Content
- Why rotavirus is dangerous
- Transfer method
- How mass infection occurs
- Etiology
- Incubation period
- Prophylaxis
- Precautions near the sick
- Rotavirus treatment video
Rotavirus is considered an infectious diseasewhich is widespread among children. It can also occur in adults. Below you can familiarize yourself with the method of transmission of infection from person to person, methods of preventing the disease, as well as precautions near the patient.
Why rotavirus is dangerous
Rotavirus is transmitted from person to person and is caused by a virus belonging to the Reovirus family. Infection occurs during the appearance of an infection on the surface of the oral mucosa. Then the disease enters the esophagus and small intestine, where it begins to multiply actively, causing bad consequences for the human body.
There are 8 types of rotavirus, but humans are not resistant to only 3. The disease is accompanied by the same symptoms. Very often, people become infected with rotavirus belonging to A.
Rotavirus infection is characterized by seasonality, the virus is very resistant to high and low temperatures, it becomes most active when the ambient humidity rises. Very often adults and especially children get sick in winter-spring, autumn-winter.
One of the main dangers of getting rotavirus infection is the loss of a lot of fluid. This leads to disruption of all body functions, dehydration and intoxication.
The volume of fluid in the body depends on its size. If a child starts to vomit and have profuse loose stools, it means that he can quickly become dehydrated. In this severe case, he only needs inpatient treatment.
Transfer method
Rotavirus is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. Often, infection occurs from an infected person with obvious symptoms of rotavirus disease or from a virus-releasing person - a person who is asymptomatic.
The patient spreads the infection from the beginning of the detection of the first signs and until the virus is completely cured. Often this period ranges from 5 to 7 days.
The disease affects almost every child under 5 years of age. In countries with low incomes, the first infection occurs between the ages of 6 and 9 months.
The percentage of GI infection in adults varies from 2 to 5%. Especially elderly people are not resistant to the disease.
The following categories of the population are potentially susceptible to the disease:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- children from 3-6 months to 6-7 years old;
- people over 60 years old, as well as those with a weakened immune system;
- people who have concomitant or chronic diseases;
- newborn babies who are artificially fed.

The routes of transmission of rotavirus infection are described in the following table:
| Transfer method | How does it manifest |
| Pool | The virus is stored in water for a long time, so one of the ways of infection can be a swimming pool. |
| Airborne droplets from an infected person to a healthy one | Often, this route of infection occurs from a child or adult in whom the virus is localized in the upper respiratory tract, and is accompanied by a sore throat or rhinitis. |
| Through water or food | Although tap water is chlorinated, it can also contain viral particles. For a very long time, the causative agent of the infection can be in products consisting of milk. At the same time, it is rather difficult to recognize its presence, since the product looks high quality and does not deteriorate for a long time. |
| Through various household items with which the patient was in contact | This transmission is the most common because the infection is highly contagious. |
The transmission mechanism of rotavirus infection is described in the following paragraphs:
- The host virus is initially located on the oral mucosa.
- Further, together with saliva, food and drink, it is relocated to the stomach. The virus is very resistant to hydrochloric acid.
- Then from the stomach it enters the duodenum, where it begins to develop pathogenic activity.
Rotavirus can develop and exist only in the epithelium of the intestinal villi. Compared to influenza, the infection does not show definite jumps in the incidence during the seasonal periods. This is due to the weakness of the body, lack of vitamins and insolation. As a result, the overall resistance of the body to infections is significantly reduced.
After recovery, a person may contract rotavirus infection again, which is associated with a seasonal change in circulating serotypes. Even if this happens, the recurrence of the disease will go away more easily. At the same time, after recovery, the body will have resistance only to the strain of the virus that the person has had.
How mass infection occurs
Rotavirus is transmitted from person to person and can manifest itself over several months. Since there are a large number of viruses in the fluids of the internal system of the body, this greatly facilitates the process of infection and explains its spread in mass cases.
Patients who have undergone a subclinical form of rotavirus infection pose the greatest danger to others. This is due to the fact that they were not provided with proper treatment.
Very often, the disease enters the water during the period of precipitation, when the liquid reaches cesspools and toilets. Also, the risk of an epidemic is increased by problems associated with centralized wastewater disposal, and pathogens are able to survive even after thorough filtering of drinking water.
Mass-household, contact method of infection is mainly typical for children's institutions, since toys, dishes or furniture can serve as habitats.
During pregnancy, rotavirus infection does not have a teratogenic effect on the developing fetus and does not in any way affect the course of pregnancy.
It is not worth bringing down the temperature of the patient immediately after raising it, because the body's defense mechanism has worked to fight the infection.
The method of spreading the pathogen is quite simple and in case of establishing the fact of the presence of rotavirus infection in a child, the kindergarten teacher should be immediately notified. In this case, the group is transferred to quarantine and children who do not have any signs of the disease are accepted.
Any surfaces that children touch must be thoroughly washed and disinfected. Sheets, pillowcases, and duvet covers with towels should be washed in very hot water. At the same time, kindergarten teachers do not have the right to accept children with symptoms indicating the presence of intestinal flu.
Since immunity during rotavirus infection is not lifelong, re-infection is possible in the future. The body, after a person has been ill, produces antibodies, which remain in the body for some time, protecting it from re-illness. The timing of antibody action varies and depends on various factors.
With a good immune system, the body's defense against rotavirus infection can last from 6 to 12 months. If the immune system is weakened, the period of protection will be shorter, and the patient will be sick very often. Despite this, the recurrence of the disease is much easier to carry.
The incubation period of the infection is influenced not by the infectiousness of the pathogen, but by the quality of the immune system. The stronger it is, the much later the disease will make itself felt.
Therefore, a clinically healthy person in whom an infection develops can infect an elderly person or a child without being sick. Infected people may show symptoms within a few hours, and in a peddler, only after a few days.
Etiology
The origin of the causative agent of the disease is described in the following list:
- genus - rotavirus;
- family - reoviridae;
- the kingdom is viruses.
The name "Rotavirus" was given to the microorganism due to its morphological variety. The rotavirus genome contains 11 stranded RNA segments from 2 rows, which are surrounded by 3 concentric viral envelopes.
The RHT segments encode 6 (VP1-VP7) structural and 6 (NSP1-NSP6) non-structural proteins. The first in the matured viral particle establish the peculiarity of the host and the ability of the infection to enter the cell, as well as its fermentation function. They are composed of epitopes that mimic the response of the immune system. The latter are involved in genome copying or viral DNA synthesis.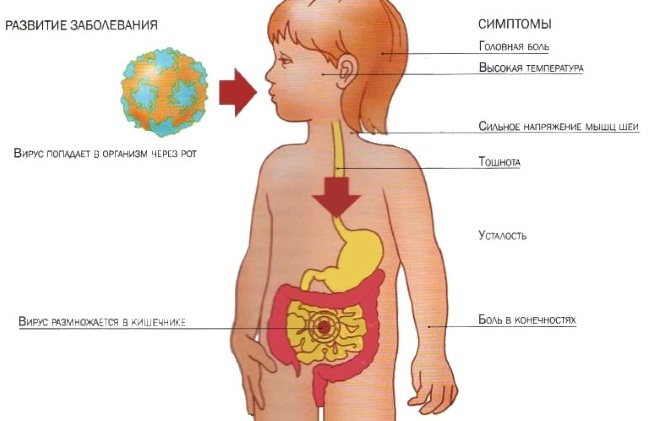
There are 10 known types of rotavirus infection from A to J. They differ in the antigens of the main constituent. Rotavirus A. This type is classified by the genotype according to different RNA segments relative to the sequence.
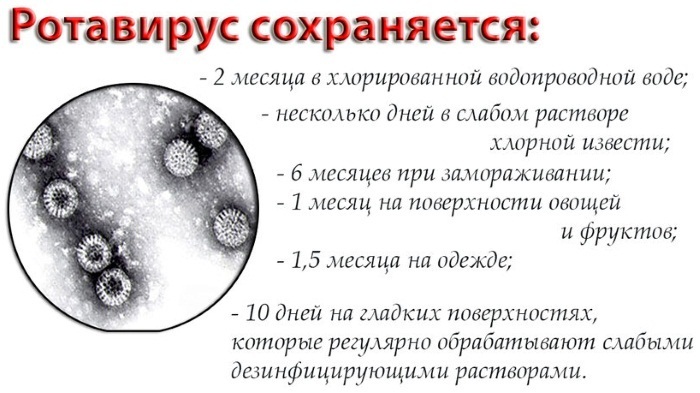
Due to the peculiarities of its own structure, the rotavirus is very resistant to the influence of external environmental factors and to many drugs intended for disinfection. Boiling liquids, however, kills the virus almost immediately. Due to this, the infection will not be transmitted from person to person.
Rotavirus infection is recognized by its severity and clinical presentation.
There are 3 degrees of severity:
- easy;
- moderate;
- heavy.
The severity of the disease can be determined by the number of vomiting episodes, stool fluid and the formation of dehydration syndrome. With mild severity, there are no symptoms of dehydration. Moderate is accompanied by dehydration of 1 and 2 degrees. A severe degree is accompanied by a desire to absorb large amounts of water, tachycardia, fainting, blanching of the skin, and a decrease in blood pressure.
The clinical picture consists of 2 types of disease: typical and atypical. The first type of illness is accompanied by diarrhea, fever, and vomiting.
The second form of infection is divided into 2 types:
- Blurred flow. Only loose stools or the release of vomit can be observed. Fever is absent in many cases. The duration of symptoms is very short, from 1 to 2 days.
- Asymptomatic course. Symptoms are absent, but when the feces are examined, the infection can be detected. Reproduction of the viral agent can last from 4 to 57 days.
Incubation period
The incubation period in time can last from 12 hours to 5 days. The clinical picture of the disease is accompanied by watery diarrhea for a long period, fever, or vomiting.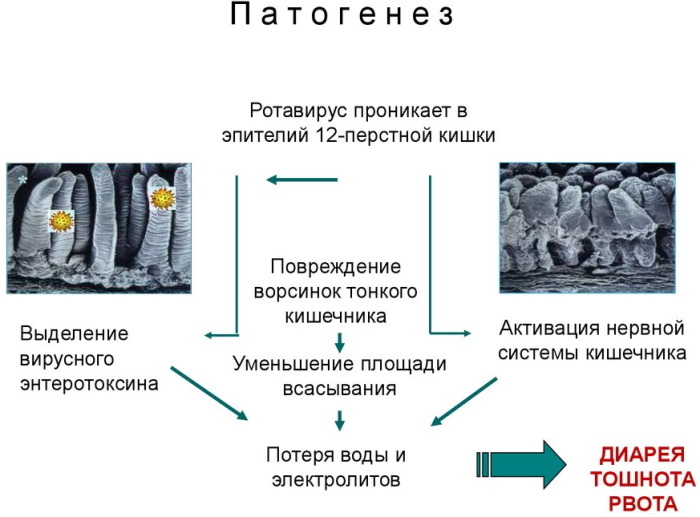
Moderate inflammatory syndrome of the mucous membranes in the form of nasal congestion, cough, or runny nose can be observed in the early days of infection. Temperature with symptoms of intoxication - lethargy, lack of appetite and weakness can persist from 2 to 4 days. Additionally, vomiting with diarrhea lasting up to 8 days and with a frequency of up to 2 times a day may develop on the first day.
An acute infectious disease with a fecal-oral mechanism is characterized by the occurrence of pain. Cramping pains begin to appear in the upper abdominal region. Flatulence, rumbling in the intestines and bloating are very common.
Complications include dehydration, especially in newborn babies.
At the very beginning of progression, the disease manifests itself with the symptoms listed in the following list:
- restless and agitated state;
- desire to drink, dry mouth and dry skin;
- minimal retraction of the large fontanelle;
- decrease in the elasticity of the skin.
With the progression of the disease, the child's reaction slows down, he becomes lethargic, does not want to drink water and eat. Breathing quickens, the amount of excreted urine decreases, which becomes cloudy and takes on a pungent odor.
In case of failure to provide full-fledged medical qualified assistance, complications may develop that threaten human health and life.
Other complications of infection are described in the following list:
- acute renal failure and the appearance of a bacterial infection;
- the central nervous system is affected, which is accompanied by convulsions, impaired consciousness.
Prophylaxis
Non-specific prevention is based on the implementation of sanitary and hygienic standards:
- hand cleaning after using the restroom or before eating;
- wet cleaning of the room;
- timely fencing of patients with intestinal infection.
Additionally, you need to monitor the quality of food and drinking water, as well as follow a diet in the prevention of disease to limit dairy products, carbohydrates and increase the amount of protein. It is useful to lead a healthy lifestyle without bad habits.
Specific prophylaxis is vaccination. Infants should be vaccinated against rotavirus infection. This is a good prevention of disease and strengthens the human immune system.
At the moment, in Russia against RVI, a vaccine called "RotaTek" is used, which is used for specific preventive measures against rotavirus infection in children aged 6 to 31 weeks.
The composition of the vaccine in a volume of 2 ml is administered to the infant through the oral cavity. The vaccination course is based on 3 doses with a pause between use from 4 to 10 weeks. All 3 injections should be given between 6 and 32 weeks of age, the first between 6 and 12 weeks of age.
The vaccine helps the body develop specific antibodies that fight the rotavirus serotype.
Also, a preventive measure can be vaccinations and Mantoux tests, which are carried out in case of an illness after 30 days.
Precautions near the sick
Rotavirus is transmitted from person to person, therefore, take good preventive measures RVI is very difficult, since the pathogen is stable in the external environment, and it spreads quite fast. Therefore, there is no prophylaxis that prevents 100% protection from the disease.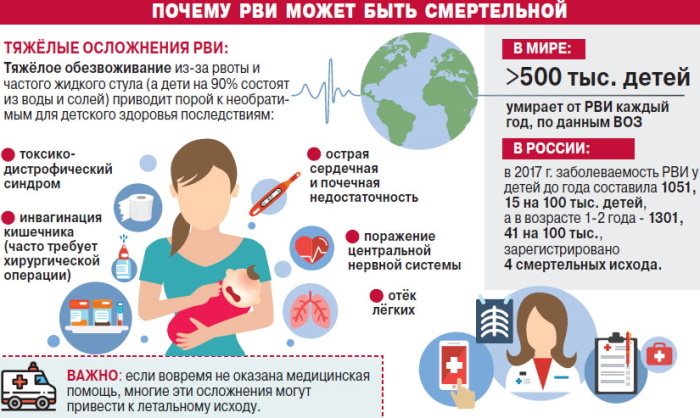
However, by observing the following rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of contracting rotavirus infection:
- If a family member becomes infected with rotavirus, he or she should be immediately isolated from the rest for up to 2 weeks, since for others it is a carrier of the infection.
- If possible, it is recommended to quartz the premises every day.
- Everyone should have their own cutlery. Raw foods that have not been cooked should be kept away from other ingredients. At the same time, they need to provide a separate utensil with a knife and a cutting board.
- The patient's belongings should be heat treated as often as possible.
- After visiting the restroom, you should always wash your hands with soap and water, since an infectious person uses it, and viruses are able to maintain their vital activity for several months. Adults must strictly abide by these rules and teach children to them.
- Vegetables and fruits must be thoroughly washed and scalded with boiling water before fresh consumption. Only boiled water should be consumed.
- In the event of an epidemic, it is required to stop eating in public catering places, and after visiting the restroom, wash your hands with soap and water and treat with a disinfectant.
The rotavirus pathogen is contagious and has good resistance to the external environment. The infection is spread from person to person through breast milk, saliva, shared objects, and dirty hands.
For therapeutic and prophylactic purposes, it is necessary to get rid of dehydration, ventilate the room daily and carry out wet cleaning. In the presence of immunity to an infectious disease, the risk of re-infection is minimized. However, the body develops resistance only to the strain of the virus that it has had.
Rotavirus treatment video
Treatment for rotavirus infection: