If a person received mechanical damage to the cranial bone or soft tissues (vessels or the lining of the brain itself), then it is usually called traumatic brain injury (TBI). This is a fairly common type of injury, which is most dangerous for its complications. It all depends on the severity of the injury, its degree and related factors.
Record content:
- 1 Classification
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms (external signs, how it manifests itself)
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
-
7 Treatment methods
- 7.1 Medications
- 7.2 Traditional methods
- 7.3 Other methods
- 8 Possible complications
- 9 Video about TBI
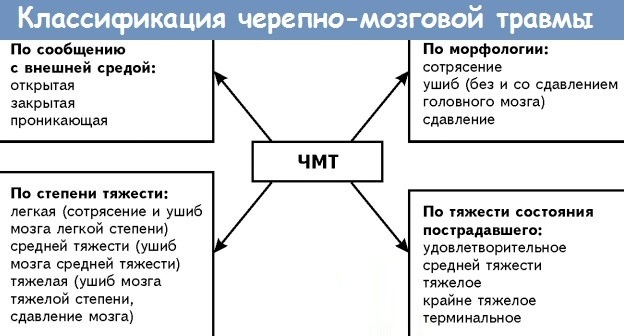
Classification
Jean-Louis Petit, who worked as a surgeon and anatomist in the 18th century, was the first to propose a classification of TBI. His version of the types of injuries in this category is relevant to this day.
First of all, injuries are classified based on the severity and can be:
- Lightweight. We are talking about a minor bruise or mild concussion.
- Average. A serious bruise or concussion is diagnosed.
- Heavy. The most difficult condition, which is characterized by severe brain contusion or acute compression.
There is also a classification according to the time that has passed since the traumatic brain injury. This is the period during which a doctor's supervision is required.
There are several such time periods:
- acute (lasts 2 to 10 weeks after injury);
- intermediate (you need to be observed for 2-6 months);
- remote (periodically it is required to undergo examination for the next 2 years).
To determine more accurately the severity of the injury, doctors use the Glasgow scale. Based on the symptomatology, indicators of the patient's confusion, reaction (motor and speech), the specialist assesses the damage on a 15-point scale. It also determines the type of damage and its degree.
Stages and degrees
There are several forms of TBI, depending on various factors.
Based on the damage to the skin, we can say that the patient suffered from:
- Open traumatic brain injury. In such a situation, characteristic lesions of the scalp will be visible to the naked eye.
- Closed TBI. A condition in which there are no obvious breaks in the skin tissue, but the damage involves the brain itself.
There is also a category of combined injuries. In this case, the point is that the damage was not necessarily obtained mechanically. Radiation or harsh chemicals could have caused the adverse effects.
Next, the doctor must determine the type of damage to the dura mater of the brain, which separates the bony part of the skull from the gray matter itself.
Based on this, the injury can be:
- Penetrating. In this case, damage to the hard part of the shell is present.
- Non-penetrating. There is no damage to the hard part.
Also, TBI can be isolated (only the head is damaged) or combined (other parts of the body are also affected, for example, the pelvis or chest).
There are also several forms of TBI, which depend on how severe the damage to the skull is, as well as its contents:
- Concussion. This form of TBI is considered the easiest. In this case, the patient complains of a short-term loss of consciousness (it can last up to several minutes), a state of weakness and autonomic disorder (manifested in a rapid heartbeat, sweating). Focal (obvious damage to a specific area of the brain) symptoms are not observed.
-
Slight contusion of the brain. A person can remain unconscious for a period from 2-3 seconds to several hours. In this case, mild focal symptoms are observed. These include weakness in the arms or legs and nystagmus (characterized by pendulum movements of the visual organs, that is, when the pupils begin to "run").
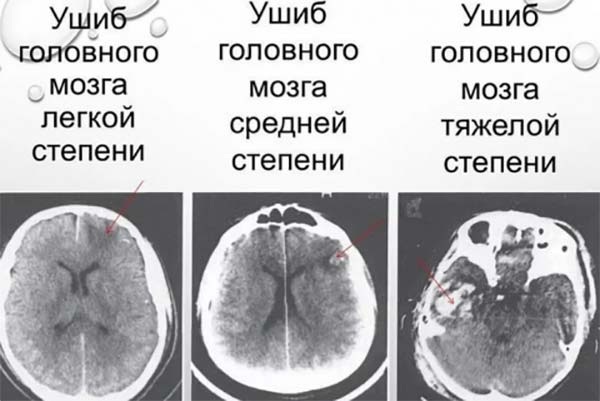
- The average degree of brain contusion. Loss of consciousness in this situation can last for several hours. Focal symptoms are also quickly detected. They manifest as severe weakness in the arms and legs and slurred speech. Additionally, the patient is diagnosed with facial asymmetry. The danger is represented by probable intrathecal (subarachnoid) hemorrhages.
- Severe contusion of the brain. The patient can remain unconscious for up to several weeks. In addition, muscle tone disorders are pronounced. A person cannot bend and unbend limbs on their own. Also shows squint, high body temperature persists for a long time. The pupils move slowly. Additional signs of severe bruising include seizures, during which the tongue is often bitten.
- Diffuse axonal injury. In this case, very severe brain damage is observed. The patient, as a rule, is not just unconscious, but in a coma. This means that he does not show any reaction to external and painful stimuli. In addition, he may have problems with breathing disorders (it becomes intermittent or disappears altogether), a sharp decrease in blood pressure, and the absence of the function of flexing the limbs. Also, patients often have a very high temperature, and strabismus appears.
Healthy! Diffuse damage is most commonly diagnosed in road traffic victims.
- Compression of the brain. This is the name of the compression of the cerebral tissues of the brain. Intracranial pressure begins to rise sharply. This condition is considered the most dangerous. The fact is that the patient can be in a coma or, conversely, conscious, feeling relatively stable. However, at this time, intracranial hematoma (a strong accumulation of blood) continues to grow.
Brain injury does not always occur in the exact spot where the impact occurred. Often, lesions are diagnosed on the opposite side of the skull, in the so-called counter-impact zone.
Symptoms (external signs, how it manifests itself)
Traumatic brain injury is a rather dangerous condition that requires an immediate medical examination. There are a number of symptoms by which, immediately after injury, it can be understood that a person has TBI (some symptoms appear immediately, and others after a certain period of time):
- Loss of consciousness. This is the most obvious sign of TBI. Loss of consciousness usually occurs immediately after injury. A person can remain in an unconscious state from a few seconds to several days or even weeks.
-
Headaches. They usually appear immediately after a person wakes up.
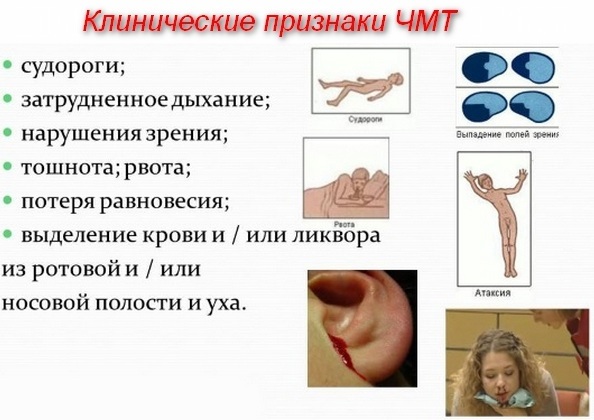
- Nausea and vomiting. At the same time, after the attack, the patient does not experience any relief.
- Dizziness and excessive sweating.
- Obvious damage to the skin and bones. For example, blood may appear at the site of a bruise. A hematoma may also appear (and not necessarily at the site of the impact, but also behind the ear, under the eye and in other places of the head). However, this feature is inherent only in open injuries.
- The appearance of cerebrospinal fluid from the nasal passages or ears. The cerebrospinal fluid itself is the cerebrospinal fluid that constantly circulates in the ventricles of the brain. She is responsible for nutrition and metabolism in the "gray matter". In a normal state, the cerebrospinal fluid is located in a slit cavity, which is located between the brain itself and the cranium. If there was serious damage to the bone, then the dura mater could break through, which contributes to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into the auditory or nasal passages.
- Convulsions. A seizure is an involuntary contraction of the muscles in the limbs. During the seizure, the patient may lose consciousness.
- Amnesia. After a severe concussion, what is known as retrograde amnesia may develop. It is characterized by the fact that the patient only remembers what happened to him before the injury. Sometimes the memory comes back, but there are times when the patient cannot remember anything.
There are also a number of individual conditions under which a certain list of symptoms is observed:
| Damage type | Symptoms |
| Injuries that lead to damage to the vessels of the brain. In some cases, we are talking about subarachnoid hemorrhage (blood enters the space between the brain and the skull) | Severe headaches (appear suddenly in the form of seizures), the appearance of signs of photophobia (pain in the eyes from bright or even daylight), vomiting, fainting. If you ask the patient to tilt his head back, then he will experience pain in the suboccipital muscles.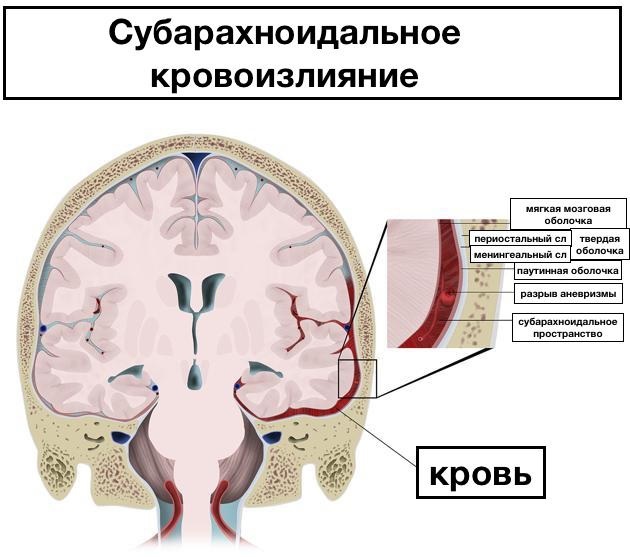
|
| Frontal lobe injury | Violation of speech (the patient cannot pronounce the simplest phrase, unconsciously changes letters in words), unsteadiness when walking, severe weakness in the arms and legs (usually on one side of the body). |
| Temporal lobe injury | Problems of speech perception (the patient hears what he is being told, but does not understand anything, the native language may sound like a foreign one to him), loss of vision (not completely, but in any one zone of the visual field), convulsions (can be in the whole body or only in limbs). |
| Damage to the parietal lobe | The patient may become completely numb on one side of the body. In this case, he will not feel any touch or pain in this area. |
| Occipital lobe injury | Vision problems (complete or incomplete blindness). |
| Cerebellar damage | Problems with coordination (movements become indistinct) and gait (the body bends more to the side while walking), the eyes begin to "run", muscle hypotonia (severe weakening of the muscles). |
| Cranial nerve damage | Strabismus, hearing problems, the appearance of facial asymmetry (one side of the mouth, cheek or eye slits may drop). |
Traumatic brain injury is a very complex condition that has many forms and varieties. Therefore, one can independently determine only theoretically how serious the damage is. It is also worth finding out what most often leads to TBI.
Reasons for the appearance
As a rule, people most often suffer from TBI during road traffic accidents. Drivers as well as vehicle passengers and pedestrians. In second place in terms of the frequency of registration in traumatology are household injuries (attacks, accidental blows, falls, etc.).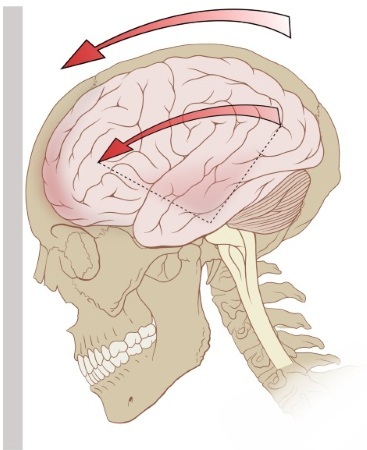
There is a risk of getting TBI at work or if a person is actively involved in sports activities.
Young people are most at risk of traumatic brain injury in the summer months, while older people are more likely to seek help in winter (ice, falling ice from roofs, and much more).
According to statistics, residents of the Russian Federation most often visit traumatology with craniocerebral injuries as a result of alcohol intoxication.
The number of such patients is about 70% of all cases. Also, such injuries are often the result of fights.
Diagnostics
Traumatic brain injury is a condition in which you should never self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, indicating a possible TBI, you should immediately contact a traumatologist. Additionally, consultation with a surgeon and a neurologist is required.
Anamnesis is collected during the initial examination. It is necessary to tell the specialist in detail when the injury occurred, whether there was a loss of consciousness after that and how long ago. It is worth indicating all the features of your condition and the circumstances of the injury (fall, road accident or other).
After that, the examination is carried out by a neurologist. He assesses the patient's level of consciousness, tests it, uses various stimuli (for example, bright light). Also, the doctor examines the patient's pupils. He clarifies their symmetry and the possible presence of blindness on one side of the view.
Also, the specialist asks you to tilt your head back and perform several simple manipulations in order to suggest the degree of damage based on the patient's reaction. In addition, the doctor will ask you to undergo simple tests to determine if the victim has confusion, amnesia, and other symptoms.
If we talk about laboratory and specialized research, then it is performed:
-
Tomography. Such a study allows you to get a picture of the structure of the victim's brain. The doctor will be able to determine the presence of bruises, detachments, and other injuries. There are two types of tomography. CT (computed tomography) is very fast, in a few seconds. Such research is preferred in emergency situations when there is no time or opportunity to ask the patient whether there are implants in his body. An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan takes more time and preparation. The procedure takes about 10 minutes. It is strictly forbidden to perform MRI if the patient suffers from bouts of claustrophobia or there are ferromagnetic implants in his body.
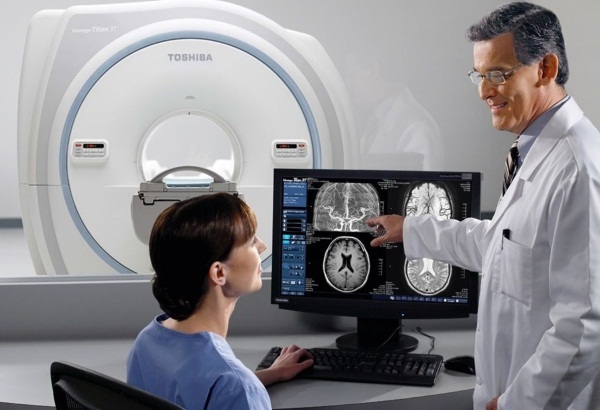
- Echo-encephaloscopy. This is an ultrasound method that allows you to clarify the displacement of the human brain. This happens in case of increased intracranial pressure or hemorrhage.
- Lumbar puncture. A needle is inserted into the space of the spinal cord, and cerebrospinal fluid is taken (no more than 2 ml). This method makes it possible to reliably determine the presence of hemorrhages.
In particularly difficult situations, it may be necessary to consult a neurosurgeon.
When to see a doctor
Traumatic brain injury is a serious disease, therefore, even if a weak TBI is suspected, a person is hospitalized. The patient can stay in the hospital for up to several days. The neuropathologist conducts an examination every 4 hours and checks whether his condition has worsened. You also need to conduct all the necessary research to exclude possible complications.
Therefore, it is worth visiting a doctor anyway. And if after an injury a person suffers from nausea and headache, then an ambulance should be called immediately.
Treatment methods
It all depends on the patient's condition, research results and the exact classification of the injury. For example, if according to the Glasgow scale it was possible to assess the condition of the victim by 8 points, then tracheal intubation is recommended. With this procedure, doctors will be sure that the oxygen that the brain receives is maintained at a normal level.
If the patient has problems with the reaction, he has photophobia or even a coma, then in this case there is a reason for performing mechanical ventilation (auxiliary or controlled type). This will also help maintain normal oxygen levels.
In severe TBI, the level of intracranial pressure is specified. It should not exceed 20 mm Hg. To maintain the required level, Minnitol is used, hyperventilation is performed, or barbiturates are prescribed.
The basis for the operation is an epidural hematoma, the volume of which exceeds 30 cubic meters. cm. To produce the so-called evacuation of the hematoma, transcranial removal is performed. Also, surgical treatment is necessary if the hematoma is more than 10 mm thick.
As a rule, TBI treatment is aimed at preventing possible secondary damage to the human brain.
Medications
The course of treatment and dosage of drugs can only be prescribed by doctors. To a large extent, these data depend on the specific case, the volume of the hematoma and other factors. There are also medications that can help relieve the condition when anxiety symptoms occur. For example, anticonvulsants will be required to prevent seizures and seizures.
Most often, the doctor prescribes:
-
Levetiracetam. Oral tablets. Accepted twice a day. The dose is determined by your doctor. The drug costs about 300-350 rubles.

- Valproate For example, Depakine for oral administration. The main component of the product is valproic acid. The dosage is also determined by your doctor. The product costs about 100-250 rubles.
If the patient has frequent headaches, the doctor may prescribe analgesics. Beta blockers may be needed when diagnosing autonomic dysfunction.
When the danger has passed and the patient's condition has stabilized, drugs may be required that normalize the blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. These drugs include Cortexin, Actovegin and Cerebrolysin.
Traditional methods
It is very dangerous to use this type of treatment as the only one in order to stabilize the condition. If there is a suspicion of TBI, then you need to take a horizontal position and move as little as possible. While the ambulance is traveling, a cold compress can be applied to the site of the injury.
Alternative methods can be used only after discharge from the hospital or if the doctor permits. As a rule, such funds are used after the main treatment, during the recovery period.
There are several infusions that have a beneficial effect on the general condition of the patient:
-
Tincture of creeping thyme. To prepare it, you need to pour one tablespoon of the herb with two glasses of water. After that, the liquid must be brought to a boil and insisted for 1 hour. When everything is ready, it remains to strain the infusion and take it in half a glass before each meal.

Tea with wild thyme outdoors. - Infusion of aralia. This plant has a positive effect on the nervous system and brain performance. To prepare a medicinal tincture, you need to pour a tablespoon of herbs with 100 g of vodka. After that, the container with the liquid must be wrapped up and sent to a dark place for 3 weeks. After that, the composition must be filtered and taken 30 drops once a day before lunch.
Other methods
When the critical consequences of the trauma have been dealt with, there is still a lot of work to do. First of all, the patient needs recovery.
In this case, the doctor may prescribe him a course of additional treatment in the form of:
- Physiotherapy. This treatment consists of exercises to change the position of the body. This stimulates motor ability, weakened muscle mass is strengthened. Thanks to this, a person quickly returns to his usual way of life.
- Vojta therapy. In this case, treatment is aimed at restoring the connection between brain activity and reflex movements. For this, various stimuli are used on different parts of the patient's body. This prompts the victim of TBI to make certain movements.
- Mulligan therapy. It relieves muscle tension. Movements cease to bring pain. For this, a setting called "Exarta" is usually used. It is a suspension system that allows you not only to relieve pain, but also returns atrophied muscles to work. Melligan therapy also includes classes on various simulators.
- Ergotherapy. This is a type of rehabilitation, which involves helping a person who has suffered from TBI to re-adapt to the world around him. The patient learns to serve himself, to perform the simplest household manipulations. In the future, a person will be able to fully return to a normal social life and get a job.
Possible complications
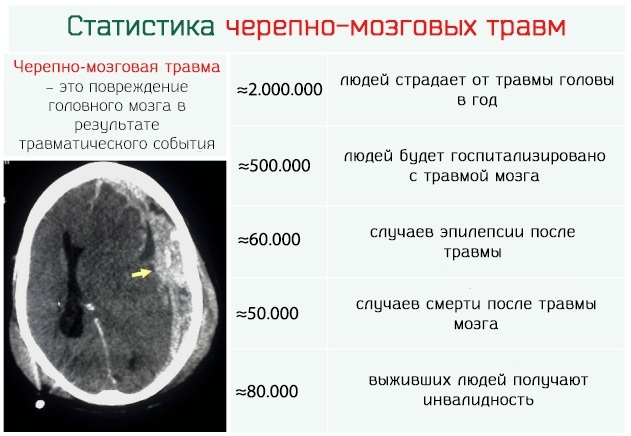
Even with timely treatment, there is a risk of serious complications. After TBI, the patient runs the risk of being disabled. Often there is a change in the psyche, people partially lose their memory, they cannot move and speak normally. There is also a risk of developing post-traumatic epilepsy.
Even with mild trauma, there is a possibility that cognitive impairment may be negatively impacted. With more complex degrees of TBI, the patient may have partial loss of vision and problems with swallowing movements. The patient's speech may remain inarticulate for many years, he may completely lose the ability to express himself.
Since traumatic brain injury is serious damage to the brain, paralysis or partial loss of function of the musculoskeletal system is another possible complication. Some patients who have suffered similar injuries may develop acute or chronic pain syndrome, migraines.
Moreover, painful attacks can last for several hours or even 2-3 days. Especially the symptoms increase during physical as well as emotional stress.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about TBI
Malysheva about TBI:



