid lupus erythematosus develop?
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Clinical picture, symptoms of DLE, course
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- What tests are needed?
- Biochemical analysis
- Lupus strip test
- Clinical blood test and urine test
- Differential diagnosis
- DHQ treatment
- Forecast
- Lupus erythematosus video
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) Is a severe dermatological disease, which is expressed by progressive scarring of the connective tissue of the body. This pathology belongs to the group of erythematous collagenoses. In the photo of patients with discoid lupus erythematosus, it can be seen that large areas of their skin are affected by multiple rashes, and also have signs of follicular hyperkeratosis.
Why does discoid lupus erythematosus develop?
Discoid lupus erythematosus is a disease that develops due to the body's autoimmune response to direct sunlight. Patients with this skin pathology are highly sensitive to ultraviolet radiation. After direct sunlight hits the surface of the epithelial tissues in such patients, the process of erythematous irritation starts. A large rash with a rich red tint appears on the human body.
As the disease progresses, follicular hyperkeratosis joins with further scarring and atrophy of the inflamed tissues.
The main danger of discoid lupus erythematosus is that it is characterized by a rapid rate of development, an acute pathological process, and also poorly responds to drug treatment. Areas of the body with signs of cicatricial atrophy have a disfiguring appearance, cause the development of internal psychological complexes, and reduce the patient's quality of life.
Pathogenesis
Discoid lupus erythematosus is a dermatological disease, the etiology of which is not fully understood. The exact reasons why some people develop an acute autoimmune reaction to direct sunlight are still unknown.
Scientific studies have shown that people with skin phototype I are at an increased risk of developing this pathology.
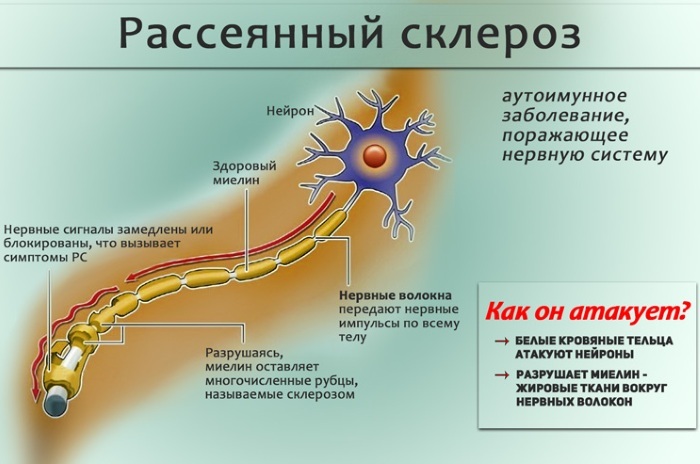
 After contact of open areas of the human body with ultraviolet radiation, a violation of the physiological process for the synthesis of T-lymphocytes, as well as dendritic cells, occurs. The immune system triggers a mechanism for the production of autoantibodies that cause local inflammation of those skin segments that have been in contact with direct sunlight.
After contact of open areas of the human body with ultraviolet radiation, a violation of the physiological process for the synthesis of T-lymphocytes, as well as dendritic cells, occurs. The immune system triggers a mechanism for the production of autoantibodies that cause local inflammation of those skin segments that have been in contact with direct sunlight.
According to medical statistics, per 100 thous. the adult population of Russia accounts for 1 person who suffers from discoid lupus erythematosus. A distinctive feature of this dermatological disease is that it is diagnosed more often in women than in men. The first signs of a pathological condition of the skin are found in adults aged 20 to 40 years. Discoid lupus erythematosus is very rarely diagnosed in older people.
There are the following risk factors, the impact of which contributes to the occurrence of discoid lupus erythematosus:
- prolonged exposure to the sun with the presence of open areas of the body;
- individual tendency of the body to manifest an allergic reaction to drugs;
- daily being in cold environmental conditions, performing work in a frosty and gusty wind;
- the presence in the body of chronic foci of bacterial, fungal or viral infection.
Men and women who have blood relatives suffering from this disease in the family are at increased risk. Construction workers, fishermen, industrial climbers, and agricultural workers are also prone to discoid lupus erythematosus.
Classification
Discoid lupus erythematosus (a photo of this disease displays the extent of skin lesions) is an autoimmune pathology, which is divided into 2 conditional forms. The table below describes the classification types of dermatological disease.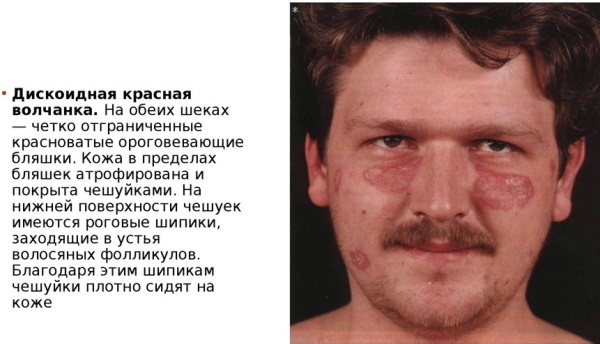
| Disease classification | Distinctive features |
| Limited discoid lupus erythematosus | This pathology is expressed by a local manifestation of erythematous inflammation of the skin. The patient has no more than 1-3 parts of the body with signs of follicular hyperkeratosis and atrophic processes. Discoid lupus erythematosus of limited type is believed to be milder and more responsive to drug treatment. This type of disease is characterized by a more stable clinical form. In the event that a large number of negative factors continue to affect the patient's skin, then the transition of limited DHQ to a disseminated type of disease is possible. |
| Disseminated discoid lupus erythematosus | This type of dermatological disease is characterized by a more extensive pathological process. In this case, on the patient's skin, there are simultaneously more than 3 foci of erythematous skin irritation with signs of follicular hyperkeratosis. For more advanced stages of this pathology, areas of the body with atrophic scarring of epithelial tissues are characteristic. Disseminated discoid lupus erythematosus is considered a more dangerous and serious disease, since it can cover large areas of the body. |
 Scientific studies have shown that there is a pathogenetic affinity between systemic and discoid lupus erythematosus. In 7% of cases, DHQ becomes the systemic type of this disease.
Scientific studies have shown that there is a pathogenetic affinity between systemic and discoid lupus erythematosus. In 7% of cases, DHQ becomes the systemic type of this disease.
Clinical picture, symptoms of DLE, course
Discoid lupus erythematosus (a photo of this pathology shows the severity of inflammatory skin lesions) occurs in open areas of the epidermis. Most often this is the surface of the face, neck, décolleté, auricles, and the frontal lobe of the head. Much less often, this disease occurs on the mammary glands, wrists and back. In women, discoid lupus erythematosus affects the scalp.
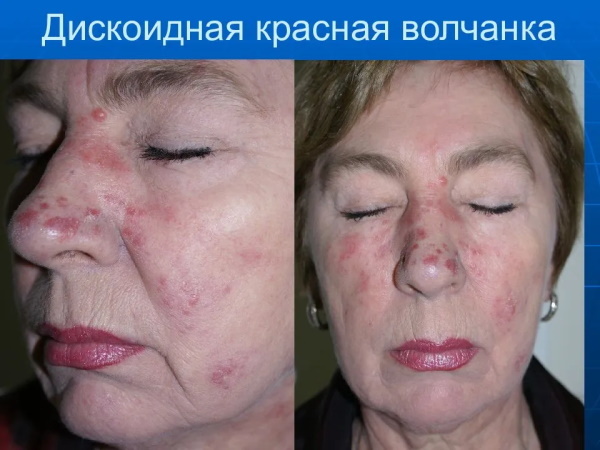
The pathological development of this disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of voluminous pink spots with outlined borders;
- the formation of small scales with a completely white or grayish color shade;
- the formation of a continuous erythematous plaque, which is an extensive focus of the inflammatory process of autoimmune etiology;
- spread of erythematous scales to healthy areas of the body;
- combining individual foci of the pathological process into one continuous erythematous-infiltrative spot;
- the appearance of horny spines, which are connected to the follicular part of the scalp or individual parts of the body;
- a feeling of sharp and burning pain that occurs with each attempt to forcibly remove the whitish scales covering the skin;
- the appearance of sebaceous horny plugs with their localization inside the auricles (upon visual examination, these neoplasms resemble the shape of a sewing thimble).
With the extinction of the inflammatory process in the focus of the pathology, degenerative changes occur. Skin affected by erythematous plaques and follicular hyperkeratosis acquires signs of atrophic scarring.
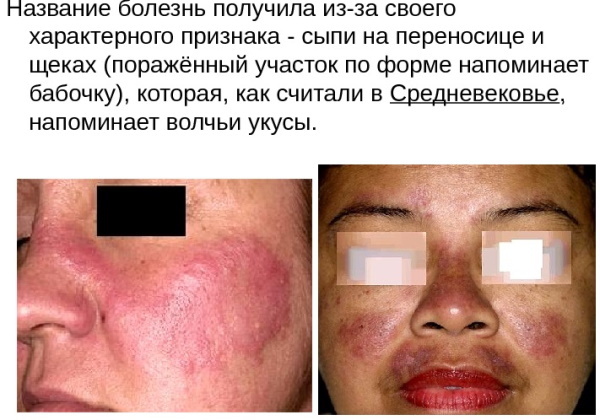
When the face area is affected, the formation of a "butterfly symptom" is characteristic, when the center of the focus of autoimmune inflammation is on the nose, and its edges cover both cheeks. Depending on the severity of the pathological process, the skin of the body resembles a burn, densely covered with small or very voluminous scales. In dermatological practice, clinical cases are often encountered when the foci of discoid lupus erythematosus are located symmetrically.
Discoid lupus erythematosus, which occurs in the scalp, is easily confused with the initial stage of seborrheic eczema. The patient has identical symptoms. As the disease progresses, the first distinctive features are noted. The scalp becomes pale, rapidly thinning, and then begins to shine.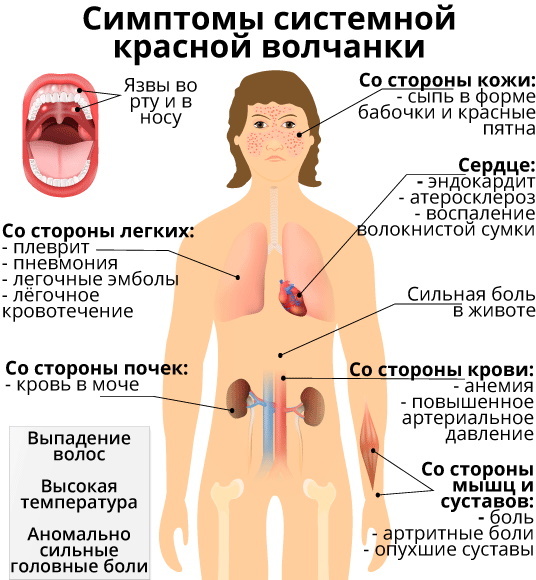
In the central part of the pathological focus, atrophy of the cicatricial type is formed, which is accompanied by total alopecia. The main danger of discoid lupus erythematosus of the scalp is that this disease can turn into squamous cell cancer.
Complications
Discoid lupus erythematosus is characterized by a stable course, or it is characterized by the rapid progression of pathological skin changes.
This disease can lead to the following complications if it has become systemic:
- complete loss of scalp;
- urticaria, which spreads over the entire surface of the body, but does not cause an itching sensation;
- the formation of erythema in the palm and nail plates of the hands;
- inflammation of the kidneys with the further development of functional failure of the organ;
- endocarditis according to Liebman-Sachs with pathological thickening of the valvular apparatus of the heart;
- arterial hypertension;
- inflammation of the walls of blood vessels, which is accompanied by their atherosclerosis;
- various kinds of neurological disorders;
- lupus pneumonia;
- anemia;
- thrombocytopenia;
- gastritis with the risk of developing an ulcerative process;
- leukopenia;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes, which may be accompanied by short-term visual impairment;
- ulcerative lesion of the duodenum;
- inflammation of the serous membrane of the pleura;
- development of antiphospholipid syndrome.
Complicated forms of this disease can lead to severe damage to internal organs with further onset of disability. Timely elimination of the causes that caused the body's autoimmune response minimizes the risk of negative consequences.
Diagnostics
Discoid lupus erythematosus (a photo of dermatological pathology confirms the vastness of erythematous plaques on the surface of patients) is a disease that is diagnosed after a preliminary examination of epithelial tissues, as well as a clinical blood test the patient. The table below lists test results that are typical for people with a diagnosis of DHQ.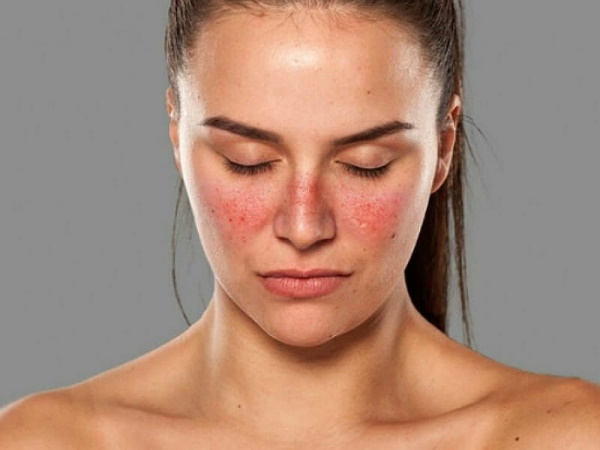
| Diagnostic indicators for discoid lupus erythematosus | Explanation of research results |
| LE-cells | In the structure of the cytoplasm of leukocytes of the neutrophilic type, there are foreign round-shaped neoplasms. LU objects are referred to as "lupus cells." During a detailed study of the blood, it is found that inside the neutrophilic leukocytes, LE-cells occupy the central part, and also have their own nucleus, which is pushed further to the periphery. |
| Antinuclear antibodies | The appearance of these antibodies is an indicator that an acute immune process is launched in the patient's body in response to external or internal stimuli. |
| Fixed antibodies | After a preliminary examination of the patient, a dermatologist will order a lupus strip test. This type of study detects fixed antibodies directly in the focus of the pathological process, where there is damage to the dermo-epidermal tissues. At the same time, the concentration of antibodies in these areas of the body is as high as possible. |
At the final stage of diagnosis, an analysis of histological signs is carried out, which, in combination with the results of laboratory studies, must meet the following characteristics:
- hyperkeratosis with the presence of horny plugs in the structure of the mouths of the hair roots;
- atrophic damage to the germ part of the epidermis;
- focal erythematous-follicular damage to the skin;
- basophilic collagen change;
- focal edema of the dermis with the formation of a lymphocytic infiltrate in the area of the skin appendages, as well as near the blood vessels.
Clinical analysis of peripheral blood has no diagnostic value. In this case, the attending physician sees only signs of thrombocytopenia, an accelerated ESR rate, leukopenia, and lymphopenia.
What tests are needed?
The list of tests that are required to examine a patient with symptoms of DLE is determined by a dermatologist after a preliminary examination of the patient. In this case, laboratory diagnostic methods can be used, confirming the fact of hyperactivity of the patient's immune system, the production of a large number of specific antibodies.
Biochemical analysis
For this diagnostic method, the patient's venous blood is used. The selection of biological material is carried out under sterile conditions in the manipulation room of a private or public clinic. You will need to donate about 3-5 ml of blood from a vein in the elbow joint. In the process of this type of diagnosis, the possible presence of lupus cells and antinuclear antibodies is determined.
