Sputum is a discharge of a different nature. (viscous, nozzle-like, liquid), formed on the mucous epithelium of the respiratory tract. Its appearance is associated with pathological reasons. In order to identify the disease that provoked the appearance of discharge, as well as to determine the method of treatment and assess the dynamics of the course of the disease, a sputum analysis is taken.
Record content:
- 1 Indications for research
- 2 Training
-
3 Carrying out
- 3.1 General sputum analysis
- 3.2 Bacterioscopic examination
- 3.3 Bacteriological (cultural) method
- 3.4 Luminescence microscopy
-
4 Decoding the results
- 4.1 General analysis
- 4.2 Luminescence microscopy
- 4.3 Bacteriological (cultural) method
- 4.4 Bacterioscopic examination
- 5 Sputum Analysis Videos
Indications for research
Sputum analysis must be taken to study the qualitative, physical, quantitative, bacteriological and cytological characteristics of the secretions. On the mucous epithelium of the respiratory tract, mucous biomaterial is regularly produced, but it is produced in a small volume and does not bring discomfort to a person, on the contrary, it possesses protective functions.
With the development of any disease, the amount of mucus secreted decreases, and pathogenic substances (microbes, leukocytes, erythrocytes and others) appear in the composition.
The indications for sputum examination are as follows:
- prolonged cough with sputum production;
- sputum production when coughing with impurities;
- prolonged hyperthermia;
- to confirm the diagnosis when detecting darkening on X-ray images;
- control of the course of the disease and the effectiveness of drug therapy.
Sputum analysis is necessary for almost any pathology, accompanied by the release of mucous secretions when coughing. However, seasonal viral infections do not require such a diagnosis due to the lack of need for it.
But for the following diseases, this research method is one of the most important in a comprehensive diagnostic measure:
- tuberculosis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- bronchial asthma;
- abscess or gangrene;
- chronic bronchitis;
- pneumoconiosis.
There are several methods for studying mucous biomaterial. General analysis shows the stage of the disease, the nature of the course and the localization of the focus. If you suspect more complex pathological processes, an analysis is prescribed for CD (Koch's bacillus), VK (specific bacteria of tuberculosis), KUM (acid-fast mycobacteria), MBT (mycobacterium tuberculosis).
Additional analyzes allow you to identify the type of pathogen and select the appropriate antibacterial drug to suppress and eliminate its pathogenic effects.
For patients diagnosed with lung cancer, lingering pneumonia, tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, sputum sampling is an integral part of treatment. Even after recovery, in order to assess the state of health, such persons are required to undergo regular examinations, since such diseases tend to have temporary rest.
An appointment for an analysis is prescribed by a phthisiatrician or pulmonologist. In some cases, when you go to the hospital with general questions, you can get a referral from your local doctor. Sputum sampling is carried out, as a rule, in a tuberculosis dispensary, but a general sputum test can also be taken in a bacterial laboratory at a city polyclinic.
Training
Sputum analysis must be taken correctly, following all the instructions of laboratory assistants and doctors. This is a demanding process that requires careful preparation. If medical prescriptions are ignored, additional impurities in the biomaterial may appear, which in the result of the research will interfere and confuse the laboratory assistant, which in turn entails an unreliable statement diagnosis.
Recommendations for the collection of biomaterial for general analysis for pneumonia and VC:
-
Preparing a container for biomaterial. It can be purchased at any pharmacy. It is a sterile container with a wide mouth and lid. A small 5 ml container is sufficient for sputum.
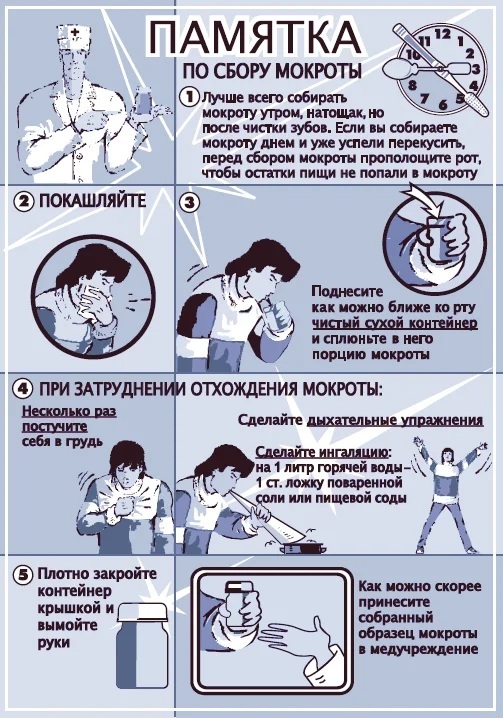
Memo: how to take a sputum test - Sputum is given in the morning on an empty stomach. During the night's rest, a sufficient volume of biomaterial accumulates in the mucous epithelium. In some cases, sputum collection can be carried out at any time of the day.
- Before taking the analysis it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the oral cavity, while brushing the teeth is strictly not recommended. This procedure is performed 2 hours before sputum collection.
- To collect the slime, you need to perform simple manipulations. Take a maximum breath, hold your breath, then exhale easily. This should be repeated three times, then exhale sharply and cough up the air from the lungs. With such an exhalation, phlegm should go away, therefore, in the last exhalation, the mouth is closed with gauze, and the container is held near the lower lip. The emerging biomaterial is spit out into the container, after which it is tightly closed with a lid. If a small amount of sputum is discharged, the procedure is repeated. The required volume of biomaterial for research is 5 ml.
If, when following the above recommendations, there are difficulties with sputum production, you should lie on your side or bend forward. For better sputum discharge, doctors recommend making a moisturizing steam inhalation before sampling, or add an expectorant to the inhaler.
Before the procedure, during the previous day, you need to perform the following actions:
- drink plenty of warm water;
- take expectorant drugs;
- rinse your mouth and throat with a furacilin solution;
- thoroughly brush your teeth in the evening.
Sometimes, along with sputum, saliva gets into the container, in which case the analysis is repeated or more a reliable method of research bronchoscopy, in which the biomaterial is obtained using a catheter directly from respiratory tract.
A prolonged cough with sputum discharge for 3 weeks or more is considered a reason for taking an analysis for tuberculosis (BC), KUM. This is a serious problem, therefore, a sputum test is taken only in a hospital under the supervision of doctors.
The sampling of biomaterial for this study occurs in three stages:
- First. On an empty stomach in the morning.
- Second. 4 hours after the first collection at a medical facility.
- The third. The next day. Sputum control sampling.
If a patient is in serious condition that he cannot visit the laboratory on his own, a laboratory assistant and a nurse with the necessary instruments are sent to his home.
The rules for preparing for the analysis in a medical institution are identical to the rules for preparing for a general analysis.
Carrying out
Sputum analysis must be taken to detect pathogenic microorganisms and tubercle bacilli.
It is carried out in several ways:
- general analysis;
- luminescence microscopy;
- bacteriological (cultural) method;
- bacterioscopic study of biomaterial.
General sputum analysis
This is the most basic and effective method for assessing the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of a biomaterial.
Its purpose:
- identification of a disease-causing process in the respiratory system;
- assessment of the nature of the disease;
- monitoring the course of chronic pathology;
- analysis of the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
This method takes into account the following factors:
- amount;
- character;
- smell;
- layering;
- Colour;
- the presence of impurities.
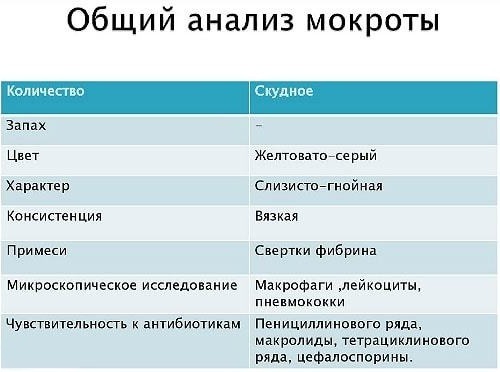
General analysis allows you to get a picture immediately after its study. This method has been used for many decades and provides reliable information about diseases. More in-depth data can be obtained by conducting a number of other analyzes.
Bacterioscopic examination
This method is also called Ziehl-Nielsen staining. This is one of the main methods of research with suspicions of the development of tuberculosis. With its help, AFB is detected, indicating the presence of severe pathology.
Sputum diagnostics is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- processing of biomaterial with carbolic fuchsin;
- discoloration of sputum with 3% hydrochloric acid solution or 5% sulfuric acid solution;
- subsequent staining of the material with 0.25% methylene blue solution.
After the performed manipulations, the obtained biomaterial is assessed using an immersion system. The presence of AFB is evidenced by the appearance of red and blue in the area of pathogenic organisms.
The result is viewed as standard in 100 fields of view. If AFBs are not detected, viewing is carried out in 200 fields of view.
The analysis is free, the efficiency is high. The only drawback of this method is its low sensitivity.
Bacteriological (cultural) method
Sputum is cultured on a nutrient medium. To detect a tubercle bacillus, only a few vital cells are enough.
The analysis uses the following types of culture media:
- liquid semi-synthetic and synthetic;
- semi-liquid based on agar;
- dense on the basis of eggs.
The primary causative agent of tuberculosis is determined, as well as the sensitivity of the pathogenic organism to antibacterial dosage forms. This is an excellent method for choosing the most effective medicine for each individual case.
The negative side of the method is its duration. The intensity of MBT growth is determined from 21 to 90 days, but with the use of modern computer technology, this period has decreased to 3-4 days.
Luminescence microscopy
This method is 30% more effective than bacterioscopic examination. Organic fluorochromes are used as coloring material. With the help of a fluorescent device under ultraviolet illumination, they begin to glow blue or violet. The presence of KUM, BK, VK is evidenced by a golden color on a dark background.
When using luminescence microscopy, not only the presence of pathogenic microorganisms is revealed, but also their quantitative characteristics. This allows you to assess the epidemic danger to others and the stage of the disease.
Decoding the results
After taking sputum, the attending physician decrypts the analysis. But the deviations in the results are self-explanatory.
The norm for the characteristics of sputum is considered:
- lack of an unpleasant odor;
- the color is grayish or closer to white;
- absence of lumps and granular consistency (the structure of the biomaterial is homogeneous and transparent);
- absence of impurities of pus, blood cells and other pathogenic components.
The presence of any deviations indicates the development of a pathological process in the lungs or bronchi. Each group of diseases of the respiratory system has its own clinical picture. This is indicated by specific factors identified by the results of the analysis.
General analysis
A general sputum test provides information on many factors. A change in quantitative or qualitative characteristics indicates the presence of diseases and infectious processes in the respiratory system.
Sputum indicators, assessed by general analysis:
| Index | Norm | Deviation |
| Quantity | In the daily rate, sputum is secreted from 10 to 100 ml. We do not even notice this feature of the body, since most of the mucus is swallowed by us along with saliva. | The course of bronchitis or other respiratory diseases is accompanied by the release of up to 200 ml of mucus per day. An excessive increase in the amount of sputum secreted indicates the accumulation of blood or pus in the respiratory tract. In the future, sputum is released through the respiratory system in a natural way. Severe illnesses are accompanied by the secretion of up to 1.5 liters of sputum per day. This is an abscess, gangrene, or bronchiectasis. |
| Character | Normally, the mucus has a homogeneous transparent consistency. | With broncho-pulmonary diseases, mucus can be:
|
| Colour | In the normal state, the mucus is grayish, whitish or transparent in color. |
|
| Smell | Sputum in 75% of cases does not emit odors. | The appearance of a smell indicates the presence of purulent impurities. This can happen when cell tissue dies. When the cyst ruptures, a fruity smell appears on the lung. |
| Layering | When coughing, mucous secretions are homogeneous. | Stratification of biomaterial can only be seen under a microscope. The appearance of this factor is facilitated by an abscess or gangrene of the lung tissue. With an abscess, 2 layers are observed (putrid and serous). With gangrene, an additional third layer (foamy) appears. The appearance of the third layer is due to the presence of vital microorganisms in the cells, released by gas bubbles. |
In addition to these indicators, the following data indicate the presence of a pathological process:
-
Leukocytes. An increased number of leukocytes is observed in any inflammatory process. Here, their number in relation to the norm is important.
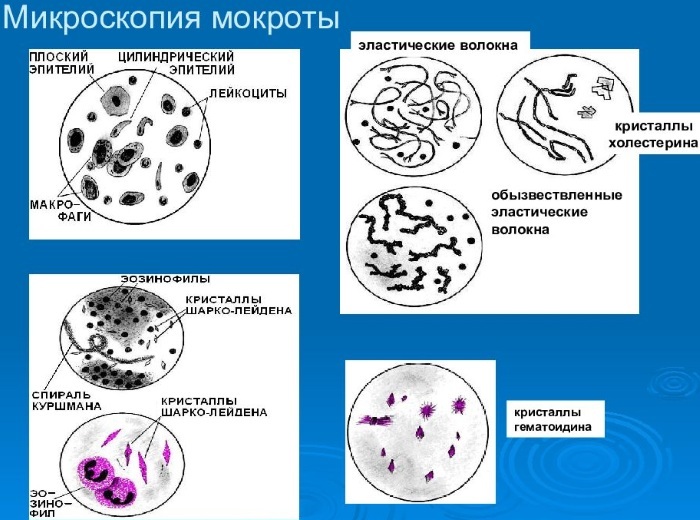
- Eosinophils. They are found in the composition of leukocytes, normally from 50 to 90% of their volume. An increase in their number indicates the presence of allergic processes, bronchial asthma, helminthic lesions, eosinophilic infiltrates.
- Neutrophils. If more than 25 neutrophils are detected in the field of view, an infectious process develops.
- Squamous epithelium. More than 25 epitheliums in the field of view are present about impurities in the sputum.
- Elastic fibers. If they are found, pneumonia with an abscess is diagnosed.
- Spirals of Kurshman. Indicates bronchospastic syndrome, indicates bronchial asthma.
Diagnosing deviations in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the biomaterial enables the pulmonologist to assess the severity of pathological lesions of the lung tissue and determine the root cause.
Luminescence microscopy
With the help of a luminescent apparatus, not only the presence of AFBs is revealed, but also their quantitative composition.
The interpretation of the diagnostic results is carried out according to a special algorithm.
| Diagnostic result | Number of fields of view | Interpretation |
| AMBs not identified | 300 | «-» |
| Revealed 1-9 AFB | 100 | «+» |
| Revealed 10-99 AFB | 100 | «+» |
| Revealed 1-10 AFB | 50 | «++» |
| More than 10 AFBs identified | 20 | «+++» |
Thanks to this technique, the following are also identified:
- Alveolar macrophages. Indicate the presence of chronic processes.
- Fatty macrophages. Revealed in abscess, gangrene, actinomycosis, pulmonary echinococcosis.
- Eosinophils. A high content of the indicator is observed in bronchial asthma, heart attack, eosinophilic inflammation, helminthic lesions of the lung tissue.
- Ciliated epithelial cells. Revealed in asthma, tracheitis, bronchitis and neoplasms.
Bacteriological (cultural) method
Thanks to modern medicine, highly sensitive and highly informative research methods have been developed, one of which is bacteriological (cultural).
Studies indicate the pathogenicity of the pathogen, which is detected by sowing sputum and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. A nutrient medium is used. To identify MBT, a small number of viable pathological cells are enough.
It will take from 21 to 90 days to assess the intensity of MBT growth.
Interpreting the results of MBT growth:
| Growth assessment | Result |
| 1 to 20 colonies | "+", Scanty isolation of pathological cells |
| 21 to 100 colonies | "++", moderate MBT allocation |
| 100 and more colonies | "+++", abundant growth of MBT |
The sensitivity of the office to dosage forms is determined by the method of absolute concentration. This method makes it possible to select high-quality antibiotic therapy on an individual basis, which significantly enhances the medical effect.
Bacterioscopic examination
The method consists in staining the biomaterial according to Ziehl-Nielsen. If mycobacterium tuberculosis is detected in the field of view, against a dark background they can be detected by their golden yellow color. When ABB is identified, their quantitative composition is an important indicator. This allows you to determine the epidemic threat and the severity of the disease.
Using the Ziehl-Nielsen method, there is the following interpretation of the diagnostic results:
| Diagnostic result | Number of fields of view | Interpretation |
| AMBs not identified | 300 | «-» |
| Revealed 1-9 AFB | 100 | «+» |
| Revealed 10-99 AFB | 100 | «+» |
| Revealed 1-10 AFB | 50 | «++» |
| More than 10 AFBs identified | 20 | «+++» |
In addition to CFM, during bacterioscopy, other pathogenic microorganisms can be detected, which provide an assessment of the disease and its stage:
- Pneumococci, Friedlander's pneumobacteria, staphylococci, streptococci, Frenkel's diplococci. Their presence means the development of pneumonia.
- Spindle stick together with Vincent's spirotech. They indicate gangrene or lung abscess.
- Druse of actinomycete. Found in actinomycosis.
- The influenza stick appears with the flu.

If yeast-like fungi are identified, an additional sputum culture is prescribed to determine their type.
The attending physician (pulmonologist) can decipher the results of sputum analysis. Only he will make an accurate diagnosis or send him to re-donate sputum to obtain more extensive information.
Sputum Analysis Videos
About sputum testing:



