Content
- Characteristics and properties
- The table is ok
- Symptoms and causes of rejection
- How is it determined
- General blood analysis
- Detailed blood test
- How to bounce back
- Diet changes
- Exclusion of certain drugs from admission
- The course of drug treatment
- Bivalirudin
- Argatroban
- Methylprednisolone
- Blood transfusion
- Nutrition correction
- Drug therapy
- Anagrelide
- Aspirin
- Dipyridamole
- Varfalan
- Eliquis
- Phenylin
- Thrombopheresis
- Video about PLT blood test
PLT blood test is a study of the number of platelets in women, the decoding of which depends on the norm of their average values. Platelets are blood cells. They are non-nuclear blood cells that are produced in the bone marrow on a daily basis and have many functions, the main one being to stop bleeding.
Platelets are an irreplaceable component of the hemostasis process. In a woman, a change in the number of platelets affects primarily women's health and causes cardiovascular diseases. For any changes in well-being, a woman is definitely recommended to take a general blood test to establish PLT indicators.
Characteristics and properties
PLT blood test with decoding, the norm in women of which are individual, reveals the level of platelets in the blood. Platelets are produced in bone marrow cells on a daily basis. They circulate in the blood for 10-12 days and die when they reach a mature state. The bone marrow regulates the number of platelets produced. However, in the presence of influencing factors, platelets can be produced abnormally.
In the blood, platelets have several important functions:
- stopping bleeding;
These cells are not only able to adhere to each other and the vessel walls, stopping open and internal bleeding, but can also change their shape, increasing the area of damage blocking.
- immune-protective;
Platelets are able to catch and absorb foreign bodies, protecting the body from outside influences.
- safety.
Platelets accumulate serotonin, which protects the body from radiation and cancer.
With a decrease in the level of platelets, the protective functions of the body are sharply reduced and the likelihood of developing diseases and large blood loss arises. Especially during critical days in women. However, an increase in the level of platelets can provoke the appearance of blood clots, rupture of blood vessels and impaired cardiovascular activity. With an increased production of platelets, the blood becomes very thick, the pressure rises, and the heartbeat becomes rapid.
Depending on age, a woman's body produces a different number of platelets. There are standards for indicators of the level of PLT in the blood for each age. A PLT blood test measures the platelet count at the time of the procedure. It is investigated most often in a general blood test and serves as an additional factor in determining the patient's health status.
The number of platelets in the event of abnormalities in the work of individual organs, internal blood loss or surgery changes within a few days. However, in a healthy person, their level remains. For prophylactic purposes, an analysis of platelets in women is carried out once a year. If there are deviations in the indicators, the procedure can be repeated for control once every 1-2 months.
The table is ok
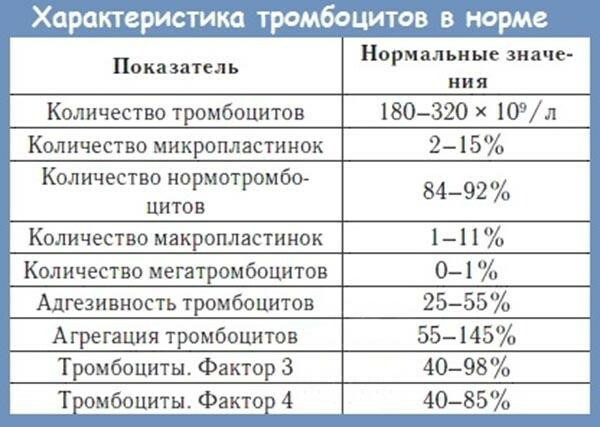
PLT blood test with decoding, the norm in women of which can be determined independently, is carried out as part of a general and detailed blood test. At different ages in a woman, the number of platelets is produced in different sizes. There is a single indicator for women of the level of platelets in the blood. It is in the period from 16 to 85 liters. 180-320 units and can be indicated in thousand / μl. or 109/л.
For a more accurate understanding of the correspondence of the platelet level, the values should be correlated with the average values for a certain age of the woman.
The rate of platelets in the blood in women by age is determined in the following values:
| Age, l. | Platelet count, 109/л. |
| 16-18 | 180-335 |
| 19-25 | 180-320 |
| 26-35 | 180-400 |
| 36-60 | 180-340 |
| 61-85 | 180-320 |
Moreover, in pregnant women, the platelet count in the blood can vary from 100 to 420 109/ l, which is considered the norm. This is due to hormonal changes and metabolic changes.
The number of platelets during critical days in women can decrease to 75 109/ l due to blood loss, therefore, the analysis is recommended after the end of the menstrual cycle. The same decrease occurs after operations, injuries or infectious diseases.
Symptoms and causes of rejection
PLT blood test with decoding, the norm in women of which depends on the disease and related factors must be performed when passing a routine examination or at the beginning of a respiratory diseases. According to the results of the analysis, the number of platelets in a liter of blood is established, which must be correlated with the normal value. In a woman's blood, the number of platelets can be increased or decreased, the symptoms and causes of which are always different.
With an increased number of platelets, a woman may experience the following symptoms:
- pain in legs and arms;
- numbness of the limbs;
- frequent headache;
- increased weakness and irritability;
- bleeding gums;
- the appearance of subcutaneous hematomas;
- a sharp drop in vision;
- increased swelling;
- pallor and cyanosis of the skin;
- in rare cases, a woman may experience itching of the extremities.
The increase in platelet levels occurs for various reasons.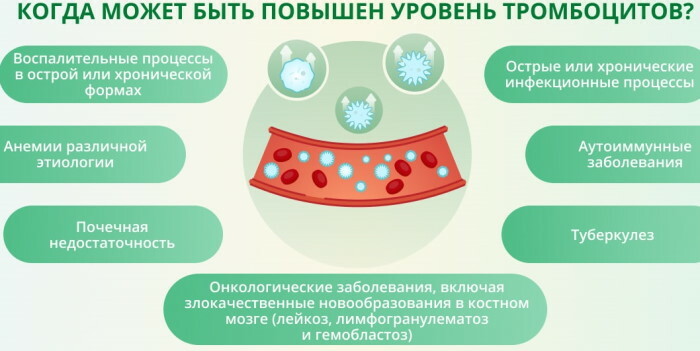
These include:
- intestinal inflammation;
- bone marrow, stomach and lung cancer;
- infectious diseases;
- renal failure;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- viral hepatitis;
- iron deficiency;
- autoimmune diseases (arthritis, lupus);
- taking medications (hormones, contraceptives, chemotherapy);
- tuberculosis;
- blood poisoning;
- bad habits (alcohol and smoking);
- removal of the spleen or disruption of its work;
- purulent skin diseases affecting large areas of the body.
In some cases, physical overload or stress, blood transfusion, affect the increase in the number of platelets.
A lowered platelet count in a woman is manifested:
- persistent nosebleeds;
- systematic bruising on the skin;
- the appearance of redness on the skin;
- bleeding gums;
- bleeding in the intestines, hemorrhoids and blood in the stool;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- profuse and prolonged bleeding (sometimes with clots) during critical days;
- increased weakness, dizziness;
- pallor of integument, blue in the area under the eyes.
Insufficient platelet production depends on internal and external factors and can be caused by:
- injuries, operations;
- cancer of the bone marrow, blood;
- hereditary predisposition;
- an increase in the size of the spleen;
- autoimmune thrombocytopenia;
- taking medications (cytostatics, hormones, painkillers).
Abuse of antipyretics, antihistamines and antibiotics affects a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood, which may not appear immediately, but within 1-2 weeks after administration.
The severity and severity of the manifestation of symptoms with an increased and decreased level of platelets is determined by the degree of deviation of indicators from the norm in women. At the same time, it is important to take into account the general state of health, immunity in each case. Some women with a significant deviation in platelet levels do not feel any symptoms at all, so it is important to systematically do a complete blood count.
How is it determined
PLT blood test with decoding, the norm in women of which gives an idea of the general state of health, is included in the research complex with a general and detailed blood test. A separate study for platelets (platelets) is not performed. To establish the level of platelets, both venous and capillary blood can be used. The type of blood sampling for research does not affect the result.
The study of the level of platelets can be carried out by:
General blood analysis
Blood for blood analysis is taken from a finger, i.e. capillary blood is used. Blood is taken on an empty stomach for testing.
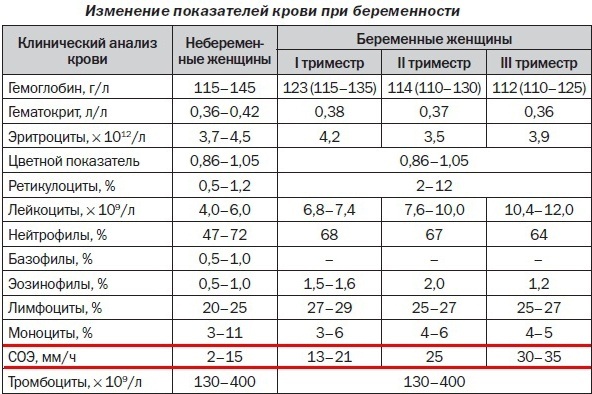
Blood from a finger allows you to determine a limited range of indicators, which includes the level of hemoglobin, ESR, erythrocytes, leukocytes.
Detailed blood test
With an expanded blood test, the material for analysis is taken from a vein. Blood from a vein is taken on an empty stomach and allows you to check the compliance with the norm of a larger number of indicators. Such a study is always carried out in hospitals upon admission, since it provides more data.
After taking blood from a finger or from a vein, the biomaterial is sent for research. Depending on the method used, the material obtained is examined manually or using a special apparatus. In the first case, blood is placed on a special glass for examination under a microscope. A small amount of blood is examined under a microscope, which gives an idea of the number of platelets in a liter of blood.
In the second case, a certain amount of blood for research is placed in a special transforming solution. This solution is placed in a hematology analyzer to determine the number of platelets in the blood.
Both studies give sufficiently accurate results that allow you to establish the deviation of platelets from the norm in women.
How to bounce back
PLT blood test, which, after decoding, allows you to give an idea of the platelet rate in a woman, is carried out periodically during routine examinations or as you turn to a therapist. If the study reveals that the number of platelets decreases below 150 thousand / μl or rises to 500 thousand / μl, then the patient may be assigned an additional examination to establish the underlying cause of the disease and prescribing treatment.
Treatment for an abnormal platelet count is to tackle the underlying cause of the change. Often such reasons are urgent and require surgery.
General treatment for low platelet counts includes:
Diet changes
With a lack of platelets, it is important to completely eliminate spicy foods. There are more apples, peppers, grapes and celery. Eat more fish, meat, liver. Give up bad habits and drink enough water.
Exclusion of certain drugs from admission
A woman with a low platelet level should completely refuse to take aspirin, pain relievers and antiallergic drugs, as well as antibiotics, if possible.
The course of drug treatment
A woman with a low platelet count is prescribed drugs that promote platelet synthesis or contain substances that replace them. These are used as:
Bivalirudin
Bivalirudin is a synthetic inhibitor of thrombin and can quickly increase its amount in the blood. The drug is administered intravenously at 0.1 mg / kg. The drug is administered once every 2-3 days for 5 days. Each dose is calculated individually for the patient.
Argatroban
Argatroban is a direct thrombin inhibitor. It effectively increases and maintains platelet levels at the desired level. The drug is administered at 0.1 mg / kg, followed by repeated maintenance dose to maintain the platelet level at the desired level.
Methylprednisolone
Methylprednisolone actively promotes platelet synthesis. The drug is administered intravenously at 1 mg / kg 1-3 times a day for 5-10 days.
Blood transfusion
In difficult cases, with a large blood loss and a lack of platelets, blood transfusions can be performed in individual patients. The procedure allows you to quickly restore the level of platelets, the state of the blood supply system and general health in case of injuries, after operations.
If left untreated, an inadequate platelet count can lead to uncontrolled bleeding, vascular damage, and blood loss. Lack of ambulance in this case can lead to death.
With an elevated platelet count, treatment includes:
Nutrition correction
If the platelet level is high, a person is advised to reduce the consumption of bananas, rose hips, lentils, nuts and pomegranates, as well as spices. You need to add lemons, ginger, beets, tomatoes, grapes to the food. Eat more olive oil. Drink plenty of fluids.
Drug therapy
Patients are prescribed drugs that interfere with the production of platelets and thin the blood. These are used as:
Anagrelide
Anagrelide helps to reduce the level of platelets in a woman's blood. The drug is taken at 0.5 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days. The exact dosage and course of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Aspirin
Aspirin interferes with platelet synthesis by inactivating platelet COX with prolonged use.  The drug is taken in 0.5 - 1 tab. 2 times a day for 20-30 days.
The drug is taken in 0.5 - 1 tab. 2 times a day for 20-30 days.
Dipyridamole
Dipyridamole effectively prevents blood clots. Prescribe the drug to be taken 75 mg up to 5 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Varfalan
The drug blocks the synthesis of blood coagulation factors in the liver, reduces their concentration in plasma and slows down the blood coagulation process. The drug is taken in 2 tabs. per day for 10 days.
Eliquis
Eliquis is a direct enzyme inhibitor that blocks the active site of this substance. Due to this, it contributes to a rapid decrease in the level of blood clots. The drug is prescribed 1 tab. 2 times a day for 7-10 days.
Phenylin
Phenylin actively prevents blood clots and blood thinning. The drug is recommended to be taken at 0.02 g 3 times a day. The reception time is 7-10 days.
The reception time is 7-10 days.
Thrombopheresis
In case of an increased number of platelets up to 520 109/ l can be urgently performed therapeutic thrombopheresis. This procedure involves filtering the blood using a special apparatus, which removes excess platelets. The procedure is carried out only in hospitals under the supervision of doctors.
An increased level of platelets is dangerous with consequences. It dramatically increases the likelihood of developing thrombophlebitis. Blockage of individual vessels causes the cessation of blood supply to tissues and organs and can provoke stagnation and gangrene. Blockage of large vessels can rupture and increase the likelihood of stroke in women.
PLT blood test and its interpretation lays the foundation for determining the level of platelets and its compliance with the norm in women. The rate of change of this indicator can be several days. Only a timely blood test can accurately establish the state of a woman's health.
A strong change (increase or decrease) in the level of platelets in comparison with the norm can cause complications for a woman's health and provoke the occurrence of chronic diseases. Existing blood test methods allow to establish the platelet level within a few hours for the purpose of effective treatment and rapid recovery of women's health.
Video about PLT blood test
PLT blood test: