Often at the conclusion of an ECG or Holter monitoring the phrase "signs of AV dissociation" appears. The article analyzes what kind of pathology it is, possible causes of its occurrence, methods and methods of treatment.
Record content:
- 1 Atrioventricular dissociation - what is it
- 2 Types, signs
- 3 Pathophysiology
- 4 Anamnesis
- 5 Conditions causing AV dissociation, causes
- 6 Differences Between AV Dissociation and Complete Heart Block
- 7 Atrioventricular dissociation with interference
- 8 Atrioventricular dissociation in children
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 ECG for AV dissociation. Examples of
- 11 Using intracardiac ECG data for diagnosis and patient management
- 12 Drug therapy
- 13 Surgical intervention
- 14 Long term monitoring
- 15 Forecast
- 16 Video about ECG blockages
Atrioventricular dissociation - what is it
The concept of atrioventricular dissociation (AV dissociation) is a collective term that unites states in which an ECG occurs - signs of a lack of coordination between the contractions of the atria and ventricles myocardium. There are 2 separate heart rhythms - ventricular and atrial.
Types, signs
In modern cardiology, there are 2 main types of AV dissociation:
- Complete. The variant, when the atria and ventricles contract in their own rhythm, independently of each other, each section has its own pacemaker. In this case, the rhythm of the ventricles is accelerated, reaching or exceeding the frequency of atrial contraction.
- Incomplete. The variant when the impulse generated in the atria partially captures the ventricles, or vice versa - when the ventricles are excited, the lower parts of the atria are captured.
Depending on the level of disturbance in the conducting system, dissociation is:
- passive - the automatism of the SA-node fades away;
- active - the automatism of subordinate departments increases.
Cardiologists distinguish benign AV dissociation as a separate class. This is a variant of the physiological norm that does not affect hemodynamic parameters. A similar condition can appear in young people during puberty, against the background of hard physical work or vigorous sports.
Pathophysiology
Normally, the conduction of an impulse along the conduction system of the heart has a strictly defined sequence.
- The impulse is generated in the sinoatrial node (SA node). It reaches the atrioventricular node (AV node) along 3 conduction beams and diffusely along the heart cells.
- A feature of the AV node cells is a low discharge rate. There is a simple physiological explanation for this. Due to inhibition in the AV node, excitation is first transmitted to the atria, causing them to contract. The blood is thrown into the ventricles and, only after that, the discharge is transmitted below.
- From the AV node, the impulse through the Gissa bundle and Purkinje fibers passes to the cells of the ventricles, causing their contraction.
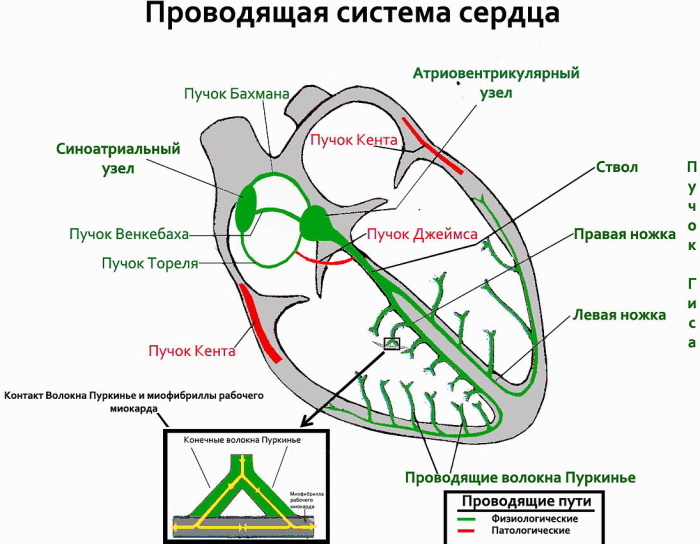
The sinoarthrial node sets the heart rate. Normally, they generate the highest number of pulses per minute.
- In the absence of sequential conduction of the impulse, a condition arises in which there is no synchronous activation of the atria, and then the ventricles. Atrial and ventricular rhythms separate - dissociation develops.
- The atria begin to contract at a rate set by the sinoarthrial node, and the ventricular rate is determined by the atrioventricular node or the pathways below it.
- Retrograde or ascending atrial excitation from the AV node in the case of dissociation is virtually absent.
In real clinical practice, the causes of dissociation are divided into 4 blocks:
- reducing the frequency of pulses generated in the CA-node;
- blockade of the CA node;
- 2nd degree AV block;
- a sharp increase in the automatism of the departments of the conducting system subordinate to the CA-node.
With complex rhythm disturbances, a combination of several blocks at once is possible.
Anamnesis
When contacting a cardiologist, patients may complain of interruptions in the work of the heart, rapid pulse, discomfort and heaviness behind the breastbone, shortness of breath with moderate physical exertion, bouts of weakness or dizziness.
A history of chronic ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, valvular defects, or long-term use of high-dose cardiovascular drugs is quite common.
In some patients, AV dissociation is asymptomatic and is an accidental finding on the ECG or during Holter monitoring.
With severe symptoms, their presence is determined by tachycardia, bradycardia, rapid heartbeat, malaise, and dyspnea.
To confirm the diagnosis of atrioventricular dissociation, a physical examination is performed, including the necessary set of medical measures.
| Physical diagnostic methods | Characteristic |
| General inspection | Deviation from the norm of blood pressure and pulse, against the background of changes in the functions of the ventricles and atria. |
| Pulse | Frequency distortion up or down, depending on the etiology of the disease. |
| Arterial pressure | Lowered |
| Jugular pulse | AV dissociation on the ECG is determined by the appearance of gun waves A, arising during the period of parallel work of the right and left heart and ventricles. If the PR interval changes, or the QRS system follows the P wave, the A waves acquire a different flow pattern. |
| Heart tones | The volume of the first tone and systolic murmur change as the ventricular rate increases in relation to the atrial rate. |
Conditions causing AV dissociation, causes
The causes of dissociation are conventionally divided into 2 groups: states that depress the SA node and states that enhance the automatism of subordinate centers.
- The automatism of the CA-unit is reduced by:
- means for general anesthesia;
- direct damage to the cells of the CA-node;
- overdose of cardiac glycosides;
- myocardial infarction, myocarditis, postinfarction cardiosclerosis;
- excessive content of K ions in the body;
- excessive influence of the parasympathetic nervous system, especially the vagus nerve;
- ventricular premature beats, tachycardia, the appearance of foci of excitation in the walls of the ventricles;
- radiofrequency ablation is a surgical method for treating a number of arrhythmias;
- conditions after electric shock, lightning or electric shock.
- The following reasons increase the automatism of II and III order nodes and fibers:
- electrolyte metabolism disorders - low level of K ions and excess Ca;
- dilated cardiomyopathies - expansion of the cavities of the heart chambers;
- poisoning with digitalis drugs;
- activation of the sympathetic nervous system, prolonged stress against the background of altered blood pH with a shift towards the acid side.
Regardless of the etiology, atrioventricular dissociation manifests itself in a secondary form. It occurs against the background of an existing disease. More often as a result of an increase in the volume of the vagal tone, with a low, high heart rate, acceleration of the idioventricular rhythm and a pathological form of connective tachycardia.
In the latter case, there is an acceleration of the heart rate in relation to the sinus node. This occurs during surgical treatment, in particular on the artery, sinus bradycardia, or Digoxin poisoning.
Long intervals promote healthy junctional rhythm. With early ventricular stroke, the node synchronization cycle is reset. Therefore, the sinus contraction lasts a long time, leading to the appearance of AV dissociation, since the activation of the nodal rhythm is faster than the sinus node.
Differences Between AV Dissociation and Complete Heart Block
When recording an ECG, each phase of the conduction of an impulse through the myocardium is reflected by teeth or intervals. 1 heartbeat is normal - this is a strict sequence of waves on the ECG, the so-called full complex.
- the P wave characterizes the conduction of excitation through the atria;
- the PQ interval shows the time of passage of the discharge in the AV connection - the rate of the indicator is 0.12 - 0.20 sec .;
- the QRS complex reflects the features of the impulse propagation along the walls of the ventricles of the heart.
AV dissociation on the ECG, in contrast to a complete blockade, is characterized by the preservation of the main teeth and complexes inherent in each contraction of the heart. Changes in their sequence, amplitude or duration are possible.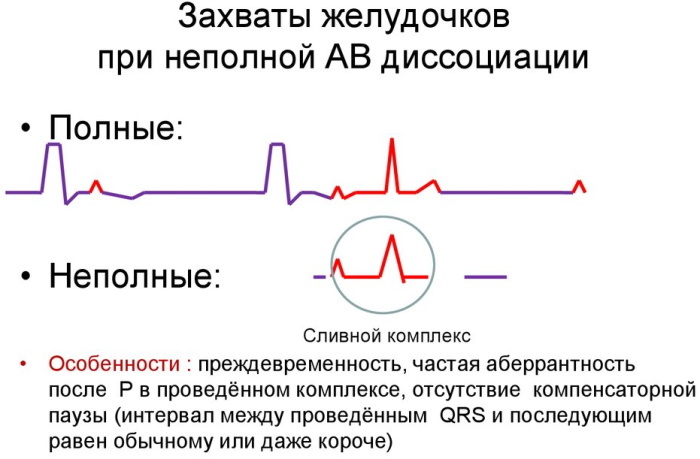
Pathology develops against the background of a slowdown in the conduction of the sinus node. There is a rivalry for rhythm control between the sinus and AV nodes. The condition often occurs in healthy people during a night's sleep.
AV dissociation on the ECG is determined by an inconsistent P-R interval due to the almost equal rhythm between the QRS system and the P wave. Their fusion is rarely observed, then the P wave is not visible for several cardiac cycles. As a result of the accelerated sinus rhythm, to restore it, the impulse can penetrate through the atrioventricular junction.
Complete heart block is characterized by the loss of one or more heart complexes. That is, during this period, an isoelectric line is recorded on the ECG. Its duration depends on the number of dropped heart cycles.
- If we are talking about a transient complete blockade, then after several dropped cycles, the rhythm is restored, the teeth are again reflected on the ECG.
- If a cardiac arrest occurs against the background of a complete blockade, the rhythm is not restored. An isoelectric straight line appears on the cardiograph monitor.
Atrioventricular dissociation with interference
AV dissociation on the ECG based on characteristic changes in the P wave and the QRS complex is divided into isorhythmic and interferential.
- Isorhythmic option occurs when the CA node is weak or stopped. The synchronized P-wave travels through the AB section. In accordance with the level of the auxiliary node, which takes over the functions of the pacemaker, the duration of the QRS complex changes. If the new pacemaker is located in the atria, the QRS complexes are narrowed, while with ventricular localization, on the contrary, they are expanded.
- Interferential option - a type of dissociation, when the ventricles and atria contract independently of each other. The rhythm that occurs in the ventricles reaches or exceeds the atrial rate. The P-wave on the ECG is recorded chaotically. There are options for recording it before, after, or even inside the QRS complex.
Among the causes of interference, myocardial infarction and overdose of cardiac glycosides are in the first place. Less commonly, pathology occurs as a complication of open heart surgery. The resulting condition requires emergency medical care.
Atrioventricular dissociation in children
AV dissociation on ECG in pediatrics is an accidental finding during a medical examination. The child grows and develops with age, does not complain. Especially often, such results are recorded during examinations in adolescents during puberty. Cardiologists associate changes in the cardiac conduction system with the growth of the child and changing hormonal levels.
To exclude organic pathology or myocardial defects, ultrasound of the heart and daily ECG monitoring - HOLTER-KG are performed.
In the absence of complaints and changes in ultrasound, special treatment for AV dissociation in childhood is not required. As the child gets older, the rhythm evens out and becomes sinus.
AV dissociation is a benign form of heart rhythm disturbance. It appears on the basis of existing cardiac pathologies, more often arrhythmias, with an acceleration or decrease in the heart rate.
In childhood, it is detected at a later stage, proceeds in the same way as in adult patients. It is associated with asymptomatic development. In the presence of signs of dissociation, they arise against the background of bradycardia, tachycardia, dyssynchrony.
Include:
- dizziness;
- feeling tired;
- shortness of breath after exercise;
- pronounced pulsation;
- accelerated heartbeat.
Possible complications
In 80% of cases, atrioventricular dissociation is of an incoming nature, without causing tangible changes in blood circulation.
According to cardiologists, episodes of AV dissociation can occur:
- in healthy people with a heart rate below 60 beats per minute;
- with sick sinus syndrome;
- various sinus arrhythmias;
- CA blockade;
- 2nd degree AV block.
Pacemaker migration in such situations is short-lived and does not require special therapy.
There are several pathologies in which the appearance of AV dissociation indicates a deterioration in the patient's condition and requires urgent care.
- Migration of the pacemaker in acute myocardial infarction. AV dissociation on ECG in heart attack patients is a prognostic unfavorable sign. Lowering blood pressure and abnormal heart rate often lead to loss of consciousness. Hypoperfusion of internal organs may develop against the background of growth or decrease in cardiac conduction. A local decrease in blood supply and myocardial infarction occurs when an increase or increase in the frequency cardiac contraction with atrioventricular dissociation leads to a decrease in coronary perfusion arteries.
- The development of dissociation while taking cardiac glycosides. Acute poisoning causes the migration of the pacemaker with the development of signs of heart failure. To provide assistance, the patient must be hospitalized in an ambulance mode in the cardiology department.
- Dissociation after heart surgery. Such patients are in intensive care units with round-the-clock heart rate monitoring. Depending on the changes in the electrocardiogram, cardiac drugs are immediately administered to normalize the work of the heart.
- Acute renal failure occurs when renal blood flow is low due to low cardiac output. Often occurs in severe bradycardia and atrioventricular dissociation.
Complications of AV dissociation are caused by a hemodynamic condition due to ventricular tachycardia and sinus bradycardia. Such clinical conditions require urgent resuscitation measures to normalize pressure, cardiac conduction in order to create the necessary organ perfusion.
ECG for AV dissociation. Examples of
AV dissociation on the ECG refers to complex rhythm disturbances. Only an experienced specialist can make a diagnosis, since there is no single standard of signs confirming migration.
The literature describes 3 main signs on the ECG as examples of changes during atrioventricular dissociation.
- Variable interval R-R, since impulses can come from different parts of the conducting system of the heart. On an ECG, where, according to the standard, an average of 5 complexes in each lead is recorded, this symptom may be mild. The dynamics of the expansion of the P-R interval is better visible with long-term monitoring of the heart rate on the HOLTER.
- The P wave is not defined in all complexes. In some cases, it merges with the QRS complex or is located behind it. It is important to remember that normally the P wave always precedes the QRS complex.
- Change in the duration of the QRS complex. If the new pacemaker is located in the atria, the complex narrows. In contrast, when impulses originate from the ventricles, the QRS expands.
Depending on the degree of dissociation, only 1 or 2 of the above signs may be present on the cardiogram.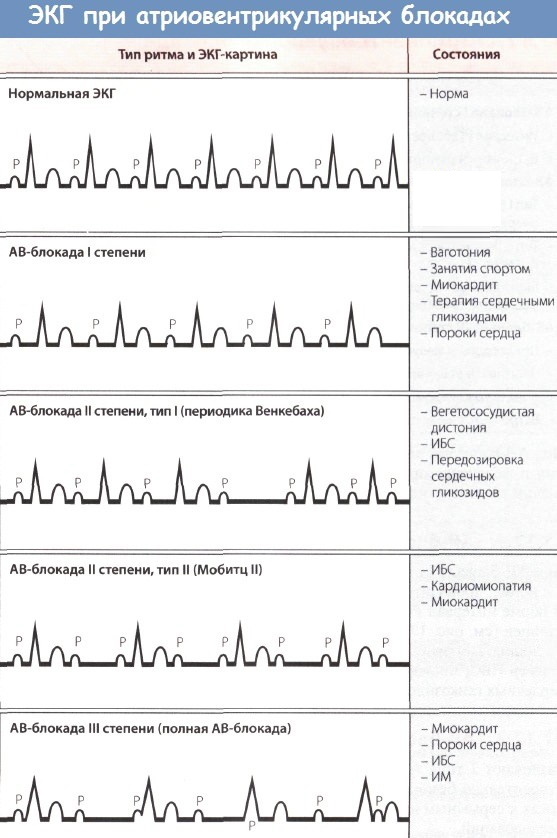
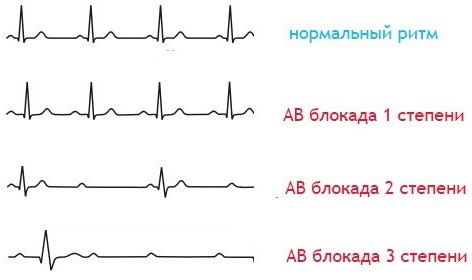
Examples of AV dissociation on an ECG:
- Incomplete AV dissociation of the type of interference with dissociation.
- Isorhythmic (complete) AV dissociation on the ECG. It can be seen that the P wave approaches the QRS system, merges and registers again from the front. There is no connection between the activity of the atria and ventricles.
Using intracardiac ECG data for diagnosis and patient management
The electrocardiogram in AV dissociation plays an important role in the diagnosis. The examination method helps to determine the need to install a pacemaker, prescribe additional medications or other surgical intervention.
To diagnose AV dissociation in medical practice, ECG and Holter monitoring are used.
- The main difference between the methods is the length of the recording. The ECG is recorded for 1-2 minutes, and the HOLTER reflects the heart rate during the day, which allows you to identify episodes of dissociation at night.
- In case of complex rhythm disturbances, before heart surgery, as well as in the postoperative period, an accurate determination of a new focus of excitation in the cardiac conduction system is required. To localize the focus, an intracardiac ECG is performed.
- This is an expensive and technically complex procedure that can only be performed in a cardiac surgery hospital.
- With the help of a probe, a sensor is inserted into the myocardial cavity, which allows recording an ECG from different parts of the myocardium.
The probe is inserted into the myocardial cavity through the femoral artery. The method allows you to take an ECG from the right heart, which is impossible with a conventional cardiogram.
Without fail, an intracardiac ECG is shown:
- Patients with frequent fainting, the presence of a blockage of the His bundle without objective confirmation of atrioventricular dissociation.
- Persons with blockade of the atrioventricular bundle and AV block of the 2nd degree. With obvious symptoms, it is possible to indicate on the picture where the blockade of conduction is localized. The location is indicated by the coming blockade of one of the bundle branch blocks together with a change in the P-R interval. If a blockade is found below the atrioventricular bundle, patients need to install a pacemaker, since the likelihood of a last-degree AV block is high.
- Patients with grade 3 AV block with latent course. The ECG will help to correctly assess the function of the nodal pacemaker, including during physical activity.
- Patients with lesions of the atrioventricular node, also with bifascicular block. ECG registration allows to prevent complications such as AV blockade and to confirm the feasibility of using a pacemaker.
For the competent management of patients with atrioventricular dissociation, it is necessary: to identify the cause of the condition, to estimate the duration of the ventricular contractions, polarity of atrial activity, conduct an examination of the esophageal abduction or blockade of the AV complex with the help of medicinal funds.
The doctor's tactics for an uncomplicated form of dissociation is observation. In severe cases, drug treatment is used, up to the installation of a pacemaker.
Drug therapy
The main goal of drug therapy is to prevent complications and reduce the likelihood of death. The selection of drugs depends on the type of atrioventricular dissociation.
The passive option is due to the primary weakness of the sinoarthrial node. Drugs are selected that enhance the excitation of CA-junction cells.
These drugs include substances of 3 pharmacological groups:
-
M-anticholinergics. A typical representative of the group is Atropine. The drug is administered intravenously. If there is no effect, the injection can be repeated 5 minutes after the first injection.

- Beta-adrenomimetics. The drug of choice is Isoprenaline. If Atropine is ineffective for stopping bradycardia with a pulse below 55 beats per minute, the drug is prescribed sublingually or intravenously. The drug is used strictly according to indications in a hospital setting.
- In some cases, effective adenosinergics, for example, Theophylline and its derivatives. The drug is administered orally in courses of 4-7 days.
Active dissociation is associated with overexcitation of the atrioventricular node. In this case, on the contrary, means are selected that slow down intracardiac conduction.
- Beta blockers. Heart rate is influenced by both selective and non-selective members of the group. In terms of side effects, the latest generation drugs are better tolerated - Bisoprolol and Nebivolol. Against the background of concomitant hypertension, Anaprilin and Carvedilol are shown.
- Ca channel blockers. Nifedipine, Amlodipine and Lercanidipine moderately reduce intracardiac conduction.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is carried out with severe dissociation, not amenable to drug therapy. Surgical tactics also depend on the type of dissociation.
For severe bradycardia, a pacemaker is indicated. In terms of complexity among all operations performed in cardiac surgery, this is the simplest.
A pacemaker is an artificial pacemaker that synchronizes the contraction of the myocardial chambers. The table lists the main types of stimulants.
| Views | number of electrodes | the part of the heart that is regulated |
| single chamber | 1 | stimulates only 1 cavity - atrium or ventricle |
| two-chamber | 2 | stimulates only 2 cavities - 1 atrium and 1 ventricle |
| three-chambered | 3 | stimulates only 3 cavities - 1 atrium and 2 ventricles |
According to the duration of use, stimulants are divided into temporary and permanent. Temporary ones are installed to relieve arrhythmia attacks against the background of a heart attack or heart surgery. In chronic bradycardia, a permanent device is indicated.
After surgery, the heart begins to beat at a constant set rate, usually 68-72 beats per minute.
Patients report an improvement in general well-being and an increase in physical activity.
The operation can reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death and prevent disability. The only limitation in daily life is to avoid devices with high electromagnetic radiation. With excessive activity of the lower nodes, ablation is indicated, which removes a high pulse.
Long term monitoring
AB dissociation is not an independent disease, but a consequence caused by a number of factors. It is possible to completely eliminate atrioventricular dissociation by removing the trigger. For example, in the case of an overdose of cardiac glycosides, the withdrawal of Digoxin restores the sinus rhythm.
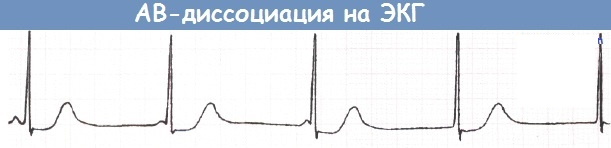
However, in most clinical cases, the reasons for the dissociation are not so obvious.
Additional examinations are required - dynamic ECG, Holter monitoring, ultrasound of the heart. Cardiologists recommend carrying out these studies at least 2 times a year. Continuous monitoring will help identify hidden episodes of dissociation and adjust treatment, help prevent recurrence of the disease and affect the effectiveness of therapy.
Forecast
In most cases, if signs of AV dissociation are detected on the ECG, the prognosis is favorable. Dynamic observation of a cardiologist and supportive drug therapy of the underlying disease is required. Surgical treatment is indicated in both acute and severe cases.
It is important to understand that the operation is carried out strictly according to vital indications. Therefore, abandoning it can lead to adverse health effects. With proper treatment, the prognosis is considered positive.
Article author: cardiologist, Olga Alekseeva.
Video about ECG blockages
Video course "EKG under the power of everyone" about blockade:



