Ovaries are an important element of the female reproductive system. It is a paired organ, which is the sex glands in which oocytes mature. Any pathology can lead to a malfunction of the reproductive function, the development of inflammatory processes. One of the most common diseases of the ovaries is cystadenoma, a tumor that is benign in nature.
Contents of
- 1 What is ovarian cystadenoma
- 2 Serous, mucinous, coarse, papillary, borderline, smooth-walled cystadenoma
- 3 Causes and factors of the development of the pathological process: menopause, abortions and other
- 4 Symptoms and signs depending on the size and location of the tumor
- 5 Diagnosis
- 6 How to treat the disease
- 6.1 Surgical intervention
- 6.1.1 Classic method
- 6.1.2 Laparoscopy
- 6.1.3 Preparing for operation
- 6.1.4 Features of laparoscopy
- 6.1.5 Rehabilitation after intervention
- 6.2 Treatment with folk remedies
- 6.2.1 Burdock
- 6.2.2 White acacia
- 6.2.3 Walnut
- 6.2.4 Cluster
- 6.2.5 Componentsfor the preparation of folk remedies - gallery
- 6.1 Surgical intervention
- 7 Prognosis of treatment and prevention
- 8 Cyst on the left or right ovary: what to do - video
What is ovarian cystadenoma
Ovarian cystadenoma is the most common type of cystsreproductive system( more than 60% of all clinical cases).The tumor is a bubble with a clear liquid. Despite the benign nature, neoplasm requires timely treatment.
There is always a risk of degeneration of cystadenoma into a malignant tumor - adenocarcinoma or cystadenocarcinoma.
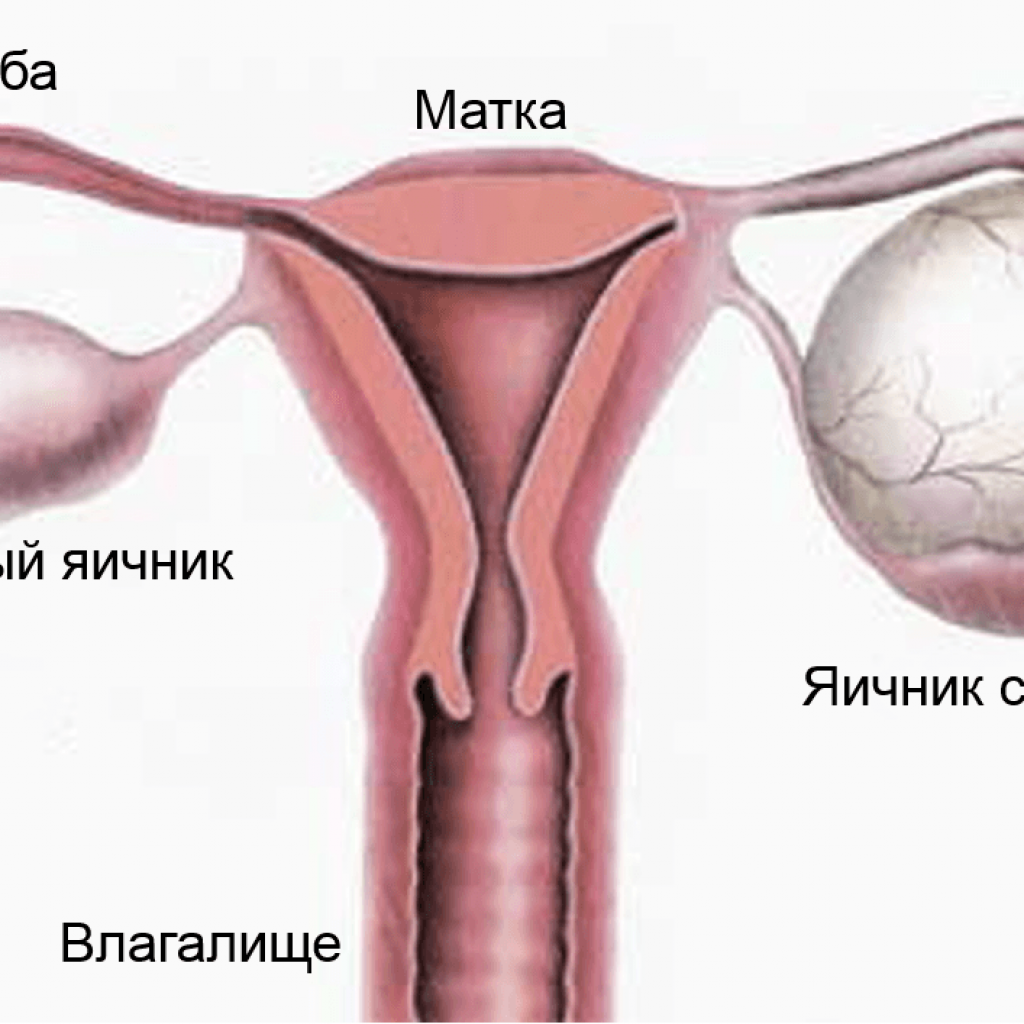
Ovarian cystadenoma is a benign tumor
Serous, mucinous, coarse, papillary, papillary, borderline, smooth-walled cystadenoma
Serous( simple) and mucinous depending on the form and content of the tumor of the cystadenoma. In the first case we are talking about a cyst with a dense epithelial tissue, inside of which is a transparent liquid.
In turn, serous cystadenomas are divided into:
- Cyloepithelial. The tissue of the cyst is homogeneous. The tumor is also called smooth-walled.
- Papillary. The disease is characterized by the presence of parietal growths. The cyst acquires a heterogeneity, which greatly complicates the diagnosis. Because of the large number of papillae, pathology has received another name - papillary cystadenoma.
- Rough-toothed. On the surface of the cyst, papillae of a more dense consistency are formed. There is a high risk of transformation of this tumor into a malignant tumor.
- Frontier. At a pathology there is an abundant growth of papillae. This type of cystadenoma is considered the most dangerous. Neoplasm rapidly increases in size, the risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor increases.
Mucinous cystadenoma is distinguished by a rather dense viscous secretion. Often there is a sediment and a suspension.
Mucinous cysts can reach huge sizes. In some cases, the weight of the neoplasm reaches 15 kg.
Depending on the location of the tumor, cystode is isolated:
- left-sided;
- right-hand.
With age, the likelihood of malignant degeneration of cysts is significantly increased. In women after 40 years, the borderline or mucinous cystadenoma can turn into cystadenocarcinoma( serous, mucinous or endometrioid) in just a few years. Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to delay the treatment of the disease.
Causes and factors of the development of the pathological process: menopause, abortions and other
Experts today can not name the exact causes of cystadenoma development. There is an opinion that initially a benign tumor is formed from functional cysts( cyst of the yellow body, follicular cyst).These tumors appear in women after ovulation as a result of the action of pituitary hormones. Over time, they dissolve on their own. However, with a broken hormonal background, functional cysts do not disappear - cystadenoma is born.

Each abortion increases the likelihood of developing ovarian cystadenoma
The most susceptible to developing cystadenum is a woman after 30 years. However, young girls may face a problem in connection with hormonal disorders. In children under 15 years of age, the pathology does not occur.
During the menopause, the risk of developing cystadenoma increases. This significantly increases the likelihood of malignant degeneration of the tumor due to impaired immunity.
In addition to functional cysts, the appearance of cystadenoma can lead to various inflammatory processes that often develop after surgical intervention in the pelvic area. Other unfavorable factors include:
- complex delivery;
- abortion;
- sexual abstinence;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
The risk of developing cystadenoma increases in women who regularly undergo weight, adhere to low-calorie diets.
Symptoms and signs depending on the size and location of the tumor
Symptoms of the disease directly depend on the size of the tumor, its location. Cystadenoma may not be felt for a long time. As the cyst grows, the following unpleasant symptoms appear:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- lumbar pain;
- sensation of foreign object in the peritoneum;
- menstrual cycle disorder;
- dysfunction of the urinary tract( marked pressure on the bladder).

Aching in the lower abdomen is one of the signs of ovarian cystadenoma
Diagnostics
To determine the type of cysts encountered, the following methods are helpful:
- Gynecological examination. The specialist evaluates the size of the tumor, the degree of its mobility, consistency.
- Ultrasound examination. Helps to accurately determine the localization and size of the tumor. In addition, it is possible to reveal the degree of growth of the superficial epithelium. Diagnosis, as a rule, is planned on the seventh day of the menstrual cycle.
- Computed tomography. It gives an opportunity to study the structure of the neoplasm in more depth.
- Pregnancy test. Eliminates ectopic development of the fetus.
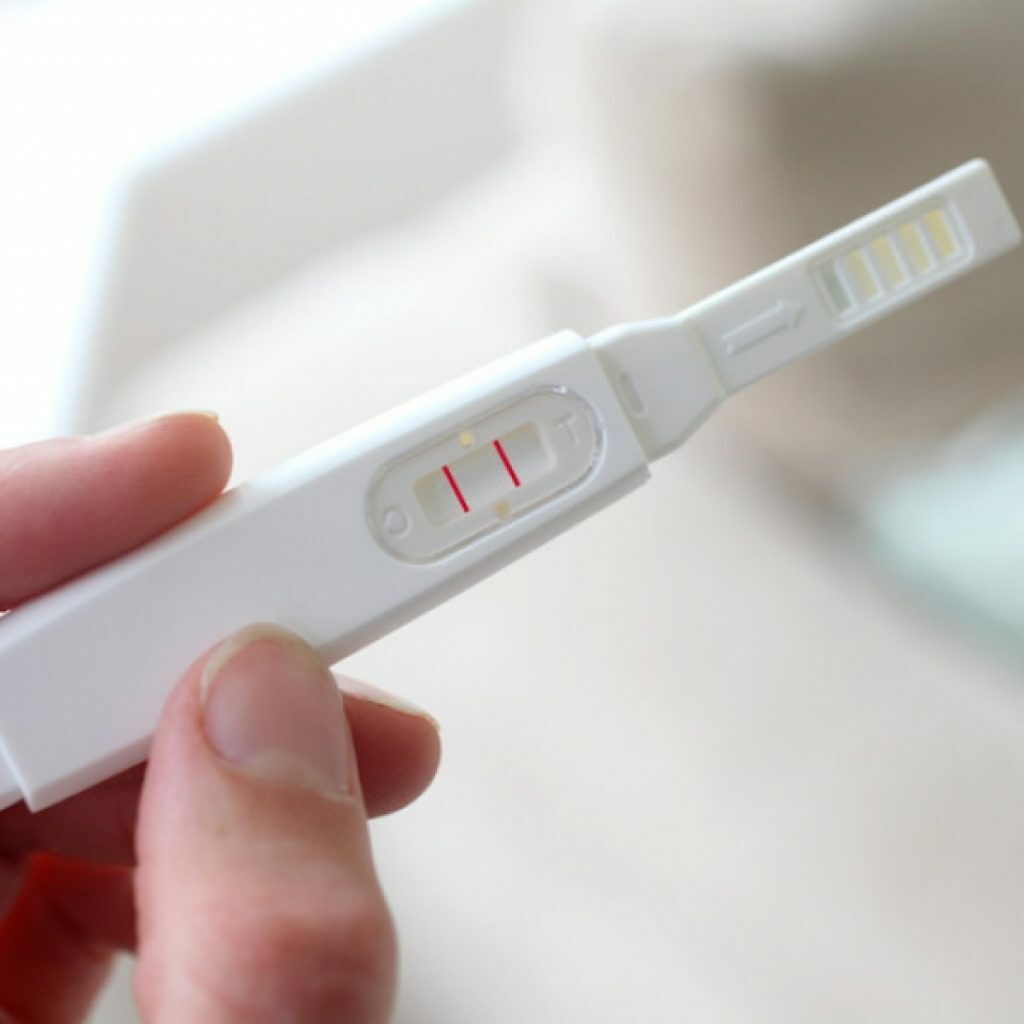
Pregnancy test excludes ectopic fetal development
- General blood test. It allows to exclude the development of the inflammatory process.
How to treat the disease
You can get rid of cystadenoma only surgically. Neoplasm does not resolve itself.
Surgical intervention
The specialist chooses the method according to the type and size of the tumor. In addition, the following factors are considered:
- the age of the patient;
- the need to preserve the childbearing function;
- risk of developing malignant neoplasms;
- presence of concomitant chronic pathologies.
The classic way of
If there is a serious risk of developing cancer complications or the cyst has reached a large size, you have to completely remove the ovary. Such a measure entails unpleasant consequences associated with a decrease in the production of female sex hormones, a deterioration in reproductive function.
Laparoscopy
A more gentle method of surgical intervention is laparoscopy, which allows to preserve healthy ovarian tissue. Manipulation is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. The image of the operation area is displayed on the monitor screen, so that the technician can monitor the entire process.
Laparoscopy as a method of cystadenoma removal has several advantages. Here it is possible to carry:
- preservation of a reproductive function of the woman;
- preservation of the ovary;
- maintaining the normal level of sex hormones;
- rapid rehabilitation after surgery;
- minimal risk of complications;
- elimination of postoperative scars and adhesions.
Serous cystadenoma can develop during pregnancy. If the new growth does not exceed 3 cm in diameter, no action is taken before the baby's birth. A large tumor size is an indication for surgical intervention.
![& lt; br /> Laparoscopy »width =» 1024 "height =" 1024 "/> & lt; / a & gt;Laparoscopy - a gentle method of removing the cyst [/ caption] & lt; / div & gt;& lt; div style =](/f/44/2f/442f24ea9ed3d9b9a9ab10f2e41c678f.jpg)
Despite the high effectiveness of such intervention, some women are not eligible for laparoscopy. The operation is not performed if:
- acute infectious processes in the body( ARI, influenza, pyelonephritis, etc.);
- in the abdominal cavity there are spikes;
- there are malignant neoplasms of the genitourinary system;
- a woman is obese 3-4 degrees.
In the presence of at least one of the above contraindications, cystadenoma is removed in a classical way.
Preparing for operation
Preoperative preparation is very important. A week before the laparoscopy, a woman needs to sit on a special diet, exclude products that promote increased gas production, such as:
- beans;
- soybean;
- black bread;
- cabbage;
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- baking.
Do not eat or drink on the day of surgery. On the eve it is necessary to have dinner no later than 18:00.You can drink until 22:00.The surgical intervention itself is usually prescribed for the morning.
Features of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy for ovarian cystadenoma is performed under general anesthesia. After antiseptic treatment of the abdominal wall from the side where the tumor is located, the doctor makes three notches for working tools.
- the first hole is for air supply;
- second - for the camera;
- the third - for the manipulator, with which the cystadenoma will be removed.
Specialist examines the tumor and neighboring organs, then cuts off the cyst shell, sucks the contents. All manipulations are carried out under close visual control due to the enlarged image on the monitor. The extracted material is sent for histology.
Surgical intervention takes 20-30 minutes. After the removal of cystadenoma, the holes in the peritoneum are sutured. The woman remains in the hospital for at least five days after the operation.
Rehabilitation after intervention of
Antiseptic treatment of sutures is performed, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection. Before discharge appoint a control ultrasound. Complete recovery of the functionality of the ovary occurs one month after the intervention.
Treatment with folk remedies
Cystadenoma can not be cured without surgery. However, some techniques help stop the growth of the tumor. At the same time, there is always the risk of losing time, missing the malignant transformation of the cyst, so the possibility of using a prescription should be discussed with the doctor.
Burdock
To prepare the medicine it is necessary:
- Take a few large leaves and rub them to a mushy state.
- Squeeze the juice of the plant.
- Store the finished medicine in the refrigerator.
Burdock juice is taken on a teaspoon three times a day for a month. At the end of the course, it is necessary to evaluate the results of treatment. If the tumor has grown, this therapy should be stopped.
White acacia
From the flowers of the plant, a medicinal tincture is prepared.
- You need to take 2 tbsp.l.raw and pour a glass of pure medical alcohol.
- The product should be left in a dark place for several days.
- Then the drug should be filtered and taken 30 drops three times a day for a month.
Walnut
For decoction it is necessary to prepare walnut partitions.
- About 4 tbsp.l.raw materials pour a liter of water and cook on low heat for 20 minutes.
- Next, remove the product from the heat and insist for an hour.
- Drug is filtered and taken in 100 ml to three times a day.
Clover
For the preparation of a medicinal product it is necessary:
- To break and dry a plant that has not yet blossomed.
- Four dry flower heads pour a liter of boiling water, cover and insist for 12 hours.
- This medicine should be filtered and drunk during the day.
Manipulation is recommended to be performed daily. The course of therapy - 2 months.
Components for the preparation of folk remedies - gallery
 With white acacia the medicinal tincture
With white acacia the medicinal tincture  is prepared. To prepare the medicine, a clover is used which has not yet blossomed
is prepared. To prepare the medicine, a clover is used which has not yet blossomed  Juice of burdock has healing properties
Juice of burdock has healing properties  For the preparation of medicine walnut partitions are used
For the preparation of medicine walnut partitions are used Prognosis of treatment and prophylaxis
With timely detection of tumorthe treatment forecast is favorable. A month after laparoscopy, a woman can lead a full-fledged lifestyle, plan a conception of a child. Disadvantageous consequences are the operation, which implies the complete removal of the ovary: the chances of conceiving a child are reduced. In addition, hormonal disorders are possible.
Often after complete removal of the ovary in women develops a commissural disease.

Infertility - one of the complications of ovarian cystadenoma
- cyst rupture;
- malignant tumor transformation;
- twisting of the cyst.
Due to the fact that the exact causes of tumor development are unknown, there are no special preventive measures for the disease. However, one can confidently say that the risk of complications is minimized in those women who lead a healthy lifestyle and are examined every six months by a gynecologist.
Cyst on left or right ovary: what to do - video of
Cystadenoma can not be ignored. Thanks to a timely appeal to a specialist, it will be possible to quickly cure the disease and reduce the risk of developing unpleasant complications.