For patients with discoid lupus erythematosus, an increase in the level of urea nitrogen, an increase in creatinine levels, and a simultaneous decrease in complement are also characteristic. Similar results of a biochemical blood test indicate an acute autoimmune reaction of the body with the creation of an additional load on the kidneys and other internal organs.
Lupus strip test
This research method involves biopsy of epithelial tissues, which are selected in the area of the pathological process. 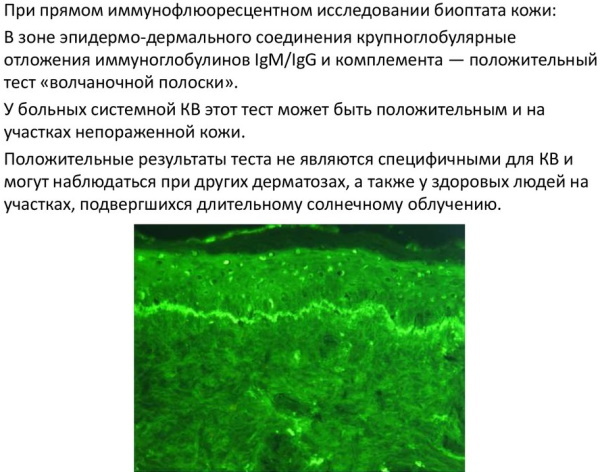 With this analysis, doctors determine the presence or absence of fixed antibodies. To obtain the most objective information, the collection of biological material can be carried out simultaneously from several parts of the body that have signs of discoid lupus erythematosus.
With this analysis, doctors determine the presence or absence of fixed antibodies. To obtain the most objective information, the collection of biological material can be carried out simultaneously from several parts of the body that have signs of discoid lupus erythematosus.
Clinical blood test and urine test
Fingertip urinalysis and peripheral blood tests provide the physician with information about the patient's general health. These diagnostic methods display indirect signs of DHQ, which indicate the presence of an immune response of the body and an acute inflammatory process.
Differential diagnosis
During the examination of patients with signs of discoid lupus erythematosus, differential diagnosis is mandatory. At this stage, the task of a dermatologist is to exclude the possible presence of a systemic form of this disease.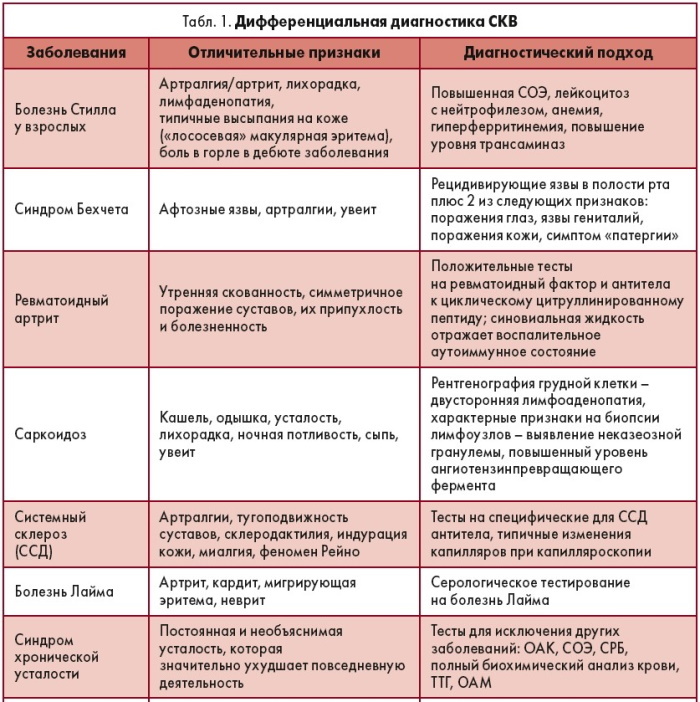
For DHQ without signs of complication, only erythematous-follicular skin lesions with local signs of cicatricial atrophy are characteristic. Systemic lupus erythematosus has no signs of follicular hyperkeratosis, but it always affects connective tissue of the joints, almost immediately causes inflammation of the kidneys, endocarditis and severe forms vasculitis.
DHQ treatment
Discoid lupus erythematosus (photo of the skin of patients with DLE reflects the focal prevalence of erythematous plaques) is treated with the use of glucocorticosteroid preparations of local action, and the patient must take antimalarial funds. The treatment regimen is developed individually by the doctor, depending on the severity of the pathological process, the rate of progression of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
For uncomplicated forms of discoid lupus erythematosus, the following therapy tactics are used:
- Fluocinolone acetonide in the form of a gel, cream or ointment is applied to the affected area of the skin 2 times a day for 12 weeks;
- Triamcinolone ointment is applied under an occlusive dressing 2 times a day for 7 days;
- cream or ointment Clobetasol rubbed into erythematous foci 2 times a day for 1 month;
- suspension of Triamcinolone is applied intralesionally at a dosage of 5 to 10 mg per 1 ml of the finished solution;
- Hydroxychlorin in the form of tablets is taken at 5-6 mg per 1 kg of the patient's body weight (the daily dose is taken once once a day with a duration of a therapeutic course of at least 60 days);
- Chloroquine tablets are drunk daily at 250-500 mg for 3 months;
- vitamin E in the form of capsules of 50-100 mg per day with a total duration of a therapeutic course from 4 to 8 weeks (this drug is prescribed for faster regeneration of skin that is damaged by autoimmune inflammation);
- Pentoxifylline tablets, which are taken 200 mg 2 times a day for 30 days;
- injection solution of Nicotinic acid in a dosage of 2-3 ml intramuscularly every other day with a general therapeutic course of 8 to 10 injections (this drug prevents damage to the walls of blood vessels, and also improves microcirculation of lymph in the foci of erythematous damage skin).
Treatment of women in a state of pregnancy is carried out only with the use of topical corticosteroids. For patients of this group, it is strictly forbidden to take antimalarial drugs, since there is a reasonable risk of intrauterine fetal pathologies. Therapy for discoid lupus erythematosus, which has no signs of complications, is performed on an outpatient basis.
In the absence of a positive result in the treatment of DHQ with the above medicines, the following second-line drugs are used:
- Tacrolimus ointment at a concentration of 0.1%, it is applied to the affected area of the skin 2 times a day for 2 months;
- pimecrolimus cream with a mass fraction of the active substance of 1%, it is rubbed into the foci of pathology 2 times a day with a therapeutic course of 4 to 8 weeks.
The severe course of discoid lupus erythematosus requires drug therapy in a hospital dermatological department. Throughout the course of treatment, the patient should avoid direct sunlight, wear long sleeves, and use sunscreen.
Forecast
Subject to timely treatment for medical help from a dermatologist and the initiation of treatment, it is possible to contain the further progression of the disease. A prerequisite for stopping foci of follicular hyperkeratosis and erythematous plaques is the elimination of pathological factors that provoke the body's autoimmune reaction. Otherwise, further spread of degenerative tissue changes in the area of healthy parts of the body is possible.
Discoid lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune-type dermatological disease that occurs in men and women aged 20 to 40 years. For every 100 thousand of residents of the Russian Federation there is 1 sick. The occurrence of DHQ is associated with abnormal reactions of the cells of the human immune system of T-lymphocytes to the contact of open skin areas with ultraviolet radiation. At risk are people with phototype I of the epidermis.
Discoid lupus erythematosus is characterized by multiple erythematous rashes, the formation of small and more voluminous grayish scales. In the center of the pathological focus there are areas with atrophic changes in epithelial tissues. Severe pain occurs when attempting to mechanically remove an erythematous plaque.
Lupus erythematosus video
Systemic lupus erythematosus - causes, symptoms: