The defeat of the mastoid process occurs against the background of various diseases or as a result of mechanical action on the temporal bone. He located behind the ear, provides multiple cavities and connects to the middle ear region.
If any disturbances or painful sensations appear, you should immediately contact an otolaryngologist to establish the cause of the discomfort. Lack of timely medical care will lead to serious consequences.
Record content:
- 1 What are mastoid processes?
- 2 Where are they located?
- 3 The structure of the mastoid process
- 4 Types of processes
-
5 Diseases and injuries of the temporal bone behind the ears
- 5.1 Inflammation
- 5.2 Cell sclerosis
- 5.3 Cholesteatoma
- 5.4 Fracture
- 6 Common complications
- 7 Diagnostic methods
-
8 Treatment
- 8.1 Medication method
- 8.2 Non-drug methods
- 8.3 Surgery
- 9 Folk remedies
- 10 Mastoid video
What are mastoid processes?
The mastoid process of the temporal bone has a rough surface on the outside. The element is conical in shape, its upper part is directed downward. The base of the appendix is located on the border with the dura mater of the brain.
Its inflammation or fracture is dangerous for a person, since any pathological processes in this area can negatively affect the most important organ of the human body - the brain.
Where are they located?
The mastoid is the temporal bone that lies behind the ear in the area of the auditory tube. It is associated with the middle ear. In most cases, the mastoid process becomes inflamed as a result of an infection. The disease is called mastoiditis.
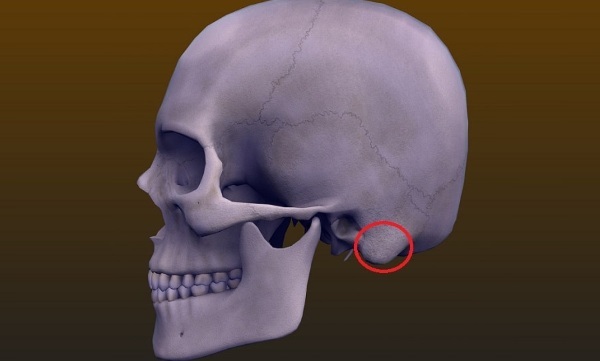
Timely diagnosis and treatment under the supervision of an otolaryngologist will help prevent serious consequences.
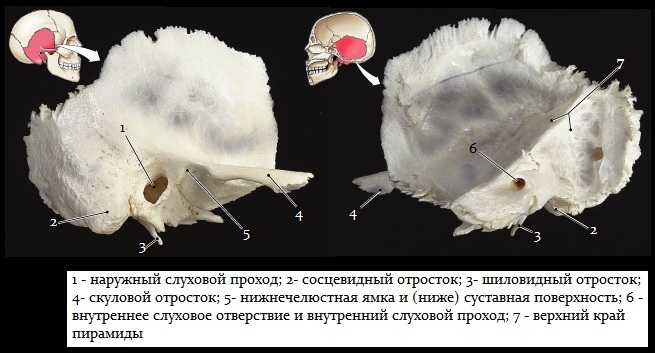
The structure of the mastoid process
The mastoid process consists of numerous cells that are filled with air and are separated by thin septa. The largest hole is called the mastoid cave. It connects to the tympanic cavity.
There are several types of mastoid cells:
| Name | Description |
| Zygomatic | The cells are located next to the cavity of the bone notch. This is the area of the upper posterior wall of the ear canal. A deeper layer of the zygomatic cells passes between the sinus and the nerve canal. |
| Sinus | The venous sinus, which is located behind the mastoid process. Some zones pass along its surface or under the cortical layer. |
| Perifacial cells | The cavities are located near the mastoid process and the canal of the facial nerve. With the development of the inflammatory process, all areas are affected. |
All cells are important and with the deepening of the inflammatory process, as their larger area is affected, the likelihood of developing mastoiditis increases. More often, the pathology is a secondary disease and occurs against the background of an acute inflammatory process in the ear area.
Types of processes
Given the structure of the mastoid process, the following types of it are distinguished in medicine: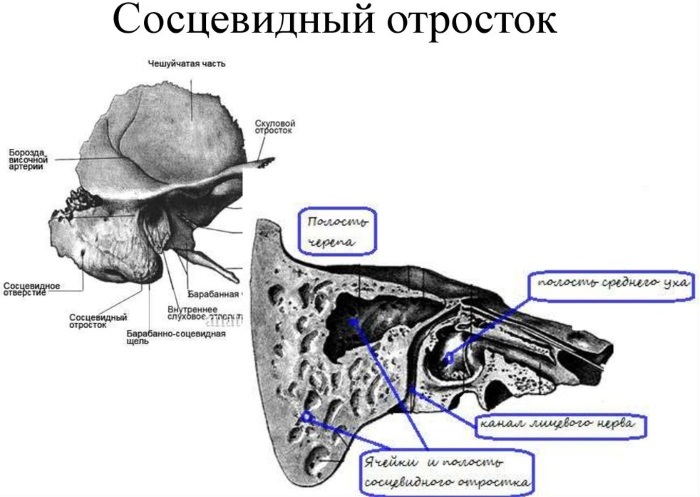
| Name | Description |
| Diploetic | The structure is provided by the accumulation of small cavities that contain the bone marrow. |
| Pneumatic | A distinctive feature is the large cells that contain air. |
| Sclerotic | The structure of the appendix is represented by a weakly expressed structure, which includes cells of various sizes. |
The pneumatic mastoid process is more prone to the development of the inflammatory process.
Diseases and injuries of the temporal bone behind the ears
Diseases and injuries of the mastoid process provoke various factors. Pathological processes are accompanied by characteristic signs, with which it is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner. An otolaryngologist is responsible for diagnostics and treatment. The specialist prescribes a comprehensive examination, based on the results of which he draws up the most effective treatment regimen.
Inflammation
The mastoid process is located behind the ear and connects to its canals, so the slightest inflammatory process can trigger a serious pathological mechanism. We are talking about mastoiditis. The main cause of the disease is an infectious lesion (Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae or Pseudomonas aeruginosa).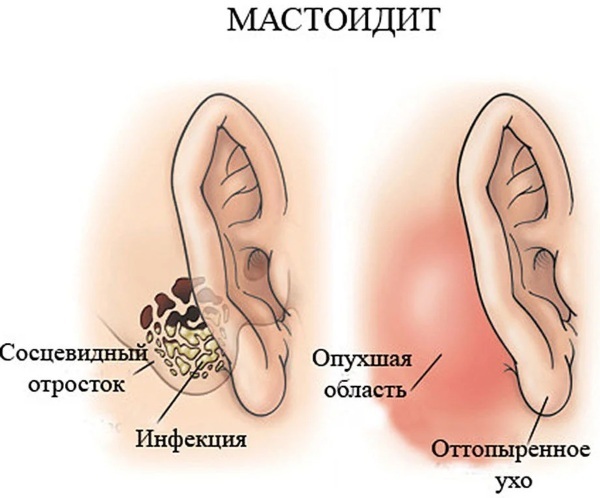
Pathology is dangerous to human life, since there is a high probability of damage to the meninges.
| Causes | Symptoms |
|
|
Mastoiditis develops in stages, each of which is accompanied by characteristic clinical symptoms:
- Exudative. The causative agents of the inflammatory process are pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the mastoid region through the middle ear. A large amount of exudate accumulates, which closes the cells and disrupts the movement of air.
- Polyiferative. The stage of the disease at which a purulent inflammatory process affects the mastoid process, contributing to its destruction. As the pathological processes progress, the partitions disintegrate, and a single cavity filled with pus is formed.
Without timely and properly selected therapy, inflammation entails serious complications that are more difficult to cope with. Hearing is impaired, an abscess develops, meningitis, or the facial nerve is damaged.
Cell sclerosis
Chronic inflammation of the middle ear provokes cellular sclerosis.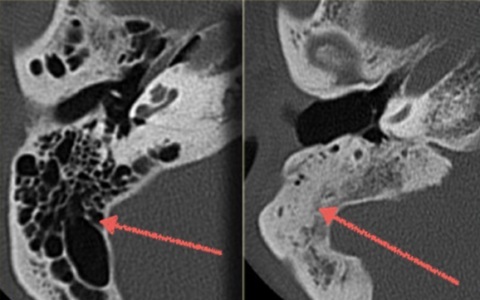
Their transparency decreases, the partitions between them collapse.
| Causes | Symptoms |
|
|
Untimely and or incorrectly selected therapy for the inflammatory process in the middle ear also provokes sclerosis of the cells of the mastoid process. Self-treatment is unacceptable, since there is a high probability of the spread of a purulent inflammatory process to the intracranial region.
Cholesteatoma
The disease is characterized by the formation of a benign tumor in the middle ear cavity. The neoplasm looks like a capsule with a layered structure.
| Causes | Symptoms |
|
|
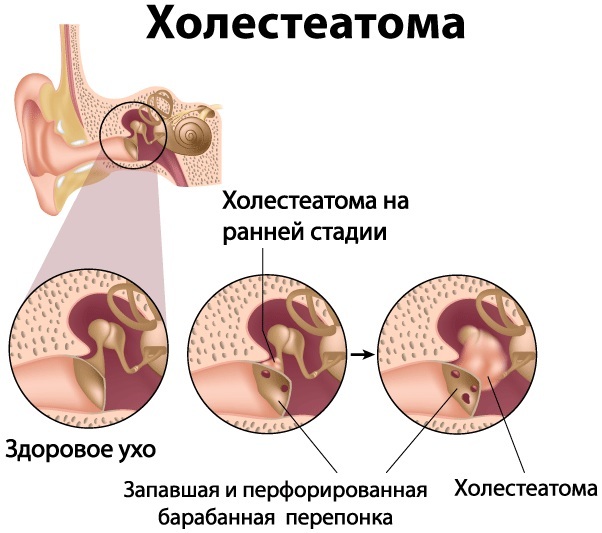
Timely comprehensive examination will allow you to choose the most effective treatment and prevent possible complications.
Fracture
The mastoid process is located in the area of the temporal bone, damage to which occurs as a result of various factors. The pathological condition radically affects a person's life, even in the case of correct and timely therapy, the likelihood of complications is high.
| Causes | Symptoms |
|
|
There are the following types of mastoid fracture:
| Name | Description |
| Transverse | It is the result of a strong blow to the temple or occiput. The fracture affects the entire structure of the temporal bone. |
| Longitudinal | It occurs as a result of direct mechanical action on the parietal or occipital region. Violation of the integrity of the temporal bone occurs in the area of the auditory tube, tympanic cavity and external ear. |
| Atypical | Thin areas of the mastoid process are damaged. There is a high likelihood of microscopic cracks and damage to brain tissue. |
The victim will need first aid and urgent treatment. Otherwise, a person will face serious complications (abscess, meningitis, otitis media in combination with mastoiditis).
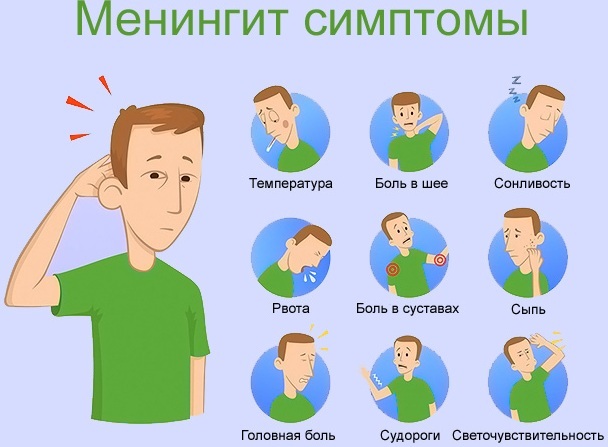
Common complications
The mastoid process is located in such a place that without timely therapy inflammation or damage, the likelihood of serious complications is high:
| Name | Description |
| Maze | The disease occurs if the inflammatory process spreads to the cavity of the middle and inner ear. Pathological processes provoke noise and hearing loss. Coordination of movements is also impaired. |
| Meningitis | The mastoid process is located next to the dura mater of the brain. The spread of infection can lead to an inflammatory process in this area. |
| Blood clots | The pathological condition develops as a result of damage to the inflammatory process of the blood vessels. The blood circulation process is disturbed. There is a high probability of not only the formation of blood clots, but also a blockage of blood vessels, against the background of which a fatal outcome occurs. |
| Facial nerve damage | The mastoid is located next to the nerve fibers behind the ears. |
A complication of damage to the mastoid process can also be brain damage, the development of encephalitis. The spread of pathogenic microorganisms throughout the human body through the blood leads to the appearance of sepsis. It is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner, undergo examination and treatment in order to prevent serious consequences.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of damage to the mastoid process and treatment is carried out by an otolaryngologist. The specialist will conduct an examination and prescribe the most informative examination. The results obtained will help you choose an effective treatment regimen.
Comprehensive diagnostics includes the following tests: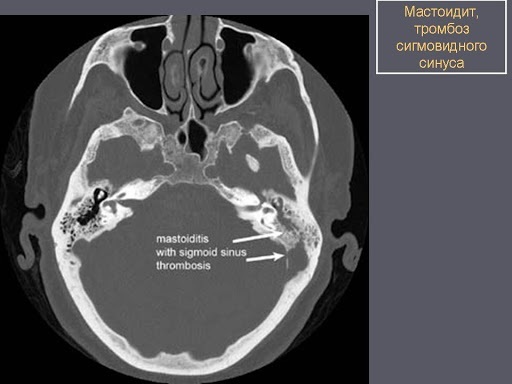
| Name | Description |
| X-ray | The most informative method of examination, with the help of which the specialist identifies lesions. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | An informative diagnostic method that allows you to determine the intensity of pathological processes and the degree of degenerative changes. |
| General and biochemical blood test | The research results will show changes in blood cell parameters and other indicators. |
| General urine analysis | Tests allow you to determine the general condition of the human body and suspect an inflammatory process. |
Differential diagnosis is necessary, since many pathological processes are accompanied by similar clinical symptoms (furuncle of the outer ear, otitis media, frontal sinusitis). The treatment that the doctor chooses for the patient depends on the results obtained.
Treatment
The mastoid process consists of cells, the inflammation of which provokes pathological changes in the structure of bone tissue. The otolaryngologist will tell you where this part of the temporal bone is located and how it is treated.
The patient is hospitalized in serious situations when specialist supervision is necessary and the likelihood of surgery is high. In some situations, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The doctor prescribes medications and a therapy regimen.
Medication method
Medicines should be taken strictly according to dosages selected by a specialist or by carefully studying the instructions for use. The drugs cause side effects, so it's important to stick to your doctor's prescriptions.
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial agents | Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone | The adult dosage is 500 mg once a day with or after meals. The course of treatment lasts 3 days. |
| Hormonal drugs | Prednisolone, Dexamethasone | The medicine is taken orally once a day, preferably in the morning. The average adult dosage depends on the patient's condition and is 5-60 mg per day. The course of treatment lasts 1-4 weeks. |
| Antihistamines | Suprastin, Claritin | Adults are prescribed 1 tablet 3-4 times a day. The medicine is recommended to be taken after meals with plenty of water. |
In addition, for patients with damage to the mastoid process, the doctor prescribes vitamin complexes that increase the body's defenses and its resistance to the inflammatory process.
Non-drug methods
If damage to the mastoid process is detected at the early stages of pathological processes, patients are also prescribed in complex therapy non-drug treatments:
| Name | Description |
| UHF therapy | The treatment uses a high frequency electromagnetic field. UHF therapy helps with fresh fractures and acute inflammatory processes. |
| Microwave therapy | Microwave therapy, which involves the impact on the human body of electromagnetic waves of various lengths. The sessions have a positive effect on peripheral blood vessels, reducing their tone. Blood circulation improves, metabolic processes are activated. |

Additionally, it is recommended to use compresses on the behind-the-ear area, but only in the absence of contraindications and complications after consultation with your doctor. These can be warming or cold lotions.
Surgery
The mastoid process is located behind the ear, where the vital nerves, organs of hearing and balance, and the carotid artery are located. Surgical intervention for patients is indicated in emergency situations or due to the lack of a positive result after drug therapy.
There are also other reasons that require urgent surgical treatment:
- development of the labyrinth;
- the appearance of intracranial complications;
- the occurrence of an abscess;
- otogenic paresis.
Surgery is necessary to remove accumulated pus in the mastoid process and drain the tympanic cavity. After the procedure, the patient is prescribed medication to prevent serious complications (changes in hearing, inflammation of the meninges, loss of taste, damage to the facial nerve).
Folk remedies
Recipes of healers and healers can be used in the complex treatment of inflammation of the mastoid process, but strictly after consulting a doctor. Many of the components used can provoke an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity. A specialist will help you choose the most effective recipe, taking into account the provoking sources of the disease.

| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Carnation | Dry plant flowers (5 tsp) pour sesame oil (1 tbsp.). Put the resulting mass on medium heat and cook for 10 minutes. Cool the liquid to room temperature and drain well. | It is recommended to drip the finished tincture into the sore ear, 3 drops 3 times a day. |
| Celandine | Chop fresh stems of the plant and squeeze the juice through cheesecloth. | The resulting nectar is used to lubricate the behind-the-ear region 2-3 times a day. Treatment is carried out until the redness and swelling disappear completely. |
| Sagebrush | Pour 1 tbsp. chopped herbs with boiling water (1 tbsp.). Leave the mixture for 60 minutes and strain. | The finished tincture is recommended to be consumed orally, 100 ml 3 times a day. |
| Calendula | Pour the flowers of the plant (150 g) with hot water (0.5 tbsp.). Insist 1 hour and strain well. | The resulting broth is recommended to be used for compresses on the inflamed area. |
| Eucalyptus | Grind 100 g of plant leaves. Add 600 ml of vodka. It is recommended to infuse the resulting mixture in a closed glass container for 30 days. Shake the jar periodically. | The strained tincture is used for compress and is taken orally 20 ml 3 times a day. |
An infectious lesion of the body requires an increase in defenses. Therefore, with mastoiditis, it is also recommended to ingest propolis, ginger, drink vitamin decoctions, teas.
The location of the mastoid process in the region of the brain is dangerous with serious complications if the person has not been provided with timely medical care. Diseases or fractures require a comprehensive examination, according to the results of which the otolaryngologist selects therapy.
Mastoid video
Topography of the mastoid area:



