Content
- How and why blood clots
- Blood clotting rates in women by age, in different conditions
- Indications for the examination
- Types of laboratory tests for coagulation
- What indicators are determined by the analysis
- General blood analysis
- Coagulogram indicators
- Thrombin time
- Prothrombin time
- APTT
- Fibrinogen level
- Antithrombin III level
- D-dimer level
- Plasminogen activity
- Protein C activity
- Free protein S level
- Having a lupus anticoagulant
- Preparation for analysis
- Research Algorithm
- Blood from a vein
- Finger blood
- What do deviations from the norm, causes and consequences mean?
- Increased clotting
- Decreased clotting
- Additional examinations in case of deviation of indicators from the norm
- How much does research cost
- Coagulation Analysis Video
Blood clotting in women Is a physiological indicator that displays the rate of thrombosis of the damaged area of the body with a complete cessation of blood loss. The formation of a blood clot in the focus of injured tissue is a complex and stepwise process. Temporal norms of venous and capillary blood clotting are the same for women of all age groups who do not have chronic diseases of internal organs, as well as pathologies of hemostasis.
How and why blood clots
Blood coagulation is one of the most important stages of hemostasis in the human body, which is responsible for stopping moderate or acute blood loss after the destruction of the vascular walls. Several systemic mechanisms are involved in the implementation of this function, aimed at narrowing capillaries, veins, arteries, redirecting platelets in the focus of the pathological process, the formation of protein filaments in the blood in the form of fibrin with further transformation of functional blood clots.
Rapid blood clotting is necessary for adults and children to prevent acute blood loss, preserve vital functions of the body in case of injury to the epithelial and soft tissues of the body, the development of local inflammatory processes.
The table below describes the 3 main phases of blood clotting in women of all age groups: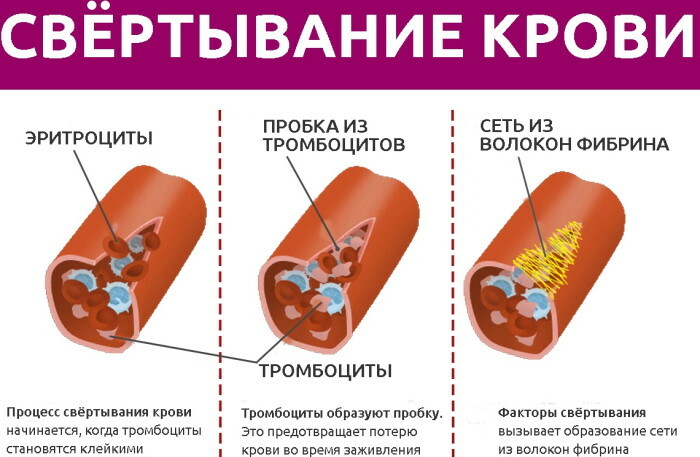
| Phases of blood clotting | Characteristics of the physiological process |
| Activation phase | The initial stage of blood clot formation. At this stage, the biological mechanisms of the formation of the substance prothrombinase are triggered with the further transition of prothrombin into active thrombin. |
| Coagulation phase | During this period, fibrin is converted. This component is produced in the process of hemostasis on the basis of the protein compound fibrinogen. |
| Retraction phase | The final stage of stopping acute or moderate bleeding. During this period, a dense blood clot is formed in the wound site, containing a high concentration of fibrin. |
Chemicals from the cation group accelerate the natural blood clotting process, while anions act in exactly the opposite way. Timely formation of a blood clot in the area of wound damage to the body allows not only to prevent large blood loss, but also to protect the vascular system from infectious invasion.
Blood clotting rates in women by age, in different conditions
The blood clotting rate is the same for women of all ages. This indicator is determined by fixing the time during which a dense thrombus will form in the injured area of the body with complete relief of blood loss. In women with a healthy body, without dysfunctions of hemostasis, the rate of wound thrombosis in the form of a puncture of soft tissues is from 30 seconds to 2 minutes.
Deviations in the direction of faster or too slow blood clotting indicate a change in blood cellular composition, as well as the possible presence of severe diseases of the liver, organs of endocrine and hematopoietic systems.
Indications for the examination
Diagnostics of the blood clotting rate (coagulogram) is carried out for preventive purposes before preparation the patient for planned operations, or is prescribed after the appearance of direct signs of too low activity blood clots.
This examination is indicated for use in the following cases:
- the state of pregnancy, as well as the comprehensive preparation of the female body before conceiving a planned child;
- recovery period after surgery (blood biochemical composition is monitored to prevent internal bleeding in the area of surgery);
- varicose veins of the legs;
- all types of autoimmune diseases of the body;
- increased tendency to bleeding of unknown etiology;
- pathology of the heart and blood vessels;
- long-term intake of drugs from the pharmacological group of anticoagulants;
- congenital or acquired liver disease.

Hypercoagulation of blood is no less dangerous for the human body than the tendency to profuse blood loss. The increased activity of platelets in terms of blood clots can lead to the development of acute heart attack, ischemic stroke of the brain, as well as thrombosis of large vessels.
Types of laboratory tests for coagulation
Blood coagulability (the norm in women does not depend on their age) is determined using the following laboratory research methods:
- thromboelastography;
- thromboplastin time test;
- determination of the rate of thrombus formation in whole blood;
- thrombodynamics;
- thrombin protein generation test;
- fixation of prothrombin time.
All of the above diagnostic methods measure the time from the moment of blood contact patient with the external environment until a dense fibrin clot forms, blocking further blood loss. The method of laboratory examination is selected individually by the attending physician, depending on the signs of the pathological state of the patient's body, as well as the goals of diagnosis.
What indicators are determined by the analysis
There are a large number of laboratory blood tests that examine hematological parameters that affect the rate of coagulation.
General blood analysis
A general analysis is aimed at determining the number and quality of all blood cells. In the process of assessing the level of coagulation, special attention is paid to the indicator of platelets.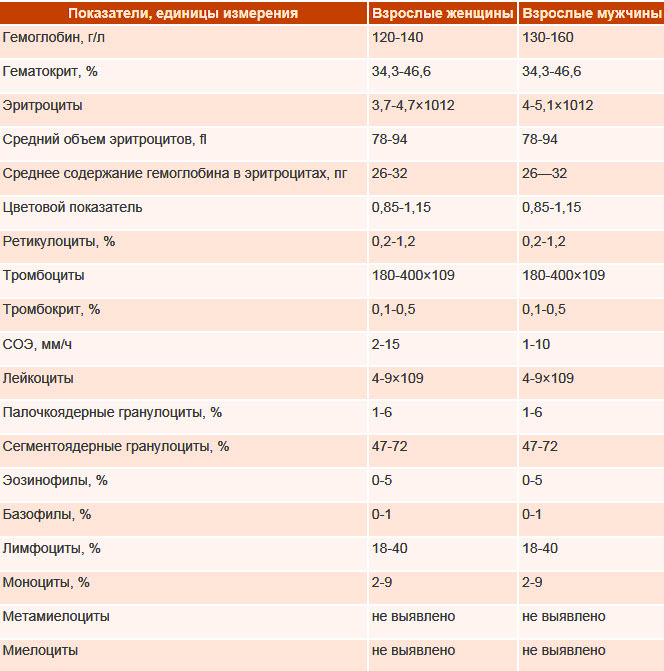 Normal values of these structural blood elements are from 180 to 320 * 10-9 / 1 l. A decrease or increase in platelet concentration affects the rate at which a blood clot forms at the site of potential body damage.
Normal values of these structural blood elements are from 180 to 320 * 10-9 / 1 l. A decrease or increase in platelet concentration affects the rate at which a blood clot forms at the site of potential body damage.
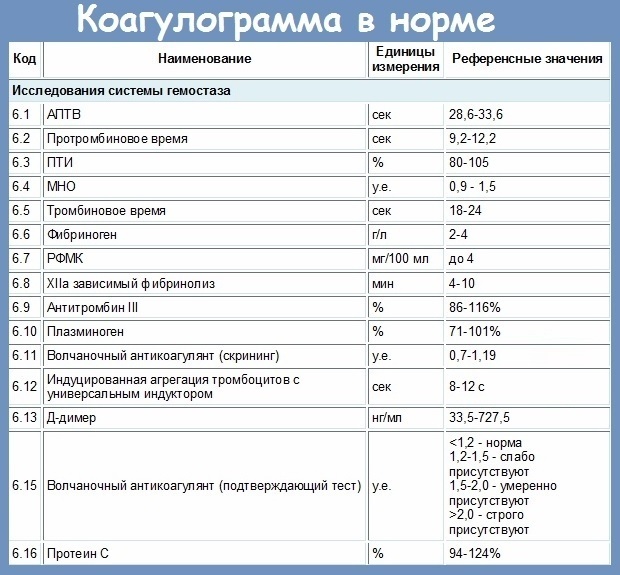
Coagulogram indicators
Coagulogram is an informative method of laboratory blood tests, which displays the level of fibrinogen, APTT, thrombin, and prothrombin time.
Thrombin time
Normal values of thrombin time in women of all ages are from 10.3 to 16.6 s. At this stage of the examination, the rate of formation of a fibrin clot is determined after the enzyme substance thrombin appears in the blood plasma. During the specified period of time, there is a change in the density of the blood in the direction of its thickening.
Prothrombin time
The norm of prothrombin time is from 9 to 15 s. During this period, a full-fledged clot is formed on the basis of platelets, which has the functional ability to stop further blood loss.  The indicator of prothrombin time depends on the state of health of the liver, blood sugar levels, quantitative and qualitative composition of hematological components.
The indicator of prothrombin time depends on the state of health of the liver, blood sugar levels, quantitative and qualitative composition of hematological components.
APTT
This indicator of the coagulogram displays the thromboplastin time of blood coagulation in the external and internal pathways. The APTT level in a healthy woman who does not have hematological diseases or severe pathologies of internal organs ranges from 25.4 to 36.9 s.
Fibrinogen level
The general rate of fibrinogen in women is 2 to 4 g per 1 liter of blood. In pregnant women, the normal values of this indicator can increase up to 5.6 g. Similar research results are typical for women in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of intrauterine development of the fetus. Determination of the level of fibrinogen is necessary to identify the qualitative composition of the blood, as well as to carry out differential diagnostics for concomitant liver diseases.
This component is an acute phase protein, and the activation of the processes of its synthesis is enhanced at the time of traumatic tissue damage or inflammation. Decreased fibrinogen levels occur in people with congenital or acquired liver disease.
Antithrombin III level
Blood coagulability (the norm in women for the content of thrombus-forming blood components changes after pregnancy) is an indicator of its quality characteristics. Antithrombin III is a specific protein substance that is involved in the activation of thrombin, and also prevents the formation of excess blood clots in the circulatory system.
To isolate this indicator, venous blood donation is required. The norm of antithrombin III in women over 16 years old is from 66 to 124%. During pregnancy, normal values for this indicator are in the range from 70 to 116%. An increase in the concentration of antithrombin III increases the risk of opening internal bleeding. The average cost of this analysis is 555 rubles.
D-dimer level
An indicator of the rate of blood clotting D-dimer is a substance that is formed in the process of destruction of the structure of a blood clot (fibrinolysis). Determination of the level of this component is necessary to diagnose diseases that cause an increased formation of blood clots inside the blood vessels.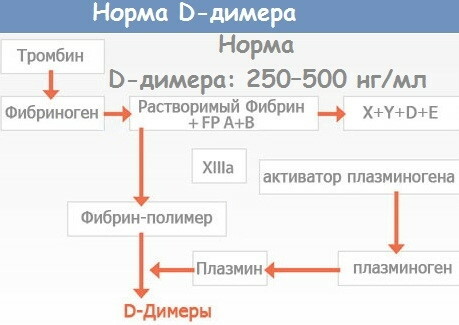
The normal concentration of D-dimer in the blood of women should not exceed 0.5 μg per 1 ml of biological material. During pregnancy, this indicator can be increased by 2-3 times, which is not a sign of pathology. The analysis for D-dimer is carried out separately from the coagulogram, and its average cost is from 850 to 1550 rubles.
Plasminogen activity
Plasminogen is a proenzyme protein found in blood plasma. In conditions of traumatic damage to tissues or walls of blood vessels, plasmin is converted into a biologically active compound.
Plasminogen is an important part of the general fibrinolytic system of the human body. The action of this component is aimed at preventing the formation of too many blood clots. Normal levels of plasminogen in healthy women are 80 to 130%. Venous blood is used as a biological material.
Protein C activity
Blood coagulability (the norm in women for the content of substances that form blood clots remains stable in the absence of hematological diseases) is determined by a laboratory assistant within 1-2 working days. Protein C is an important inhibitor of blood clotting.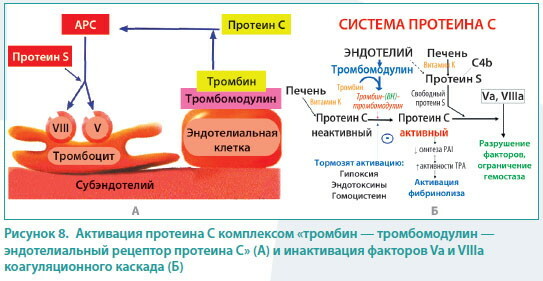
This component activates the process of fibrinolysis, limits the physiological dimensions of the thrombus. The synthesis of protein C is carried out by the liver tissues, and the rate of its activity in women is from 0.7 to 1.30 U. For laboratory analysis, venous blood is used. The average cost of this diagnostic is 1995 rubles.
Free protein S level
Protein S is a protein found in blood plasma. This substance acts as a natural anticoagulant. Determination of the level of free protein S is extremely important during the differential diagnosis of thrombophilia, as well as thrombosis of the veins and arteries of the lower extremities.
In girls aged 9 to 17 years, the norm of this blood index is from 60 to 140%. In adult women, the level of free protein S is in the range of 54.7 - 123.7%. Reducing the level of this substance is much more dangerous than maintaining its high concentration in the blood. A low level of free protein S occurs in women with severe liver disease, nephrotic syndrome, lupus erythematosus. The price of this analysis is about 2295 rubles.
Having a lupus anticoagulant
The appearance of lupus anticoagulants indicates an acute immune reaction of the body, directed to its own phospholipids. The latter substance plays a key role in the formation of blood clots. Phospholipids are attached to the platelet surface. They take an active part in the activation of thrombus-forming factors in response to traumatic damage to tissues and blood vessels.
This anticoagulant is called lupus due to the fact that it was first diagnosed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. For this analysis, venous blood is used. The physiological norm is the appearance of a lupus anticoagulant 31 - 44 seconds after the introduction of a chemical reagent into a biological material. The price of this examination is 1090 rubles.
Preparation for analysis
Blood coagulability (the norm in women of enzymatic factors of thrombus formation changes due to concomitant hematological diseases) is determined by a basic laboratory analysis in the form of a coagulogram. A screening method is used.
Conducting a coagulogram requires compliance with the following preparation rules:
- do not have breakfast on the day of blood donation;
- arrive at the laboratory in the morning from 8 am to 10 am;
- 2 days before the analysis, do not abuse fatty, fried, protein and sweet foods;
- avoid psycho-emotional overstrain and stressful situations;
- avoid overwork.
Preparation for a coagulogram involves adherence to the usual drinking regimen. Patients who take any medications on an ongoing basis should inform the attending physician about this fact.
Research Algorithm
Blood clotting tests are carried out in a sterile biochemical laboratory by appropriately qualified medical personnel.
Blood from a vein
Venous blood sampling is carried out in compliance with the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient goes to the manipulation room.
- Place the right or left hand on the table.
- A medical professional applies a tourniquet on the forearm of the upper limb to improve access to the great vessel, and also performs antiseptic treatment of the skin.
- Blood is drawn from a vein on the inside of the elbow.
- The biological material is transferred to the laboratory to perform the type of analysis that was prescribed by the attending physician.
Depending on the type of diagnostic technique that is used in a particular clinical case, laboratory staff will need from 2 to 5 ml of the patient's venous blood. Coagulation indicators are determined within 1-2 days, and in emergency cases they can be isolated in 2 hours.
Finger blood
Peripheral blood donation is carried out in compliance with the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient goes to the sterile conditions of the manipulation room.
- The nurse performs antiseptic treatment of the beams of the patient's ring finger.
- With the help of a scarifier, the skin of this part of the upper limb is dissected.
- The sampling of biological material is carried out.
Peripheral blood from the ring finger bundle is taken for clinical analysis for platelets and other physiological components involved in the coagulation process.
What do deviations from the norm, causes and consequences mean?
Blood clotting (the norm in women of thrombus-forming substances depends on the functional state of their liver) may be accompanied by hypercoagulability or too slow formation of blood clots.
Increased clotting
A high clotting index indicates an increased concentration of platelets and other components involved in the formation of blood clots.
The following factors cause hypercoagulation:
- progressive arterial atherosclerosis;
- radiation sickness;
- low physical activity;
- severe pathologies of the liver and spleen;
- endocrine disorders that cause hormone imbalance;
- autoimmune processes in the body;
- dehydration;
- diabetes;
- infectious inflammation of the blood vessels.
Increased blood clotting is observed in women in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy, but this factor is not pathological. The danger of active thrombus formation is that dense blood clots can form in the veins and arteries. It is fraught with stroke, heart attack, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, varicose veins.
Decreased clotting
The low level of blood clotting in women of all ages is caused by an insufficient concentration of platelets and protein complexes that perform a thrombus-forming function.
This is a pathological condition of blood and hemostasis that causes the following diseases:
- hemophilia;
- purpura;
- thrombohemorrhagic syndrome;
- von Willebrand-Diana disease (a genetic abnormality manifested by spontaneous bleeding).
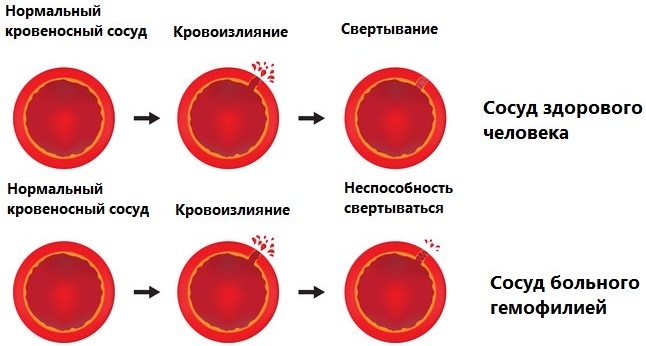
The consequences of reduced blood clotting are dangerous to the life and health of the patient. The above pathologies provoke local and extensive bleeding, damage to the walls of blood vessels, a systematic decrease in hemoglobin. Death from acute blood loss is a critical complication.
Additional examinations in case of deviation of indicators from the norm
Depending on the results of a laboratory blood test for the rate of clotting, the patient may be assigned the following additional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the liver and spleen for the timely detection of tumor neoplasms, cirrhosis, as well as other changes in the structure of these organs;
- MRI examination of the whole body, if signs of chronic inflammation were found at the stage of preliminary diagnosis of the patient, or degenerated cells were isolated in the blood;
- donating blood for glucose levels to exclude the factor of diabetes mellitus;
- testing venous blood for the presence of the pathogen of HIV;
- duplex scanning of blood vessels of the lower extremities and other parts of the body, if there are signs of thrombosis, inflammation of the endothelial layer, atherosclerosis.
The above diagnostic methods can be performed on the same day with the delivery and analysis of venous blood. According to the results of a comprehensive examination of the body, a phlebologist, cardiologist or therapist form a further course of the therapeutic process.
How much does research cost
The average cost of a coagulogram with the release of the level of fibrinogen, thrombin, and also prothrombin time is from 1360 to 3790 rubles. Capillary or venous blood is used as a biological material, depending on medical indications.
Blood clotting is a defense mechanism of the human body aimed at stopping acute blood loss in critical health situations. Thrombosis of damaged tissue areas occurs in several stages. An increased number of platelets is redirected to the area of the body with injured vascular walls, which within 2 minutes. under the influence of enzymatic factors of blood clotting, they are transformed into dense blood clots.
In women with normal functions of hemostasis, the rate of thrombosis of the wound area of the body in the form of a small puncture with a needle is from 30 s to 2 minutes. Hypercoagulation indicates a too high platelet count, an increased risk of thrombosis, myocardial infarction, and ischemic cerebral stroke. Too slow blood clotting is the first sign of hemophilia.
Coagulation Analysis Video
Komarovsky about the blood coagulation system: