Content
- General information
- Research method and biomaterial
- Protein S deficiency classification
- Indications for analysis
- What else is assigned with this study?
- Significance of analysis results
- What is the risk of low protein S during pregnancy?
- Protein C and S Deficiency Videos
Protein S belongs to the group of important inhibitors of fibrinolysis, which increase blood clotting. Sometimes this plasma protein can be lowered during pregnancy, which is fraught with venous and arterial thrombosis, various complications in the form of repeated miscarriages, pronounced edema, intrauterine growth retardation of the fetus, characterized by a lag in growth, weight and other fetometric indicators from the average normative for a specific period gestation.
To assess the anticoagulant system of the blood, doctors prescribe a free protein S test as part of the differential diagnosis of pregnancy pathologies.
General information
Protein C is one of 100 proteins found and constantly circulating in the blood. It belongs to the category of physiological anticoagulants that inhibit the activity of coagulation hemostasis (blood coagulation system).
The synthesis of this substance with the participation of vitamin K is carried out in the liver, bone marrow cells (fragments of the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes) and endothelial cells.
In proteomics, there are two forms in which this clotting inhibitor circulates in the blood:
- free - about 45% of the total;
- in combination with plasma proteins capable of a sequential activation cascade with a final nonspecific cytotoxic (microbicidal) effect - about 60% of the total.
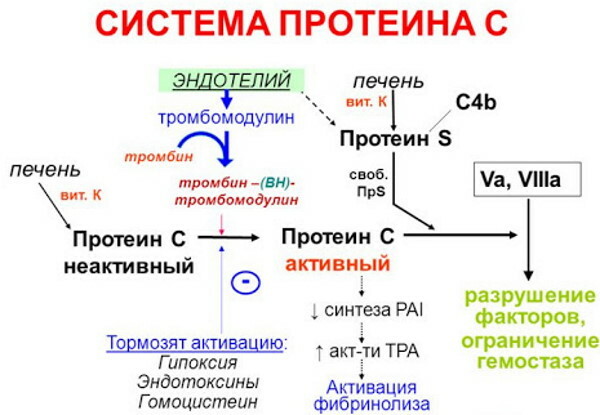
The C4b-transfer protein acts as a binding element of the free and complex forms of the protein S between each other. The peculiarity of the activated coagulation element XIV is to accelerate the destruction of activated V and VIII factors, which, in turn, leads to inhibition of the intravital formation of blood clots inside the blood vessels, preventing its free flow through the bloodstream system.
In case of traumatic damage to blood vessels, bleeding stops due to a complex of platelets - colorless disc-shaped, nuclear-free blood cells.
They flatten and acquire the ability to adhere to each other and to the vessel wall, overlapping its damaged wall. Then, the plasma protein C is added to them in order to balance the action of the coagulation system. Also, this protein helps to remove damaged cells from tissues and protects against inflammation when they die.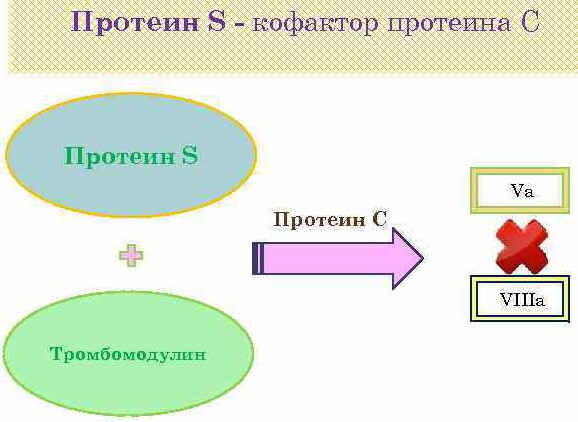
Protein S, or rather its quantitative ratio in the body, depends on the person's age, the efficiency of the endocrine glands synthesizing hormones, and gender. In women, it can also be lowered or raised during pregnancy, which has certain negative consequences.
Research method and biomaterial
It is impossible to detect whey protein by classical clinical chemistry methods, therefore, the method of conducting a study for free protein C is immunoturbidimetry. After taking venous blood, it is tinted with the suspension absorbed by it, and then scattered light is directed at it, so that, as a result of its interaction with particles in solution, set the amount of protein in percentage ratio.
First of all, the study is assigned to identify the deficiency of protein S, which is a hereditary and transmitted autosomal gene. The procedure is included in the comprehensive diagnosis of thrombophilia, and is also required for arterial / venous thrombosis, thromboembolic complications occurring in people who have not yet turned 50-55 years old.
During the period of bearing a child, determining the level of free protein synthesized by the liver is advisable with a complex diagnostics of the causes of deep vein thrombosis, saphenous vein thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and pulmonary thromboembolism arteries.
Protein S deficiency classification
Deficiency of one of the most important clotting inhibitors can be congenital, which appears immediately after birth and passed from parents to children, or acquired - able to reveal themselves both in the first days / months of life, and after many years.
As for congenital deficiency, there are 3 main types in medicine:
- A decrease in the amount of total and free protein C occurs along with a sharp decline in its ability to perform its anticoagulant functions.
- The liver synthesizes fat-soluble protein, dependent on plasma glycoprotein, in sufficient volume, but due to defectiveness of its molecules, forming a kind of crystals and stretching the erythrocyte, there is no interaction with protein S.
- A decrease in the level of the main clotting inhibitor against the background of a normal volume of total protein.
Protein S lowered during pregnancy can be in the homozygous or heterozygous form of the carriage of the defective gene. The first case is characterized by complete defectiveness of the protein constantly circulating through the bloodstream in an inactive state, which leads to thrombocytopenic purpura in infants, a type of hemorrhagic diathesis characterized by a deficiency platelets.
Early disseminated intravascular coagulation is also not excluded - a pathological nonspecific process characterized by the formation of disseminated blood clots, which is characterized by an increased risk of death.
The heterozygous form is often diagnosed during puberty, when puberty is triggered by signals from the brain to the sex glands. The risk of blood clots in the vessels of the main organ of the central nervous system, lungs and heart increases 6 times in the absence of treatment.
Pregnant women are at risk for acquired protein S deficiency (especially those who are already in the 3rd trimester), patients with pathologies that are treated with medications that inhibit the activity of coagulation hemostasis.
This also includes people with serious kidney disease who use oral contraceptives and undergoing HRT - therapy aimed at pharmacological replacement of lost hormonal function ovaries. Such treatment involves the use of estrogens, gestagens, and in some cases androgens.
Indications for analysis
You can get a referral for immunoturbidimetry from a family doctor, whose task is to provide primary medical care. And cardiologists, gynecologists, oncologists, therapists with additional education specializing in blood diseases are engaged in decoding the results of the protein S test.
The list of indications signaling the need for diagnostics includes:
- complications of pregnancy in the form of premature placental abruption, spontaneous interruption of gestation at any time, stillbirth, preeclampsia and eclampsia;
- monitoring the condition of patients at risk (with a congenital form of protein S deficiency, which was transmitted to the patient from relatives);
- timely detection and comprehensive diagnosis of a predisposition to the development of recurrent vascular thrombosis (mainly venous) of various localization.

Protein S lowered during pregnancy can cause thrombotic occlusion of the pulmonary artery or its branches, leading to life-threatening disorders of pulmonary and systemic hemodynamics. Women with this symptom increase the risk of death or necrosis of all layers of the skin.
What else is assigned with this study?
To study blood clotting indicators in more detail and, if necessary, prescribe effective treatment, doctors can, in conjunction with immunoturbidimetry, prescribe a number of other studies. Some of the procedures that patients may still encounter are listed in the table below.
| Research method | Description |
| APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time) | Screening test, which is a medical test that simulates clotting processes blood to assess the presence and determine the level of clotting factors, anticoagulants and inhibitors. After the venous blood is taken, it is purified and forced to interact with the koalin-cephalin reagent. |
| Hemostasiogram | A comprehensive hematological study that allows you to assess the state of the hemostasis system and blood coagulation indicators. It is usually prescribed after a serious injury and before surgery to eliminate the risk of developing bleeding / formation of intravital blood clots in the lumen of a blood vessel or in a cavity hearts. |
| Antithrombin III test | It is a specific protein whose main task is to inactivate several major factors. clotting, including thrombin, and preventing increased blood clotting (blood clots). It is strongly discouraged to carry out this analysis in patients with a history of rheumatoid arthritis, exacerbated pancreatitis and infectious diseases. |
| D-dimer analysis | In most cases, it is prescribed as an auxiliary study aimed at diagnosing disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, additional assessment of the severity of thrombus formation and monitoring of the ongoing anticoagulant therapy for pulmonary thromboembolism, stroke. |
| Plasminogen blood test | Allows you to assess the reserve of blood plasma protein, a proenzyme, which under certain conditions turns into an active form (plasmin). This substance is a component of the fibrinolytic system necessary to prevent excessive blood clots (thrombi) from forming during blood clotting. |
 It is worth considering one important point: it is strictly forbidden to carry out laboratory tests involving the collection of venous blood in a period of exacerbation of thrombotic processes in the superficial veins, which may be accompanied by damage to deep veins (deep vein thrombosis, DVT). Even though it is easier to exclude a plasma protein deficiency in S.
It is worth considering one important point: it is strictly forbidden to carry out laboratory tests involving the collection of venous blood in a period of exacerbation of thrombotic processes in the superficial veins, which may be accompanied by damage to deep veins (deep vein thrombosis, DVT). Even though it is easier to exclude a plasma protein deficiency in S.
Significance of analysis results
Based on the test results, the doctor can already establish the level of protein in the body, which can be normal, be increased or decreased. If the increased value has no negative consequences and clear clinical significance, then attention should be paid to the decrease in free protein C.
Protein S is lowered during pregnancy if there are deviations from the norm, which ranges from 55 to 125%. Patients with low rates are prescribed treatment aimed at minimizing complications during gestation, childbirth, or the postpartum period.
In babies from 24 hours after birth to 3 months of age, the amount of protein S should not be higher than 55% and below 15%. In older children, this parameter increases to 45-130%. For adult men, the indicators are from 75 to 147%, for women - from 55 to 125%.
If the results of the analysis are increased, it means that one of the following pathologies takes place:
- a metabolic disorder of vitamin K, which can lead to celiac disease - a disease in which food containing gluten (baked goods, pasta, breakfast cereals, yoghurts), damages the mucous membrane of the small intestine and leads to a deficiency of significant for the body elements;
- processes associated with a chronic infectious disease, which is provoked by the human immunodeficiency virus, which affects the cells of the immune system (HIV);
- septic conditions (severe blood infection), shock, intoxication;
- cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease accompanied by irreversible replacement of the parenchymal tissue of the liver with fibrous connective tissue, or stroma;
- the development of malignant tumor pathologies.
Also, a decrease in free protein S is characteristic of nephrotic syndrome - a symptom complex, developing against the background of kidney damage, including massive proteinuria, protein-lipid disorders exchange and swelling. It is observed in lupus erythematosus, treatment with L-asparaginase - an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of amino acids.
What is the risk of low protein S during pregnancy?
If a woman has a low protein S during the period of gestation, there is a risk of thrombosis. The symptomatic picture of this condition is represented by thrombophlebitis, acute arterial and venous thromboembolism, damage to the vascular plexus. As a result of pathology, a violation of the uteroplacental blood flow and damage to the placenta often occur. The patient may simply not bear the child before the end of the term and give birth to him prematurely.
The Leiden mutation, which occurs against the background of protein S deficiency, affects about 45% of women. This is a condition in which one or two regions of the gene that codes for the activity of coagulation factor V are altered. In the first or second trimester, with such a diagnosis, a miscarriage may occur.
Protein S plays the role of an important clotting inhibitor, the synthesis of which is carried out by the glandular organ - the liver. If it is lowered during pregnancy, you need to immediately begin treatment with drugs prescribed doctor in order to avoid pathologies and eliminate the risk that the child will be born with some deviations. Protein S deficiency should be dealt with only after undergoing examination and consultation with a specialist.
Protein C and S Deficiency Videos
Protein C and S deficiency:



