Content
- What it is
- Classification
- Pathogenesis
- Biological theory
- Hereditary theory
- Social and psychological theory
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of the disease
- Drug therapy
- Psychotherapy
- Prophylaxis
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder Videos
Schizotypal personality disorder (SD) - a deviation in the normal functioning of the psyche, manifested in abnormal, in the opinion of others, strange behavior, emotional coldness and a desire to isolate oneself from society, anomalies of thinking and emotions in person.
From time to time, individuals with pathology may experience inadequate responses, paranormal ideas, or severe obsession. In rare cases, hallucinations or episodic illusions may also occur. Treatment of psychiatric pathology is carried out in stationary conditions with a combination of medication and psychiatric techniques.
What it is
Timely started therapy can reduce the decline in intellectual activity and prevent social isolation, and also helps the patient to adapt in society, prevent the development of disabilities and even keep their work a place.
In the 90s of the last century, the pathology was characterized by psychiatrists as “sluggish schizophrenia ", because its manifestations are not intense enough to diagnose the classic schizophrenia.
People suffering from schizotypal disorder are characterized by indifference and impartiality inherent in schizophrenia, a tendency to loneliness, and also the occurrence of inappropriate paranormal reactions, but here they are not sufficiently pronounced in order to be attributed to schizophrenic delirious.
The schizotypal disorder, which is found, according to statistics, in about 3% of the population is more often possible observed in men than in women whose relatives have previously undergone psychiatric treatment due to schizophrenia.
According to the ICD-10 classification of diseases adopted in the Russian Federation, schizotypal personality disorder is considered a full-fledged pathology, which is a sluggish and gradually a progressive process caused by endogenous (internal) factors, with mental disorders, occupying an intermediate part between schizophrenia and pathological personality disorder.
The first signs of pathology can appear already at the age of 3-5 years, after strong emotional stress or stress, and she herself pathology has an imperceptible onset, gradual development and chronic nature, without pronounced periods of exacerbation and remission.
Classification
Schizotypal personality disorder (it is completely impossible to recover from pathology) is considered a phenotypic variant of the schizophrenic genotype. Individuals suffering from this pathology have various oddities of thinking, worldview, behavior and statements, but the degree of their severity is insufficient for the diagnosis of schizophrenia.
People with schizotypal personality disorder are characterized by a deficit in interpersonal and social communication, leading to an inability to build close relationships. From an early age, one can also observe a tendency to distort the perception of reality and eccentric behavior that provokes ridicule from others. Criticism and laughter, in turn, make the patient want to "get rid" of society, making him behave even more strangely and completely withdrawn into himself.
In the future, such patients may also develop a pathological tendency to perform any rituals, for example, constantly washing hands for fear of germs or washing clothes, carried out strictly at the same time and at a certain okay. The relatives and friends of such patients also noted that they heard strange requests from their relatives, for example, not to turn on the TV, sleep with them, or take certain medications.
According to clinical manifestations, psychiatry divides pathology into 6 types, highlighting:
| Latent type | A pre-psychotic stage in the development of pathology, characterized not by psychotic somatics, but by mild, atypical manifestations. |
| Neurosis-like schizophrenia | A disease in which psychopathological symptoms (hypochondria, phobia, obsession) can be noticed in the patient's behavior. |
| Pseudopsychopathic type of disease | A pathological condition accompanied by a change in the character and behavior inherent in schizophrenia. |
| Sluggish schizophrenia | Psychiatric disorder characterized by apathy, asthenic defect and social loneliness, without episodes of hallucinations and delusions. |
| Schizophrenic reaction | Psychogenically conditioned psychotic reaction with signs of schizophrenia. |
| Unspecified schizotypal psychopathy | A pathological condition with an unclear etymology, in which psychosomatic disorders are accompanied by hallucinations and delusions. |
Pathogenesis
Schizotypal personality disorder (it is possible to recover from pathology only in stationary conditions) in in most cases manifests itself under the influence of stress or emotional experience in childhood or adolescence age. In psychiatry, there are several theories of the occurrence of pathology:
Biological theory
It connects the development of the disease with a high production of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain, which disrupts the physical process of conducting nerve impulses, provoking the formation of foci of hyperexcitability. Such activity negatively affects mental properties and processes, provoking the development of a pathological background.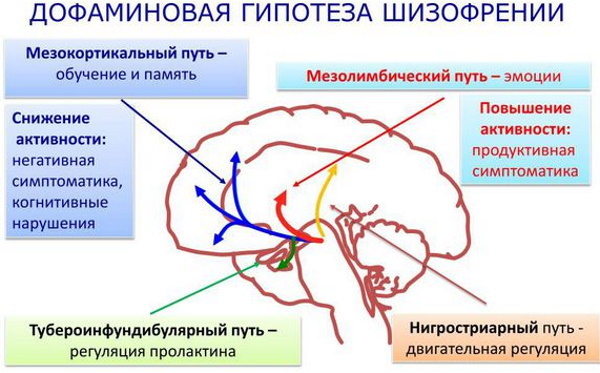
Biological factors also include:
- brain injury;
- severe toxicosis;
- intrauterine brain damage.
Hereditary theory
According to research, about 50% of all cases of development of schizotypal personality disorder occur in people whose relatives were previously treated for schizophrenia.
Social and psychological theory
In most cases, the disease occurs in childhood, and its prerequisite is the atmosphere in which the child grows up.
So, according to studies, the development of pathology can be provoked:
- Physical or emotional abuse of a child. In addition to physical harm, also includes emotional pressure on the child's psyche, infringement of his rights and verbal aggression.
- Emotional coldness of parents. Lack of attention and parental love provokes the emergence of a chronic stressful situation, which subsequently transforms in the development of the child's emotional poverty with the inability to enter into full-fledged close contacts with others people.
- Constant conflicts between close relatives, witnessed by a small child.
- The peculiarity of the interaction of parents with a child, manifested in the gradual formation of his fear of a certain object or person.

In addition, the development of schizotypal personality disorder leads to:
- alcohol or drug addiction;
- chronic stress;
- psychological trauma.
Symptoms
Schizotypal personality disorder (it is possible to recover from the disease with the help of drugs and psychiatric techniques) can be predicted by the behavior of a child at the age of 5-7 years.
For such children, loneliness and unwillingness to play in the company of peers are characteristic. In their behavior, you can also notice signs of obsession, manifested by repetitive monotonous movements or fixation on certain objects. So the baby can drink strictly from only one cup, refusing to use other dishes.
The emotional background in children prone to the development of schizotypal personality disorder is unstable, and to bring them out of balance absolutely any, even an insignificant detail, such as the refusal of parents, to provide them with a favorite toy, plate or a cup. In the event of a sharp refusal of such a child, an attack of hysteria covers, after which he looks tired and depressed, but if you try to hug or calm him down, the hysteria will resume.
Characteristic for such children, rancor and an awkward gait, accompanied by a violation of coordination. In adulthood, schizotypal disorder becomes more symptomatic.
For such people, the appearance is characteristic:
- strange beliefs and speech;
- a tendency to esoteric thinking;
- bodily illusions associated with unusual sensations;
- excessive suspicion, manifested, including obsessive thoughts about possible persecution;
- emotional coldness, or vice versa, the manifestation of emotions inappropriate in a situation;
- strange objects in clothes and unusual behavior;
- difficulties in establishing social contacts and in communicating with strangers, with the exception of blood relatives.

The most common symptom for such patients is deep apathy or impotence, in which you want to lie down all the time and do nothing.
Those suffering from pathology may complain of a lack of mood and complete indifference, in which there are no emotions of joy or grief. The only feeling that persists at this moment is anxiety, which manifests itself in the form of internal tension and provokes tachycardia, dizziness or rapid breathing. To reduce the patient's internal stress, movement or swaying in place, as well as the constant turning over of an object with his hands, helps the patient.
Another sign of pathology is emotional coldness, in which a person not only does not feel empathy for feelings of other people, but he himself loses sensitivity, perceiving life events only from the position of "good" or "Bad".
Emotional coldness is accompanied by indifference and lack of facial expressions in behavior, periodically replaced by uncontrolled outbursts of aggression. This behavior becomes the cause of problems with others and loved ones, provoking the forced loneliness of a person with schizotypal disorder.
The appearance of a person is also perplexing, and involuntarily attracts attention with its eccentricity. During periods of depression, such people may wear torn, dirty clothes or dress provocatively, instantly standing out from the crowd. The speech of patients is incoherent, since it is difficult for them to keep thinking on any one thought.
People with schizotypal personality disorder are characterized by mystical thinking and passion for esotericism, or, on the contrary, increased religiosity. Hallucinations during the disease do not manifest themselves brightly and are associated with the animation of foreign objects.
In addition to the strangeness in behavior, patients with SR are characterized by the appearance of various phobias.
Diagnostics
Schizotypal personality disorder (a person will not be able to completely recover from pathology, but regular medication will allow to stop further development in time complications of the disease) is diagnosed by a psychiatrist, on the basis of studying the patient's behavior, conducting clinical studies, collecting information about his life and the state of blood relatives.
Various symptoms of the disease can complicate the diagnosis, such as severe anxiety, neurotic conflicts or pathological adherence to magical ideas, giving the possibility to assume in the patient:
- developmental and concentration disorder associated with defects in the nervous system;
- social phobia;
- autism;
- dysthymia;
- increased emotional response to stressors;
- bipolar disorder;
- depression or psychopathy.
It is also necessary to separate schizotypal personality disorder from schizophrenia, which is characterized by hallucinations, movement disorders and confusion.
In addition, SR does not have a complication characteristic of schizophrenia — a psychopathological syndrome that combines apathy and abulia and is characterized by emotional and volitional impoverishment of the personality.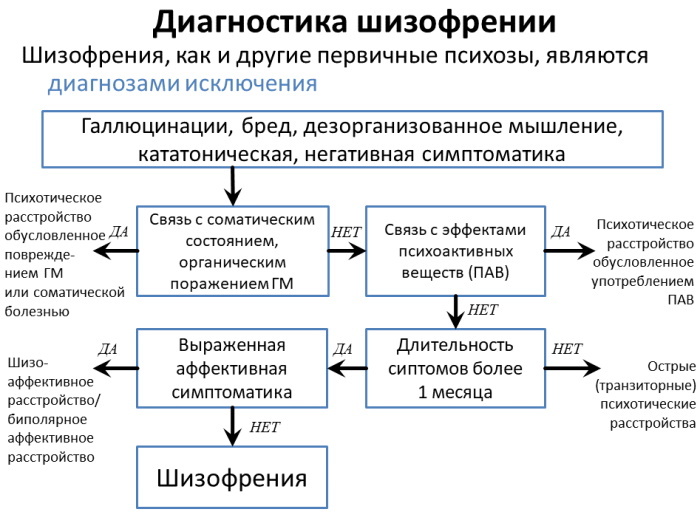
Additionally, for diagnostics, it is carried out:
| Experimental psychological examination | Allows to reveal the state of cognitive functions of a person, the content, quality and dynamics of his emotions and feelings, and their regulation, as well as the personal characteristics of the patient. |
| Neurophysiological examination of the brain | Determines to detect the degree of damage to the functions responsible for cognition of the surrounding world and the ability of the brain to adapt to changing conditions. |
| Neurotest | Establishes the state of the nervous system affected by the pathological process. |
Treatment of the disease
It is possible to recover from schizotypal personality disorder only in inpatient conditions of a psychiatric clinic, and timely started therapy will allow to stop painful symptoms pathology, as well as to prevent the development of complications that provoke persistent disability, the development of severe forms of schizophrenia, the emergence of addiction and suicidal inclinations.
After the disappearance of painful symptoms associated with severe depression, psychosis, severe obsessions and compulsions, the patient is discharged from the hospital to continue treatment in the outpatient conditions. Disease therapy is carried out in a comprehensive manner and consists of:
Drug therapy
Therapy for schizotypal personality disorder is carried out using:
- antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptics);
- psychotropic drugs used to treat depression;
- normotimics;
- anxiolytics.

The dosage and dosage regimen is selected individually, depending on the clinical picture of the pathology and the patient's condition.
Therapy should be long-term and be not only therapeutic, but also preventive in nature, since after elimination of the symptoms of the disease with a certain frequency, preventive courses of admission should be carried out drugs.
Psychotherapy
Work with a psychologist can be carried out both individually and in groups, and is aimed at teaching and helping the patient in prevention and relief of symptoms of the disorder, in the establishment of social ties and correction of pathological personal characteristics. In contrast to schizophrenia, in SR, any methods of psychotherapy are permissible, which make it possible to increase the patient's stress resistance and prevent the development of auto-aggressive behavior.
Prophylaxis
Prevention of schizotypal personality disorder should begin in early childhood and consists in the gradual enrichment of the inner world and the external environment of the child.
Specialists refer to prevention methods:
- increasing the physical activity of children;
- cognitive stimulation;
- normalization of communication with parents and peers;
- improving nutrition that contributes to the formation of the brain.
Psychiatrists advise paying special attention to maintaining a good psychological climate in the family, as well as fencing a child from adult conflicts that turn into severe stress for the child's fragile emotional sphere, excitement.
Schizotypal personality disorder is a serious pathological condition associated with behavioral disturbances, social isolation, the appearance of phobias and inappropriate reactions. The disease that occurs in early childhood due to severe emotional damage can cause severe mental disorders, the development of schizophrenia or disability of the patient.
It is impossible to completely recover from the pathology, but with timely treatment started, it is possible to achieve stable remission and complete the disappearance of internal tension, as well as to teach the patient the ability to stop signs and establish a full-fledged social communication.
Schizotypal Personality Disorder Videos
Schizotypal Personality Disorder - Treatment, Symptoms, and Causes:


