Content
- Causes of Frederick's Syndrome
- Risk factors
- Frederick's syndrome symptoms
- How is Frederick's syndrome diagnosed?
- Signs of the syndrome on the ECG
- Could ECG results be erroneous?
- What diagnostic methods will help confirm the ECG results
- Analyzes
- Instrumental diagnostics
- Treatment
- Conservative therapy
- Surgery
- Complications and projections
- Video about Frederick's Syndrome on ECG
If the ECG detects a combination of complete blockade of the atrioventricular beam with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter diagnose Frederick's syndrome. The anomaly complicates the course of other cardiac pathologies. Clinical signs include weakness, periodic dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Causes of Frederick's Syndrome
The etiological factors of the cardiac symptom complex have not been established. Frederick's syndrome, called complete atrioventricular block III degree, accompanies functional disorders of the cardiac apparatus. The anomaly is considered to be a polyetiological disease.
The probable causes of severe AV block include:
- inflammatory reactions;
- dystrophic condition of the heart organ;
- sclerotic changes in the structure of the myocardium;
- infectious lesion;
- congenital anatomical abnormalities;
- hemodynamic disorders.
Frederick's syndrome on the ECG has signs in the form of a disorder of the conduction of electrochemical impulses. On the cardiographic tape, the condition is noticeable by the absence of the P wave with the replacement of the peak by fibrillation waves.
Pathologies frequently encountered in clinical practice that can provoke an atrioventricular block are presented in the table.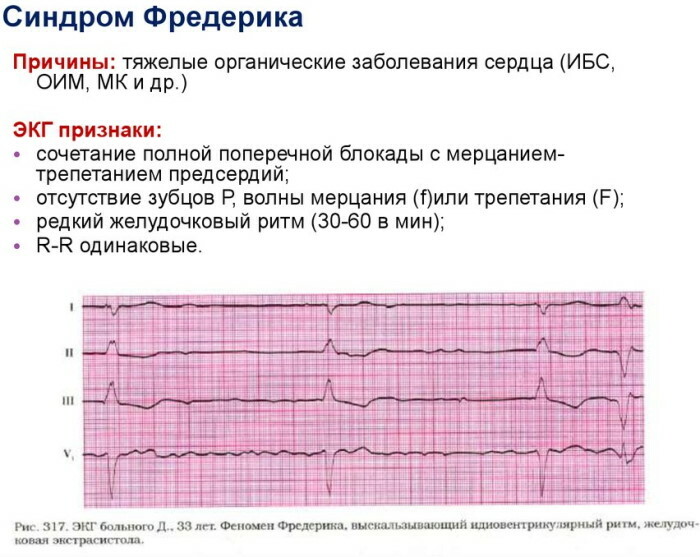
| Pathology | Clinical characteristics |
| Ischemia | Functional organic damage to the fibers of the heart muscle, caused by a violation or complete cessation of blood supply to the myocardium. The ischemic process disrupts the innervating connection of the atria with the ventricles. |
| Myocardial infarction | Necrotization of individual parts of the heart muscle is called a common cause of arrhythmic paroxysms inherent in Frederick's syndrome. |
| Pathologies of non-coronary origin | Severe disturbance of nerve conduction is presumably caused by thyrotoxic or autoimmune myocarditis, myopathic conditions of the organ. Frederick's syndrome is often seen in patients with chronic heart disease or necrotic lesions a large area of the myocardium, fibrosis or sclerotic vascular lesions against the background of morphological changes. |
| Drug intoxication | Signs of severe AV block are recorded with regular intake of antiarrhythmic drugs outside the recommended therapeutic range. These drugs include inhibitors of beta-adrenergic receptors and calcium channels, cardiological glycosides. |
Any of the listed pathologies causes vascular sclerosis, which provokes the proliferation of connective tissue structures. As a result, the conduction of nerve signals is impaired.
Risk factors
The symptom complex is characteristic of patients with severe congenital dysfunctions or anatomical anomalies in the structure of the organ. The pathological condition is provoked by psychoemotional overload, stressful conditions, regular physical overstrain. Such factors increase the heart rate.
The onset and progression of Frederick's syndrome is facilitated by:
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- stressful conditions that cause increased secretion of adrenaline;
- non-compliance with cardiovascular diseases of the indicated lipid-lowering diet;
- hereditary factors;
- neurocirculatory dystonia - a symptom complex caused by a disorder of the function of cerebral regulation;
- disturbed electrolyte balance.
The likelihood of developing atrioventricular block of the III degree is increased by untimely or incompletely healed vascular pathologies. The risk increases with uncontrolled use of the above drugs.
Frederick's syndrome symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the nature of the disorder and the localization of the AV block. Typical signs are periodic arrhythmic manifestations in combination with hemodynamic disorders.
Perceptible symptoms:
- constant weakness;
- chronic fatigue;
- shortness of breath when walking or climbing stairs;
- darkening in the eyes;
- light-headedness;
- periodic loss of consciousness.
Frederick's syndrome (on the ECG, signs of abnormality are often manifested by sinus bradycardia) causes a noticeable pallor of the skin of the hands and face. There are stabbing pains of varying intensity and duration in the chest area.
With complete atrioventricular block in the periorbital zone, around the wings of the nose, near the lips, acrocyanosis is observed - a cyanotic coloration of the epidermis, provoked by hemodynamic disturbances.
Depending on the clinical characteristics of Frederick's syndrome, aching or pulling discomfort periodically occurs in the projection of the heart organ - in front or under the scapula.
In some patients, squeezing or pressing painful sensations of the anginal type are observed. Paroxysmal manifestations are accompanied by shortness of breath or intermittent breathing, nausea, excessive sweating.
A strong slowing of the rhythm frequency, characteristic of third-degree atrioventricular blockade, is combined with fibrillation atrial divisions - a type of ventricular tachycardia characterized by chaotic electrical activity myocardium.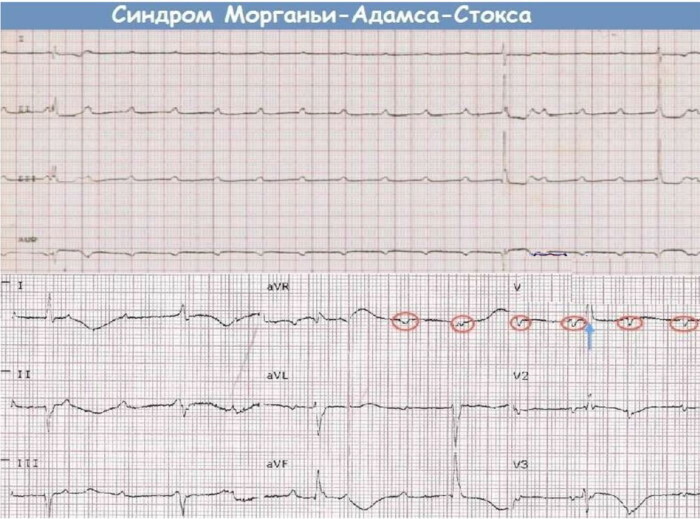
Syncope conditions called Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome develop. Attacks are caused by a sharp decrease in the volume of blood ejected from the heart. The manifestations of the MAC syndrome lead to periodic loss of consciousness.
How is Frederick's syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of impaired atrioventricular conduction is a complex and multi-stage process. The first stage is a physical examination, during which clear clinical signs of the syndrome are revealed.
These include bradycardic dysfunction, decreased intravascular pressure. The cardiologist performs an auscultation examination. This method fixes functional disorders, organic murmurs, muffled heart sounds.
Based on the results of the initial examination, a set of hardware diagnostic measures, a standard set of laboratory tests are prescribed.
The latter provide:
- a study of blood electrolyte parameters in order to identify hyperkalemia characteristic of the syndrome of complete AV-blockade;
- UAC;
- Analysis of urine;
- hematological test for cardiospecific enzymes - creatine kinase, troponin, myoglobin.
According to acute phase indicators and the content of prostaglandins in the blood, inflammatory activity is assessed. From instrumental diagnostic methods, electrophysiological examination is used.
The hardware technology makes it possible to clarify the localization of the AV block for the subsequent surgical operation or to determine the tactics of conservative treatment. During the procedure, the morphological characteristics of the disorder are determined.
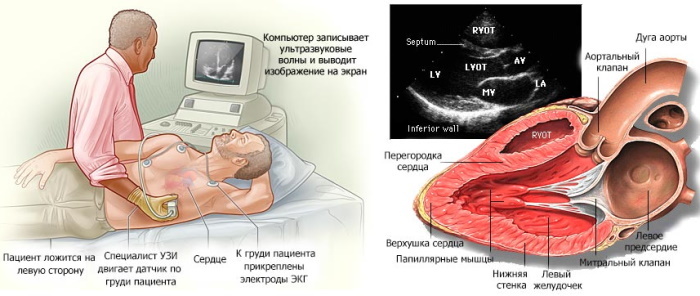
An effective instrumental method for diagnosing Frederick's syndrome is an echocardiographic examination aimed at determining the volume of blood output. With AV block of III degree, this indicator does not exceed 40% of the norm.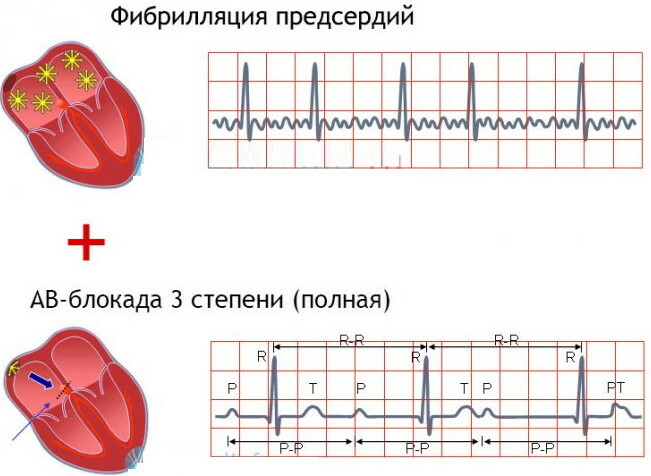
Echocardiography allows you to detect the discoordination typical of Frederick's syndrome between the contractions of the right and left ventricles, atrial sections. To determine the thickness of myocardial fibers, an ultrasound method is used.
Ultrasound of the heart allows you to establish the internal volume of the chambers of the organ. Inflammatory symptoms are diagnosed by the presence of pathological liquid exudate in the cavities. To clarify the clinical picture, fluoroscopic methods are used.
The picture shows the expanded contours of the shadow of the heart, deformation of the natural anatomical outlines. In patients with functional insufficiency of a congestive nature, there is a deterioration in the transparency of the lung fields.
Additionally, computed tomography and angiographic examination of the coronary arteries are prescribed. CT creates a clear three-dimensional model of the heart apparatus with a high level of detail. Angiography allows you to study in detail the state of the vascular walls.
Signs of the syndrome on the ECG
An electrocardiographic study registers f-wave changes in the structure of an organ. Atrial fibrillation is indicated by large F peaks, which should not be normal.
Frederick's syndrome manifests itself on the ECG with the following signs:
- extended QRS complex;
- deformations of the R peak;
- rare occurrence of extrasystoles on the electrocardiographic recording - extraordinary contractions of the myocardium;
- the same distance between adjacent R teeth;
- lengthening the QT interval.
In acute conditions, electrocardiographic examination is carried out according to the Holter method with daily monitoring of the heart rhythm. Recording is performed using a special portable recorder.
The method allows to establish ECG signs of complete blockade of the atrioventricular connection in dynamics. The examination provides cardiologists with detailed diagnostic information about interval changes in the PQ and QT regions.
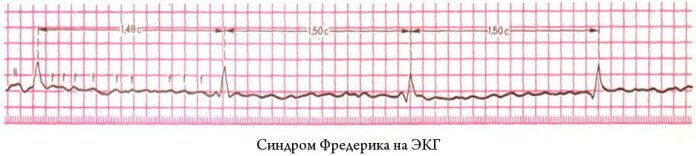
They are characteristic of Frederick's syndrome and any other disorders of intraventricular conduction. Daily dynamic monitoring records the change in the end section of the ST segment, the configuration of which during standard electrocardiography can correspond to the reference value.
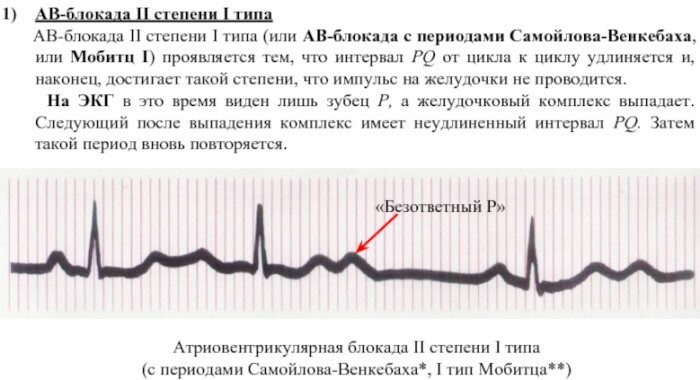
Could ECG results be erroneous?
The method is distinguished by high diagnostic accuracy. Electrocardiography gives reliable results. Errors occur only due to misinterpretation of the recording or incorrect calibration of the equipment.
The results are distorted by examination against the background of unplanned physical activity, after a stressful situation or taking cardiac stimulating drugs. If there are doubts about the reliability of the examination, a second diagnosis is prescribed.
Errors are often associated with incorrect placement of the electrodes on the patient's body. In such a situation, negative values of the P peak and the QRS complex are recorded in lead I. Incorrect overlap of scan elements is the most common cause of a diagnostic error.
The syndrome of premature excitation of ventricular structures can be mistaken for a blockade of the legs of the plexus of His, hypertrophic pathology or infarction manifestations in the myocardium.
The widening of the QRS complex is sometimes caused by improper calibration of the equipment or increased voltage. There is an inversion of the T peak and a pseudoinfarction Q wave configuration.
An inexperienced cardiologist may confuse isorhythmic atrioventricular dissociation with a complete blockade characteristic of Frederick's syndrome. In the first case, impulse signals emanating from the sinus node and AV plexuses are isolated. The frequency of the complex has not been changed.
With a complete blockade, there is a slowdown in the ventricular rate in relation to the atrial rate. Errors in electrocardiographic diagnostics are rare. In most cases, the survey results can be trusted.
What diagnostic methods will help confirm the ECG results
To check the data obtained by the electrocardiographic method, echo-KG is used, which is an ultrasound scan. The method visualizes the structure of the organ, allows you to assess the state of the valve mechanism.
With the help of echocardiographic examination, the contractile characteristics of the myocardium are specified, the volume of blood output is determined, and hidden ischemic areas are detected. On the echo-KG, valve prolapses and other abnormalities are noticeable. The results of electrocardiography are checked using a radiopaque method, which determines the hemodynamic parameters of the coronary vessels.
Indirectly confirm or refute the data obtained during the ECG with a laboratory test for a lipid profile. A coagulogram is prescribed to establish the rheological properties of blood.
Analyzes
Frederick's syndrome, on the ECG, the signs of which are typical for atrioventricular block, often requires clarification of the clinical picture and confirmation of the diagnosis by laboratory methods.
With the help of a general blood test, the number of cells, their shape and size parameters are counted. Such a study allows you to find out the hemoglobin content, establish the leukocyte formula, hematocrit.
A biochemical test is even more informative. He is appointed to determine a large number of indicators.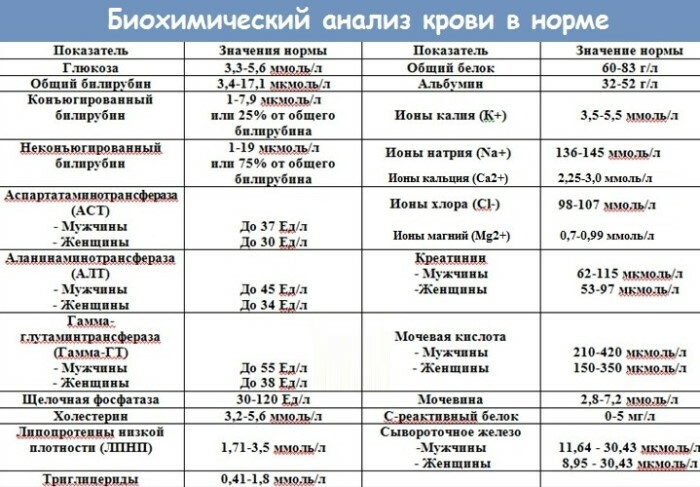
For the diagnosis of Frederick's syndrome are important:
- the content of residual nitrogen of non-protein origin - the normal concentration in the serum fraction of blood is 14.3-28.6 mmol / l;
- creatinine, which reflects the work of the renal apparatus;
- total lipids - reference value 4-8 g / l;
- cholesterol - an organic component of cell membranes;
- low density lipoprotein;
- coefficient of atherogenic factor - reflects the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries;
- triglycerides that perform structure-forming, energy and other functions;
- the content of calcium, which ensures the work of the cardiovascular apparatus and the nervous system.
A biochemical test allows you to establish the physiological parameters of internal organs, the characteristics of metabolic reactions - lipid, carbohydrate, protein metabolism.
A Roberts test is prescribed, aimed at assessing the clearance of endogenous creatinine. Clinical analysis of urinary sediment is intended to determine the physicochemical properties and composition of the fluid released during deurination.
Instrumental diagnostics
If a complete atrioventricular block is suspected, hardware examinations are never limited to electrocardiography. The final diagnosis is established by a complex method.
The standard set of instrumental examinations for Frederick's syndrome includes:
- Holter monitoring. The diagnostic method is a dynamic examination of the functional parameters of the cardiovascular apparatus for a certain period of time.
- Electrophysiological examination through the esophagus. The method is used to detect transient signs of AV block that cannot be diagnosed by other means.
- X-ray examination anatomical structures of the chest. In addition to determining the configuration of cardiac shading, diagnostic technology is used to detect venous congestion inherent in Frederick's syndrome.
-
Ultrasonic method. With a high degree of reliability, it reveals pathological changes in the structure of the heart muscle.
If necessary, an additional treadmill test is prescribed, alternatively called veloergometry. Such an examination involves the fixation of the functional parameters of the heart by the electrocardiographic method after physical exertion. The treadmill test accurately determines the signs of ischemic heart disease, assesses the change in the rhythm of the organ.
Treatment
When a complete atrioventricular block is detected, long-term therapy is required.
Its main tasks:
- minimizing the likelihood of sudden death due to severe cardiac dysfunction;
- restoration of normal contractile activity of the myocardium;
- improving the blood supply to the organ;
- mitigation of tangible clinical symptoms;
- prevention of exacerbations.
Frederick's syndrome, the signs of which are usually clearly expressed on the ECG, are treated with medication, non-drug methods, and surgical intervention.
Diet food is prescribed. Compliance with a therapeutic and prophylactic diet is especially important for patients with a history of ischemia and with sclerotic damage to the coronary arteries.
Minimize the consumption of fatty foods. Eliminate carbonated drinks, caffeinated foods, and spicy foods from the diet. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the patient's age, biological tolerance, and the severity of clinical manifestations.
Conservative therapy
In the acute phase, the patient is admitted to a hospital or intensive care unit under round-the-clock medical supervision. If necessary, connect to artificial life support systems.
Drug treatment for Frederick's syndrome is symptomatic or etiotropic. The first is aimed at stabilizing the physiological state, stopping life-threatening signs of acute heart failure.
Cancellation of drugs taken to treat the underlying disease that provoke a blockade of the atrioventricular plexus. These drugs include antiarrhythmic drugs, calcium antagonists.
Drug therapy is supportive. Frederick's syndrome does not respond to drug treatment. For temporary relief of AV blockade, muscarinic cholinergic receptor inhibitors are used.
As part of etiotropic therapy, drugs are prescribed that affect the cause of the development of the syndrome - antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of an emergency, resuscitation measures are indicated.
They are aimed at eliminating atrioventricular shock, restoring cardiac and cerebral blood supply. Etiotropic therapy aims to prevent recurrent crises, to compensate for the underlying pathology.
For angina pectoris, antiplatelet medications are used. Patients with diagnosed myocarditis are injected intravenously with antibacterial or antiviral drugs, depending on the established strain of the pathogen.
Additionally, oral administration of anti-inflammatory drugs on a non-steroidal basis, infusion of corticosteroids-stimulants is prescribed. The use of atropine or another anticholinergic drug is highly undesirable due to the increased risk of developing a deliric condition.
Surgery
To stabilize the heart rhythm, prevent lethal functional failure of the organ, a pacemaker is implanted. This is the only treatment for Frederick's syndrome that provides relative guarantees of prolongation of life.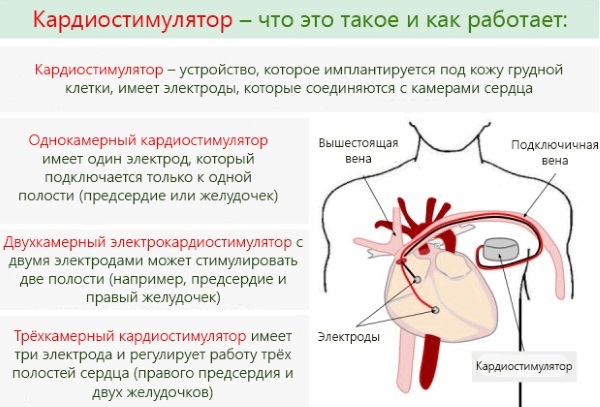
Among the indications for surgical intervention are regular loss of consciousness, the frequency of myocardial contractions is less than 40 beats / min., The transferred ischemic infarction. A single-chamber ventricular or a full-fledged two-chamber pacemaker is implanted.
He is called an artificial pacemaker. With bradycardia, a conventional electric pulse device is used. Patients with tachyarrhythmic disorders are implanted with a model with cardioversion and defibrillation functions.
Complications and projections
Life expectancy with complete atrioventricular block is determined by timely surgical intervention and the quality of the implanted pacemaker. Usually it is possible to stabilize the condition, stop clinical manifestations.
The most severe consequence of Frederick's syndrome is sudden death from cardiac arrest. After the implantation of a pacemaker, the condition is monitored with the help of periodic medical examinations. The cardiologist directs the patient for an ECG to detect possible signs of AV block and take appropriate action.
Video about Frederick's Syndrome on ECG
AV block and its degree on the ECG: