Content
- Norms of chloride content in blood for women, men, children
- What analysis reveals the level of chlorides, can the results be erroneous
- What affects the reliability of the study
- Causes of increased chloride levels (hyperchloremia)
- Excess chlorine in the diet
- Dehydration
- Kidney disease
- Diarrhea
- Dysfunctions of the adrenal cortex
- Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes insipidus
- Alcoholism
- Myxedema
- Meningitis
- Obstructive jaundice
- Cystic fibrosis
- Taking corticosteroids
- What to do when indicators increase
- Correction of nutrition, limiting the consumption of foods rich in chlorine
- The amount of water you drink
- Drugs
- Possible consequences of elevated chlorine in the blood
- Video about chlorides in the blood
Chlorides are among the main electrolytes in the body.involved in maintaining acid-base balance. Chlorine is a part of gastric juice, contributes to the retention of water by tissues, participates in water-salt metabolism. In a number of painful conditions, its concentration in the blood plasma increases, which is determined using laboratory methods.
Norms of chloride content in blood for women, men, children
Electrolytes, that is, mineral salts, are composed of a positively charged metal atom and a negatively charged acid residue. The salt dissolves in the liquid, and its two parts become ions with opposite charges, which "float" by themselves. The ratio of positively and negatively charged ions in the body is maintained at a constant level.
Chlorine (Cl-) is a negative ion. Being in blood plasma and extracellular fluid, it interacts with positively charged sodium (Na +) and potassium (K +) ions. Thus, the acid-base balance is maintained and the volume of fluid in the body is regulated.
Like other electrolytes, chlorine conducts an electrical charge. Moving through the membranes into and out of the cell, chlorides maintain electrical neutrality. In addition, with their participation, the transfer of nutrients into the cell and the removal of metabolic products from it is carried out.
Chlorides enter the body with food, and are excreted mainly by the kidneys. Some come out in feces and sweat. Balance implies a balance between their intake, distribution in body tissues and excretion.
The body normally maintains a constant level of chlorine. With its excess, acidosis develops - a shift of the acid-base state to the acidic side. With the loss of chlorides - alkalosis, "alkalinity" of the blood.

The concentration of chlorine ions in blood plasma is an important indicator of the health of many systems, mainly of the kidneys and heart.
When establishing the norms for the content of chlorides in the blood, the following features were taken into account:
- In infants under 1 month of age, the concentration of chlorine is higher than in adults and older children.
- The indicators for men and women do not differ, since the physiological characteristics associated with gender do not affect the chlorine content.
The approximate chlorine values corresponding to the standards for different ages are shown in the table:
| Age | Cl- concentration, mmol / l |
| Newborn | 98-113 |
| Children from 1 month to a year | 94-114 |
| Children from 1 to 18 years old | 95-106 |
| Adults (men and women) | 101-110 |
| People over 90 | 98-111 |
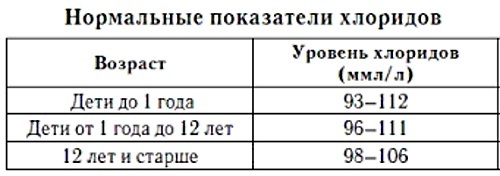
The limits of the norm may differ depending on the reagents and equipment used for the analysis. When evaluating the research results, it is worth focusing on those reference values that are indicated in the form of a particular laboratory.
What analysis reveals the level of chlorides, can the results be erroneous
Chlorides in the blood are increased, decreased, or their concentration is normal - determined by analyzing peripheral blood taken from a vein at the elbow in a volume of 5-8 ml. The ion-selective research method is used. The chlorine level is determined by taking into account the potential difference between the indicator and reference electrodes placed in the blood sample.
The direction can be issued for the following types of research:
- Blood chemistry.
- Chlorine in serum.
- Potassium, sodium, chlorine in serum.
In the course of biochemical analysis, many indicators can be examined. The doctor chooses from the list those that will help assess the work of any organ or system of the body. Chlorine and other electrolytes are noted in the direction of diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, heart and blood vessels.
An analysis for chlorine in blood serum is prescribed to control diseases accompanied by a violation of acid-base balance: diabetes insipidus, adrenal pathology. The study may be needed during the treatment of arterial hypertension, heart failure, liver and kidney disease. The indicator is important if alkalosis or acidosis is suspected.
Chlorine tests are carried out in patients with the threat of a serious violation of the water-electrolyte balance:
- during hemodialysis;
- with extensive burns;
- with vomiting and diarrhea;
- with long-term diuretic therapy.
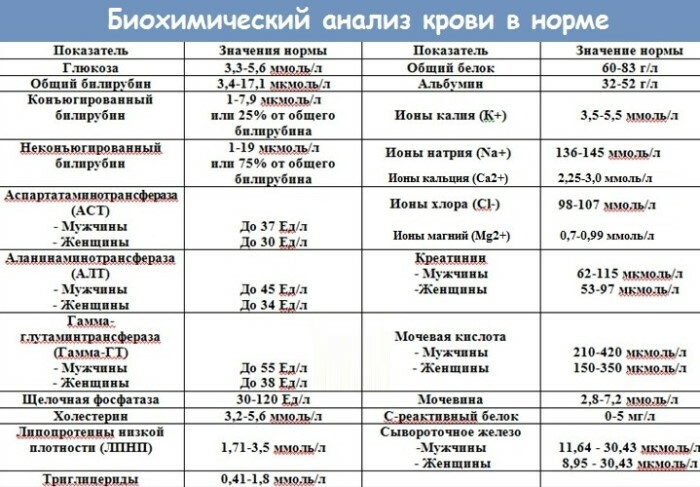 Most of the chlorine is found in the blood as sodium chloride. Therefore, its concentration is closely related to the amount of sodium ions. Analysis for electrolytes potassium, sodium and chlorine is prescribed for edema, weakness, arrhythmias of the heart.
Most of the chlorine is found in the blood as sodium chloride. Therefore, its concentration is closely related to the amount of sodium ions. Analysis for electrolytes potassium, sodium and chlorine is prescribed for edema, weakness, arrhythmias of the heart.
Chlorine test results are not always informative enough. Due to the peculiarities of the analysis technique, under certain conditions, errors in the results are possible. So, with an increase in total blood protein, cholesterol and triglycerides, a lower level of chlorine is recorded than it actually is.
To avoid misinterpretation, sodium and bicarbonate tests are performed to determine the amount of chlorine. There are the following dependencies: with an increase in sodium, the chlorine content increases; the concentration of bicarbonates decreases.
To clarify the reasons for changes in the water-electrolyte balance and confirm the diagnosis of renal tubular acidosis, blood tests are not limited and the amount of chlorine in daily urine is measured.
What affects the reliability of the study
It should be borne in mind that immediately after eating, the chlorine level temporarily decreases. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the electrolyte is part of hydrochloric acid and is actively lost during the digestion of food in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
A salt-free diet and exercise-induced sweating can lower chlorine levels.
Based on this, blood is taken for analysis in the morning, on an empty stomach. You can drink still water. The day before the procedure, alcohol is excluded, physical and emotional stress is avoided. Do not smoke for half an hour before taking blood.
For children under 1 year old, the restrictions are milder: the child is stopped to feed 30-40 minutes before the study. For children under 5 years of age, food intake is limited 2-3 hours before the procedure.
The reliability of the results is influenced by the intake of certain medications. For example, the adrenergic blocker propranolol and diuretics (triamterene, diacarb, hypothiazide) lower the values.
Chlorides in the blood are increased due to the intake of androgens, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (acetylsalicylic acid, diclofenac), anticoagulants (sodium heparin). The use of drugs that affect blood pressure (captopril, dopamine) also leads to an increase in concentration.
Causes of increased chloride levels (hyperchloremia)
When the concentration of Cl- in the blood plasma (serum) is excessive, hyperchloremia occurs. As a rule, the condition is associated with metabolic acidosis, when abnormally high acidity of the blood is explained by disturbances in the metabolic process. In this case, the reabsorption of bicarbonates in the kidneys, which provide the "alkalinity" of the blood, is suppressed. The bicarbonate buffering mechanism for restoring the acid-base balance of the blood does not work.
The growth of chlorides in blood plasma causes causes that are conventionally divided into relative and absolute.
Increased salt intake, dehydration and increased blood viscosity are considered to be relative causes. In this case, excess acid is excreted by the kidneys within a few days, provided that the excretory capacity of the kidneys is normal. Excess chlorine often occurs in people who are forced to inhale chlorine vapors while working in some industries.
The absolute reasons include states when the elimination of excess chlorine is difficult due to functional reasons. These are kidney diseases in which their ability to filter and reabsorb (reabsorb) is affected.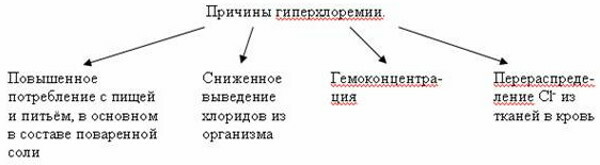
An increase in acidity and, accordingly, an increase in chlorine, may be due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide, when the lungs are not able to remove its excess. An increase in the concentration of Cl- leads to disturbances in the work of hormones: aldosterone and ADH (antidiuretic hormone).
Excess chlorine in the diet
Chlorine enters the body through food and table salt, which is a compound of sodium and chlorine (NaCl). To some extent as potassium chloride (KCl), a salt substitute. Consideration should be given to the consumption of foods rich in chlorine.
Consumption of edible salt in the amount of 4-6 g is considered to be within the physiological norm of an adult. In hot climates and increased sweating, the need for salt increases.
Ultimately, the presence of chlorine in the blood is determined by the amount of fluid consumed and the ability of the kidneys to excrete electrolytes. Excess chlorine from food can lead to high blood pressure and impaired heart and kidney function.
Dehydration
With dehydration, the fluid content drops below the physiological norm, and the body has difficulty excreting chlorine naturally - through urine and sweat. The electrolyte builds up in the blood.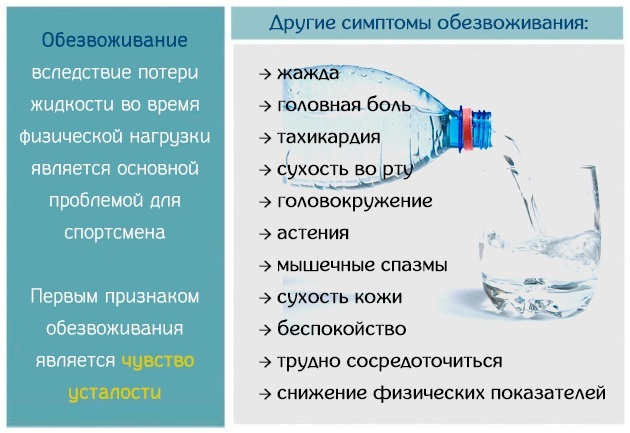
Low water intake, intake of diuretics, and heavy sweating lead to dehydration. Fluid deficiency occurs with diabetes insipidus. As a rule, with a strong loss of fluid, not only the concentration of chlorides increases sharply, but also the concentration of positive ions of potassium and sodium.
Severe dehydration occurs with extensive burns. The body loses blood plasma when bubbles with interstitial fluid form at the sites of the burn injury.
Kidney disease
Chlorides in the blood are elevated when the kidneys are unable to excrete acidic foods. This condition is called tubular acidosis and is seen in kidney failure. With kidney damage, accompanied by the destruction of connective tissue and the glomerular apparatus (nephritis, nephrosis), the elimination of excess chlorine is difficult. The amount of electrolyte in the blood rises.
Diarrhea
With diarrhea caused by intestinal infections, alkaline ions (sodium bicarbonate) are excreted along with the liquid. Acidosis develops, the acid-base balance of the blood shifts to the acidic side. This condition is especially dangerous in young children with diarrhea. Their situation is deteriorating rapidly and threatens with disruption in the work of many organs and systems of the body.
Diseases such as salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera and acute gastroenteritis of a non-infectious nature lead to severe diarrhea.
If vomiting predominates in the symptomatology of the disease, then chlorine, on the contrary, is lost. Its amount in the body decreases, and the blood reaction shifts to the alkaline side. The condition is called hypochloremia.
Dysfunctions of the adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex, in the cells of the glomerular zone, secretes aldosterone. It is a corticosteroid hormone that regulates blood levels of sodium and potassium. The volume of circulating blood and, therefore, blood pressure depends on its work.
Aldosterone is responsible for sodium reabsorption in the renal tubules. With the growth of sodium in the blood, chlorine also increases. The increased function of the adrenal cortex leads to an excessive concentration of electrolyte in the blood.
Excess chlorine is characteristic of Itsengo-Cushing's disease and the syndrome of the same name. In the first case, the disease is associated with an increased formation of corticosteroid hormones in the adrenal cortex, in the second - with the presence of a tumor in the adrenal glands that produces hormones.
In Addison's disease, on the other hand, adrenal function is reduced. The amount of chlorine is also reduced.
Atherosclerosis
Coronary atherosclerosis obstructs the blood supply to the heart and is often the culprit for arrhythmias. In this disease, blood electrolytes are controlled - sodium, chlorine, potassium and calcium. They form the basis for the correct conduction of an electrical impulse into the heart muscle. Disruption of their balance leads to irregularities in the heart rhythm and heart block.
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus is characterized by increased urine output (polyuria) with its low specific gravity. The disease is associated with insufficient production of antidiuretic hormone. ADH is synthesized in the hypothalamus, enters the pituitary gland and from there is released into the blood. Neurohormone stimulates the absorption of water in the kidneys, reduces urine output, narrows peripheral blood vessels.
Excess chlorine in the blood in diabetes insipidus is ultimately due to insufficient production of ADH.
Alcoholism
Chronic alcoholism is a serious condition in which water-electrolyte disturbances are combined with all kinds of organ dysfunctions. Due to the suppression of ADH secretion, polyuria develops, accompanied by dehydration (dehydration). Metabolic acidosis develops. Elevated levels of chlorine and sodium are found at the electrolyte level.
The increase in Cl- may be associated with damage to the renal tubules in alcoholism.
In case of poisoning with methanol (wood alcohol), an excess of acidic products that are formed in as a result of various chemical reactions in the body, gives rise to an abnormal increase in negative ions in blood.
Myxedema
A severe form of hypothyroidism, which develops with a lack of production of thyroid hormones. In advanced cases, it can cause heart failure and coma.
Mucinous edema is a characteristic feature of the condition. The amount of mucin increases in the tissues, hydrophilic substances accumulate, trapping excess water. The connective tissue structures become edematous. The balance of essential electrolytes is disturbed.
Meningitis
With meningococcal infection, a biochemical blood test is performed, including electrolytes being tested once a day.
The analysis is needed to identify the possible ADH (syndrome of inadequate secretion of antidiuretic hormone), which is possible with meningitis of the SNS, which threatens with acute hyponatremia and hypochloraemia. The consequence is the passage of fluid from the external space into the cells, the development of cerebral edema and an increase in intracranial pressure. This condition limits the ability to administer fluid therapy, which is standard in the treatment of meningitis.
Obstructive jaundice
Rather, we can say that excessive consumption of chlorides, namely, medicinal mineral water with a high content of Cl-, can cause obstructive jaundice (and not vice versa). Such water stimulates the outflow of bile and, in the presence of gallstone disease, can cause the movement of stones. Large stones block the bile ducts. Bile pigments (bilirubin) are absorbed into the bloodstream, staining the skin yellow. A picture of extrahepatic jaundice develops.
Cystic fibrosis
With cystic fibrosis, there may be a change in the concentration of electrolytes, both up and down.
Cystic fibrosis is a systemic lesion of exocrine (exocrine) glands. The content of electrolytes (Na and Cl) exceeds the norm by 2-5 times, but in the sweat fluid. The electrolyte composition changes in the secretion of the salivary and lacrimal glands. A strong loss of electrolytes during overheating and physical activity in patients with cystic fibrosis leads to the development of collapse.
The first clinical manifestation of the disease in children and adults is metabolic alkalosis with hypochloremia, hyponatremia, and hypokalemia. The condition is manifested by nausea, fever, loss of appetite and weight. With the correction of electrolyte disturbances, the condition improves.
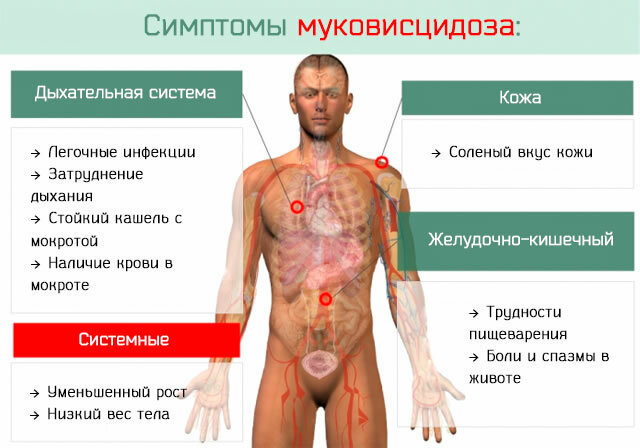
The lungs are often affected by the disease. Viscous mucus accumulates in their tissues, which ultimately interferes with free breathing. Carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood, which increases the acidity of the blood and the number of negative chlorine ions.
Taking corticosteroids
Chlorides in the blood are increased when aldosterone is synthesized in large quantities by the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone is a mineral corticosteroid. When taking corticosteroid drugs with the appropriate activity (hydrocortisone), its synthesis increases. Water and sodium in the body are retained, but the excretion of potassium and calcium increases. Hence the well-known side effects of corticosteroids: increased blood pressure and fragility of bones.
Prednisolone and dexamethasone have the least effect on water-salt metabolism. With prolonged use of corticosteroid drugs, it is possible to suppress the secretory function of the adrenal cortex. In this case, the values of electrolytes Na and Cl, on the contrary, decrease.
What to do when indicators increase
When hyperchloremia is detected, the treatment tactics depend on the cause that caused the increase in the levels of chlorine ions in the blood. If the disorder is due to a disease, the attending physician will prescribe appropriate therapy. The patient, for his part, can adjust the diet and change the drinking regimen.
Correction of nutrition, limiting the consumption of foods rich in chlorine
With an increase in chlorine, it is important to monitor the consumption of those foods that contain this trace element in large quantities.

These include:
- meat and meat offal (brains, heart and kidneys);
- poultry (turkey, goose, chicken);
- fish (pink salmon, pollock, perch and cod);
- chicken egg (in the protein, the chlorine content is higher);
- kefir and milk;
- peas;
- rice;
- oats.
However, the most important measure is to limit the consumption of table salt. The Federal Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor reports that the physiological need for NaCl in adults is only 2.3 g per day. For children - from 300 mg to 2.3 g. Moreover, babies should receive salt only from food.
The amount of water you drink
To ensure adequate chloride excretion, you need to increase the amount of fluid you drink.
This is especially important with dehydration, which is a consequence of a number of situations:
- diarrhea and vomiting due to poisoning or intestinal infection;
- increased sweating during hot weather or increased physical activity;
- increased urination;
- diet aimed at losing weight.
A weakened feeling of thirst occurs in the elderly. It is necessary to ensure that the volume of fluid consumed is sufficient, at least 1.5 liters per day.
Drugs
In severe acidosis caused by an increase in chlorine, sodium bicarbonate is prescribed in the form of a solution for intravenous administration to remove chlorides.
To reduce polyuria, synthetic analogs of vasopressin (aldosterone) are prescribed in the form of injections or a drug intended for administration into the nose (desmopressin).
The decrease in chloride causes the intake of antacids and baking soda solution.
Possible consequences of elevated chlorine in the blood
A change in the level of chlorine in the blood leads to sharp fluctuations in the pH of the blood, which negatively affects the state of various body systems. In acute hyperchloremia, heart rate increases, blood pressure rises, and edema develops. The condition is dangerous with respiratory failure, in severe cases a coma develops. With a constant increase in chlorine, the nervous system suffers. The damage is expressed in central and peripheral nephropathies, in damage to the nerve fiber.
A general picture of the balance of chlorides in the body can be obtained by passing a test for the electrolyte content in the blood. Its increase requires correct interpretation and, possibly, the appointment of additional analyzes.
Video about chlorides in the blood
Blood tests:



