State when reduces cheekbones and jaw, primarily associated with pathologies of the temporomandibular joint. The reasons for this are very varied. Most often, inflammation occurs in the joint. In more rare cases, the source of pain are injuries or disorders in the development of the dentoalveolar system. Damage can occur not only from a direct blow, but also when eating hard food.
In addition, there are additional symptoms - pain in the chewing, cervical muscles, headache, clicks in the joint, hearing impairment, dizziness, increased mobility of the lower jaw. The method of treatment depends on the true cause of the condition.
Record content:
-
1 Why does it reduce the cheekbones and jaw?
- 1.1 If only the lower jaw
- 1.2 Simultaneous cheekbones and jaw
- 1.3 When yawning
- 1.4 Bruxism
- 1.5 Nerve cramp
- 1.6 While eating
- 1.7 Dental diseases
- 1.8 Psychosomatic and neurological disorders
- 1.9 Other reasons
-
2 What to do if the jaw is cramping?
- 2.1 Massage
- 2.2 Heat and cold
- 2.3 Relaxation
- 2.4 Drugs
- 2.5 Folk remedies
- 3 Jaw Pain Videos
Why does it reduce the cheekbones and jaw?
Reduces the cheekbones and jaw (the reasons will be established by a comprehensive diagnosis) due to several factors:
-Injuries and diseases of the temporomandibular joint:
- congenital;
- acquired, inflammatory nature:
- osteoarthritis (osteoarthritis) - thinning of the cartilage in the joint, accompanied by the growth of bone tissue;
- neoarthrosis - the formation of a false joint in an unusual place;
- ankylosis - fusion of the articular ends of the bones and decreased mobility of the temporomandibular joint;
- injury.
-Functional states:
- juvenile temporomandibular joint dysfunction;
- arthritis (joint inflammation) and arthrosis (non-inflammatory joint changes), which can be caused by autoimmune disorders, infections (tuberculosis, syphilis, viral pathologies), systemic disorders (systemic lupus erythematosus, purpura) and other diseases (hepatitis and others).
-Dental diseases (premature decay or abrasion of teeth, periodontal disease and other infectious lesions).
-Conditions not associated with organic disorders (neurological):
- bruxism - clenching of the jaws and gnashing of teeth;
- damage to the trigeminal nerve;
- muscle spasms.
The temporomandibular joint can move in 3 directions. It is a combination of 2 separate joints. The joint is highly susceptible to age-related changes.
The critical periods in its development are:
- germination of milk teeth;
- replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones;
- loss of teeth in old age.
The growth of the joint stops by the age of 20, but throughout life, adaptation processes and changes continue in it. The features of its structure largely determine the severity of the condition in the event of inflammatory processes.
If only the lower jaw
If only the lower jaw reduces and this is accompanied by severe pain, then the cause may be trigeminal neuralgia. Most often, this violation is of a right-sided nature.
It develops as a result of the influence of the following factors:
- facial bone tumors;
- vascular diseases;
- the presence of uncomfortable dentures that violate the bite;
- ossification of the mandibular canal or infraorbital foramen;
- versicolor (simple or shingles);
- metabolic disorders;
- allergy;
- stress, emotional and physical stress.
Most often, this disorder occurs in women aged 50-70 years. In this case, there are attacks of acute facial pain, similar to an electric shock. It can last from a few seconds to several minutes.
The provoking factors for the occurrence of unpleasant sensations are conversations, eating, washing and other movements of the facial muscles. When it appears, redness of the skin of the face, lacrimation, twitching of the chin and eyes may occur.
Simultaneous cheekbones and jaw
Reduces the cheekbones and jaw (the reasons for this may be arthrosis or arthritis of the temporomandibular joint) as a result of a chronic inflammatory process, due to which degenerative changes.
This condition is characterized by pain, decreased jaw mobility, and difficulty opening the mouth due to pain. X-rays reveal the erosion of the surface of the joint, its deformation. When pressing on the joint, the pain increases.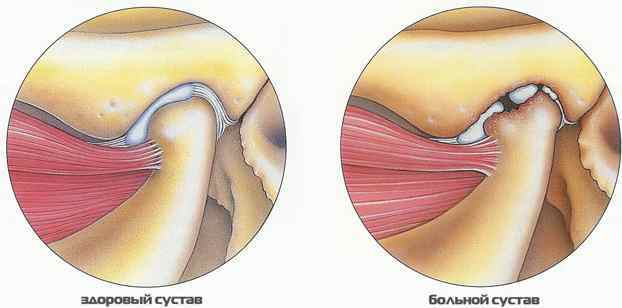
There are several types of arthritis:
- Purulent. Due to purulent inflammation, soft tissues swell, when pressed with fingers, a sharp pain occurs in the joint area.
- Rheumatoid. It is formed against the background of systemic damage to the connective tissue. Usually several joints are damaged at once - hand, wrist, foot. To diagnose this disease, rheumatoid factor (autoantibodies) is determined.
- Psoriatic. In addition to unpleasant sensations in the jaw, the patient has psoriatic lesions of the skin and nails.
- Infectious. Bacteria can be introduced into the joint directly when it is injured or hematogenously (through the blood channel) from sources of other localization with purulent otitis media, furunculosis, sore throat, tuberculosis, rubella and others pathologies.
- Reactive. It is a type of infectious disease and occurs 1-2 weeks after dysentery, chlamydia, salmonellosis, syphilis, enteritis, viral hepatitis and other diseases.
- Traumatic, arising from a bruise, impact or injury, with chronic microtrauma, malocclusion.
When yawning
When yawning, this condition occurs as a result of injury to the joint with too wide abduction of the lower jaw, or as a consequence of a previous illness or injury. To reduce muscle tension, reduce the load on the temporomandibular joint. You should also avoid rough, tough foods.
Bruxism
Bruxism is the grinding of teeth resulting from the involuntary tension of the masticatory muscles. Most often, it manifests itself at night. Bruxism significantly affects the condition of the dentoalveolar apparatus, leading to a decrease in the height of the bite. This, in turn, serves as a risk factor for the development of pain in the temporomandibular joint.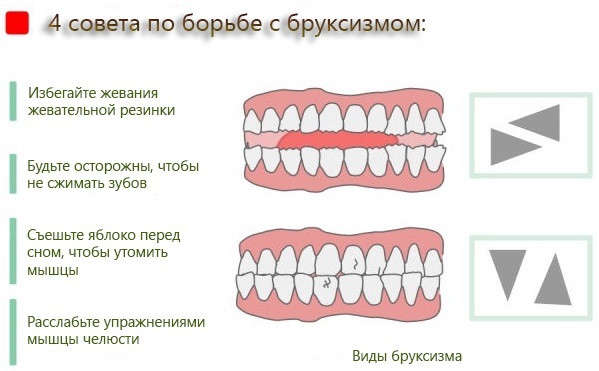
In modern medicine, the main cause of bruxism is considered to be emotional stress and pathologies of the central nervous system. Therefore, in this case, the help of a neurologist and a psychologist is required. Certain medications can also aggravate this phenomenon.
Nerve cramp
Nervous and emotional stress can also increase the tone of the facial muscles during wakefulness. The provoking factors are a state of fear, anger, or a long wait. In this case, muscle spasms occur, which cause discomfort. In this case, sedatives are shown first.
While eating
The main reason for the appearance of cramps during a meal is overstrain of the chewing muscles.
Risk factors include:
- malocclusion;
- chronic microtrauma of the temporomandibular joint when eating nuts, raw carrots and other solid foods that require significant effort to chew;
- increased physical activity;
- previous trauma;
- eating acidic foods that cause reflex muscle contraction;
- Difficulty swallowing saliva
- psycho-emotional arousal.
Dental diseases
The development of spasms and damage to the temporomandibular joint is facilitated by such dental diseases as:
- malocclusion;
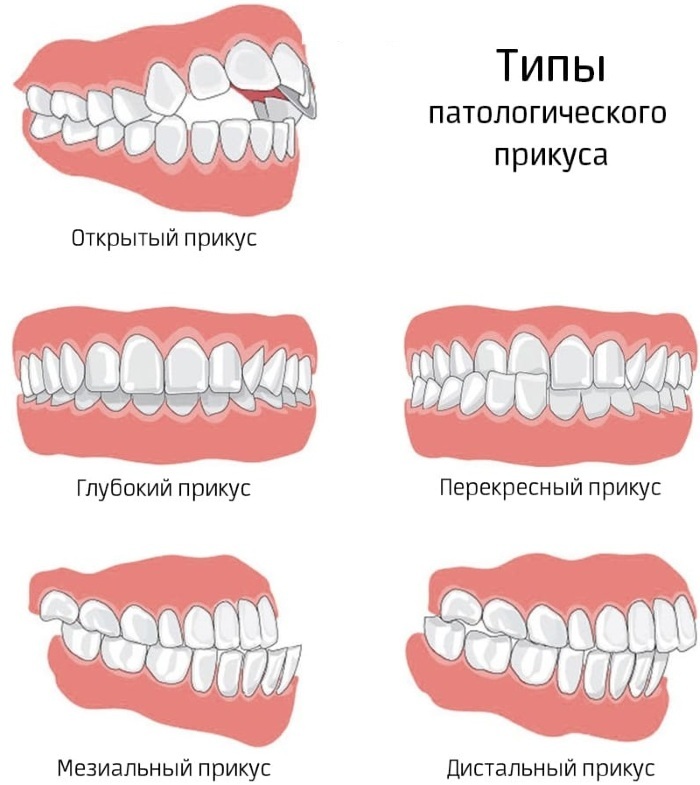
An abnormal bite can be the reason for which the cheekbones and jaw are reduced. - violation of the dentition when using prostheses or implants;
- caries, stomatitis, pulpitis, gingivitis, periodontal disease and other inflammatory pathologies.
In addition, with age, with the loss of teeth, there is a decrease in articular height. As a result, there is a shift in the head of the joint, trauma to the blood vessels and nerves; the articular disc, consisting of connective tissue, atrophies. As a result, deforming arthritis may develop.
Psychosomatic and neurological disorders
In addition to stress and overstrain, the following causes of spasms in the masticatory muscles are distinguished in psychosomatics:
- a sense of responsibility for other people and solving other people's problems;
- various phobias;
- feelings of shame or guilt;
- lack of attention from relatives and close people;
- feeling powerless in difficult life situations;
- separation or loss of a loved one.
Other reasons
It also reduces the cheekbones and jaw for the following reasons:
- Dislocation and subluxation of the temporomandibular joint. Subluxation is often asymptomatic and does not require medical intervention to reposition it. The most common symptom is clicks in the joint when lowering the jaw, when talking and on palpation. Also, patients note pain of varying intensity, aggravated by chewing, yawning or screaming. She can give in the ear, back of the head, temple. Risk factors are infectious diseases (including influenza), metabolic disorders.
- Fracture of the condylar process, which serves to articulate the lower jaw with the temporal bone.
- Formation of pathological bone growths (osteophytes) in the temporomandibular joint. They can appear with frequent deforming loads and in violation of calcium metabolism in the body.
-
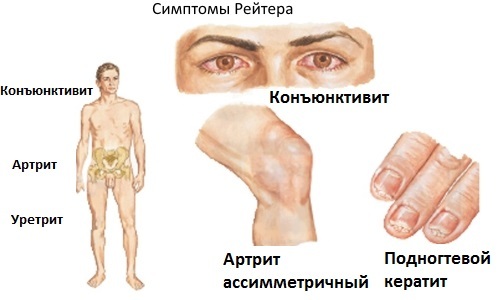
Reiter's disease - an allergic reaction that occurs after infectious diseases.
- Medical errors by dentists, orthodontists, surgeonsleading to a malfunction of the temporomandibular joint (placement of inflated fillings, violation of symmetry in prosthetics, causing the formation of one-sided loads, lengthy dental procedures leading to overstretching of ligaments).
- Activities associated with overexertion of the facial muscles - singing, recitation of poetry.
What to do if the jaw is cramping?
The method of treatment depends on the true cause of this condition. Therefore, you first need to be diagnosed by a neurologist, therapist, dentist, surgeon, orthopedist and other specialists.
So, if the jaw reduces for dental reasons, then the following methods are used:
- grinding teeth, the use of removable and non-removable orthopedic structures for correcting malocclusion;
- carrying out orthodontic correction using braces;
- osteotomy of the jaw - surgical elimination of violations;
- splint therapy.
If the cause is a jaw injury, then first it is necessary to exclude its fracture or subluxation using X-ray diagnostics. Sometimes microtrauma can be detected only on computed tomograms. The patient is prescribed rest and cold in the first 2 days, the jaw is immobilized using bandages.
During the recovery period, the following physiotherapy procedures are used:
- reflexology by methods of electropuncture, laser puncture, ultrasound puncture;
- exposure to an ultra-high frequency (UHF) electric field;

- myoelectrostimulation - the use of electric current pulses to restore the activity of muscle fibers;
- magnetic therapy;
- dry heat;
- electrophoresis and phonophoresis with the use of drugs (potassium iodide, hydrocortisone);
- physiotherapy exercises and massage (a set of exercises is described below).
With the development of infectious arthritis, antibacterial drugs and physiotherapy are used. In the formation of bone adhesions at the first stage, conservative treatment methods are prescribed (phonophoresis in hydrocortisone, electrophoresis with lidase, potassium iodide).
If there is no effect, then they resort to surgical intervention, which is carried out in hospitals in the departments of maxillofacial surgery.
If the reason lies in bruxism, then it is necessary to undergo consultation and treatment with a neurologist and neuropsychiatrist. Also, to prevent premature abrasion of teeth, you need to visit a dentist who can recommend orthopedic treatment methods.
If the jaw is cramping due to muscle spasms, then several methods of treatment are used:
- medication (pain relievers and antispasmodics, antidepressants and tranquilizers to relieve tension);
- physiotherapy treatment (magnetotherapy, reflexology, laser therapy, dry heat);
- to consolidate a positive result - massage, relaxation, myogymnastics.
In the presence of concomitant osteochondrosis, a neurologist can prescribe massage of the cervical-collar zone, physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy. During the period of treatment, in all cases, trauma to the jaw should be avoided: exclude coarse food, do not open your mouth wide, avoid intense sports.
Massage
Self-massage for diseases of the temporomandibular joint is carried out according to the following method:
- With gentle circular motions, stretch the trapezius muscle at the level of the shoulders and base of the neck.
- Then, while continuing the massage, slowly lower your hands along the spinal column as much as possible.
- Turn your head, stretch your sternocleidomastoid muscle with your fingers, first on one side, then on the other.
- Place the thumbs of both hands under the lower jaws and massage the chewing muscle in a circular motion, while kneading its upper part on the cheeks with the help of the rest of the fingers.
This complex allows you to relax your muscles. After it, it is recommended to do the exercises described below.
Heat and cold
On the first day after the injury, as well as in the presence of acute pain in the jaw, cold compresses can be used. For this, ice wrapped in a towel or plastic bottles with cold water are used.
This helps to block the transmission of impulses along nerve fibers and reduce pain. A cold compress should be applied to the temporomandibular joint for 5-10 minutes. several times during the day.
For a faster relief of the inflammatory process, thermal procedures are used. To do this, you can use a heating pad or a towel dipped in hot water. The compress is applied to the sore spot for 15-20 minutes. The heat also helps to relax tense muscles in the area.
Relaxation
It reduces the cheekbones and jaw (the reasons may be harmless), often with overstrain of the facial muscles. To eliminate this condition, you can use the following set of exercises (perform each type of movement 10 times):
- Press the pads of the fingers lightly against the temporomandibular joint. Gently move the jaw to the left and right.
- Then move your jaw back and forth. These movements should not cause discomfort.
- After that, make circular movements with the jaw, first in one direction, then in the other (5 approaches each).
- Close your teeth and lips, smile, then tighten your lips, pulling them forward.
- Relax the lower jaw so that they go down. In this case, it is necessary to press slightly with your fingertips in the lower part of the cheeks.
- Also, in a relaxed state, exhale the air.
- Make a semicircle with your head first in one direction, then in the other, stretching the muscles of the neck.
All exercises must be performed with a straight back. They help with muscle pain, tension and spasms of the chewing, facial muscles.
Drugs
The main groups of medications used for this disorder are described in the table below.
| Name | Main effect | Dosage for adults, mg per day | Average price, rub. |
| Drugs affecting neuromuscular transmission | |||
| Miolastan (Tetrazepam) | Regulation of the functions of the central and autonomic divisions of the nervous system | 25-50 | 200 |
| Ixel (Milnacipran) | 50 mg 2 times | 1600 | |
| Fluoxetine | 20 | 80 | |
Angioprotectors | |||
| Venoruton | Improvement of metabolic and reparative processes in bone tissue, intraosseous blood circulation | 300 mg 3 times a day | 1300 |
| Troxevasin | 500 | ||
| Pentoxifylline | 200 mg 2 times a day | 300 | |
| Chondroprotectors | |||
| Structum | Improving metabolic processes in cartilage tissue, increasing its resistance to damaging enzymes | 500 mg 2 times a day | 1600 |
| Inoltra | 3.8 g 3 times a day | 4000 | |
| Honda | 0.5-1 g 3 times a day | 250 | |
| Vasodilators | |||
| Papaverine | Improving peripheral circulation, relieving facial muscle spasms | 0.02 g | 45 |
| No-shpa | 40-80 | 160 | |
| A nicotinic acid | 1% solution, 5-7 ml (intravenous) | 50 | |
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | |||
| Ketonal | Reducing inflammation in arthritis, arthrosis | 100-200 (topically, in the form of a gel) or by mouth 25 mg 2-3 times a day | 100 |
| Diclofenac | 70 |
If the pain is very severe, then blockade according to Bersha (Egorov) is applied using a 1-2% solution of Novocaine (Lidocaine). They are given in the form of injections once every 3 days.
Folk remedies
From folk remedies for this condition, the following sedative recipes are used to help relax the facial muscles:
- Valerian root tea. 1 hour l. chopped roots pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 10 minutes. and taken as tea 2-3 times a day. This remedy is not recommended for people with liver disease or for pregnant women.
- Motherwort decoction. 15 g of herbs pour 250 ml of boiling water, add sugar to taste and bring to a boil. Keep on fire for 5 minutes. Take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day before meals.
- Passion flower tea. Cut off the stem and leaves of the plant, rinse them. Chop with a knife. The volume of the herb should be 1 tbsp. (free, without seal). Pour 1 liter of water and put on fire. Bring to a boil and keep on the stove for another 20 minutes. Then remove from heat, strain. This broth is taken 3 times a day, diluted with drinking water in a 1: 1 ratio.
Hard foods should also be excluded from the diet, which increase the load on the chewing muscles (meat, sausages, coarse bread crusts, crackers, raw carrots, apples, cucumbers, and so on).
When the cheekbones and jaw come together, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostics, which will reveal the true causes of this condition. They can be very diverse: from systemic connective tissue diseases to emotional stress. In some cases, surgery is required.
Jaw Pain Videos
Causes and treatment of jaw pain:



