Menopause is a blow not only for the emotional health of a woman, but also for her health. In addition to internal changes, many illnesses are exacerbated or manifested. One of these diseases is the uterine myoma, which is most often found during the menopause.
Myoma of the uterus is a female disease during which uterine tumor nodes appear on the uterine tissues that are benign. The size of these knots can be only a few millimeters, but they can grow to huge sizes in tens of centimeters. Despite the fact that the disease is "younger", most often this diagnosis is heard by women in the period of premenopause, menopause and postmenopause. It is at this time that this diagnosis is made for every third woman. This disease has not been studied to the end and there is no single-valued reason for its appearance.

Uterine fibroids: signs and symptoms during menopause
material Content
- 1 Types
- 2 symptoms during menopause
- 3 reasons
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Treatment
- 5.1 Drug
- 5.2 Video - Uterine fibroids
- 5.3 Surgery
- 6 Complications
- 7 Prevention
- 7.1 Video - Fibroidsthe uterus. Symptoms and treatment with
medications Types of
There are several types of uterine fibroids, characterized by its location:
- subserous - myoma develops externally on muscle tissue. This kind is also called the subperitoneal. Gradually developing, it begins to grow into the pelvic bone, presses on the organs and causes pain;
- intramural - develops inside the muscles of the uterine tissue, enlarging the abdomen;
- submucous - develops under the mucous uterine membrane, therefore it is also called submucosa;
- intraligamentary - a tumor appears between the ligaments.
Warning! It should be remembered that myoma is not a malignant tumor, that is, it is not a cancer of the uterus.
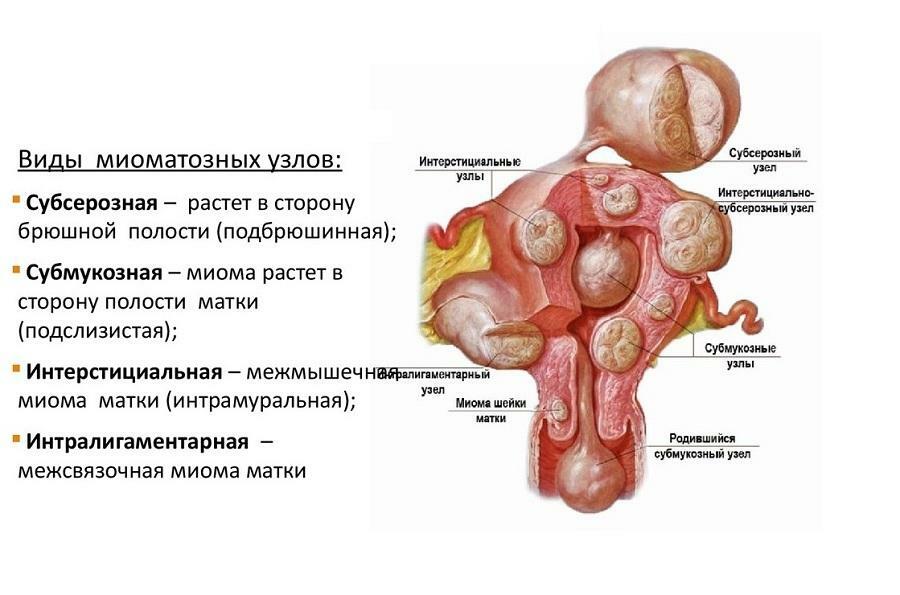
Types of myomatous nodes
Symptoms in the climax
The development of fibroids can begin in many women even before menopause. But because of the absence of signs of illness, the patients are not aware of its existence. During menopause, it begins to manifest. Most often, the diagnosis is made when the education is large and complicates.

Menorrhagia with myoma of the uterus
To the symptoms of appearing of fibroids include:
- Disorders in the menstrual cycle. Many women think that this is quite normal and is caused by an approaching menopause, but it is better to protect yourself and check with a gynecologist.
- Bloody discharge in the intervals between menstruation.
- Abundant discharge and pain during menstruation, the menstruation itself lasts longer than usual.
- Pain in the lower abdomen. Most often weak, but with cramping periods during which the pain becomes acute and severe.
- Digestive problems. There is bloating, constipation.
- The abdomen increases in size.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- In some cases, symptoms of anemia manifest due to large blood loss. They manifest weakness, fatigue, dizziness.
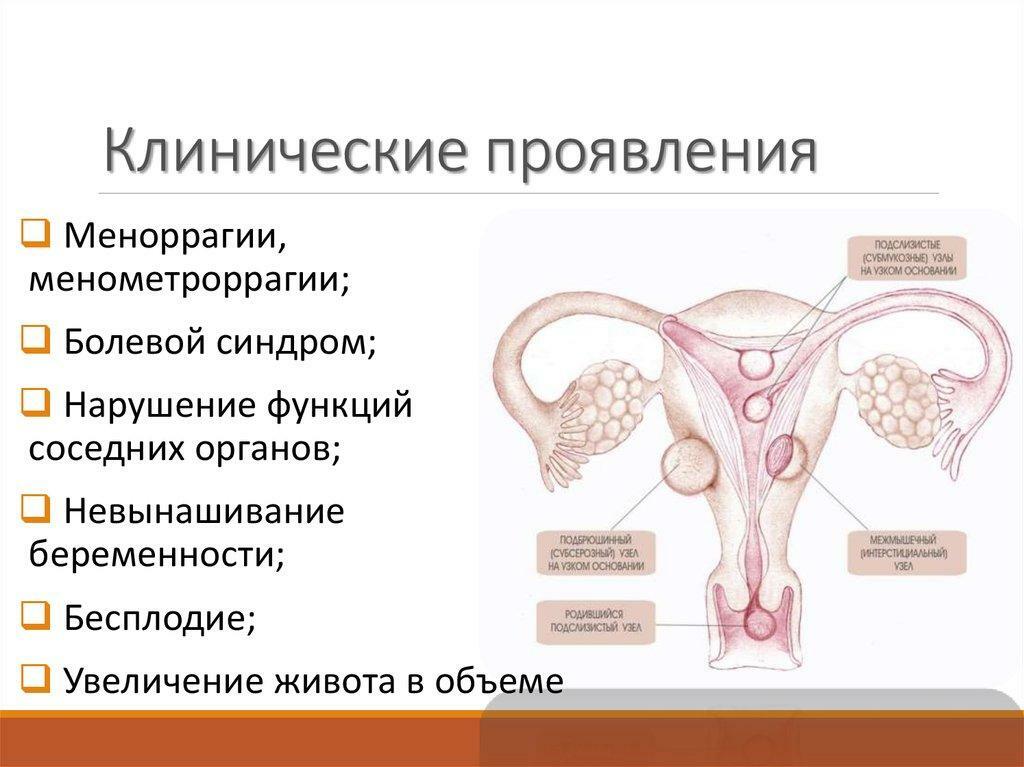
Clinical manifestations of uterine fibroids
All these signs are often taken by women during the period of premenopause, they do not attach much importance to them and do not appeal to the gynecologist. Thus seriously launching the disease.
Causes of
The period of menopause is accompanied by a serious change in the hormonal background. That is why many diseases, including myoma of the uterus, appear during this time. So, for the main reasons are:
- Change in the level of hormones. The appearance of fibroids affect the hormone estrogen, as well as progesterone, the level of which increases during menopause.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- The presence of endocrine diseases.
- Infections that are accompanied by an inflammatory process.
- Presence in the patient's anamnesis of abortions and other operations injuring the uterus.
- Avitaminosis. Insufficient intake of vitamin D in the body leads to disruption of the functions of cells and formation of fibromatous nodes on the muscular wall of the organ.
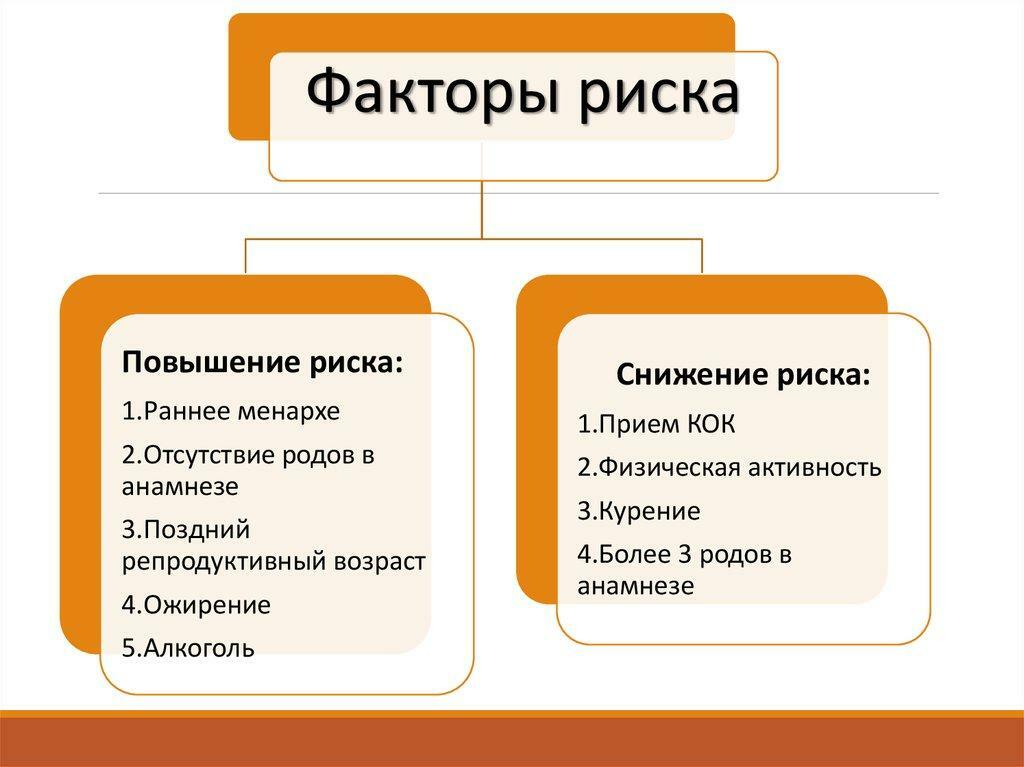
Risk factors for the appearance of uterine fibroids
Note! Often, the disease is observed in patients with diabetes and obesity.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease can be carried out in several ways. Usually a tumor-like formation is detected during a routine examination with a gynecologist. To determine the nature of education, the doctor prescribes the examination by one of the following methods:
- The ultrasound examination of is the most common and accurate way of diagnosing fibroids during menopause. With it, you can see the exact location, size, structure and even the degree of increase in the uterus itself if it is a diffuse fibroid.
- Hysterography is a research method related to the filling of the uterus with a special contrast agent in an amount of 5-7 ml. After filling, observe the changes.
- Hysteroscopy - a method of investigation using a device with a video camera. Such a survey will allow to see the uterine cavity. In addition, with the help of hysteroscopy, a biopsy should be performed, followed by a study.
- Analyzes of - take an overall blood test from a vein. There are no specific analyzes for determining uterine fibroids. But on some characteristics it is possible to specify, for example, whether there are suppurations in the uterine node.
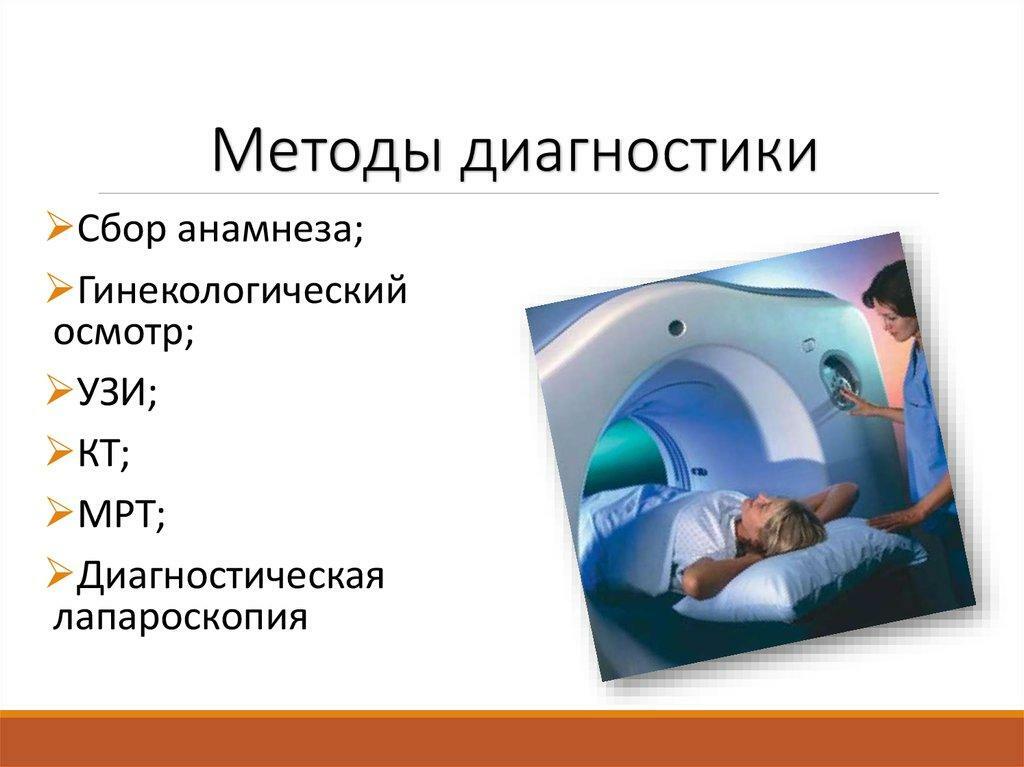
Methods for diagnosis of uterine fibroids
Treatment of
Treatment of uterine fibroids in menopause can be either medications or surgery.
Attention! Drug treatment is not an alternative to surgery, the treatment regimen is prescribed by a doctor.
Medication
Medication treatment can be used in the following cases:
- no symptoms and minor symptoms of the disease;
- slow growth of nodes;
- mild uterine enlargement;
- fibroid size less than 12 weeks;
- subserosal or intramural arrangement of nodes;
- absence of diseases of neighboring organs.

Methods of treatment of uterine fibroids
Separate hormonal as well as non-hormonal treatment of myoma by medicines.
Hormonal
Hormonal treatment is aimed at reducing the size of myomatous nodes, as well as regression of clinical symptoms. The following drugs are used for hormonal treatment.
| Type | Name | Image | Name | Admission rules | Duration of admission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonadotropin-releasing factor agonists | Triptorelin, Differelin | 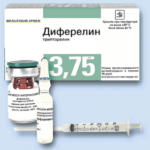 | From 3 day cycle at 3.75 mg | 6 months | |
| Goserelin | 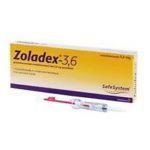 | 3.6 mg subcutaneously | 6 months | ||
| Buserelin | 200 μg nasally once a day | 6 months | |||
| Zoladex |  | Injection 1 to 5 day of the | cycle 3 months | ||
| Gonadotropin hormone antagonists | Danazol | 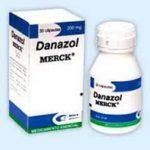 | In a day of 400-800 mg | 6 months | |
| Progesterone medicationsPoison | Norestesterone Acetate |  | From the 5th day of the cycle to 5-10 mg twice daily | 6 months | |
| Medroxyprogesterone acetate |  | Twice daily from 5 day cycle to 5-10 mg | 6 months | ||
| Primolute, Norkolut |  | From 16 to 25 day cycle | 3-6 Months |
Hormonal medications can give good results in treatment, as well as reduce the size of the tumor. However, there is no guarantee that after the cancellation of admission, it will not reach previous or larger sizes.
Non-hormonal treatment of
Non-hormonal treatment is to improve metabolism in myocytes. For this, the following groups of drugs are used: antioxidants, antiplatelet agents, vitamins. Symptomatic therapy with uterotonics, hemostatics, antispasmodics is also used. In addition, it is necessary to correct the diseases that contribute to the development of the tumor. Often, treatment with drugs is used as a preparation for the operation.
Video - Hysteromyoma
Surgical
Surgical intervention in myomas has the following indications:
- the presence of a symptomatic myoma accompanied by pain, bleeding, copious discharge, diseases of the urinary system and rectum;
- presence of fibroids, the size of which is 12 or more weeks even if there are no complaints and symptoms;
- if the tumor grows rapidly against the backdrop of menopause, this indicates its malignant nature and requires immediate operation;
- submucous myoma is required to operate regardless of size;
- necrosis of the myomatous node, nodes in an atypical site, nodes growing in the uterus from the side of the vagina;
- fibroids in combination with other diseases of the genital organs( cyst of the ovaries or uterus, polyps, prolapse of the uterus);
- no positive results from hormonal treatment.

Indications for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids
The operation can take place either with complete removal or with preservation of the uterus. To organ-saving operations carry:
- myomectomy - removal of the myomatous node;
- embolization of uterine arteries, which leads to a violation of blood supply to the node and its regression.
The radical methods include:
- supravaginal amputation;
- expiration of the uterus;
- subtotal hysterectomy.

Indications for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids. Part 2
Complications of
If you do not take into account the symptoms of the disease, you can soon face complications.
Note! During the menopause, various complications with myomas appear more often than before.
Often this is due to the fact that women take symptoms of the disease for menopause and do not rush to go to a gynecologist, believing that such symptoms are signs of menopause. Thus you can lose valuable time and earn a complication.
Among the complications are:
- bleeding;
- dying of the myomatous node - causes peritonitis, endometritis, or abscesses;
- torsion of the knot;
- maligination;
- stagnation in the urinary organs - lead to hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis.
- of the GI tract.

What the myomatous node consists of
Prevention of
In order to avoid the appearance of the disease or detect it at an early stage, you must carefully monitor your health, as well as not neglect the planned visit of doctors. You can not take lightly of the changes in the body, writing off them for the onset of menopause.
Note! All women after 45 years of age must regularly visit a gynecologist, because he will be able to notice changes, diagnose and prescribe treatment in time.
In addition, women at this age should carefully monitor blood sugar levels and their weight, because they can be one of the reasons for the appearance of the disease. When changes are worth visiting an endocrinologist, who will be able to identify the cause of metabolic disorders and help to reduce weight to normal.