Dysarthria - this is a violation of the pronunciation side of speechcaused by impaired coordination of muscle groups responsible for speech. The disorder is one of the important problems of speech therapy and social psychology.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about dysarthria
Views
Dysarthria is all forms of impairment of sound speech from blurred speech shade to nasal slurred pronunciation.
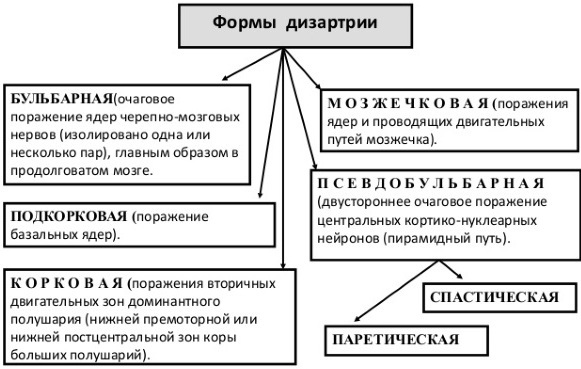
The classification of dysarthria is based on the localization of brain damage:
- Bulbar dysarthria. The disorder occurs with inflammatory diseases or the development of a tumor in the posterior part of the brain. It is characterized by a decrease in the strength of the muscles of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate. At the same time, the muscles of the vocal cords are weakened, and it is difficult for a person to hear voiced sounds. Rhinolalia, nasal nasal develops, since the movement of air through the nose is inaccessible.
- Pseudobulbar. This form is typical for children who have suffered a birth trauma at birth. Signs of a pseudobulbar form: impaired general and verbal motor skills, articulation, manifestation of a hoarse, weak, nasal voice.
- Cerebellar. A rare form caused by damage to the cerebellum. This species is characterized by slow, nasal speech, accompanied by loud cries of individual sounds.
- Subcortical. This type of speech disorder is caused by damage to the basal subcortical nuclei of the brain. The pronunciation of individual sounds is preserved, but there is no fluidity of speech, a decrease in physical and phonemic hearing, an increase in the muscle tone of the neck and shoulder girdle are expressed.
-
Cork. The disorder is caused by a lesion in a group of nuclei in the gray matter of the brain. In this case, the sound-syllable structure of the word is violated. Isolated sounds are pronounced clearly, but in combination with each other, at the moment of switching from one sound to another, there is a hitch, distortion of sounds or their replacement. Disturbances in the pronunciation of consonants are especially noticeable. Often, speech resembles a stutter.
Dysarthria (in speech therapy - this is a violation of pronunciation) can affect both adults and children.
Internal causes of the development of dysarthria can be:
- brain injury;
- cerebral paralysis;
- tumor process;
- muscular dystrophy;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- Lyme disease, Huntington;
- myasthenia gravis.
Stages and degrees
On the basis of a complex of interrelated signs, a number of stage forms of dysarthria are distinguished:
- Atactic dysarthria. Usually occurs as a result of strokes or degenerative diseases. It develops against the background of pseudobulbar paralysis, bilateral cerebral infarction. The patient may have classic symptoms similar to those of drunkenness: slurred speech, sudden increase in volume, general lack of coordination.
- Flaccid dysarthria. It develops as a result of strokes, congenital disorders, ALS, cerebral palsy, tumors, MNS, or other brain injuries. It is manifested by low muscle tone of the speech apparatus, hoarse nasal speech. Other signs: drooping jaw, difficulty swallowing.
-
Hyperkinetic dysarthria. Is a consequence of Huntington's disease or hyperkinetic cerebral palsy,

The disorder causes tremors, dyskinesia, athetosis, and dystonia. The sounding of the voice is characterized as harsh, this is often due to a spasm of the laryngeal muscles.
- Hypokinetic dysarthria. Observed in Parkinson's disease, it is characterized by a hoarse, quiet speech or a decrease in the volume of the voice. Speech can be monotonous, slow, and the onset of speech is difficult, resulting in prolonged inappropriate silence, which is mixed with short bursts of speech. This form of dysarthria is often associated with cognitive impairment, sometimes affecting treatment.
- Mixed. This form of dysarthria occurs in patients with multiple sclerosis, a severe traumatic brain injury. Patients can speak very slowly and with great effort. Articulation is markedly impaired, and the sound of the voice is low, strained or suffocated. Difficulty swallowing, salivation is observed.
Dysarthria in children is usually congenital, while in adults it is often acquired.
Pseudobulbar dysarthria has 3 degrees of severity, which depend on the degree of impairment of speech and articulatory motility:
- Lightweight. Defects occur from insufficient mobility of the tongue and lips. The main defect is impaired phonetics of speech. Mental and physical development in this case corresponds to the norm, hearing has no defects. The acts of chewing and swallowing are not pronounced.
- Average degree. At this stage, the movement of the facial muscles is disrupted, the mobility of the tongue is limited. A severe defect in pronunciation is clearly expressed, speech is slurred, which limits communication and affects overall development.
- Severe degree. It is characterized by deep muscle damage, inactivity of the speech apparatus. The lack of normal speech leaves an imprint on the face: the lower jaw sags, the mouth is constantly open. Chewing and swallowing are difficult. Sounds are perceived incorrectly due to impaired motor skills, so there is no speech or only isolated inarticulate sounds are reproduced. With a severe degree of impairment, only close relatives can understand speech.
Symptoms
Dysarthria (in speech therapy, this is primarily a focus on improving speech) has a number of signs that differ depending on the underlying cause and type of disorder:
- Slurred speech.
- Slow speech.
- Inability to raise your voice or speak louder than a whisper.
- Fast, hard to understand speech.
- Nasal, raspy, or strained voice.
- Irregular or abnormal speech rhythm.
- Uneven speech volume.
- Monotonous speech.
- Stiffness of tongue and facial muscles.

The risk of developing dysarthria increases with symptoms:
- high likelihood of developing a stroke;
- degenerative brain disease;
- neuromuscular disorder;
- alcohol or drug abuse.
Reasons for the appearance
The muscles used to make sounds are controlled by the brain and nervous system. The development of dysarthria is associated with disorders occurring in one of these areas.
Types of disorders occurring in the central nervous system, brain that affect the development of dysarthria:
- stroke;
- intracranial tumor;
- traumatic brain injury;
- cerebral paralysis;
- Bell's palsy;
- multiple sclerosis;
- muscular dystrophy;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- Huntington's disease;
- myasthenia gravis;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Wilson's disease;
- trauma to the tongue;
- infectious sore throat;
- drugs or tranquilizers that have affected the central nervous system.
Acquired injuries causing dysarthria:
- brain damage during childbirth, for example, with cerebral palsy;
- surgery on the head, neck, tongue, vocal cords;
- trauma to the face or mouth.

Brain and CNS structures that contribute to the onset of the disorder:
- Cerebral hemispheres that control muscle movement.
- The cerebellum, which coordinates body movements.
- Basal ganglia. Nerve cell structures help coordinate and smooth movement.
- Brain stem. Controls the muscles that are used for breathing and those that help make sounds.
- Nerve fibers. These structures connect the outermost layer of the brain, the cortex, to the brain stem. These nerve fibers carry the information needed to control and coordinate the muscles used to make speech, including the muscles of the lips, tongue, palate, and vocal cords.
- The neuromuscular junction. These are nerves that connect to muscles at the neuromuscular junction.
Diagnostics
Dysarthria is diagnosed on the basis of symptoms, physical examination, tests, diagnostic studies. In the presence of a disorder that is not accompanied by internal diseases, the doctor refers the patient to a neuropathologist, speech therapist.
Experts use tests to assess the severity of dysarthria. In this case, the mobility of the muscles of the tongue, lips, face, aspects of sound quality and breathing are assessed.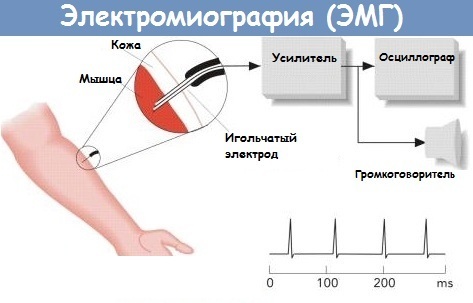
What examinations and tests a doctor needs to make a diagnosis:
| Study | Why is it carried out | Price |
| Oropharyngeal dysphagia disorder | Swallowing function study | From 1 thousand rub. |
| Electromyography | A nerve conduction study to measure the strength and speed at which nerves send electrical signals. | It is 600 rubles. |
| Study of the composition of cerebrospinal fluid using lumbar puncture | This is done to check for infections, central nervous system disorders, or brain cancer. | From 3 thousand rub. |
| Neuropsychological tests | Conducted to measure cognitive skills, ability to understand speech, reading and writing. | From 1 andys. 500 rubles. for each test |
| MRI | For a detailed image: brain |
|
| From 2 thousand rub. | ||
| neck | From 1 thousand rub. | |
| CT scan | brain | From 900 rub. |
| Neck. | From 900 rub. | |
| Electroencephalogram | To obtain a detailed image of the brain, head and neck to measure the electrical activity of the brain. | From 3090 rub. |
At the meeting, the speech therapist will ask you to do some simple exercises, observe the person performing the tasks. This will help the practitioner assess the strength and movement of the muscles involved in speech, detect problems such as shortness of breath, speech quality.
Standardized neuropsychological tests are performed by a neuropsychologist or speech therapist to help doctors plan treatment and determine the likelihood of recovery.
When to see a doctor
Dysarthria can be a sign of a serious medical condition. You should see your doctor if there are sudden or unexplained changes in your ability to speak. Different forms of dysarthria require the participation of different doctors. This is a therapist, neurologist, psychotherapist, speech therapist.
Prophylaxis
Dysarthria (which is a common disorder in speech therapy) can be caused by numerous diseases, so it is difficult to prevent it, but the risk of developing it can be reduced.
A healthy lifestyle should be followed, especially to prevent the risk of developing a stroke, after which dysarthria often appears:
- Exercise regularly.
- Keep your weight at a healthy level.
- Increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet.
- Limit cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt in your diet.
- Reduce alcohol consumption.
- Avoid active and passive smoking.
- Do not use medications on your own that are not prescribed by your doctor.
- If high blood pressure is diagnosed, take steps to control it.
- For diabetes, follow your doctor's recommendations.
- If you have obstructive sleep apnea, seek medical attention.

Tips for family members with a patient with dysarthria:
- A person with dysarthria should be given more time to express their thoughts.
- Do not finish sentences for him or correct mistakes.
- You should look your interlocutor in the face when he speaks.
- Remove distractions and background noises while talking
- If you have problems understanding his speech, you should tell the person about it so that he can repeat it.
- Have a paper, pencil, or pen handy to write words that are difficult to understand or the other person is difficult to pronounce.
- Help a person with dysarthria create a book of words, pictures and photographs that can be used later in a conversation.
- Involve him in conversations as often as possible.
Communication should be normal, because many people with dysarthria understand others without difficulty. There is no need to slow down speech or speak loudly when talking to someone with dysarthria.
Treatment methods
Dysarthria is an addictive disorder, it develops under the influence of disorders occurring in the central nervous system. Comprehensive treatment is prescribed, taking into account all the side symptoms.
Depending on the degree of dysarthria, the following methods are used:
- medicinal;
- speech therapy correction;
- physiotherapy.
If the dysarthria is caused by a tumor or damage to the brain or spinal cord, your doctor will recommend surgery.
A speech therapist will help improve communication skills by developing an individual plan that includes the general goals of treatment in speech and language therapy:
- development of the correct tempo of speech:
- strengthening muscles;
- increased movement of the mouth, tongue and lips;
- improving articulation to develop clarity of speech;
- family strategy training for better communication with a person suffering from dysarthria;
- exploring alternative methods of communication (for example, simple gestures, alphabet boards, or electronic or computer equipment).
For severe dysarthria, therapists recommend using a board for letters, pictures, or a computer device with a keyboard and display for messages. In dysarthria, the medical goal is not to repair the damaged part of the brain, but to find compensatory ways of communicating.
Here are some ways you can do this:
- Teaching the patient to speak more slowly so that the brain gets used to a certain speed of communication.
- Teach the patient to choose alternative words and develop monosyllabic speech.
- Encourage the patient to write expressions when they are not understood by others.
- Creation of personalized communication signals for the patient and his relatives.
Medications
Doctors prescribe drugs that remove the symptoms of the underlying disease, alleviate the general condition of a person. Medication therapy is prescribed by a neuropsychiatric doctor to improve the nutrition of the tissues of the nervous system.
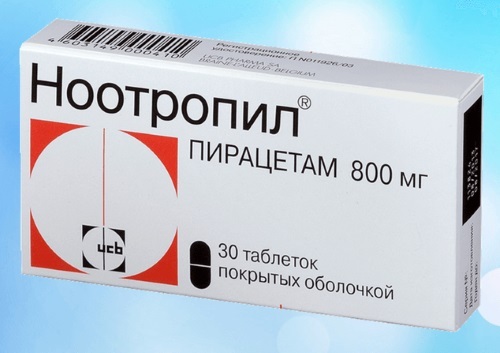
| Group of drugs | Name | Indications | Price |
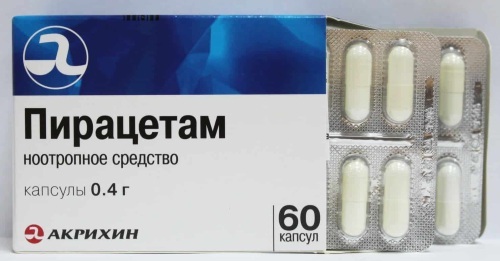
| Brain Nourishing Drugs | Nootropil | Psychoorganic syndrome, conduct disorder, dyslexia. | RUB 200 |
| Phenibut | Alarming mental, obsessive states, neuroses. | RUB 100 | |
| Piracetam | Symptomatic treatment of psychoorganic syndrome, dyslexia. | RUB 50 | |
| To relieve hypertonicity | Persen | Increased excitability, insomnia, irritability. | RUB 250 |
| Tenoten | Psychosomatic diseases, neurotic, CNS lesions. | RUB 400 |
To maintain general well-being, vitamin B preparations are prescribed as an additional source of magnesium. Magnesium B6 relieves muscle pain, eliminates dysfunctions of the nervous system, restores sleep.
Traditional methods
Dysarthria in speech therapy is a disorder in which the efforts of a doctor, relatives and a patient must join forces to correct and restore speech.
For anyone who has had a stroke, head injury, or other medical condition that affects speech, the road to recovery is long and difficult. Rehabilitation can begin in a hospital setting and move to outpatient and home speech recovery.
The best way to overcome dysarthria is to retrain your muscles by strengthening them.
Below are some simple muscle building and strengthening exercises that you can do at home.
A complex of articulatory and vocal exercises is carried out, consisting of:
- coughing;
- pronouncing vowel sounds;
- imitation of gargling;
- imitation of swallowing.
A set of exercises aimed at stimulating the mobility of the soft palate, muscles of the posterior and lateral walls of the pharynx:
- yelling with simultaneous pronunciation of vowels;
- coughing with exhalation and vowel pronunciation;
- imitation of gargling;
- pronouncing the sound combinations "mm... mm... mm" with a single impulse.
Exercise should alternate with a massage to relax the facial muscles:
- stroking from the middle of the forehead to the temples;
- stroking the eyebrows, from the bridge of the nose to the hair;
- light smoothing of the forehead line extending down to the chin and neck;
- light pinching of the edge of the lower jaw.
Exercises for lip mobility:
- collecting lips in a tube;
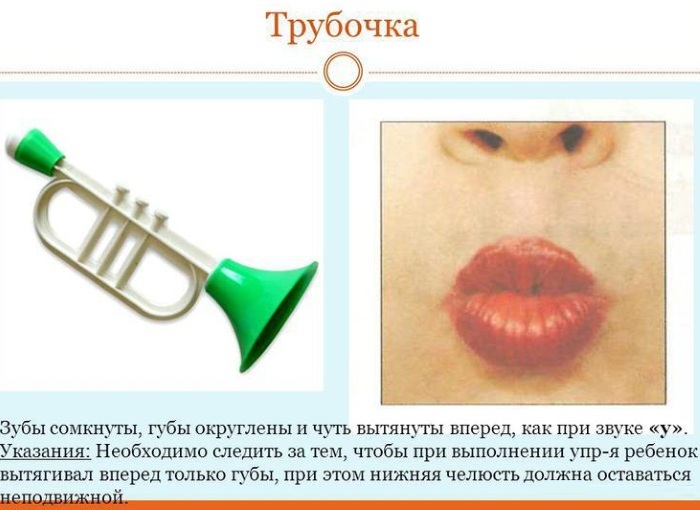
- stretching into a smile;
- lowering of the lower lip;
- extension of the upper lip up.
Exercises for the tongue:
- pulling back;
- removal from the mouth forward;
- raising to the upper lip;
- lowering to the bottom;
- smooth movements to the sides.
After several sessions, the muscles, the musculature begin to smooth out, become soft, pliable.
Other methods
Additional methods of therapy play an important role in the restoration of speech:
- Speech therapy massage. Special exercises, smoothing, kneading muscles, help restore facial nerves, raise their tone and eliminate lethargy. Massage can be carried out using special dysarthric probes, which have a point effect on biologically active points of the cervical collar and facial zones.
- Breathing exercises. In this case, techniques are used that contribute to the formation of correct breathing in children with pseudobulbar dysarthria.
Possible complications
Complications arising from the disorder are communicative in nature:
- Social difficulties. Communication problems can affect relationships with family and friends and complicate social situations.
-
Depression. In some people, dysarthria can lead to social isolation and depression.

Some of the symptoms that caused the speech disorder remain stable, while others may worsen over time, which will aggravate the speech situation.
There is no guarantee that speech and language therapy can improve the speech of a person with dysarthria. Whether treatment is successful depends on the extent and location of the brain damage or dysfunction. personal circumstances of the person, correct speech therapy, joint efforts of the doctor and relatives.
Video about dysarthria
The structure of the defect in dysarthria: