Heavy speech disorders - this is a number of abnormalities that affect the child's speech ability and can provoke mental disorders during normal brain activity. Children with TNR require a special approach and complex treatment, which includes classes with a speech therapist or a speech pathologist, as well as taking medications.
Record content:
- 1 What are severe speech impairments?
- 2 Causes
-
3 Classification, signs and symptoms
- 3.1 Dysarthria
- 3.2 Dislalia
- 3.3 Dysglossia
- 3.4 Dysphemia
- 3.5 Aphasias
- 3.6 Dyslexia
- 3.7 Specific speech disorder
- 3.8 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- 3.9 Dyscalculia
- 4 Severe speech impairments and mental retardation: differences, comparative table
-
5 Characteristic of THP
- 5.1 For preschoolers
- 5.2 Schoolchildren
- 6 What causes severe speech disorders
- 7 Diagnostics
- 8 Treatment methods
- 9 Disorder therapy
- 10 How can I help my child at home?
- 11 How do you help your child at school?
- 12 Video about TNR
What are severe speech impairments?
Severe speech disorders are the presence of significant dysfunctions of the speech apparatus in a child with normal mental development. Speech defects affect the formation of the psyche of children in the process of development. Young patients have difficulty constructing sentences, have a poor vocabulary, or do not speak at all.
Despite the normal functioning of the brain, due to impaired communication with peers, a secondary mental disorder occurs. In some cases, this gives reason to consider children as intellectually deficient.
Causes
There are 2 groups of factors contributing to the occurrence of THR: endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external).
Endogenous factors include:
- the consequences of intrauterine pathology, which occurs against the background of toxicosis, transferred viral and endocrine diseases, or as a result of Rh-conflict;
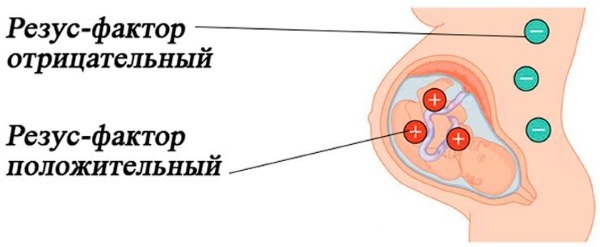
- intracranial hemorrhage resulting from fetal asphyxia during childbirth;
- transfer of infectious and viral diseases in the first year of a child's life (encephalitis, meningitis, frequent gastrointestinal disorders);
An important role in the development of TNR is assigned to the hereditary factor. At the same time, speech disorders develop in combination with disorders of the nervous system and motor activity, as well as general intellectual underdevelopment.
Exogenous factors include:
- traumatic brain injury;
- unfavorable living conditions leading to the development of psychoemotional disorders.
Classification, signs and symptoms
Severe speech disorders are specific abnormalities that have various forms, which are divided into 2 groups:
- disorders related to improper sound formation of speech (dysarthria, rhinolalia, dyslalia, bradilalia, tachyllalia, stuttering, aphonia, dysphonia);
- disorders of the structural design of speech (alalia, aphasia).
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a disorder expressed by a disorder of articulation and incorrect pronunciation of phonemes, as a result of which speech loses its ability to be segmented into its component parts. Difficulty in articulation is caused by the limited mobility of the speech organs due to their innervation.
The main symptoms of dysarthria:
- fuzzy slurred speech;
- the presence of sound distortion;
- slowdown and inexpressiveness of speech;
- rapidity and shortness of breath when trying to speak;
- skipping and replacing sounds.
External manifestations of pathology are expressed:
- the presence of a half-open mouth with the flow of saliva;
- limiting lip articulation;
- lethargy of the tongue;
Dysarthria is characterized by sufficient durability of defects and difficulty in overcoming them.
Dislalia
Dislalia is a violation of the pronunciation of sounds with normal hearing and the absence of innervation of the articulatory apparatus.
There are 2 forms of pathology:
- functional - impaired sound pronunciation, not caused by a violation of the central and peripheral nervous system;
-
mechanical - speech disorders associated with deviations in the structure of the articulatory apparatus.

Symptoms of functional dyslalia include:
- replacement of sounds and their distorted pronunciation;
- lack of ability to correctly select sounds and pronounce them correctly;
- mixing of two sounds similar in sound.
Dysglossia
Dysglossia is a form of mechanical dyslalia associated with the pathological structure of the organs of the articulatory apparatus.
Incorrect pronunciation of words and sounds is caused by:
- changes in the shape of the lips (cleft lip, wolf mouth);
- violation of the shape of the upper and lower jaw;
- clefts of the palate;
- the absence or incorrect location of the incisors;
- pathological changes in the structure of the language.
Dysphemia
Dysphemia is a speech disorder caused by psychological factors.
The main symptoms of pathology are associated with the difficulty of pronouncing individual words, namely:
- repeated multiple pronunciation of full syllables;
- repeated pronunciation of incomplete syllables;
- unnatural length of sounds;
- trouble breathing when trying to start talking.
Aphasias
Aphasia is a disorder of already formed speech, which is expressed in the loss of the ability to use it or perceive someone else's. Pathology concerns children over the age of 3 years. In patients suffering from the disorder, systemic speech disorders are manifested, covering the pronunciation of sounds, grammatical composition, the ability to perceive and understand phrases.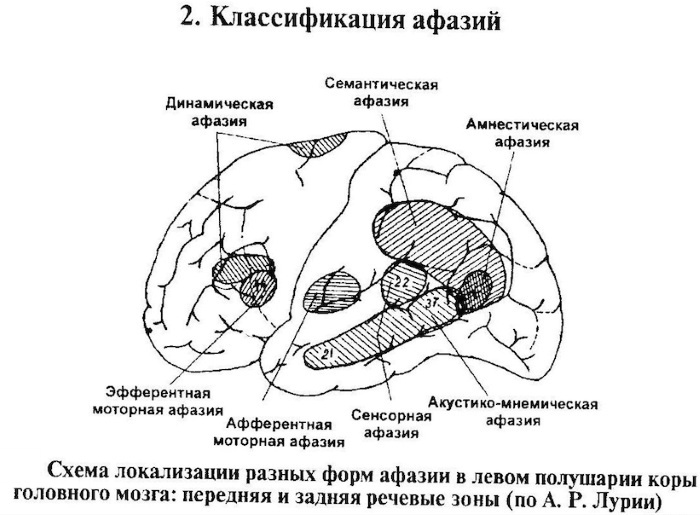
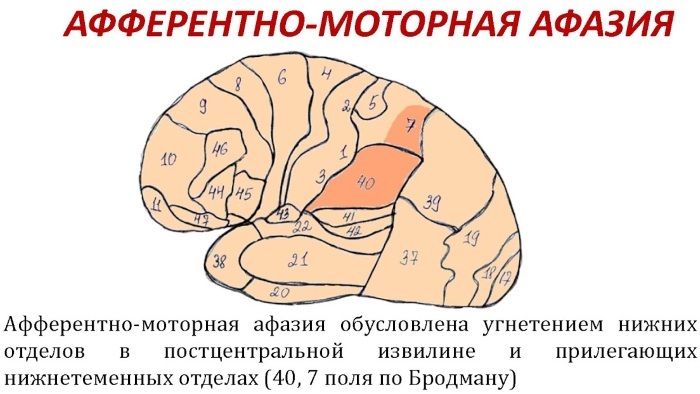
The manifestation of the symptoms of aphasia depends on its forms:
| Motor |
|
| Sensory |
|
| Acoustic-mnestic |
|
| Semantic |
|
| Dynamic |
|
Dyslexia
Dyslexia is a disorder of reading skills that is caused by the destruction of mental functions involved in the formation of the reading process.
The main symptoms of the disorder include:
- poor vocabulary;
- lack of narrative sentences in speech;
- incoherence of words in a sentence;
- replacement and mixing of similar articulatory sounds when reading;
- lack of the ability to memorize letters;
Specific speech disorder
Specific speech disorder is a form of disorder in which the child's speech skills do not correspond to the age norm.  At the same time, the child has a correctly developed articulatory apparatus, normal hearing, adequate mental development and communication skills inherent in age. Children with this disorder begin to pronounce the first words at the age of 2 years.
At the same time, the child has a correctly developed articulatory apparatus, normal hearing, adequate mental development and communication skills inherent in age. Children with this disorder begin to pronounce the first words at the age of 2 years.
The main manifestations of pathology include:
- lexical paucity of vocabulary;
- difficulty learning new words;
- the inability to perceive complex sentences;
- inability to form simple phrases;
- complete absence of own speech at the age of 3 years.
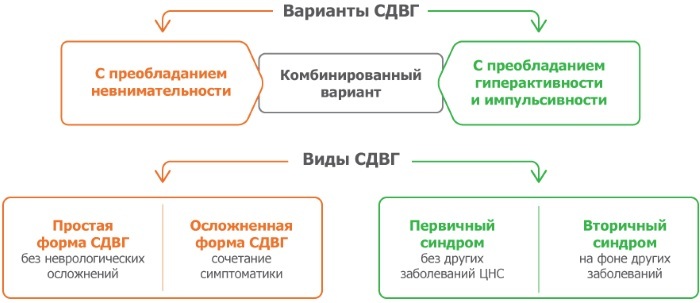
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a syndrome of increased physical and mental activity in which arousal processes prevail over inhibition processes. A hyperactive child has difficulty concentrating and perseverance, as well as processing and retaining information received from outside.
Other signs of ADHD include:
- in early childhood: sleep disturbance, increased muscle tone, frequent unreasonable bouts of vomiting, increased sensitivity to external stimuli;
- at the age of 4-7 years: inattention, forgetfulness, restless behavior, the presence of stereotyped movements in the hands and feet, impatience, haste in completing tasks, impulsivity.
Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia is a disorder in school-aged children that results in a decreased ability to learn math. Pathology is manifested by difficulties in understanding digital symbols, comparing values, performing the processes of multiplication, division and subtraction.
In the perception of such children, there is no connection between the drawn or written number, and its verbal name. Elementary school students have difficulties in recognizing mathematical symbols. At an older age, adolescents poorly master algebra, geometry and any sciences where arithmetic calculation is required.
Severe speech impairments and mental retardation: differences, comparative table
Severe speech impairment is a diagnosis that is difficult to differentiate from general mental retardation, since the connection between speech and intelligence is inextricable. Mental underdevelopment in most cases is accompanied by problems with speech, and, conversely, with complex speech disorders in a child, an uneven or insufficient development of intelligence is observed.
Below is a table that allows you to distinguish THP from general mental retardation:
| TNR | Mental retardation | |
| The mechanism of speech disorders | Difficulty with tasks that require direct participation of speech, the manifestation of interest and ingenuity when performing tasks for logical thinking. | Difficulty in all types of intellectual tasks, impaired verbal and logical thinking. |
| Pre-speech development | Pre-speech development corresponds to age norms. | There is a delay in humming and babbling in infancy. |
| Learning Degree | High | Low |
| Establishing causal relationships | The child's understanding of the speech addressed to him, the perception of complex sentences. Children with TNR try to express causal relationships using the methods available to them - intonation, kinetic speech, sound gestures. | Many complex speech structures are difficult to understand. |
Characteristic of THP
Severe speech disorders are a group of deviations that are conventionally divided into levels, each of which has a specific set of violations:
-
Level I. Children have limited speech means of communication. A child's active vocabulary consists of an insignificant amount of indistinctly pronounced words and onomatopoeia. As a means of communication, children choose facial expressions and gestures.

Severe speech disorders - Level II. It is characterized by increased speaking activity. Children communicate using a limited number of commonly used distorted words. Difficulties are observed in building correct grammatical constructions. The phonetic side is expressed by numerous sound substitutions and displacements.
- III level. The presence of detailed phrasal speech with grammatical and phonemic underdevelopment is characteristic.
For preschoolers
In preschool children with TNR, there is a general impairment of attention and memory. Children often forget complex speech structures and change words.
They are characterized by a limited development of cognitive activity and the emergence of difficulties with the description of objects and actions. Such children have a reduced need for communication due to unformed dialogical and monologic speech. In addition, motor activity and fine motor skills of the hands are impaired in children with TNR.
Schoolchildren
Schoolchildren with TNR perceive educational information in slow motion. They have a reduced performance and have difficulty establishing a connection between visual, auditory and speech analyzers.
Students find it difficult to navigate in space and lack the ability to organize voluntary activities. Problems with oral speech impede the full assimilation of the material of the Russian language program, which leads to difficulties in the process of mastering writing. Difficulties in learning provoke a weakening of motivation to overcome the speech barrier.
What causes severe speech disorders
A speech disorder that has not undergone timely correction can lead to a number of consequences that will affect not only the work of the articulatory apparatus, but also the psyche of the child.
THP in children results in:
- to mental retardation;
- to severe mental trauma of a child associated with a violation of communication;
- to difficulties in mastering new information in the process of teaching at school;
- to the development of secondary disorders: dysgraphia and dyslexia.
Diagnostics
A speech therapist is involved in the diagnosis of severe speech impairment in children. At the first examination, the doctor gets acquainted with the medical documentation, which contains information about the presence of concomitant pathologies. The TNR examination begins with the clarification of the child's speech characteristics.
The speech therapist shows the child images of various objects on which the little patient must compose a story. Then the speech therapist assesses the correctness of word formation and inflection, the ability to correctly coordinate parts of speech and construct sentences.
The main tasks of diagnostics include:
- identification of deviations in oral and written speech;
- determination of the type of speech defects;
- final diagnosis;
- development of an individual correction program.
Treatment methods
Severe speech disorders are a list of disorders that require an integrated approach to treatment: taking medications, physiotherapy, classes with a speech therapist and a speech pathologist. Drug therapy is used in cases where the development of THR is caused by disorders in the functioning of the brain and central nervous system.
For the treatment of speech disorders, nootropics are used - substances that have a positive effect on integrative brain functions. The action of nootropics is aimed at improving mental performance, stimulating cognitive function and improving memory.
Nootropic drugs are divided into several groups:
- neurotransmitters GAM (Pantogam);
- products containing penitinol (Encephabol);
- psychostimulating nootropic (Ceraxon);
- multivitamins (Gliatinin);
- amino acid-based preparations (Glycine, Cogitum)
Among other, most prescribed nootropics are prescribed
- Phenibut;
- Semax;
- Cerebrolysin;

- Cortexin;
- Cerepro.
As part of the THR complex therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed that allow:
- stimulate speech development;
- correct the muscle tone of the speech apparatus;
- normalize speech breathing;
- improve blood circulation.
Among the methods of physiotherapy are:
- magnetotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- darsonval;
- amplipulse.
Exercise therapy and massage are used as additional methods.
Disorder therapy
Therapies for THP depend on the nature of the abnormalities. For the treatment of stuttering, a comfortable and calm environment is created for the child, in which they give the opportunity to speak out loudly and slowly, without constant remarks and haste.
If a child has alalia, the work of a speech therapist is aimed at accumulating a vocabulary, understanding phrases and speech structures, as well as the correct grammatical structure of speech.
Dysarthria therapy consists of taking medication, working with a speech therapist and physiotherapy procedures. Speech therapy classes involve the development of fine motor skills of the hands with the help of finger gymnastics. The development of the speech apparatus is carried out by articulatory and respiratory gymnastics.
In the treatment of aphasia, the key role is assigned to the elimination of the disease that caused the development of the pathology. Complex therapy consists of taking medications, massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy, as well as working with a speech therapist. Speech therapy classes are aimed at restoring the ability to correctly pronounce words and understand speech.
With dyslexia, the work of a speech therapist is aimed at:
- development of full-fledged phonemic processes;
- enrichment of vocabulary;
- assimilation of grammatical norms.
Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder require an integrated approach with the use of psychological and pedagogical correction, drug therapy and psychotherapy. The hyperactive child is shown learning in classes with a minimum number of students, good sleep and limited attendance at public events.
How can I help my child at home?
Severe speech disorders are disorders for the treatment of which not only qualified help is needed, but the diligence of parents. Additional home activities can help speed up the healing process. The intensity of the classes will depend on the degree of the existing violations.
Basic methods of working at home:
- finger gymnastics;
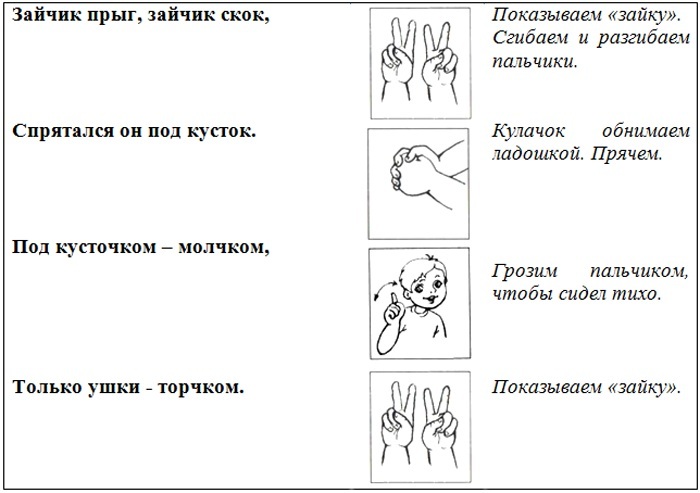
- development of an articulatory apparatus in front of a mirror: protruding the tongue, folding it into a tube, trying to reach the tip of the nose with the tongue;
- maintaining a constant dialogue with the child, reading books and singing;
- performing exercises in several approaches, with a change in activity;
- use of visual material during classes: cards, posters, audio and video recordings;
- the use of small items for the development of hand motility: modeling from plasticine, folding mosaics, gluing small paper parts;
- creative activities using finger paints;
- repetition of the passed material.
In order for the child to be maximally interested in the classes, traditional methods of motivation should be used - praise and encouragement.
How do you help your child at school?
Severe speech disorders are a pathology in which the child needs to create special learning conditions. To this end, special schools are opened for children suffering from TNR, designed to correct speech disorders. These institutions are attended by children, for whom pathology becomes an obstacle to communication and learning in a comprehensive school.
Schools for children with TNR set themselves the following tasks:
- overcome violations of oral and written speech;
- create the most comfortable conditions for learning;
- eliminate the peculiarities of mental development associated with THR;
- provide vocational training.
Specialized schools consist of 2 departments. The first department admits children with severe disabilities that impede learning in a regular school. The second department trains children with severe forms of stuttering. Classes consist of 12 people. An important place in the learning process is given to work and the correction of speech and writing disorders.
Severe speech disorders in children significantly complicate the process of learning about the world and assimilating new information. This is due to the fact that speech disorders affect not only the articulatory apparatus, but also the formation of the child's psyche.
A favorable prognosis for pathology depends on the degree of neglect of speech disorders and the intensity of training. Identification of disorders at the age of 2-4 years allows you to completely restore full-fledged speech without consequences.
Video about TNR
Speech therapist work with children with TNR: