Content
- What is urobilin and why is it needed
- The norm of urobilin in urine in men and women by age
- What test determines the level of urobilin in urine?
- Preparation and delivery of analysis
- Decoding the results
- Reasons for increasing urobilin
- Viral hepatitis
- Leptospirosis
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Medicinal hepatitis
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Tumor neoplasms
- Alcohol intoxication
- Hemolytic anemia
- Reasons for a decrease in urobilin
- Normalization of the indicator
- How to lower the level
- Detoxification
- Antiviral therapy
- Treatment with hepatoprotectors
- Antibacterial therapy
- Surgery
- Antianemic therapy
- Lowering the level
- Video about urobilin
Urobilin contains in urine in adults and children. This substance is a bile pigment, and its formation occurs during the metabolic breakdown of bile components. The physiological norm of urobilin is determined in laboratory conditions by examining urine for biochemical parameters.
What is urobilin and why is it needed
Urobilin (urochrome) is a rich yellow pigment substance that belongs to the chemical group of linear tetrapyrroles. This component is formed as a result of the metabolic breakdown of urobilinogen.
Normal values of urochrome in urine give it a light yellow tint. This color of urine indicates a satisfactory condition of the liver and gallbladder. Urobilin is an intermediate in the multi-stage process of synthesis and distribution of bile in the human gastrointestinal tract.
The mechanism of the appearance of urochrome is as follows:
- The formation of urobilin occurs at the stage of metabolic degradation of heme.
- Initially, heme is converted to biliverdin.
- Then this biochemical compound is converted into bilirubin.
- Together with bile, bilirubin enters the duodenal cavity through the bile ducts.
- Inside the large intestine, bilirubin is attacked by beneficial intestinal microorganisms, which decompose it to the state of urobilinogen.
- In the gastrointestinal tract, urobilinogen is reabsorbed into the general bloodstream.
- In the blood, the reabsorbed urobilinogen is metabolized to urobilin.
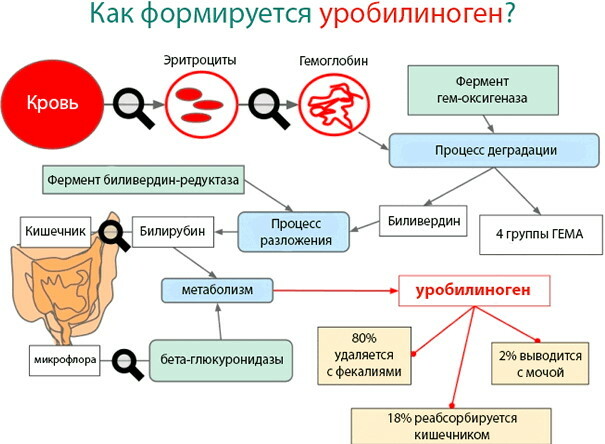
Urobilin enters the urine through the kidneys in the process of filtering the blood with the excretion of metabolic decay products. Light yellow urine, which resembles the shade of wheat straw, indicates the normal content of urochrome in the human body. Most laboratory urine tests take into account the total concentration of urobilin to determine the functional state of the patient's liver, gallbladder and urinary system.
The norm of urobilin in urine in men and women by age
Urobilin in urine (the norm of this substance is determined by specialists in a biochemical laboratory) is the result of a complex metabolic breakdown of bile into its constituent components. Urochrome is contained in the urine of children, men and women.
Under the condition of stable functioning of the liver, gallbladder and its channels, kidneys and excretory organs, the concentration of urobilin in the urine remains stable regardless of the person's age. The norm of urochrome for men and women does not exceed 17 mmol per 1 liter of the test material. Deviations from these values indicate the possible development of latent diseases of the body.
What test determines the level of urobilin in urine?
The level of urobilin in urine is determined by clinical analysis. Urine collected in the morning immediately after awakening from sleep is used as biological material. Urine collection is carried out at home with further delivery to the diagnostic center, or directly at the clinic, where laboratory analysis will be carried out.
In combination with the study of the concentration of urobilin, accompanying chemical components are released from the patient's urine, which are important in the diagnosis of most diseases of internal organs.
Preparation and delivery of analysis
Urobilin in urine (the norm of bile pigment indicates the functional state of the liver) is determined using special chemical reagents.
Before the delivery of biological material for its laboratory study for general indicators, each patient must comply with the following preparation rules:
- 24 hours before the appointed date of urine collection, stop drinking alcohol, sugary carbonated drinks, which contain a dye;
- 2 days before the test, do not take medications with diuretic properties, as this will lead to false and biased laboratory test results;
- the last meal should take place in the evening before the trip to the clinic (it is not recommended to overeat, or to consume excess fluid);
- 12 hours before the examination, intake of too salty, spicy or acidic foods is contraindicated;
- in the evening on the eve of urine collection, do not eat carrots, beets, red, black and yellow berries (pigments, contained in these products, cause a change in the color of urine, which will complicate its clinical study);
- 12 hours before the test, it is forbidden to take B vitamins, medicines based on acetylsalicylic acid, Furagin and Antipyrin preparations.
To obtain the most objective results of a clinical study of urine 1 day before the test, it is necessary to refrain from physical and psycho-emotional stress. Women should not have this laboratory test during their period.
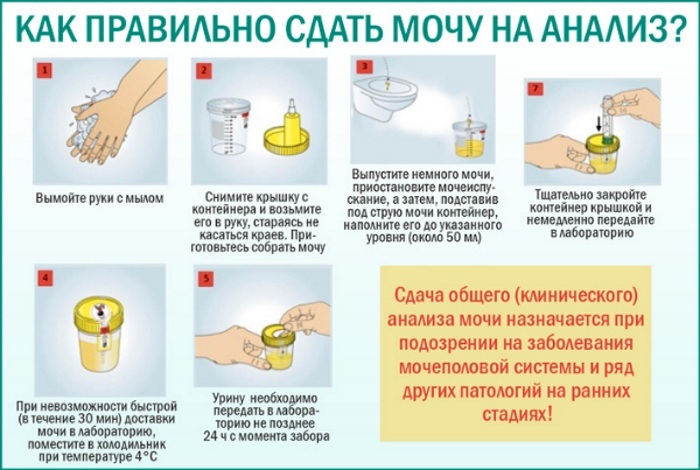
The table below describes in detail the step-by-step process for passing a clinical test to determine the level of urobilin in urine:
| Procedure | Description of the urine collection procedure |
| Step 1. Genital hygiene. | After waking up from sleep, you need to go to the bathroom, where you can perform hygiene of the external genital organs. In this case, you cannot use any antiseptic agents. It is enough to take a warm shower with soap. Upon completion of the water procedures, the genitals are wiped with a clean dry towel. |
| Step 2. Preparing the container. | A disposable plastic container is used to collect urine. The container for biological material must be sterile. This container can be obtained from the laboratory staff who will conduct the examinations, or you can purchase it yourself at the pharmacy. The urine collection container is opened just before urinating. |
| Step 3. Collection of urine. | The process of passing the analysis begins with the fact that the subject pours 100-150 ml of morning urine into the toilet. The remainder of the urine is sent to a sterile dry container. Upon completion of urination by the shaking method, uniform mixing of the biological material is carried out. After that, the container with analyzes is closed with a tight lid. |
A plastic can of collected urine should be delivered to the laboratory as soon as possible. Storing urine in hot conditions, in direct sunlight, can lead to a change in its biochemical composition. In the future, this will affect the objectivity of the results of clinical analysis.
Decoding the results
Urobilin in urine (the norm of this substance indicates a healthy liver and gallbladder) is determined using clinical analysis along with other components of urine. Deciphering the results takes no more than 3-5 minutes. The attending physician who has prescribed an examination of the patient with the release of the level of urochrome draws attention to the concentration of this substance in the morning urine.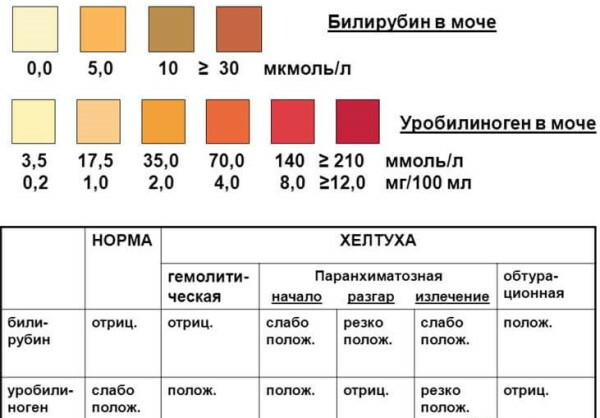
The results of clinical analysis for urobilin over 17 mmol per 1 liter of biological material indicate a painful state of the liver, gallbladder, its ducts, and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, the patient is shown an additional examination using hardware diagnostic methods.
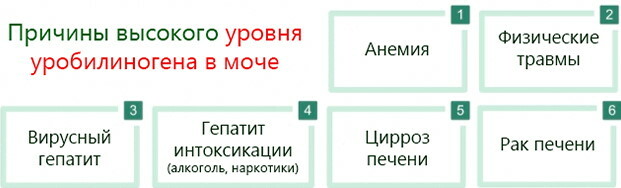
Reasons for increasing urobilin
A sudden increase in urobilin levels is manifested by a color change in urine. Urine takes on a rich maroon or beer hue. Such symptoms indicate that in the process of metabolism, most of the bilirubin is excreted through the kidneys, and not in the bile. An increase in the level of urobilin always provokes pathological causes in the form of acute or chronic diseases of the body.
Viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is a group of inflammatory diseases characterized by the rapid destruction of liver cells. This pathology has an acute or chronic course.
Viral damage to liver tissue is caused by the following strains of infectious microorganisms:
- hepatitis B virus;
- hepatitis C virus;
- hepatitis D virus (also known as delta).
Urobilin in urine
The hepatitis A virus strain causes acute liver inflammation in 90% of cases. Chronic hepatitis is provoked by the C virus. In the presence of these diseases, an increase in urinary urobilin levels is considered a direct result of liver dysfunctions.
The hepatocytes of this organ undergo total destruction by viral microorganisms, and then cease to perform their physiological functions. The more severe the damage to the liver by the virus, the higher the level of urobilin in the urine.
Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is an acute infectious disease. The causative agent of this disease is the bacterial microorganism Leptospira. Leptospirosis is manifested by the destruction of the structure of the capillaries, damage to the tissues of the liver, kidneys, skeletal muscles.
The disease is accompanied by extensive intoxication of the patient's body, yellowing of his skin, bouts of aching pain in the muscles, tachycardia. Leptospirosis causes an increase in urobilin in the urine, as it provokes focal liver damage. This disease can cause the onset of hepatic coma.
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Urobilin in urine (the norm of this substance is the same for people of all genders and age categories) increases in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. This is a rare autoimmune disease with a chronic course. In this case, the violation of the norm of urochrome in the urine is due to the fact that the own cells of the human immune system perceive the bile ducts as foreign agents.
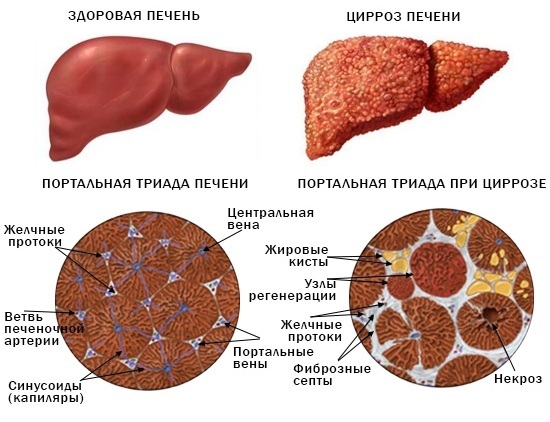
As the disease progresses, there is a gradual destruction of the tissues of the liver and bile ducts. Primary biliary cirrhosis is difficult to treat with medication.
Medicinal hepatitis
Medicinal hepatitis develops in exactly the same way as viral liver damage. The difference in trauma to the tissues of an organ is that its cells are destroyed not by an infectious invasion, but by the effects of chemicals in medications.
The damaged areas of the liver cannot cope with the function of processing bilirubin derivatives. In this regard, an excess amount of urobilin enters the blood. Medicinal hepatitis occurs in people who have to take powerful drugs for life with many side effects.
Infectious mononucleosis
The causative agent of infectious mononucleosis is the DNA-genomic viral microorganism Epstein-Barr. Replication of this pathogenic agent occurs in the B-lymphocytes of the human body. This disease is manifested by extensive intoxication, severe fever, inflammatory damage to the liver and spleen.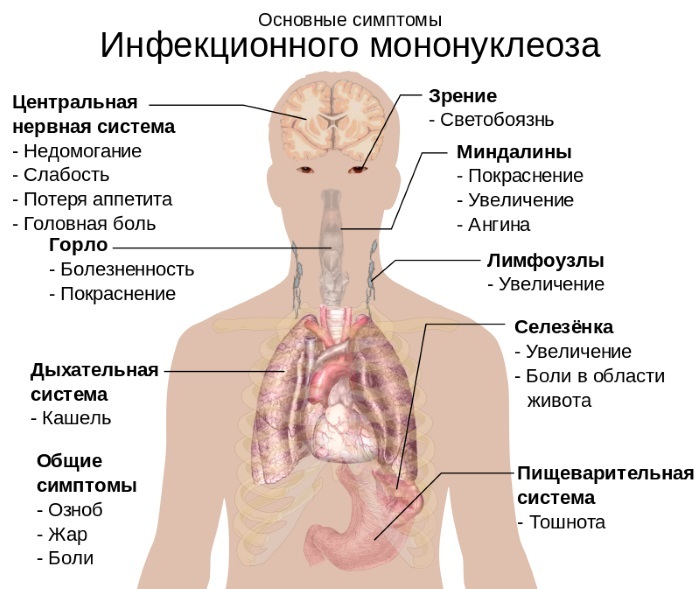
Infectious mononucleosis provokes an increase in urobilin in the urine, and also causes a change in the qualitative composition of the blood. The main danger of this pathological cause of an increase in the level of urochrome is that today there is no single protocol for the specific therapy of infectious mononucleosis.
Tumor neoplasms
Benign and cancerous growths in the liver lead to the destruction of the hepatocytes of this organ. The pathological growth of the tumor causes compression of the bile ducts, the metabolism of bilirubin is disrupted, and a gradual increase in urobilin in the urine occurs. The severity of the clinical manifestations of the disease depends on the location and type of extraneous neoplasm.
Alcohol intoxication
An increase in urobilin indices in the urine composition periodically occurs in patients with chronic alcohol intoxication. In patients of this category, the occurrence of a pathological state of the liver is the result of daily drinking that lasts for a long period time. A high level of urobilin in urine persists until the patient's liver tissue is cleared of excess toxins.
Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia is an acute disease of a heterogeneous type, which is accompanied by premature destruction of red blood cells.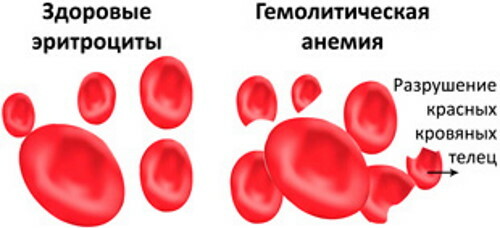
Pathological hemolysis of blood cells occurs in the liver tissues, which causes damage to its hepatocytes. This disease is characterized by an increase in the level of urobilin in the urine, yellowing of the skin, discoloration of feces.
Reasons for a decrease in urobilin
Low urinary urobilin levels are a sign of healthy liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. In the results of a clinical study of urine, the optimal values of the level of urochrome are from 0 to 17 mmol per 1 liter of biological material. Excess of this amount of urobilin is considered a sign of acute or latent liver disease. A reduced level of this substance is not a symptom of pathology.
Normalization of the indicator
A decrease in the concentration of urochrome in the composition of urine is carried out by treating the main diseases of the liver, which provoked damage to its tissues.
How to lower the level
To lower the too high level of urobilin, drug therapy is used, the properties of which are aimed at restoring impaired liver functions. Surgery is possible depending on the clinical situation.
Detoxification
Normalization of the level of urobilin, which increased due to alcohol intoxication of liver tissue, is carried out using the following sorbent preparations:
- Enterosgel;
- Smecta;
- Activated carbon;
- Polyphepan;
- Polysorb MP.
The dosage regimen for the above drugs is determined by the attending physician. The duration of detoxification therapy is from 5 to 15 days, depending on the functional state of the liver tissue.
The normalization of the level of urobilin in the urine occurs gradually as the hepatocytes are cleared and the working capacity is restored.
Antiviral therapy
Patients in whom a high concentration of urochrome in the urine is caused by hepatitis C is prescribed a course of the following antiviral medications:
- Ribavirin;
- Simprevir;
- Sofosbuvir;
- Harvoni;
- Viekira Pak;
- Ritonavir.
Medicines of these types improve the functional state of the liver, prevent fibrotic changes in it tissues, suppress the pathogenic activity of viral microorganisms, increasing the resistance of the immune system sick. The duration of the therapeutic course with antiviral drugs is from 1 to 6 months.
Treatment with hepatoprotectors
Prescription of drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors is indicated for patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. Medicines in this category protect hepatocytes from premature destruction and death.
In this case, hepatoprotectors of the following types are used:
- Tykveol;

- Hepatosan;
- Legalon;
- Carsil;
- Liv-52;
- Hepa-Merz.
The advantage of these drugs of the hepatoprotective group is that they prevent further death of liver cells, promote their active recovery, normalize urobilin indices in the composition urine.
Antibacterial therapy
The use of antibiotic therapy is indicated for patients with high levels of urobilin caused by leptospirosis.
In this case, the following treatment methods are used:
- injection of antileptospirotic gamma globulin (it is recommended to give preference to the donor drug, and not to the equine one);
- taking antibacterial agents from the group of aminoglycosides, penicillins, or tetracyclines;
- detoxification of the body from harmful substances that are the waste product of the causative agent of leptospirosis.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the patient is shown taking hemostatic agents, as well as correcting the acid-base balance. The indicator of urobilin in urine is normalized immediately after the restoration of liver function and the formation of stable immunity to bacterial infection.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is prescribed for patients with extraneous neoplasms in the liver tissues. A cancerous or benign tumor is removed under sterile conditions in the operating unit. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
After excision of an extraneous neoplasm, a gradual restoration of the level of urobilin, functions of the liver, gallbladder and its bile ducts occurs. To consolidate a positive result, the patient is prescribed a supporting course of chemotherapeutic drugs and medicines from the cytostatic group.
Antianemic therapy
This method of treatment is used in patients with hemolytic anemia, which provokes an increase in the level of urobilin in the urine.
After eliminating the causes that cause premature death of erythrocytes, therapy is prescribed with drugs of the following pharmacological groups:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- immunosuppressants;
- means for removing excess iron in the blood (in most cases, Desferal is used).
In combination with drugs, erythrocyte transfusion is indicated for patients with hemolytic anemia. Doses and duration of injection of blood components are determined individually, depending on the results of the examination.
Lowering the level
A low level of urobilin in the urine does not require taking medications, since it is not a sign of a disease or a pathological condition of the body.
Urobilin is a bile pigment that results from the metabolic breakdown of bilirubin and urobilinogen. This substance stains the urine in a light yellow tint. The norm of urobilin in the urine of men and women of all ages is from 0 to 17 mmol / 1 L. A low level of this substance indicates a satisfactory condition of the liver, gallbladder and its ducts.
An increase in the concentration of urobilin is the first sign of an acute or chronic disease of these organs. In medical practice, there are occasional cases when an increase in urochrome in the urine is caused by hemolytic anemia. Restoration of full-fledged liver functions contributes to the normalization of urobilin parameters.
Video about urobilin
Bilirubin exchange:
