Hare lip - congenital malformation, in which the newborn suffers from partial or complete underdevelopment of the upper lip. According to statistics, about 700 babies with congenital clefts of the face are born in the world every day. Pathology is formed in utero between 4 and 12 weeks of pregnancy.
The disease is characterized not only by local anatomical changes, but by concomitant systemic disorders. Children with cleft lip cannot breathe, swallow, eat, or speak normally.
Record content:
- 1 Symptoms, signs of pathology
-
2 Causes of occurrence
- 2.1 Exogenous
- 2.2 Endogenous
- 3 Specialists to contact
- 4 Diagnostics
-
5 Initial treatment and care
- 5.1 Feeding features
- 5.2 Care features
- 6 Surgical intervention
- 7 Possible consequences and complications
- 8 Cleft lip video
Symptoms, signs of pathology
The cleft lip is determined immediately after birth by external examination. The main sign of pathology in a newborn is a defect of the upper lip, which extends from the edge along the entire height and captures the lower region of the nasal passage.
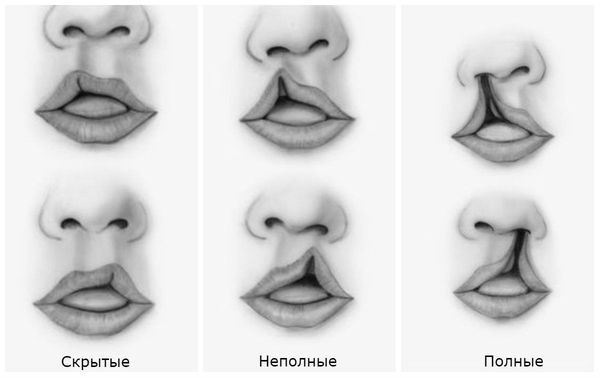
Different degrees of damage are characterized by a set of specific signs:
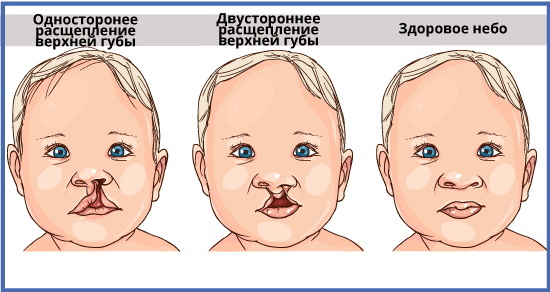
| Partial splitting | Complete cleavage |
|
|
Causes of occurrence
The cleft lip in a newborn develops under the influence of gene interventions caused by endogenous and exogenous causes.
If we consider the causes of the development of pathology in utero, we can distinguish 3 theories of the occurrence of a cleft in the fetus:
- The theory of fusion of shoots. The development of the disease is associated with non-union of the facial processes during the period of intrauterine development.
- Theory of germination of the mesoderm. According to the theory, the cause of the pathology is insufficient germination of the mesoderm, which is involved in the formation of the circular muscle of the face. As a result, the rapid growth of the embryo leads to rupture of the thin membrane, which entails the formation of a through or incomplete cleft. The formation of pathology occurs at the 7th week of pregnancy.
- Combined theories. Both processes become the cause of congenital malformation - both the non-union of the facial processes and the insufficient germination of the mesoderm.
Exogenous
External reasons affecting the development of pathology include:
- the influence of environmental factors on the fetus - radiation, taking medications, drugs, poisoning with household chemicals;
- vitamin deficiency of varying severity;
- the impact of staphylococcal infection, viral diseases;
- severe trauma of a mental nature to the mother during pregnancy;
- abdominal trauma.
Endogenous
Internal factors include:
- hereditary factors;
- infectious diseases carried by the mother during pregnancy;
- exposure to toxic factors in early pregnancy;
- late pregnancy in women over 40.
Specialists to contact
A cleft lip in a newborn requires an integrated approach to treatment.
From birth, a number of specialists monitor the child's condition, each of which performs its own functions:
- Pediatrician organizes medical supervision and monitors the physical indicators of the child. The specialist plans the main ways to improve the child's health and monitors the prevention of other diseases - rickets, anemia, infectious diseases. Provides rehabilitation measures after operations.
- Dentist surgeon. The doctor performs defect elimination operations, provides surgical correction of secondary defects. The specialist constantly contacts with the parents of an infant suffering from pathology, and also monitors the dynamics of recovery and the effectiveness of measures taken.
- Orthodontist. Provides the baby with the conditions for proper feeding. Prevents and treats secondary pathologies associated with the dentition, and also deals with the restoration of the dentition.
- Lor. Is engaged in conservative or surgical treatment of concomitant diseases of the ENT organs, controls hearing. Also, the doctor ensures the timely conduct of planned operations.
From the moment milk teeth appear, the child visits a dental therapist. The specialist is engaged in the planned rehabilitation of the oral cavity, as well as dental treatment in the preoperative periods.
During the period of speech formation (1-2 years, 4-5 years), the child visits a speech therapist. The doctor works on the development of the speech apparatus, speech breathing, phonemic hearing. Promotes the formation of colloquial speech.
From the first month of life until the moment of deregistration, the rehabilitation of the child is carried out by the exercise therapy doctor, who develops treatment programs according to the condition of the little patient. The specialist takes into account the degree of lag in physical and mental development and carries out exercise therapy with the use of special techniques and physical exercises.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out when examining the child after birth. In addition to external signs of the disease, a child with a cleft lip may suffer from other concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
Therefore, instrumental research methods are used to diagnose pathologies:
- ECG. A diagnostic method based on the registration and study of electrical impulses that are formed during the contraction of the heart. Special sensors are connected to the child's body, recording electrical impulses and recording the received data on paper. For the ECG of a child, smaller sensors are used, which are fixed in the chest, wrists and knees. The procedure takes about 5 minutes. The cost of an ECG with decoding is 400-500 rubles.
- EEG. A method for studying the functional state of the brain substance, which allows us to identify abnormalities in the central nervous system of a child, as well as to determine the level of his psychoemotional development. EEG in children is carried out in a state of sleep, wakefulness or anesthesia. The technique of the procedure consists in putting on a special helmet on the head, to which electrodes connected to the device are attached. The duration of the diagnosis is about 15 minutes. Price - from 2000 rubles.
- CT scan of the brain. The method gives a layer-by-layer, detailed image of the examined organ. Scanning is carried out using X-rays that penetrate the thickness of the area being viewed. The study for children under 1 year old is carried out under medication sleep, which allows the child to be completely immobile. During the scan, the baby lies on the table of the tomograph, and the doctor watches him through the opening in the booth. The CT scan lasts 7-10 minutes. Cost - 4000-5000 rubles.
-
MRI of the brain allows you to study the state of the organ and teach a clear picture of all its structures. The method is not associated with exposure to ionizing radiation and the introduction of radioactive substances. During the examination, the child is placed in a tomograph tunnel, 70-80 cm wide. If necessary, use medication sleep. The duration of the examination is about 20 minutes. Cost - from 6000 rubles.
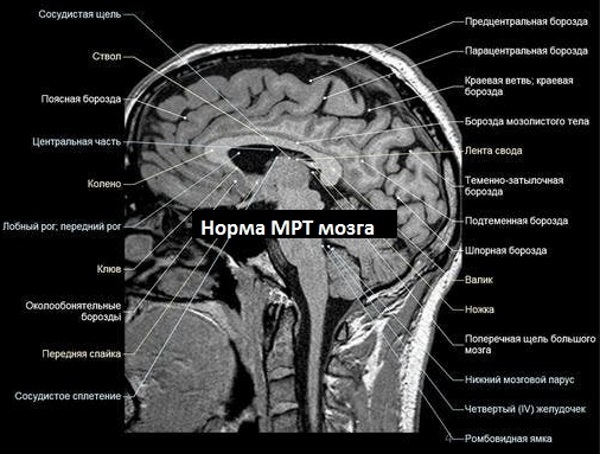
MRI of the head. What shows is normal
Also, the diagnosis of pathology is possible even during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. The accuracy of the diagnosis will depend on the capacity of the technical equipment. Prenatal diagnosis of maxillofacial anomalies is possible at 16 weeks.
A cleft is diagnosed when the integrity of the lip is lost on one or both sides in the coronary view. When using color Doppler, you can track the flow of amniotic fluid, which normally passes through the nasal passage when breathing, and through the palate in the presence of a cleft.
Initial treatment and care
The hare lip in a newborn requires a special approach to care and feeding. In the first days and months of life, it is important to provide the child with all the conditions for normal weight gain, as well as to prevent the development of ear infections and aspiration, which babies with a cleft lip are prone to.
Feeding features
How babies with a cleft lip are fed depends on the severity of the anatomical disorder.
With a partial lip cleft, breastfeeding is considered a priority feeding method. It is easier for children with disabilities to master breastfeeding, since the breast tissue is capable of to cover the birth defect better than special nipples designed for feeding babies with hare lip.
With a full or through cleft, the child is not able to suckle on his own without assistance and special devices. To facilitate feeding, special abturators made of medical oilcloth are used.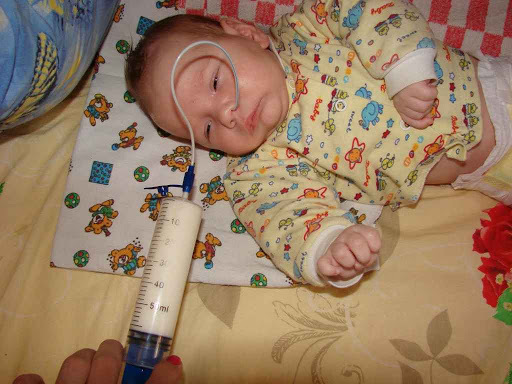
When feeding a baby, it is important to remember that loose communication between the mouth and nasal cavity can cause aspiration.
To prevent this from happening, you must:
- position the baby in a semi-vertical position;
- control air access through the nose;
- after feeding, hold the baby in a column until belching comes out;
- in a supine position, turn the baby's head to one side.
The entire feeding process should take about 15-30 minutes, otherwise there is a risk that the baby will become excessively tired, lose energy and weight.
If breastfeeding is not possible, babies with a cleft lip are formula-fed using specially adapted nipples. They are elongated to cover a crevice as well as several holes. In addition, special syringes, drinking cups, and spoons are used.
Care features
A baby with a cleft lip needs to thoroughly clean the nasal passage with cotton sticks and sterile vegetable oil - sea buckthorn, olive, as well as a decoction of chamomile or calendula.
Due to the cleft in the lip area, part of the oral mucosa remains in constant contact with air. This causes the formation of cracks and crusts on the mucous membrane of the upper lip. You should carefully cleanse the upper lip area from the formed crusts, pre-soaking them with sterile oil.
Surgical intervention
Treatment of pathology with surgical intervention is carried out at the age of 4-6 months. The operation to eliminate pathology is called cheiloplasty, the purpose of which is restoration of the correct anatomical shape of the upper lip and nose for further elimination cosmetic defect.
The main tasks of cheiloplasty:
- suturing the cleft of the upper lip;
- lengthening the upper lip and creating the desired shape of the red border;
- elimination of deformation of the nose and restoration of the bottom of the nasal passage.
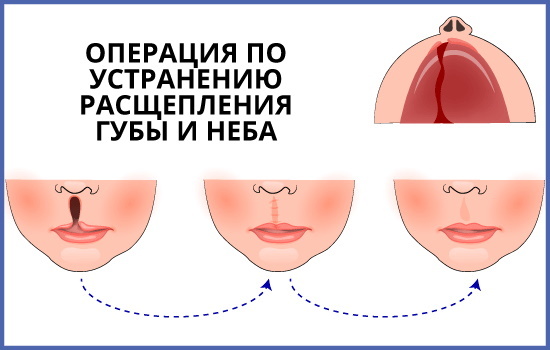
Primary cheiloplasty is performed using several methods, depending on the nature of the cleft:
| Cheiloplasty according to Miro | According to Evdokimov | According to Limberg |
| During the operation, the edges of the cleft are refreshed. For this, an incision is made through the entire thickness of the tissues of both fragments of the upper lip, as a result of which 2 flaps of the red border are formed. The flap on the larger fragment is cut obliquely, and a flap is sewn in its place from the opposite side. |
During the operation, one flap is formed on the medial fragment of the lip, and then work with the red border takes place. On the right and left side of the lip, from the level of the canines, an incision is made towards the cleft. Using a smaller flap, the base of the nasal passage is reconstructed. Lip suturing occurs in layers. | The operation provides for the simultaneous restoration of the lip and elimination of the deformation of the base of the nasal passage. |
Postoperative sutures are treated with an antiseptic, then a sterile bandage is applied to the wound. The stitches are removed for 7-10 days.
During the rehabilitation period, the baby is prescribed treatment aimed at preventing the development of postoperative scars. If the cleft was deep and goes deep into the nasal cavity, in the postoperative period it is necessary to use an endosal fixator, which is a nasal insert. It allows you to create the correct shape of the baby's nostril.
After the operation, the child needs to be regularly examined by an otolaryngologist, and a systematic visit to the dentist will allow for timely oral hygiene.
Possible consequences and complications
Children with a complete cleft lip have impaired sucking function, which prevents the baby from eating normally. Against this background, a disorder of the act of chewing and swallowing develops.
Other consequences of a cleft lip in a child include:
- decreased immunity;
- frequent ENT diseases and bronchitis;
- speech impairment;
- underdevelopment of the upper jaw.
Sometimes complications develop in the postoperative period.
The most common negative consequences of surgery include:
- in the first days after surgery - narrowing of the larynx, bronchitis, pneumonia, delayed urination;
- during the operation - excision of a large number of tissues in the cleft area, improper layer-by-layer stitching of tissues, inflammation and swelling;
- in the postoperative period - divergence of sutures, aesthetic defects, the presence of a pronounced scar.
Cleft lip in newborns is a rather serious pathology that requires immediate surgical intervention. The goal of treating a child with a congenital cleft lip is not only to eliminate the cosmetic defect, but also the achievement of ideal facial contours, the development of normal functioning of the speech apparatus and the formation of the correct dental row.
Cleft lip video
Malysheva on the cleft lip:



