Content
- General information about the disease
- Causes and pathogenesis of craniostenosis
- Why is craniostenosis dangerous?
- Which doctor should I go to?
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Forecast
- Video about craniostenosis
Craniostenosis is a pathological condition.due to premature overgrowth of the metopic suture connecting the halves of the skull. As a result, a deformation bulge forms on the child's forehead, distorting facial features, leading to severe clinical symptoms.
General information about the disease
The skull consists of the facial and cerebral segments connected by anatomical sutures.
The cerebral zone, containing the brain structures, is composed of 8 bones - 4 paired, which include the parietal and temporal, and a similar number of single bones:
- frontal;
- occipital;
- wedge-shaped;
- lattice.
The contact lines of solid structures are called cranial sutures. In the embryonic and postpartum periods, they go through 3 stages of development - membranous, cartilaginous, bone. The curing process is completed by the age of 25.
In newborns, the sagittal suture remains open throughout the first year of life. With pathological changes of various etiologies, it overgrows too quickly, which interferes with the normal growth of hard fibers.
The anomaly is accompanied by a violation of the development of cranial bones, cerebral tissues, nerve fibers. Craniostenosis is characterized by consistently high blood pressure and hemodynamic disorders.
Pathology that affects the optic nerves leads to a noticeable lag in mental development. The prevalence of various forms of anatomical deformity in the world is recorded at the level of 0.03-3.5% of the total number of newborns.
A metopic suture on the forehead of a male child is more common than a female child. The most common in pediatric practice is the monosynostotic form of anatomical anomalies at an early age.
Premature fusion of the sagittal suture, called scaphocephaly, accounts for approximately 50-65% of clinically reported craniostenoses. The most rare and prognostically unfavorable type of pathological disorder is syndromic.
It is accompanied by an extensive complex of severe clinical symptoms. Such craniostenosis is characterized by an increased likelihood of infant death during the first 10-12 months of life. Insufficient expansion of the cranial cavity leads to mechanical and compression damage to the brain.
Causes and pathogenesis of craniostenosis
The etiological factors of premature overgrowth of the sagittal suture have not been reliably established.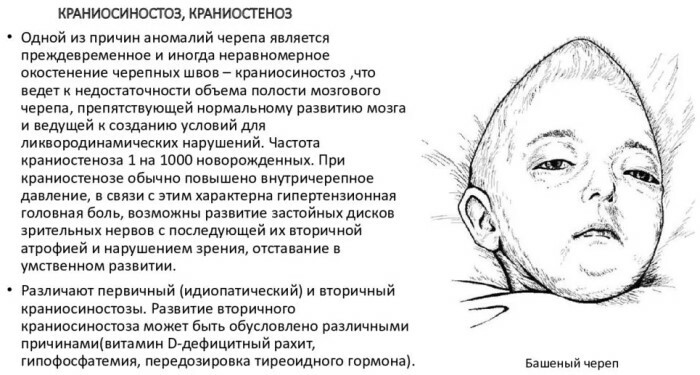
Presumably, craniostenosis is provoked by:
- hormonal disorders during intrauterine development;
- perinatal damage;
- stress suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- squeezing the cranial bones of the embryo with the narrow inner space of the uterine cavity;
- genetic pathologies;
- chromosomal mutations;
- radiation exposure;
- carcinogenic effects;
- reception by a woman while carrying a child of prohibited medications with teratogenic properties;
- hypoxic damage to the nervous system of the fetus;
- bacterial-viral or fungal diseases of the mother in the gestational phase;
- prematurity.
The reasons presented are purely hypothetical and have no scientific basis or evidence base. Presumably, Aper's syndrome plays a role in the formation of the metopic suture.
This genetic pathology disrupts the process of cranial ossification. With the same degree of probability, craniostenosis occurs against the background of Cruson's syndrome, a rare hereditary disease.
The deviation is clinically expressed by progressive deformity of the facial and cerebral lobes of the cranium. Another probable genetically determined cause of premature overgrowth of the sagittal suture, researchers call Pfeiffer syndrome.
Violation of the hereditary nature characterizes the dominant autosomal transmission mechanism. The disease disrupts the formation of skeletal structures, including the limbs and skull.
Recent studies have relatively accurately determined the leading role in the development of craniostenosis of a gene mutation responsible for the formation of receptor elements of the growth factor of fibroplastic cells.
Pathogenetically, the anomaly is caused by early synostosis of one or more bone joints. In addition to the sagittal suture, the coronary and lambdoid lines are susceptible to premature fusion.
The violation causes the effect of perpendicularly directed compensatory growth of bone tissue in accordance with the law of Rudolf Virchow, which substantiates the formation of new cellular elements as a result of the division of the original structures.
The metopic suture on the forehead in a child occurs as a result of an abnormally rapid proliferative process, which causes cranial deformities. Pathogenetic features are determined by the time of fusion, the growth rate of inert structures, the number and location of prematurely closed joints.
Why is craniostenosis dangerous?
The anomaly is accompanied by a hypertensive effect, which is manifested by neurological symptoms, venous congestion of the fundus, partial or complete atrophy of light-sensitive optic fibers.
Craniostenosis is characterized by a large number of negative consequences, systemic pathologies, and severe complications. They depend on the pathogenetic picture of the anatomical anomaly.
The most common complications of craniostenosis include:
- spinal hernial protrusions;
- deformation bulging of the frontal lobe of the skull;
- decreased visual acuity with the prospect of complete blindness;
- lag in intellectual development;
- cosmetic defects;
- strabismus;
- underdevelopment of the eye sockets;
- regular cephalgic paroxysms of varying intensity and duration;
- spontaneous muscle cramps;
- development of epileptic pathology;
- articular dysfunctions leading to persistent musculoskeletal disorders;
- hydrocephalic syndrome;
- sleep apnea;
- respiratory disorders.
The nature and severity of the consequences is determined by the form of craniostenosis. Approximately every 5th child with premature fusion of the sagittal suture has intracranial hypertension, supplemented by severe disorders of higher nervous activity.
For craniostenosis, ophthalmic pathologies, congestion in the cervical spine are typical. According to international studies, in 50-60% of cases of metopic suture formation, a decrease in the child's cognitive abilities is observed.
A common complication of craniostenosis is exophthalmos, which is a mono- or binocular displacement of the eyeballs in the antero-facial direction outside the anatomical bed.
The danger of a congenital disorder is regular convulsive seizures, severe headache, nausea and vomiting. Such children have a sharply impaired ability to memorize information and learn.
Which doctor should I go to?
The treatment of craniostenosis, the accompanying symptoms and complications caused by the anomaly is carried out by a neonatologist who conducts the initial examination of the baby in the maternity hospital. In the future, the patient is supervised by a district pediatrician.
Taking into account the specificity and pathogenesis of the disease, one cannot do without the intervention of maxillofacial and pediatric neurosurgeons. The pediatrician directs the parents to consult the child with a specialist of this profile in order to prepare for the operative correction of deformational changes.
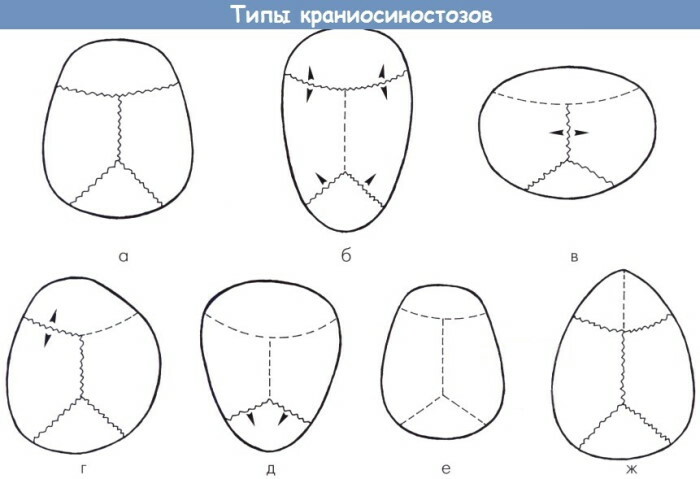
Classification
Craniostenosis, in accordance with the observed clinical picture, the alleged etiological factors and the number of prematurely fused cranial joints, are divided into 5 forms.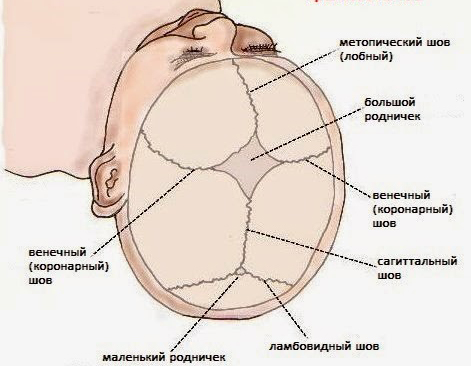
The current classification of congenital anomalies is presented in the table:
| Variety | Pathogenetic and clinical characteristics |
| Syndromic | The most severe form of anatomical disorder. Syndromic pathology is combined with numerous intrauterine malformations. This classification category includes linkage of the X chromosome, monogenic and other craniostenoses. This form is characterized by a combination of premature fusion of sutures with dysplasia of the bones of the facial surface. |
| Isolated | Pathology arises independently and does not depend on concomitant pathologies. Often, such craniostenosis proceeds without severe systemic complications and pronounced anatomical deformity of the cranium. |
| Monocraniostenosis | The violation occurs as a result of the premature fusion of one suture connection. The most common forms of monocraniostenosis are coronary and lambdoid destruction. |
| Polycraniostenosis | The pathological process involves 2-3 connecting lines, which causes severe complications and noticeable neurological symptoms. |
| Pansiocraniostenosis | The anomaly is characterized by premature fusion of all cranial sutures. The rarest form of congenital anomaly is difficult to reconstruct surgically. |
Metopic suture has other classification systems. Depending on the alleged cause of the formation of an abnormal bulge on the forehead in the child the following variants of craniostenosis are distinguished:
- Congenital. This pathology is due exclusively to intrauterine disorders, not provoked by genetic mutations.
- Acquired. In frequent cases, it develops against the background of systemic pathologies of skeletal bones.
- Physiological. Such craniostenosis has no embryonic causes, arising during the growth of the skull.
- Pathological. It is associated with hormonal, endocrine and other factors.
- Artificial. Such craniostenosis is specially created by a surgical method to eliminate large-scale structural defects of the cranial bones. The deformity is corrected at the next surgery.
Craniostenosis is post-traumatic. This abnormal disorder occurs as a result of damage to the skull during childbirth or neonatal deforming effects.
Symptoms
Clinical signs of pathological abnormality are noticeable at the first examination of the newborn. All forms of craniostenosis are characterized by plagiocephaly - an asymmetric structure or a curved state of the skull.
There is a premature infection of the large fontanelle, which normally closes at the age of 12-18 months. With a polyostenotic type of disease or hydrocephalic anomaly, it remains open for up to 3 years.
In the neonatal period, the clinical symptoms of craniostenosis are:
- stable intracranial hypertension;
- neurological disorders;
- anxiety;
- active crying;
- nausea with vomiting;
- sleep function disorder;
- lack of appetite;
- Gref's syndrome - excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular regions of the brain;
- constant convulsive readiness.
Each form of abnormal deviation has individual pathogenetic characteristics in the neonatal period. Premature closure of the sagittal suture, called scaphocephaly, is determined by the scaphoid configuration of the skull.
Symptomatically, this form of craniostenosis is manifested by an increased size of the anteroposterior plane of the skull with a pathologically small width of the head.
Upon visual inspection, it is noticeable:
- elongated structure of bone formations;
- depressed state of the temporal lobes;
- overhang of the frontal surface and the occipital part of the skull;
- narrowing of the front plane with the acquisition of an oval configuration.
A typical symptom of any type of craniostenosis is mental retardation. Premature infection of the lambdoid junction characterizes a noticeable flattening of the occipital zone.
With this form of craniostenosis, neurological symptoms are minimal or absent. Coronary anomaly is unilateral or bilateral. The first is characterized by deformation flattening of the frontal plane of the skull.
With growing up, the symptoms grow and manifest themselves:
- curvature of the bridge of the nose;
- a change in the shape of the zygomatic bones;
- violation of bite due to deformation of the upper jaw;
- squint.
In bilateral coronary craniostenosis, flattening of the edges of the orbits, expansion of the frontal plane, acrocephaly - an abnormally elongated "tower-like" shape of the skull is observed.
Neurological symptoms are nonspecific and identical to other types of pathology. Called trigonocephaly, a nontopic form of craniostenosis is characterized by a triangular section of the skull and the formation of a bony keel.
The metopic suture on the forehead in a child is combined with hypertelorism - orbital displacement and a reduction in the distance between the orbits. As they grow older, the bone crest smoothes out, the shape of the forehead acquires a configuration close to normal. Trigonocephalus is symptomatically manifested by visual disturbances, mental disorders.
In the most severe syndromic form of the disease, the following are observed:
- respiratory failure;
- difficulty swallowing;
- pronounced ophthalmic pathology;
- severe headaches;
- excessive psychomotor agitation.
Dysplasia of the bone structures of the facial part of the skull, protrusion of the eyeballs are noted. Severe violations lead to the death of the child within 12 months. after birth.
Diagnostics
The type, depth of abnormal changes, pathogenetic characteristics of a congenital disease are determined by primary physical examination, instrumental and laboratory methods.
The history is not very informative, but it allows the neonatologist or pediatrician to track the dynamic changes in the condition of the newborn. Laboratory tests do not identify specific markers.
They are used exclusively for diagnosing the severity of complications and detecting concomitant pathologies. Hardware methods for visualizing bone deformities are the standard for craniostenosis.
Methods for assessing the degree of damage to cerebral tissues include:
- neurosonography - two-dimensional sectoral scanning of the internal cavities of the skull with ultrasonic waves;
- X-ray - radiation diagnostics with fixation of the image of the studied area of the head;
- computed tomography, which allows you to create a three-dimensional model of the investigated area;
- magnetic resonance imaging, detailing the internal structure of cerebral structures.
Neurosonographic technology is used to assess the state of intracranial tissues and the size of the ventricular cavities, to identify hypertensive signs. The X-ray image determines the nature of bone deformities, the degree of hardening of the cranial joints.
A metopic suture on a child's forehead is necessarily diagnosed using CT and magnetic resonance imaging. Such procedures provide more informative results.
Additionally, ophthalmoscopy is performed to determine the degree of visual impairment. Differential diagnosis of craniostenosis is performed to clarify the type of anatomical anomaly and select a method of surgical reconstruction.
Treatment
The only way to restore the natural shape of the skull and reduce the severity of complications is surgery. The most appropriate time for surgical correction is considered to be the age of a child 6-9 months.
Such periods are due to the intensive development of tissue structures of the cerebral zone during this period of life. Their growth is impeded by bone distortions. At this age, incompletely hardened tissues quickly restore their natural structure without the risk of serious complications.
The scope of reconstruction and the technique of the operation are selected based on the type of pathology, the degree of abnormal changes. When a child reaches the age of 2-3 years, surgical reconstruction is possible only to eliminate minor cosmetic defects.
Correction consists in remodeling of the bony formations of the cranial vault. The best result is obtained by an operation performed jointly by a pediatric maxillofacial and neurosurgeon.
With trigonocephaly, subsequently, corrective orthotics are prescribed, which involves wearing a specialized fixing helmet. Such a dynamic system is designed to eliminate residual deformations caused by intensive head growth.
A helmet-orthosis gives the best results in the first 6-18 months of a baby's life. In addition to surgical correction and the use of a dynamic fixation system, a change in the child's nutritional regimen is shown in accordance with age requirements and observed violations.
With the progression of intercurrent pathologies or an increase in neurological symptoms, complex drug therapy is prescribed.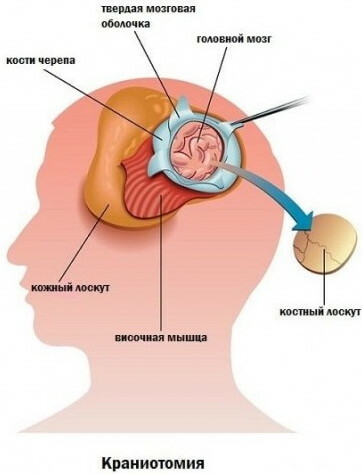
The following types of craniotomy are used to reconstruct deformities of the cranial bones:
- linear, providing for partial amputation of the periosteum;
- circulatory, carried out for children 3-5 years old and aimed at eliminating intracranial hypertension;
- fragmentary - cutting the cranial vault;
- double-sided flap, designed to correct the decompensated form of craniostenosis.
The resection lines are marked in advance with a medical marker. Typical areas of influence are the frontal lobe, the anterior fontanelle, the coronary junction.
Forecast
With a timely and successful surgical operation, the chances of a full life are assessed as high. Accurate predictions depend on the form of the anomaly, the etiological factor, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Often it is possible to completely eliminate the metopic suture, arrest neurological symptoms and intracranial hypertension. The pathological formation on the child's forehead disappears as the reconstructed bones grow. Only syndromic craniostenosis is prognostically unfavorable.
Video about craniostenosis
Malysheva about the deformity of the skull in a child: